Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 7 (Old NCERT) > NCERT Summary: Water
Water Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 5
Water Cycle
- Water is present in rivers, lakes, ocean etc.
- The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water vapour.
- When the water vapour cools down, it condenses and forms clouds.
- From there it may fall on the land or sea in the form of rain, snow or sleet.
- The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the water cycle.
Terrarium: It is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants.
- The major sources of fresh water are the rivers, ponds, springs and glaciers.
- The ocean bodies and the seas contain salty water as it contains large amount of dissolved salts.
- Most of the salt is sodium chloride or the common table salt that we eat.
Distribution of Water Bodies
- Saline Water
- Oceans: 97.3 %
- Fresh Water
- Ice-caps: 02.0 %
- Ground Water: 0.68 %
- Fresh Water Lakes: 0.0009 %
- Inland seas and salt lakes: 0.0009 %
- Atmosphere: 0.0019 %
- Rivers: 0.0001 %
Ocean Circulation
- Ocean water keeps moving continuously and never still.
- The movements that occur in oceans can be broadly categorised as:
- Waves
- Tides
- Currents
Waves
- When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves.
- An earthquake, a volcanic eruption or underwater landslides can shift large amounts of ocean water. As a result a huge tidal wave called tsunami.
- The largest tsunami ever measured was 150m. high. These waves travel at a speed of more than 700 km. per hour.
- The tsunami of 2004 caused wide spread damage in the coastal areas of India. The Indira point in the Andaman and Nicobar islands got submerged after the tsunami.
Tides
- The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called a tide.
- When water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level, it is high tide.
- When water falls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore, it is low tide.
- Cause of tides: The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface.
- The water of the earth closer to the moon gets pulled under the influence of the moon’s gravitational force and causes high tide.
- Spring Tides: During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line and the tides are highest. These tides are called Spring Tides.
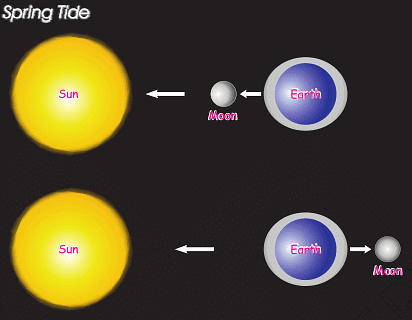
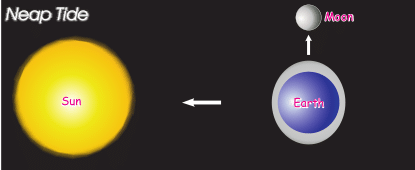
- Neap Tides: When the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and earth resulting in low tides. These tides are called neap tides.
Importance of Tides
- High tides help in navigation. They raise the water level close to the shores which helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
- The high tides also help in fishing as many more fish come closer to the shore during the high tide.
- The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
Ocean currents
- The streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions are called ocean currents.
- Ocean currents are of two types:
- Warm Ocean Currents: These ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles. Example: Gulf Stream.
- Cold Ocean Currents: These ocean currents carry water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. Example: The Labrador Ocean current.
Importance of Ocean Currents
- The ocean current influence the temperature conditions of the area. Warm currents bring about warm temperature over land surface.
- The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing grounds of the world. Seas around Japan and the eastern coast of North America are such examples.
- The areas where a warm and cold current meet also experience foggy weather making it difficult for navigation.
The document Water Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 is a part of the Class 7 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 7 (Old NCERT).
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Water Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 5
| 1. What is the importance of water in our daily lives? |  |
Ans. Water is essential for various bodily functions such as digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation. It is also crucial for maintaining healthy skin, lubricating joints, and flushing out waste products from the body.
| 2. How much water should I drink in a day? |  |
Ans. The amount of water one should drink in a day varies depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and climate. However, a general guideline is to drink at least 8 glasses (around 2 liters) of water per day to stay adequately hydrated.
| 3. What are the common sources of water pollution? |  |
Ans. Common sources of water pollution include industrial waste, agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, oil spills, and improper disposal of chemicals. These pollutants can contaminate water bodies, affecting aquatic life and posing risks to human health.
| 4. How can we conserve water at home? |  |
Ans. Water conservation at home can be achieved by adopting simple practices such as fixing leaky faucets and pipes, using low-flow showerheads and toilets, collecting rainwater for gardening, and watering plants during cooler hours of the day.
| 5. What are the consequences of water scarcity? |  |
Ans. Water scarcity can have severe consequences, including limited access to clean drinking water, reduced agricultural productivity, sanitation issues, and conflicts over water resources. It can also lead to health problems, economic setbacks, and overall societal instability.
Related Searches
















