Vaccines & Types of Vaccines | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How do vaccines work? |

|
| Types of vaccines |

|
| mRNA Vaccine |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Vaccine
- A biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity against a specific disease.
- Contains an agent resembling the disease-causing microbe.
Acquired Immunity
- Immunity developed over a lifetime.
- Can result from vaccination, exposure to a disease, or receiving antibodies from another person.
- When pathogens are introduced via vaccination or infection, the immune system learns to target and create antibodies against them.
- Immune system memorizes how to respond to these microorganisms in the future.
How do vaccines work?
- Exposing the Immune System: Vaccines contain a harmless piece of the disease-causing microorganism, such as a protein or a weakened or inactivated virus or bacterium. When you receive a vaccine, your body is exposed to this harmless part of the microorganism.
- Immune Response: Your immune system recognizes this foreign substance (antigen) as a potential threat, even though it's not causing illness. It responds by producing antibodies, which are proteins designed to target and neutralize the antigen.
- Memory Cells: Along with producing antibodies, your immune system creates memory cells. These cells "remember" the antigen and how to produce the specific antibodies to fight it.
- Immunity Development: While the immune response generated by a vaccine is similar to that of a real infection, vaccines don't cause the disease. Instead, they prepare your immune system for future encounters with the actual pathogen.
- Faster and Stronger Defense: If you're exposed to the disease-causing microorganism in the future, your immune system's memory cells recognize it immediately. This enables your body to produce antibodies rapidly and efficiently, effectively preventing the infection or significantly reducing its severity. This faster and stronger response is why you don't get sick from the disease, or you experience milder symptoms if you do.
Types of vaccines
Vaccines are made up of viruses or bacteria that are altered or weakened so that they only cause an imitation of the disease and not the disease. There are a variety of different ways to alter or weaken the viruses or bacteria so that vaccination develops immunity instead of serious disease.
Following are the different types of vaccines based on how they are made:
- Inactivated Vaccine: These vaccines use pathogens that have been killed or inactivated, typically through heat or chemicals, while keeping the pathogen's structure intact.
- Attenuated Vaccine: Attenuated vaccines use weakened forms of the disease-causing microorganism that can't replicate enough to cause illness but can still trigger an immune response.
- Toxoid Vaccine: These vaccines target diseases caused by toxins produced by bacteria. Toxoids are inactivated toxins that can no longer cause harm but can stimulate an immune response.
- Subunit Vaccine: Subunit vaccines use specific parts of the pathogen, often isolated proteins, as antigens to provoke an immune response.
- Conjugate Vaccine: Conjugate vaccines combine pieces of bacterial coats with carrier proteins to enhance the immune response.
- Valence Vaccine: Vaccines can be monovalent (against a single antigen or microorganism) or multivalent (against two or more strains of the same microorganism or against multiple microorganisms).
- Heterotypic Vaccine: Heterologous vaccines use pathogens from other animals that either don't cause disease or cause mild disease in the treated organism.
- mRNA Vaccine: mRNA vaccines use a small piece of genetic material (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce a harmless piece of the pathogen, stimulating an immune response.
mRNA Vaccine
- mRNA Vaccine Mechanism: mRNA vaccines work by injecting a fragment of the RNA sequence of a virus into human cells. This mRNA fragment carries instructions to build the antigen of the virus. Unlike traditional vaccines, mRNA vaccines stimulate an adaptive immune response by directly involving cells in the process.
- Cellular Immunity: mRNA vaccines have an advantage in that they stimulate cellular immunity, in addition to the antibody response. This broadens the immune response and can enhance protection against the virus.
- Fragility and Storage: mRNA molecules are fragile and degrade quickly when exposed to the external environment. This is why mRNA vaccines need to be stored at extremely low temperatures to maintain their stability.
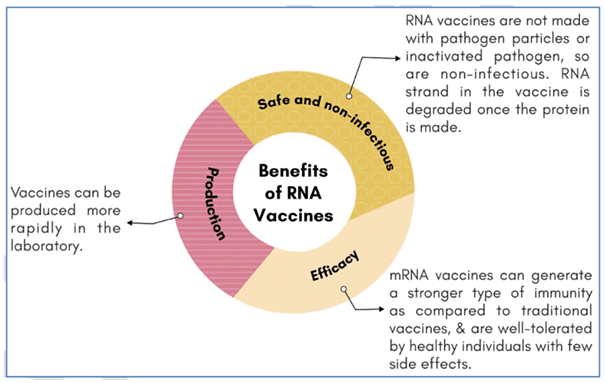
- Safety: mRNA vaccines are considered safe because mRNA is non-infectious, non-integrating, and can be degraded by standard cellular mechanisms.
- High Efficacy: These vaccines are highly efficacious due to their ability to directly translate into the protein structure inside the cell cytoplasm.
- Synthetic Nature: mRNA vaccines are fully synthetic and do not require a host for growth, such as eggs or bacteria. This characteristic allows for quick and cost-effective manufacturing, ensuring their availability and accessibility for mass vaccination.
How are mRNA Vaccines Different From Traditional Vaccines?
- How Vaccines Work: Vaccines function by educating the body's immune system to recognize and respond to proteins produced by disease-causing organisms, such as viruses or bacteria.
- Traditional Vaccines: Traditional vaccines typically consist of small or inactivated amounts of the entire disease-causing organism or specific proteins produced by that organism. When introduced into the body, these components provoke the immune system to mount a response, including the production of antibodies.
- mRNA Vaccines: mRNA vaccines, like those used for COVID-19, employ a different approach. They use messenger RNA (mRNA), a molecule responsible for translating DNA instructions into action within a cell. In the case of mRNA vaccines, a small piece of mRNA that encodes a viral protein is introduced into the body. Once inside cells, the mRNA acts as a template to produce the viral protein. This protein is then recognized by the immune system, prompting an immune response that includes the production of antibodies.
Concerns regarding vaccines
- Side Effects: Like all medications, vaccines can have side effects. These side effects are typically mild and can include soreness or swelling at the injection site. Serious side effects from vaccines are rare.
- Importance of Vaccines: Despite concerns about side effects, vaccines are crucial tools in the battle against diseases. They are highly effective at preventing various infectious diseases and have played a significant role in reducing the spread of illnesses and saving lives.
- Adapting to Changing Diseases: Diseases can evolve over time, leading to new strains or variations. To address this, vaccines may need to be updated or modified to remain effective. The scientific community continuously monitors and researches diseases to ensure that vaccines stay current and provide the best protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vaccination is widely regarded as a safe and effective method for preventing infectious diseases. Scientists overwhelmingly support vaccination as a crucial tool in public health. The immune system's ability to remember vaccination agents, recognize them as foreign invaders, and mount a defense when encountering the virulent form of the agent is the basis of how vaccines work. This recognition and response mechanism help prevent infection and protect individuals from the harmful effects of diseases. Vaccination has played a significant role in improving public health by reducing the spread and impact of infectious diseases.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|















