Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st June 2025) - 1 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
Iran-Israel Conflict 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
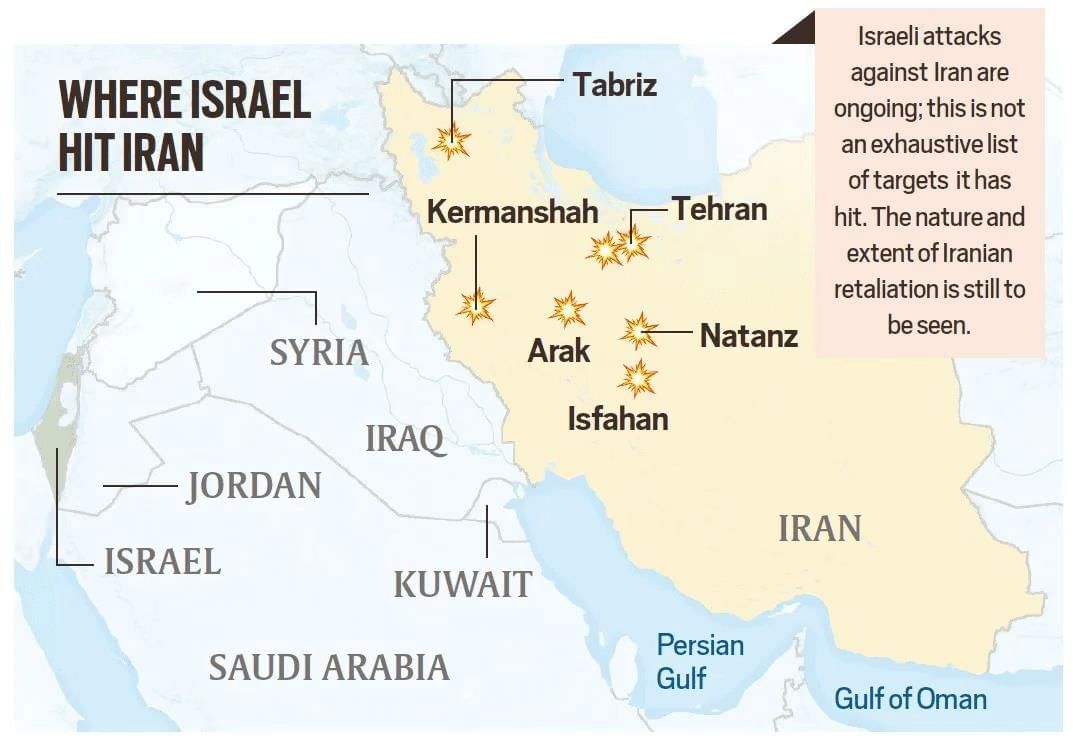
- The ongoing conflict between Iran and Israel has escalated significantly in 2025, with Israel launching "Operation Rising Lion," which involved airstrikes and drone attacks on critical Iranian nuclear and military facilities. In response, Iran initiated "Operation True Promise 3," targeting Israel with ballistic missiles, leading to widespread explosions in major cities such as Jerusalem and Tel Aviv.
Key Takeaways
- The conflict has deep historical roots dating back to the 1979 Iranian Revolution.
- Religious and ideological differences between Iran and Israel contribute to ongoing hostility.
- Iran's support for groups opposing Israel, including Hamas and Hezbollah, exacerbates tensions.
- Geopolitical rivalries in the region, including conflicts in Syria and Yemen, intensify the situation.
- Israel perceives Iran's nuclear ambitions as a direct threat to its national security.
Additional Details
- Historical Roots: The relationship between Iran and Israel deteriorated post-1979, transforming from alliance to antagonism.
- Religious Divide: The stark differences between Shia Islamic governance in Iran and the predominantly Jewish state of Israel fuel mutual distrust.
- Geopolitical Rivalry: Both nations are engaged in a struggle for dominance in the Middle East, impacting their involvement in regional conflicts.
