Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th January 2025) Part - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
IPBES Transformative Change Assessment
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- A recent report from the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) titled Transformative Change Assessment emphasizes the crucial role of governance in combating biodiversity loss. It underscores that effective governance, which emphasizes inclusivity and sustainability, is vital for preserving biodiversity and fostering long-term systemic change.
Key Takeaways
- Prevent Ecological Damage: Urgent shifts in societal interactions with nature are needed to avert biodiversity loss, with inaction risking irreversible damage, including the loss of coral reefs and rainforests.
- Economic and Employment Opportunities: Immediate actions could unlock USD 10 trillion in business opportunities and support 395 million jobs globally by 2030, particularly in nature-dependent industries.
- Causes of Biodiversity Loss: Key drivers include disconnection from nature, dominance over natural resources, concentration of power and wealth, and prioritization of short-term gains over sustainability.
Five Key Strategies for Transformation
- Conserve and Regenerate: Focus on biocultural diversity areas that integrate environmental restoration with cultural values, exemplified by community-driven forest management in Nepal.
- Systematic Change in Key Sectors: Address critical sectors such as agriculture, fisheries, and infrastructure to implement sustainable practices that reduce biodiversity loss.
- Transform Economic Systems: Transition towards nature-positive economies by reforming harmful subsidies and endorsing sustainable business models.
- Adaptive Governance: Develop governance systems that incorporate diverse actors, including Indigenous communities, prioritizing biodiversity in policy-making. Adaptive governance allows for ongoing strategy adjustments in response to changing environmental conditions.
- Shift Views and Values: Encourage recognition of human-nature interconnectedness through education, experiential activities, and integration of diverse knowledge systems.
What is Transformative Change and How Can it be Achieved?
- Transformative Change: This refers to a fundamental, system-wide reorganization that encompasses technological, economic, and social factors, including shifts in paradigms, goals, and values, essential for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Steps to Achieve Transformative Change:
- Carbon-Neutral Actions: Promote carbon neutrality as a norm for individuals, businesses, and governments while supporting legitimate climate-friendly offsets.
- Earth-Positive Choices: Facilitate easy, enjoyable, and affordable ways for individuals to positively impact the environment through supply chain adjustments and policy influences.
- Reforming Subsidies: Redirect subsidies to promote environmental stewardship and transition from resource-extractive industries to sustainable practices.
- Precautionary Decision-Making: Embrace precautionary, adaptive, inclusive, and cross-sector decision-making to proactively address environmental threats.
- Strengthening Environmental Laws: Advocate for robust environmental legislation, consistent enforcement, and support for global initiatives that protect nature and encourage sustainable economic activities.
What are India’s Initiatives for Transformative Change?
- National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP)
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- National Action Plan on Climate Change
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME)
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
SDGs for Transformative Change
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):Focus on inclusive growth for sustainable development, addressing key areas such as:
- Life Below Water
- Climate Action
- Clean Energy
- Clean Water
- Responsible Consumption
- Life on Land
India's initiatives, including the Smart Cities Mission and Green India Mission, align with various SDGs and aim to make substantial investments in renewable energy, targeting 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030 under the International Solar Alliance.
Mains Question
- Discuss the concept of transformative change. How can this be implemented to address biodiversity loss and achieve sustainable development?
Muslim League and Rise of Communal Politics in India

Why in News?
- On 30th December 1906, the All India Muslim League was founded in Dhaka, marking the inception of a political organization that played a pivotal role in India’s Partition. Over the years, the League evolved from a group of elite Muslim men to a mass political party under the leadership of Muhammad Ali Jinnah, advocating for the creation of Pakistan.
Key Takeaways
- The Muslim League was founded to protect the political and religious rights of Muslims.
- Under Jinnah's leadership, the League transformed into a significant political force advocating for Pakistan.
- The Lucknow Pact marked a moment of cooperation between Congress and the Muslim League.
- The Lahore Resolution in 1940 became the ideological foundation for Pakistan's creation.
- Direct Action Day led to significant communal violence, escalating the demand for partition.
