Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st May 2025) - 1 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
Evolution of India's Space Program
Why in News?
- The Global Space Exploration Summit (GLEX) 2025 is being held in New Delhi under the theme “Reaching New Worlds: A Space Exploration Renaissance.” The Prime Minister emphasized that India’s space programme goes beyond scientific discovery, serving as a tool to empower citizens and drive economic and social development. In a related development, the European Space Agency (ESA) highlighted its willingness to collaborate and explore larger, uncharted areas of space exploration.
Key Takeaways
- India's space program has evolved significantly over the decades.
- Recent missions have positioned India as a key player in global space exploration.
- Challenges remain, including budget constraints and geopolitical competition.
Additional Details
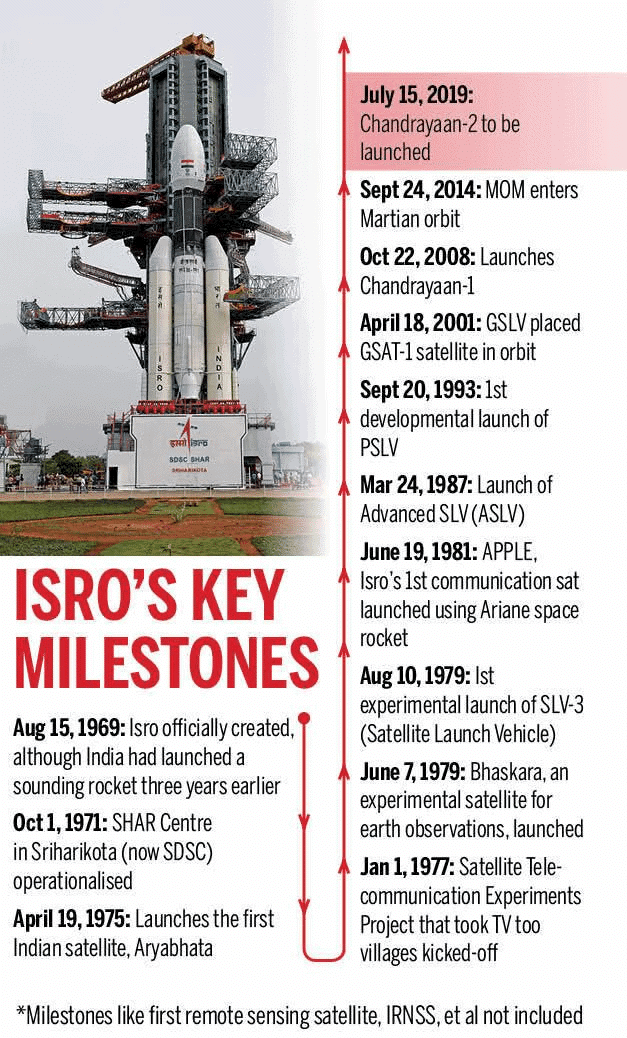
- Humble Beginnings (1960s–1970s): In 1963, India launched its first sounding rocket (US-made Nike-Apache) from Thumba, Kerala, focusing on basic atmospheric studies and establishing foundational infrastructure.
- Building Indigenous Capabilities (1980s–1990s): The development of the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) and the INSAT series for communication and weather monitoring marked significant advancements during this period.
- Global Arena Entry (2000s–2010s): India achieved milestones with the launch of Chandrayaan-1 in 2008, which discovered water molecules on the Moon, and the successful Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) in 2014.
- Future Ambitions (2020s–2040s): The Gaganyaan mission aims to send Indian astronauts to space, with plans for lunar missions by 2040 and the establishment of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station by 2035.
- Rise of the Private Sector: The growth of 250 space startups has fostered innovation in propulsion systems and satellite technology, exemplified by Skyroot Aerospace's Vikram-S, India's first private rocket launched in 2022.
- Economic and Social Development: ISRO's satellite data supports various public service schemes, enhancing rural land ownership rights and aiding disaster management effectively.