- Impact on India: India's energy security and strategic interests, particularly regarding projects like Chabahar Port, are at risk due to regional instability.
The Iran-Israel conflict poses significant risks to global security and regional stability, necessitating diplomatic efforts and strategies for de-escalation. Key solutions include pursuing a two-state solution, fostering dialogue, addressing nuclear proliferation, and enhancing regional cooperation.
Bureau of Civil Aviation Security and India’s Aviation Sector
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS), which operates under the Ministry of Civil Aviation, has revoked the license of Celebi Aviation, a Turkish ground-handling company active at key Indian airports. This decision was made due to 'national security concerns,' particularly in light of Turkey's support for Pakistan following India's Operation Sindoor, which was launched in response to a terror attack in Pahalgam.
Key Takeaways
- The BCAS is responsible for civil aviation security in India.
- Celebi Aviation's license cancellation is linked to geopolitical tensions.
- Legal provisions under the Aircraft Rules, 1937, allow for the suspension of ground-handling agency licenses on security grounds.
Additional Details
- Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS): This body serves as the national regulator for civil aviation security in India, based in Delhi and led by a Director General of Police. It was initially formed as part of the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) in January 1978, and became an independent entity in 1987.
- Key Functions: BCAS establishes aviation security standards in line with Annex 17 of the Chicago Convention, ensuring compliance through oversight, training, and regular checks at airports.
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO): As a UN agency formed by the Chicago Convention in 1944, ICAO is dedicated to the safe and efficient regulation of global civil aviation, influencing standards for air safety and the rights of international flights.
In conclusion, the revocation of Celebi Aviation's license by BCAS underscores the intersection of national security and civil aviation regulation in India. With India poised to become a leading global air passenger market, maintaining stringent security standards is vital for the sector's growth and integrity.
Sighting of Eurasian Otter in Kashmir
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Common Otter, known locally as Vuder, has been sighted in Kashmir after a gap of 25 to 30 years. This species was historically present in areas such as Dachigam, the Dal Lake tributaries, the Rambiara stream, and the Lidder river in Pahalgam.
Key Takeaways
- The Eurasian Otter (Lutra lutra) is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal native to Eurasia.
- It is considered a keystone species in river ecosystems, indicating clean water and healthy aquatic biodiversity.
Additional Details
- Taxonomy: The Eurasian Otter belongs to the genus Lutra, family Lutrinae, and order Carnivora.
- Diet: Its diet mainly consists of fish, crustaceans, amphibians, and occasionally includes reptiles, birds, eggs, insects, and worms.
- Habitat & Behaviour: This species is found in the Himalayas, northeast India, and the Western Ghats. It prefers clean freshwater ecosystems such as rivers, lakes, streams, and wetlands, and is also observed in coastal areas. The Eurasian Otter is mostly nocturnal, builds dens (holts) near water, and typically lives a solitary life, although mothers may be seen with their cubs.
- Conservation Status: The IUCN lists the Eurasian Otter as Near Threatened. It is protected under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 (Schedule II) and is listed in CITES Appendix I.
This recent sighting of the Eurasian Otter highlights the importance of conservation efforts in Kashmir, emphasizing the need to protect their habitats to ensure the survival of this species and the biodiversity of the region.
3rd UN Ocean Conference
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The 2025 UN Ocean Conference (UNOC3), held in Nice, France, adopted the declaration “Our Ocean, Our Future: United for Urgent Action,” which reinforces global commitments to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) 14 (Life Below Water). Indigenous leaders called for a binding plastics treaty ensuring justice for vulnerable communities, with 95 countries supporting regulation of plastics from production to disposal. The declaration aims to address the triple planetary crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution that threatens the world’s oceans.
Key Takeaways
- The conference focused on accelerating action towards SDG 14 to conserve and sustainably use oceans.
- Indigenous leaders advocated for a binding treaty on plastics to protect vulnerable communities.
- Key outcomes included strengthening ocean governance and addressing climate change impacts.