Additional Details
- Founders: Key figures included Nawab Salimullah of Dhaka, Nawab Viqar-ul-Mulk, Nawab Mohsin Ul-Mulk, and Aga Khan.
- Initial Objective: The League aimed to secure separate representation for Muslims in legislative bodies.
- Emergence of Jinnah’s Leadership: Jinnah's Fourteen Points in 1929 outlined significant Muslim political demands, including autonomy and minority safeguards.
- The Lucknow Pact (1916): This agreement between Congress and the Muslim League called for increased Indian representation in councils and accepted separate electorates for Muslims.
- The Lahore Resolution (1940): Emphasized the demand for "Independent States" for Muslims, laying the groundwork for Pakistan.
- Direct Action Day (August 1946): Resulted in communal riots, deepening the Hindu-Muslim divide and accelerating the partition process.
- Post-Partition Role: The League became Pakistan's dominant political party but later fractured into various factions.
The All India Muslim League played a critical role in the political landscape of pre-independence India, particularly in the context of communal politics. Its evolution from an elite group to a mass movement under Jinnah's leadership was instrumental in shaping the demand for Pakistan, which ultimately led to the Partition of India in 1947. The rise of communal politics during this period not only impacted the future of India and Pakistan but also set the stage for ongoing communal tensions that continue to influence the subcontinent.
India’s Journey of Infrastructure Development
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India's infrastructure has undergone significant transformation over the past 25 years, marked by enhanced progress and increased private participation. However, considerable challenges persist, as approximately 90% of the necessary infrastructure remains to be constructed to realize the goal of a USD 30 trillion economy by 2047.
Key Takeaways
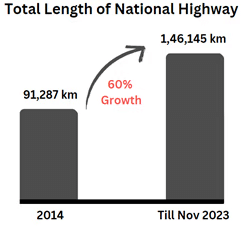
- India's road network has nearly tripled since 2000, reaching 146,000 km.
- Introduction of modern access-controlled expressways and GPS-based toll systems.
- Railway electrification has improved significantly, with 93.83% of broad-gauge tracks electrified by December 2023.
- India aims to invest Rs 54 trillion in the maritime sector to emerge as a top-five shipbuilding nation by 2047.
- Weekly domestic flights increased from 3,568 in 2000 to 22,484 in 2024.
Additional Details
- Roads and Highways: Since 2014, the government has constructed 3.74 lakh km of rural roads, enhancing accessibility to over 99% of rural areas. Toll collections have reached Rs 2.1 trillion over 25 years, indicating strong private sector involvement.
- Railways: India's first bullet train is expected to be completed by 2026, with a significant reduction in consequential accidents over the past decade.
- Maritime Sector: Development of mega ports and 839 Sagarmala projects are underway to improve trade connectivity.
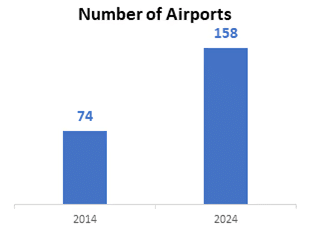
- Aviation: The operational number of airports has increased to 158, with 84 airports built between 2014 and 2024.
- Urban Metro: The metro network expanded from 248 km in 2014 to 945 km by 2024, serving 21 cities and 1 crore daily passengers.
- Ropeways Development: The Parvatmala Programme initiated 32 ropeway projects to improve connectivity in difficult terrains.
Challenges in India’s Infrastructure Sector
- Stalled and Delayed Projects: Major projects like the Rs 10 trillion Bharatmala Project and the Rs 20 trillion Vision 2047 plan face delays due to bureaucratic hurdles.
- Sluggish Progress: Railway route expansion has been slow, averaging only 231 km of new tracks added per year since 2000.
- Private Sector Dependency: Increasing reliance on the private sector has raised concerns regarding toll collection and capital recycling strategies.
- Maritime Disruption: Global events have hindered progress in the maritime sector, affecting India’s aspirations in shipbuilding.
- Aviation Sector Bottlenecks: Intense competition has led to the bankruptcy of several airlines, raising concerns about market consolidation.
Way Forward
- Integrated Infrastructure: The PM GatiShakti National Master Plan will enhance project synergy and reduce delays.