India's space program has evolved from its humble beginnings to a significant player in global space exploration, facing challenges such as budgetary constraints and competition from other countries. Emphasizing indigenous technology, talent retention, and international collaborations will be crucial for India's future space endeavors.
Mains Question:
- India's space program has evolved from basic atmospheric research to global space exploration. Discuss the key milestones and the challenges India faces in its space journey.
Growth in CSR Spending
Why in News?
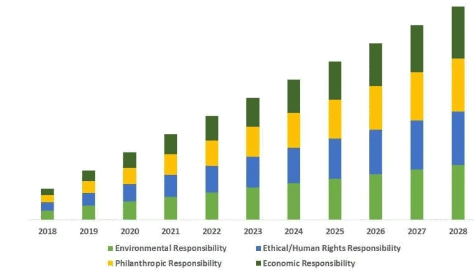
- The report by PRIME Database, an Indian market data firm, highlights a significant 16% increase in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure by listed companies in FY 2023-24. This increase is attributed to improved profitability across various sectors and reflects the evolving priorities in corporate philanthropy and compliance culture.
Key Takeaways
- CSR spending by listed companies rose to Rs 17,967 crore in FY 2023-24 from Rs 15,524 crore in FY 2022-23.
- Approximately 98% of companies met their CSR obligations, with nearly half exceeding the required spending.
- Education received the largest allocation at Rs 1,104 crore, followed by healthcare at Rs 720 crore.
- Top three states receiving CSR funds were Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu, accounting for 60% of total expenditure.
Additional Details
- What is Corporate Social Responsibility? CSR refers to a company's commitment to social and environmental accountability. It is a self-regulating model ensuring that businesses are aware of their broader roles in sustainable development.
- Legal Framework: India is the first nation to mandate CSR spending under Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013, which establishes a structured framework for eligible CSR activities.
- Applicability: CSR regulations apply to companies with a net worth exceeding Rs 500 crore, a turnover over Rs 1,000 crore, or a net profit above Rs 5 crore, requiring them to spend at least 2% of their average net profit from the last three financial years on CSR activities.
As CSR in India evolves from a voluntary act to a regulated tool for inclusive growth, it is crucial to enhance its strategic approach, transparency, and alignment with national priorities. Addressing challenges and implementing suggested measures can significantly improve CSR's impact on socio-economic development.
Dongria Kondh Tribe
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Dongria Kondh tribe, recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG), resides in the Niyamgiri Hills of Odisha. They are noted for their strong spiritual connection with nature and have a rich cultural heritage.
Key Takeaways
- The Dongria Kondh worship Niyam Raja, the deity of the hills.
- They practice Podu (shifting) cultivation and speak Kui, an ancient Dravidian language.
- This tribe has several sub-tribes, including Kovi, Kuttia, Languli, Penga, and Jharnia (the protector of streams).
Additional Details
- Land Rights and Legal Victory: In the 2000s, the Dongria Kondh firmly opposed Vedanta's mining operations on their ancestral land. This resistance led to a significant Supreme Court judgment in 2013 that upheld the Gram Sabha's constitutional right to reject mining projects in their area.
- PVTG: A sub-classification of Scheduled Tribes, PVTGs are considered more vulnerable than regular Scheduled Tribes. India has 75 PVTGs, with the largest number (13) located in Odisha, followed by 12 in Andhra Pradesh.
- Niyamgiri Hill Range: Located in the Kalahandi and Rayagada districts of Odisha, this area is bordered by Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary to the northwest and Kotgarh Wildlife Sanctuary to the northeast.
The Dongria Kondh tribe exemplifies the resilience of indigenous communities in protecting their rights and culture against external pressures. Their ongoing struggle for land rights highlights the importance of legal frameworks in safeguarding the interests of vulnerable groups.
Global Report on Internal Displacements 2025
Why in News?
- The Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) has released a report highlighting the number of disaster-related internal displacements and climate refugees globally in 2024.