Additional Details
- About the Conference: The UN Ocean Conference is a high-level global summit aimed at mobilizing action to conserve and sustainably use oceans, seas, and marine resources.
- Themes and Objectives: The conference addressed critical ocean challenges such as ocean warming, acidification, marine pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction.
- Major Past Outcomes: Previous conferences have led to significant pledges, including a target to protect 30% of marine areas by 2030.
The declaration from UNOC3 emphasizes the need for global cooperation to strengthen ocean governance and combat climate change, ensuring a sustainable future for marine ecosystems and communities dependent on them.
How the Triple Planetary Crisis is Harming Oceans and Marine Ecosystems
- Climate Change Impacts: Oceans absorb 90% of excess heat, leading to thermal expansion and increased salinity. This has made oceans 30% more acidic, harming marine life.
- Coral Reef Destruction: Rising temperatures are causing mass bleaching events, impacting biodiversity hotspots globally.
- Overexploitation of Marine Resources: Overfishing is leading to significant declines in key species, threatening marine biodiversity.
- Plastic & Chemical Pollution: Millions of tons of plastic enter oceans annually, causing harm to marine life and ecosystems.
- Habitat Destruction: Vital coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, are being cleared for development, affecting marine biodiversity.
What is the Need of Safeguarding Oceans?
- Ecological & Biodiversity Significance: Oceans produce over 50% of Earth’s oxygen and support 94% of all life.
- Climate Regulation: Oceans help regulate global temperatures and play a key role in climate balance.
- Economic & Livelihood Support: 3 billion people rely on seafood as a primary protein source, with fisheries and aquaculture supporting millions of jobs.
- Scientific & Medicinal Value: Marine organisms contribute to medical breakthroughs and enhance our understanding of the Earth's systems.
What Actions are Needed to Promote Ocean Sustainability?
- For Governments & Policymakers: Expand Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) to protect 30% of oceans by 2030 and finalize the Global Plastic Treaty.
- For Businesses & Industries: Adopt sustainable fishing practices and green shipping methods to reduce environmental impact.
- For Individuals: Choose sustainable seafood, reduce plastic use, and participate in local cleanups to help protect oceans.
- Indigenous & Local Knowledge: Embrace traditional fishing methods that promote sustainability and preserve marine life.
The 2025 UN Ocean Conference reinforced global commitments to protect oceans from overexploitation. Urgent, inclusive, and science-based actions—such as ending plastics and empowering Indigenous stewardship—are vital to ensure climate stability and sustain livelihoods for future generations.
Mains Question:
- What are the major threats facing the world’s oceans today? Suggest measures to ensure ocean sustainability.
Reforming Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010
Why in News?
- India is contemplating reforms to the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 (CLNDA 2010) to alleviate penalties on suppliers related to accidents, addressing concerns from foreign firms regarding unlimited liability. This initiative aims to revive stalled nuclear projects and support India's clean energy objectives.
Key Takeaways
- The CLNDA 2010 establishes a framework for compensation in case of nuclear accidents.
- It imposes strict liability on operators while introducing unique supplier liability provisions.
- Concerns over liability are hindering foreign investment in India's nuclear sector.
- Reforms are necessary to align India's nuclear laws with global standards.
Additional Details
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA, 2010): This law ensures compensation for victims of nuclear accidents and outlines the responsibilities of operators. It aligns with the Convention on Supplementary Compensation (CSC, 1997), which sets minimum compensation standards globally.
- Supplier Liability: Unique to the CLNDA, it allows operators to seek recourse from suppliers for damages arising from incidents involving defective equipment or sub-standard services, expanding accountability beyond traditional frameworks.
- Key Concerns: Suppliers face risks due to ambiguous definitions of nuclear damage and unclear insurance requirements, leading to hesitations in foreign investments.
- India's liability laws are viewed as barriers to nuclear agreements with nations like the United States, impacting collaboration and investment in the nuclear energy sector.
- Current liability clauses may disrupt progress towards India's clean energy goals, particularly the target of achieving 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030.