- Safer and Resilient Infrastructure: Initiatives like KAVACH for railways will improve safety and reduce accident rates.
- Incorporating Green Technologies: Transitioning to electric vehicles and alternative fuels will aim to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation.
- Technological Integration: Innovations such as FASTags and Digiyatra will streamline travel and enhance convenience.
- Policy and Regulatory Reforms: A clear framework is needed to encourage private sector investment in critical infrastructure sectors.
In conclusion, while India has made remarkable strides in its infrastructure development over the past 25 years, significant challenges remain. Addressing these challenges through integrated planning, technological advancements, and robust policy frameworks is essential for achieving the ambitious goal of a USD 30 trillion economy by 2047.
Quad Marks 20 Years of Cooperation
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Quad Foreign Ministers commemorated the anniversary of Quad cooperation, reaffirming their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific in the face of China’s increasing assertiveness.
Key Takeaways
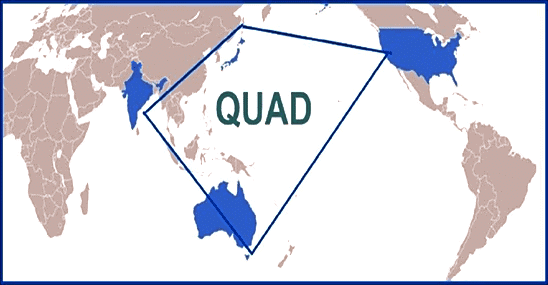
- Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) includes the US, Japan, India, and Australia.
- Quad aims to enhance regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
- Key initiatives include maritime security, health, technology, and climate change responses.
Additional Details
- About Quad: The Quad is a strategic forum focused on promoting a free and open Indo-Pacific, upholding democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, while countering China's expansive influence.
- Formation: The Quad originated from the collaborative tsunami relief efforts in 2004, officially formed in 2007, and was revived in 2017.
- Key Initiatives: The Quad has introduced several initiatives such as the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) and the Quad Cancer Moonshot aimed at improving healthcare and regional cooperation.
- Significance for India: The Quad enhances India's maritime security, provides a platform for addressing regional challenges, and promotes economic opportunities, particularly post-COVID-19.
- Contemporary Relevance: The Quad plays a crucial role in counterbalancing China’s influence, engages in diverse global issues, and strengthens ties through institutional mechanisms and people-centric initiatives.
- Challenges: The Quad faces issues like a lack of formal structure, divergent priorities among members, and resource constraints which could hinder its effectiveness.
In conclusion, the Quad's strategic significance for India is marked by its role in safeguarding maritime interests, providing a counterweight to China's assertiveness, and fostering economic and scientific collaboration, thus enhancing regional stability and cooperation.
Tapping Renewable Energy Potential in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
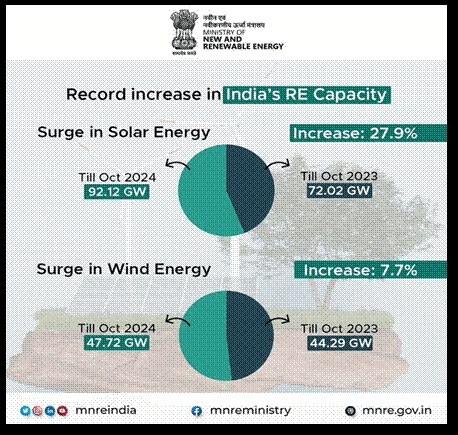
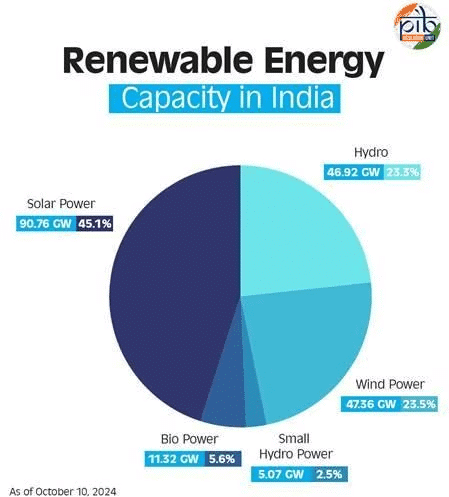
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has recently urged states to facilitate land availability for renewable energy projects, emphasizing wind power development. Currently, India has a renewable energy capacity of 47.95 GW, with ambitions to double this to 100 GW and enhance land access to achieve a target of 500 GW of non-fossil energy by 2030.