Key Takeaways
- Total global internal displacements reached 45.8 million, the highest since records began in 2008.
- Disasters drove most displacements, with 99.5% linked to climate-related extreme weather.
- India experienced 5.4 million displacements in 2024, primarily due to floods.
Additional Details
- Disasters as Displacement Drivers: The majority of displacements were caused by climate-related disasters, exacerbated by climate change.
- India Related Findings: Floods were responsible for two-thirds of displacements, while violence accounted for 1,700 displacements, mainly in Manipur.
- Conflict and Climate Relation:20.1 million were displaced by conflict, particularly in climate-vulnerable regions.
Who are Climate Refugees?
- About: Climate refugees are individuals or communities forced to relocate due to the adverse effects of climate change and environmental degradation.
- Causes:
- Rising Sea Levels: Low-lying areas are becoming uninhabitable, with millions potentially displaced, e.g., 2–110 million in Bangladesh.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increasingly severe disasters, such as storms and floods, destroy homes and livelihoods, with 32.6 million displacements in 2022.
- Desertification: Areas like sub-Saharan Africa face forced migration due to land degradation.
- Water Scarcity: Climate change leads to reduced freshwater availability, with over 1 billion migrants affected.
Consequences
- Humanitarian Crises: Climate displacement often results in food shortages, health crises, and overcrowded living conditions.
- Urban Strain: Displaced populations add pressure to already strained urban areas.
- Social Conflicts: Competition for resources can lead to conflicts between displaced persons and host communities.
- National Security Concerns: Unmanaged displacement can pose security risks, particularly in fragile regions.
Legal and Policy Challenges for Climate Refugees
- Lack of Legal Recognition: Current international law does not recognize climate refugees under the 1951 Refugee Convention.
- Gaps in Migration Plans: The Global Compact on Migration recognizes climate displacement but is non-binding.
- Strict Border Controls: Various countries implement strict measures that inhibit the movement of climate migrants.
Current Provisions for Protection of Climate Refugees
- Limited Applicability of 1951 Refugee Convention: Some cases of drought-related famine may qualify for protection.
- Regional Refugee Instruments: Some regional frameworks offer broader definitions of refugees that can include climate-related displacement.
Improving Management of Climate Refugees
- Legal Reforms: Establish a new UN Convention on Climate Refugees and expand regional protection schemes.
- National-Level Innovations: Introduce initiatives like Climate Humanitarian Visas.
- National Adaptation Plans: Countries should integrate climate migration into disaster risk reduction strategies.
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Support mechanisms for climate-resilient infrastructure for displaced communities.
The IDMC 2025 report underscores the escalating crisis of climate-induced displacement, highlighting that disasters are driving unprecedented displacements worldwide, including in India. Despite increasing vulnerabilities, legal protections for climate refugees remain insufficient, necessitating urgent reforms and climate-resilient strategies to manage these challenges effectively.
India’s Battle Against Tuberculosis
Why in News?
- The Prime Minister recently chaired a high-level review meeting on the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) and emphasized the necessity for targeted, data-driven interventions and the application of technology to expedite India’s goal of eliminating tuberculosis (TB) by 2025.
Key Takeaways
- India's TB incidence has decreased by 18% from 2015 to 2023, exceeding the global decline of 8%.
- TB mortality rates fell by 21%, with a reduction from 28 to 22 deaths per lakh population.
- India accounted for over 26% of global TB cases and deaths in 2023.
- 85% of TB treatment coverage achieved through decentralized care.
- 12.97 crore individuals screened during the 100-Day TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan campaign.
Additional Details
- Reduction in TB Incidence and Mortality: The WHO Global TB Report 2024 highlights significant progress, with a reduction in incidence from 237/lakh in 2015 to 195/lakh in 2023.
- Nikshay Mitra Initiative: This initiative has seen 2.55 lakh volunteers distribute 29.4 lakh nutrition baskets to TB patients, showcasing community involvement.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana: Since 2018, this scheme has enabled Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) payments to 1.28 crore TB patients, enhancing nutritional support.