To effectively address these challenges, it is essential for India to reform the CLNDA 2010. By aligning with international norms, easing supplier concerns, and ensuring victim compensation, India can enhance its nuclear energy landscape and meet its clean energy aspirations.
India’s PM Historic Visit to Cyprus
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India’s Prime Minister's recent visit to Cyprus marks the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister in 23 years, representing a pivotal moment in strengthening bilateral relations. The focus of this visit includes enhancing cooperation in energy security, counterterrorism, and aligning strategies between India and the European Union (EU).
Key Takeaways
- This visit is significant for boosting relations between India and Cyprus.
- It is aimed at enhancing collaboration on energy security and counterterrorism.
- Strategic alignment with the EU is a key aspect of the discussions.
Additional Details
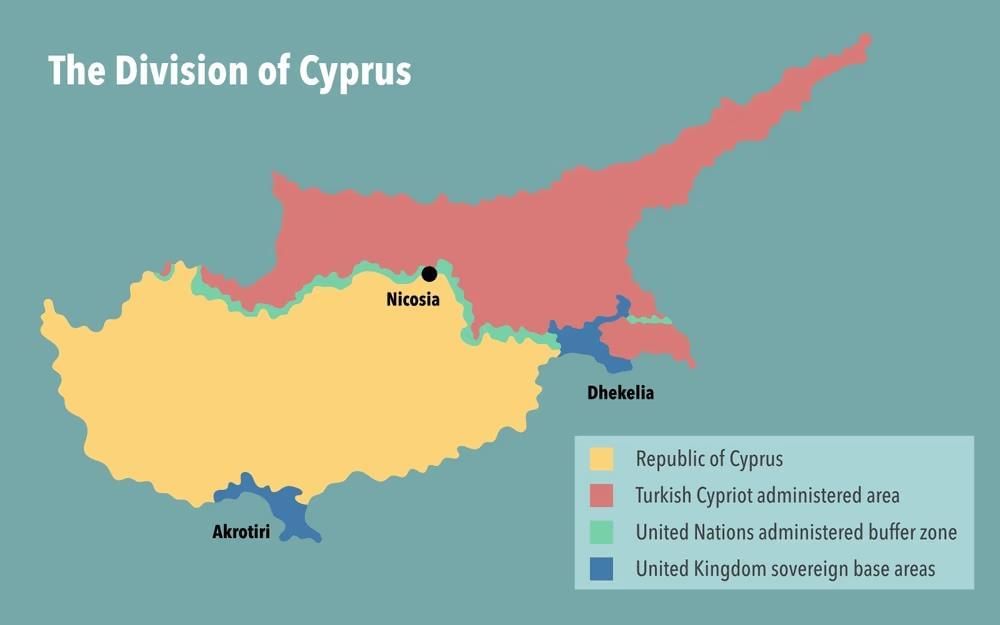
- About Cyprus: Cyprus is an island nation located in the northeastern Mediterranean Sea, at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. It is the third largest Mediterranean island after Sicily and Sardinia.
- Historical Background: Cyprus gained independence from Britain in 1960. However, a Turkish invasion in 1974 resulted in the island being divided into the Turkish-controlled northern region, recognized only by Turkey, and the internationally recognized Republic of Cyprus in the south. The UN maintains peace through patrols along the Green Line that divides the two regions.
- Political Division: Cyprus is politically divided between the internationally recognized Republic of Cyprus, which is a member of the EU, and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.
- Geography: Cyprus has a Mediterranean climate characterized by hot, dry summers and wet winters. Rainfall is crucial for agriculture on the island.
- India-Cyprus Relations: Diplomatic ties between India and Cyprus were established in 1962. India supports a bi-zonal, bi-communal federation for resolving the Cyprus issue, aligning with UN Security Council resolutions and international law. The relationship is further strengthened by historical ties, such as the shared vision of Archbishop Makarios and Pandit Nehru in the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
- Cyprus's consistent support for India's bid for membership in the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) and its stance on issues such as Kashmir and terrorism enhances India’s strategic engagement with Cyprus, serving as a counterbalance to the growing military ties between Turkey and Pakistan.
In conclusion, the Prime Minister's visit to Cyprus is not only a diplomatic milestone but also an opportunity to deepen strategic partnerships in various critical areas, establishing a stronger foothold in the Mediterranean region.
Reforming Subordinate Judiciary
Why in News?
- The subordinate judiciary, responsible for managing 87.5% of India's legal cases, is a crucial element of the country's legal framework. However, it currently faces significant challenges such as high vacancies, extensive case backlogs, and outdated processes that hinder India's economic progress. Reforming this essential component can lead to accelerated socio-economic development, as demonstrated by the experiences of Singapore and Kenya, where improvements in judicial efficiency have positively impacted economic growth.
Key Takeaways
- The subordinate judiciary experiences a silent economic drain of about 0.5% of GDP annually due to approximately 45 million pending cases.
- Reducing judicial vacancies can enhance investment and business confidence, with estimates suggesting a potential GDP per capita growth increase.
Additional Details
- Macroeconomic Impact: The World Bank reports that lowering judicial vacancies from 25% to 15% could significantly boost business confidence and investment.
- Stifled Business Growth: Ongoing land lease disputes create operational risks for MSMEs, discouraging investment and contributing to India's low ranking in the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business index.
- Fiscal Drain: Pending cases lead to the inefficient use of land, capital, and labor, as unresolved disputes drive businesses to operate informally, thus undermining tax compliance.
The subordinate judiciary in India faces various challenges that undermine its effectiveness.
Challenges in India’s Subordinate Judiciary
- Judicial Vacancies: With 5,388 vacancies in lower courts, judges handle an average of 746 cases annually, significantly above the global benchmark of 200-300 cases.
- Outdated Systems: Insufficient digitization and lack of integrated digital platforms hinder the efficiency of e-Courts, affecting the accessibility for rural litigants.
- Flawed Recruitment Policies: The requirement for three years of practice for district judge appointments limits diversity, as only 15% of practicing lawyers are women.
- Inefficient Case Management: Manual processes dominate, resulting in prolonged delays and ineffective case handling.
- Digital Divide: Rapid digital reforms risk excluding less-educated litigants, highlighting the need for inclusive technological implementations.
To strengthen the subordinate judiciary, several steps can be undertaken.
Steps to Strengthen India’s Subordinate Judiciary
- Fill Judicial Vacancies: Implement centralized, merit-based recruitment similar to the IAS to attract qualified candidates and enhance judicial efficiency.
- Digitization & AI-Driven Case Management: Establish a unified digital platform that utilizes AI to prioritize backlogged cases and transition to paperless operations.
- Expand Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): Encourage pre-litigation mediation and enhance community-based dispute resolution mechanisms to alleviate court case loads.
- Optimize Court Infrastructure: Introduce night courts and AI-based scheduling to improve case disposal rates and infrastructure utilization.
- Ensure Last-Mile Access: Create Village Legal Kiosks to facilitate e-filing and implement multilingual AI interfaces to aid non-English speakers.
In conclusion, India's subordinate judiciary is currently hindered by outdated systems and various challenges. However, reforms such as digitization, expansion of mediation, and optimized court hours, inspired by successful global models, can transform the judiciary into a catalyst for economic growth. Swift justice delivery will enhance social equity and help realize the full potential of a developed India.
Mains Question:
- India’s subordinate judiciary forms the backbone of justice delivery, yet suffers from systemic challenges. Discuss key reforms required to strengthen subordinate courts.
|
1452 docs|722 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st June 2025) - 1 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What are the main factors contributing to the Iran-Israel conflict? |  |
| 2. How does the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security impact India's aviation sector? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the sighting of the Eurasian Otter in Kashmir? |  |
| 4. What were the key outcomes of the 3rd UN Ocean Conference? |  |
| 5. How does reforming the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 impact nuclear safety in India? |  |
