Key Takeaways
- India's total installed renewable energy capacity as of November 2024 is 158.55 GW.
- Wind power capacity stands at 47.96 GW with an addition of 2.07 GW in FY 2024-25.
- Solar power leads with an installed capacity of 94.17 GW.
- Hydro power contributes 5.08 GW from small hydro projects.
- Biomass energy adds 10.72 GW to the renewable mix.
- Waste-to-energy projects contribute 0.61 GW.
Additional Details
- Solar Energy: India enjoys over 300 sunny days a year; the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) estimates a potential of 748 GW if 3% of wasteland is utilized for solar PV.Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu are leading states in solar energy development.
- Wind Energy: India's wind energy potential exceeds 300 GW, primarily found in Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka. Offshore projects in coastal regions like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu could further enhance capacity.
- Hydro Energy: India has more than 148 GW of hydroelectric potential, with 46 GW untapped.
- Geothermal Energy: Significant potential exists in regions like Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Jharkhand, with projects in the Puga Valley showcasing this potential.
- Ocean Energy: India can harness approximately 40 GW of wave energy, particularly in coastal regions such as the Gulf of Kutch and Sundarbans.
Despite progress, challenges such as land scarcity, financing issues, and integration into the grid persist. Addressing these challenges through improved policies, infrastructure investment, and community engagement is crucial for meeting the ambitious renewable energy targets.
DILRMP and Digitalisation of Land Records
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- As of 2024, a remarkable 98.5% of rural land records in India have been digitized, representing a significant milestone in the nation’s land reform efforts aimed at enhancing transparency. This achievement stems from the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP), launched in 2008, which focuses on digitizing and modernizing agricultural land records to improve accessibility and minimize disputes.
Key Takeaways
- The DILRMP aims to ensure transparency and accessibility in land records.
- As of now, 98.5% of rural land records have been digitized.
- The program is part of the broader efforts towards land reforms in India.
Additional Details
- About DILRMP: The National Land Record Modernization Programme (NLRMP) was revamped to DILRMP in 2016. It is a central sector scheme funded entirely by the government, focusing on modernizing the land records system and implementing a conclusive land-titling system with title guarantees.
Key Initiatives Under DILRMP:
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN): This 14-digit alphanumeric code, known as "Bhu-Aadhar", is assigned to each land parcel based on its geo-coordinates, aiding in property transactions and dispute resolutions.
- National Generic Document Registration System (NGDRS): This system standardizes the registration process across India, facilitating online entry and payments.
- e-Court Integration: Linking land records with e-Courts aims to streamline access to authentic land information for faster judicial resolutions.
- Transliteration of Land Records: This initiative allows land documents to be available in any of the 22 languages listed in the Indian Constitution, thus breaking language barriers.
- Bhoomi Samman: Recognizes districts achieving high completion rates in the core components of the program, enhancing the overall efficiency of land record management.
India's agriculture sector employs over 45% of the workforce, highlighting the necessity for a modernized land record management system to support the economy and promote equitable land reforms. The digitization of land records serves multiple purposes:
Benefits of DILRMP
- Improve Land Records Quality: Enhances the accuracy and reliability of land ownership and transaction records through digitization.
- Reduce Litigation and Frauds: Establishes a conclusive land-titling system, ensuring clear ownership rights and minimizing disputes.
- Promote Development and Growth: Facilitates efficient land markets, reduces transaction risks, and promotes investment in various sectors.
Challenges Associated with Land Record Digitisation
- Language and Dialect Barriers: Linguistic diversity may impede understanding and acceptance of digitization among rural populations.
- Community Shareholdings: Traditional practices in community-based land ownership complicate the standardization of records.
- Lack of Awareness: Many stakeholders are unaware of the benefits and procedures related to DILRMP.