- Expansion of Diagnostic Infrastructure: The establishment of NAAT labs and AI-enabled X-ray units has improved accessibility and early detection of TB.
- Screening in Vulnerable Areas: Efforts have been made to screen high-risk populations in settings like mines and urban slums.
Despite these advancements, challenges persist, particularly for vulnerable groups. Addressing issues such as inadequate nutrition, delayed diagnosis, and social stigma will be crucial for achieving TB elimination by 2025. Targeted interventions, including early detection strategies and community participation, are essential for overcoming these hurdles and ensuring that all groups receive the support they need.
Gig Economy in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
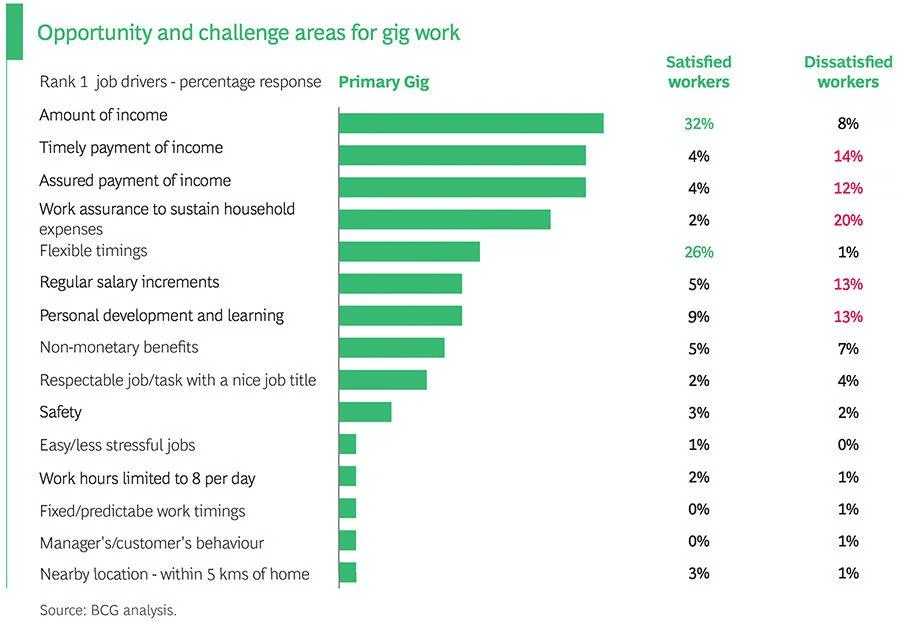
- The recent meeting of gig workers on "Current Developments, Challenges, and the Way Forward," organized by the Gig Workers Association, emphasized significant issues in India’s gig economy. It recommended the establishment of minimum wages, social security, and legal protections for gig and platform workers. Furthermore, it called for the creation of tripartite welfare boards at state and national levels, including representatives from workers, employers, and the government.
Key Takeaways
- The gig economy is defined as a labor market characterized by short-term, flexible jobs.
- There are approximately 7.7 million gig workers in India, projected to reach 23.5 million by 2029-30.
- Key factors driving growth include increased digital access, an e-commerce boom, and changing work preferences.
Additional Details
- Gig Worker Definition: A gig worker is defined by the new Labour Codes of 2019 as someone who performs work outside of a traditional employer-employee relationship.
- Status of India’s Gig Economy: According to a NITI Aayog report, most gig workers are engaged in medium-skilled jobs, with significant growth anticipated due to various economic factors.
- Opportunities: The gig economy offers flexible work options, enhancing personal and professional balance, especially for women.
- Challenges: Major issues include a lack of legal protections, employment instability, and inadequate government responses that leave gig workers vulnerable.
In conclusion, the gig economy holds significant potential for job creation and economic growth in India, but it requires urgent reforms to address the challenges faced by gig workers, ensuring their rights and protections are upheld.
