Hybridisation | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
What is Hybridisation?
Hybridisation is defined as the mixing of the atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom but having slightly different energies so that redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new orbitals of equal energies and identical shapes. The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals.
Some Important Points about Hybridisation
- Only those orbitals which have approximately equal energies and belong to the same atom or ion can undergo hybridisation.
- The number of hybrid orbitals produced is equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
- It is not necessary that all the half-filled orbitals must participate in hybridisation. Similarly, it is not necessary that only half-filled orbitals should participate in hybridisation. Even completely filled orbitals with slightly different energies can also participate.
- Hybridisation never takes place in isolated atoms but it occurs only at the time of bond formation.
- Type of hybridisation indicates the geometry of molecules. One can tell the shape of a molecule by knowing the kind of hybridisation involved.
- The bigger lobe of the hybrid orbital always has +ve sign while the smaller lobe on the opposite side has a -ve sign.
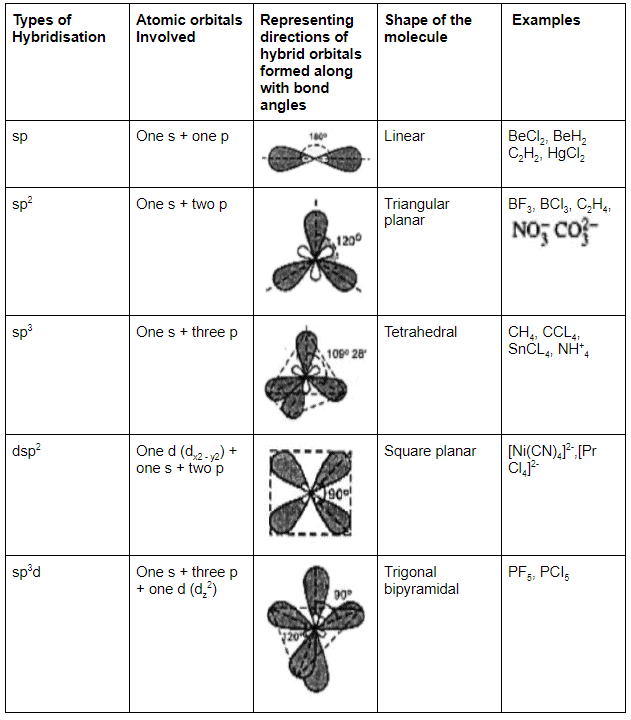
Type of Hybridisation
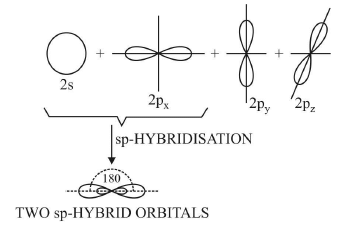
1. Diagonal or sp hybridisation
- When one s and one p orbital belonging to the same main shell of an atom mix together to form two new equivalent orbitals, this type of hybridisation is called sp hybridisation or diagonal hybridisation.
- The new orbitals formed are called sp hybrid orbitals.
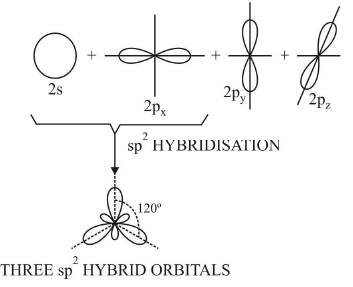
2. Trigonal or sp2 hybridisation
- When one s and two p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form three new equivalent orbitals, this type of hybridisation is called sp2 hybridisation or trigonal hybridisation.
- The new orbitals formed are called sp2 hybrid orbitals.
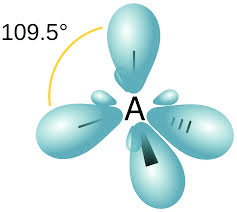
In such hybridisation one s- and three p-orbitals are mixed to form four sp3– hybrid orbitals having a tetrahedral structure with bond angle 109 degrees 28′, that is, 109.5 degrees.
Studying the Formation of Various Molecules
1) Methane
4 equivalent C-H σ bonds can be made by the interactions of C-sp3 with an H-1s
2) Ethane
6 C-H sigma(σ) bonds are made by the interaction of C-sp3 with H-1s orbitals and 1 C-C σ bond is made by the interaction of C-sp3 with another C-sp3 orbital.
3) Formation of NH3 and H2O molecules
In NH2 molecule nitrogen atom is sp3-hybridised and one hybrid orbital contains two electrons. Now three 1s- orbitals of three hydrogen atoms overlap with three sp3 hybrid orbitals to form NH3 molecule. The angle between H-N-H should be 109.50 but due to the presence of one occupied sp3-hybrid orbital the angle decreases to 107.80. Hence, the bond angle in NH3 molecule is 107.80.
4) Formation of C2H4 and C2H2 Molecules
In C2H4 molecule carbon atoms are sp2-hybridised and one 2p-orbital remains out to hybridisation. This forms p-bond while sp2 –hybrid orbitals form sigma- bonds.
5) Formation of NH3 and H2O Molecules by sp2 hybridization
In H2O molecule, the oxygen atom is sp3 – hybridized and has two occupied orbitals. Thus, the bond angle in the water molecule is 105.50.
Predicting Hybridisation
Calculate the number of hybrid orbitals (X) to be formed by the central atom as follows:
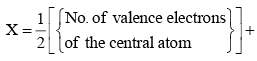
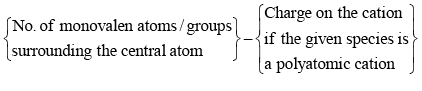
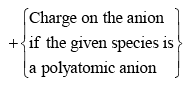
i.e. X = 1/2 [ VE + MA - c + a]
Note that only monovalent atoms (MA) or groups are to be considered. For divalent ions, MA = 0.
- If X = 2, it means two hybrid orbitals are to be formed. Hence, hybridization is sp.
- If X = 3, it means three hybrid orbitals are to be formed. Hence, hybridisation is sp2
- And so on, as given in the following table:
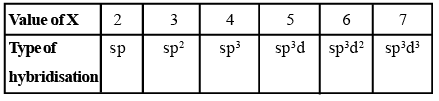
|
117 videos|223 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Hybridisation - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is hybridization in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of hybridization? |  |
| 3. How can hybridization be predicted? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of hybridization in molecular geometry? |  |
| 5. How does hybridization affect the strength of chemical bonds? |  |