- Quality of Land Records: Outdated titles and cadastral maps hinder the accuracy of digitized records.
- Complexity of Land Management Systems: Multiple regulations and departments complicate the digitization process.
- Lack of Resources: Insufficient funds and infrastructure challenge the effective implementation of DILRMP.
Way Forward
- Integration of Land Records: Develop a unified platform that links land records with registration, tax payments, and government services.
- Updation of Records: Regular audits and technology-driven mapping should be employed to maintain accurate land records.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educate stakeholders on the benefits of digitization and how to access digital records.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Establish online platforms for efficient handling of land disputes.
- Policy Framework: Create a comprehensive policy that aligns technology integration with national goals.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Foster collaborations to leverage technological expertise in land record management.
Mains Question:
- What are the advantages and challenges associated with the digitalisation of land records in India?
2025 as Year of Reforms for Defence Force
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recently, the Ministry of Defence has decided to observe 2025 as the ‘Year of Reforms’ to transform the Armed Forces into a technologically-advanced combat-ready force capable of multi-domain integrated operations.
Key Takeaways
- The reforms aim to enhance jointness, integrate emerging technologies, simplify acquisition processes, and position India as a credible defence exporter.
- Focus areas include veteran welfare and the promotion of indigenous culture in the military context.
Additional Details
Jointness & Integration: Strengthening cooperation among military services through the establishment of Integrated Theatre Commands (ITCs) such as:
- China-focused northern command in Lucknow
- Pakistan-focused western command in Jaipur
- Maritime command in Thiruvananthapuram
Emerging Technologies: Focus on domains like Cyber and Space, and technologies including:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Hypersonics
- Robotics
Associated tactics, techniques, and procedures will also be developed.
- Simplifying Acquisition: Streamlining acquisition procedures to accelerate capability development.
- Defence Exporter: Efforts to establish India as a credible exporter of defence products, with exports having risen from Rs 2,000 crore in 2014 to over Rs 21,000 crore.
- Veteran Welfare: Ensuring the welfare of veterans while leveraging their expertise to foster pride in Indian culture.
Need for Reforms
- Lack of National Security Strategy (NSS): The absence of an NSS creates a gap between political intentions and military operations, leading to unpreparedness against emerging threats.
- Rise of Cyberwarfare: Cyberspace has become a critical domain for warfare, with state-sponsored cyber attacks highlighting vulnerabilities.
- Dependence on Imports: India remains the world's top arms importer and faces challenges in developing a competitive domestic defence industry.
- Cultural Resistance to Jointness: Service-specific approaches hinder the adoption of integrated military models.
- Insufficient Funding: Despite considerable allocations, funding only constitutes 1.9% of India's GDP, limiting modernization efforts.
- Ad-hoc Procurement Processes: Emergency procurement powers have highlighted a lack of strategic readiness.
- Short-term Policy Concerns: The Agnipath scheme's short training period raises concerns about combat readiness and retention of experienced personnel.
Way Forward
- Institutional Reforms: Establishing the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and the Department of Military Affairs (DMA) to improve military decision-making.
- Integrating Technologies: Emphasis on autonomous systems and AI to gain a technological edge against adversaries.
- Boost Domestic Defence Industry: Encourage public-private partnerships to strengthen domestic defence capabilities.
- Maximise Defence Cooperation: Strengthening ties with global powers like the US to enhance strategic autonomy.
- National Defence University (NDU): Establishing an NDU for advanced training and research in defence strategies and technologies.
In summary, the proposed reforms for the Indian Defence Forces in 2025 focus on modernization, integration, and self-reliance, addressing both current challenges and future needs for a more robust military framework.
|
39 videos|4393 docs|930 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th January 2025) Part - 1 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the IPBES Transformative Change Assessment for India? |  |
| 2. How did the rise of communal politics impact the Muslim League in India? |  |
| 3. What are the key milestones in India’s journey of infrastructure development? |  |
| 4. What are the main objectives of the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) and its impact on regional cooperation? |  |
| 5. How is India harnessing its renewable energy potential? |  |






