Geographical and Climatic Factors Influencing Heatwaves
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Andhra Pradesh and Telangana experience intense heat waves during summer due to a combination of unique geographical features and climatic conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Heat waves are significantly influenced by geographical and climatic factors.
- The regions near the Tropic of Cancer are particularly vulnerable to extreme heat.
Additional Details
- Latitude and Solar Intensity: Areas close to the Tropic of Cancer, like Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, receive intense solar radiation during summer when the sun is almost directly overhead. This vertical solar incidence increases ground heating, causing significant temperature rises.
- Terrain and Surface Characteristics: The Deccan plateau in Telangana has rocky and barren landscapes that absorb more heat compared to vegetated areas. Black soils retain heat longer, contributing to elevated daytime temperatures. Conversely, regions with dense vegetation experience cooling effects due to evapotranspiration.
- Landlocked Regions: Most of Telangana is landlocked, leading to greater temperature variations due to the absence of nearby water bodies, which moderate temperatures. Coastal areas benefit from the cooling effects of large water bodies.
- Urban Heat Islands: High population density and extensive concrete surfaces in urban areas absorb and retain heat, creating localized zones with elevated temperatures, exacerbating heat waves.
- Rainfall and Humidity: Low pre-monsoon rainfall leads to dry soils, reducing moisture and limiting evaporative cooling. High humidity exacerbates heat stress by hindering sweat evaporation.
- Wind and Atmospheric Conditions: Weak winds during heat waves prevent heat from dispersing, causing surface temperatures to intensify. Stable atmospheric conditions can trap heat, prolonging heat waves.
- El Niño Effect: The El Niño phenomenon reduces cloud cover and rainfall, leading to higher surface temperatures and conditions conducive to heat waves.
In summary, a combination of geographical and climatic factors significantly influences the intensity and frequency of heat waves in regions like Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, highlighting the need for effective management and response strategies.
What are Heat Waves?
- Heat waves are periods of unusually high temperatures relative to the normal climate of a region. The threshold for declaring a heat wave varies by location, depending on historical temperature patterns. In India, heat waves typically occur from March to June, peaking in May.
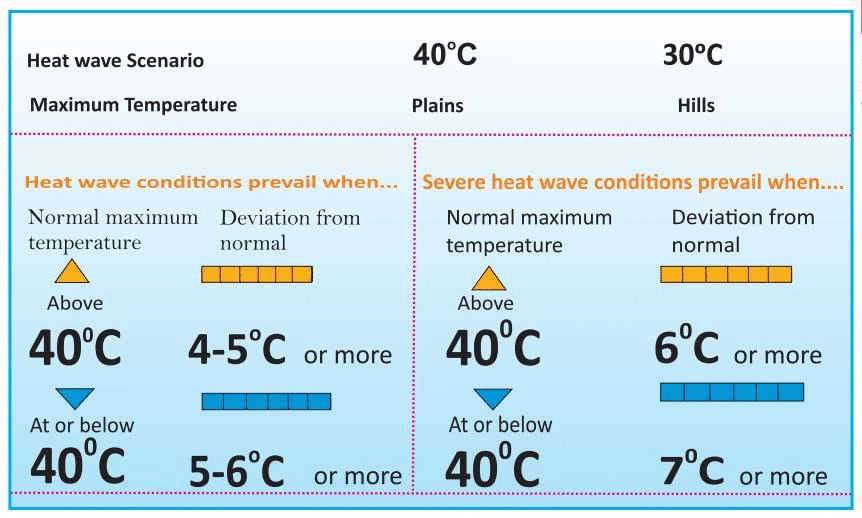
India Meteorological Department (IMD) Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave
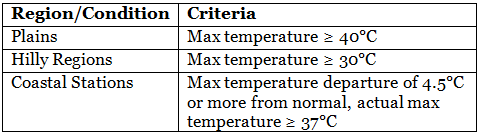
What is the Impact of the Heat Waves?
- Impact on Human Health: Heat waves can cause severe illnesses such as heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke, especially affecting vulnerable groups like the elderly and outdoor workers.
- Economic Impact: Prolonged heat exposure affects productivity in industries, leading to significant economic losses.
- Environmental Damage: Increased forest fires and evaporation rates threaten ecosystems and water availability.
- Agricultural Impact: Extreme heat affects crop yields and threatens food security, particularly for Kharif crops.
What are India’s Initiatives to Tackle Heat Waves Issue?
- Heat Action Plans (HAPs): Updated across 23 states to manage heat waves strategically, including heat profiles and vulnerability assessments.
- IMD Heat Wave Warnings: A color-coded warning system issued in collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on water conservation and restoration of water bodies to aid hydration during heat waves.
- Smart Cities Mission: Promotes green cover and climate-resilient infrastructure to mitigate urban heat.
- Cool Roof Initiatives: Programs to use reflective materials to reduce indoor temperatures in urban areas.
Overall, understanding the geographical and climatic factors behind heat waves is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts.
Child Wellbeing in an Unpredictable World

Why in News?
- A recent report from the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF) titled “Child Wellbeing in an Unpredictable World” highlights a significant decline in the academic performance, mental health, and physical wellbeing of children in the wealthiest nations since the Covid-19 pandemic began.
Key Takeaways
- Academic performance has deteriorated, with many children lacking basic literacy and numeracy skills.
- Mental wellbeing has declined, particularly in 14 of the 32 countries surveyed.
- Physical health issues, such as obesity, have increased significantly across various countries.
- The Netherlands and Denmark rank highest in child wellbeing metrics.
Additional Details
- Academic Setbacks: School closures lasting from 3 to 12 months disrupted education. By 2022, about 8 million 15-year-olds (~50% of that age group) were not functionally literate or numerate, a 4% increase since 2018.
- Mental Wellbeing Decline: Life satisfaction among children fell sharply in most countries, with Japan being the singular exception reporting improvements.
- Physical Health Concerns: Obesity rates rose in 14 out of 43 countries, which reflects a concerning trend towards poor physical health among children.
- Best in Child Wellbeing: The Netherlands and Denmark lead in child wellbeing, followed by France, indicating a model for other nations to emulate.
What is the Status of Child Wellbeing in India?
In India, the child wellbeing situation is concerning, with numerous challenges affecting mental and physical health.
- Mental Well-being: A significant number of children with mental health issues remain undiagnosed and untreated, with 50 million affected even before the pandemic.
- Physical Health: Over 27 million children in India may be obese by 2030, prompting serious economic repercussions.
- Skills Development: Despite having one of the largest school systems, learning outcomes in literacy and numeracy remain poor, with a learning poverty rate of 70% post Covid-19.
What are the Causes of Declining Child Wellbeing?
- Economic Inequality: Disparities lead to inadequate access to basic needs, impacting children's health and education.
- Social Causes: Discrimination and harmful practices adversely affect many children's rights and wellbeing.
- Digital Inequality: The shift to digital education has excluded many children lacking access to technology.
- Climate Change: Environmental stressors exacerbate health issues and disrupt education, impacting children's overall wellbeing.
What Measures India can take to Improve Child Wellbeing?
- Strengthening Nutrition and Health Interventions: Improve Integrated Child Development Services to enhance nutrition, immunization, and early education.
- Addressing Mental Health: Implement school-based mental health programs to support children effectively.
- Digital Literacy: Integrate cyber safety courses into school curricula to prepare children for online challenges.
- Combating Child Abuse: Ensure strict enforcement of laws protecting children's rights and wellbeing.
In conclusion, UNICEF’s findings serve as a crucial reminder for global governments to prioritize child wellbeing through comprehensive policies addressing education, mental health, and nutrition. Immediate and sustained action is essential to safeguard the future of an entire generation.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the multidimensional impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on child wellbeing and suggest policy measures to address these challenges.
|
287 docs|142 tests
|





















