Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th July 2025) - 2 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
UN Women & the Global Gender Agenda
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- As we approach the 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, the 25th anniversary of UNSC Resolution 1325 on Women, Peace and Security (WPS), and its own 15th anniversary, UN Women has issued a warning that women's rights are encountering a "historic and precarious moment." This is largely due to escalating violence, worsening poverty, and increasing digital and political exclusion affecting women globally.
Key Takeaways
- Political Backlash: In 2024, nearly 1 in 4 countries noted a backlash against women's rights.
- Violence Against Women: In 2023, 85,000 women and girls were intentionally killed, averaging one woman killed every 10 minutes by a partner or close relative.
- Economic Disparity: Women earn 20% less than men for equal work and undertake 2.5 times more unpaid care work.
- Education and Food Insecurity: 119 million girls are out of school, and 47.8 million more women face food insecurity compared to men.
- Climate Vulnerability: By 2050, climate change may push an additional 158 million women into extreme poverty.
- Health Risks: Nearly 800 women die daily from preventable pregnancy-related causes.
Additional Details
- Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (BPfA): Adopted in 1995, this landmark global framework aims to advance the rights of women and girls, focusing on legal protection, access to essential services, youth engagement, and social transformation. India is a signatory to the BPfA.
- Beijing+30 Action Agenda: This initiative marks the anniversary (1995-2025) of the BPfA and reviews its implementation, focusing on six key areas for gender equality.
- UN Women’s Proposed Solutions: These include strengthening commitment and leadership, promoting gender-inclusive peacebuilding, advocating for economic empowerment, eradicating poverty and food insecurity, and expanding access to education and technology.
In conclusion, despite global commitments to women's rights, significant barriers persist. Governments must enforce legal reforms, promote economic empowerment, foster inclusive peacebuilding, and address climate justice to reverse the regression and ensure continued progress for women's rights.
Custodial Torture in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The recent custodial death in Tamil Nadu has once again highlighted the critical issue of custodial torture in India.
Key Takeaways
- Custodial torture involves the infliction of physical or mental suffering on individuals held by police or authorities.
- It is a severe violation of human rights, often leading to custodial deaths.
- India recorded 490 custodial deaths between 2016 and 2022, with Uttar Pradesh having the highest number.
Additional Details
- What is Custodial Torture? It refers to causing physical or mental suffering to individuals held in custody, which can lead to fatal outcomes known as custodial deaths.
- Types of Custodial Torture:
- Physical Torture: Includes beatings, electric shocks, suffocation, sexual violence, forced stress positions, and denial of medical care.
- Psychological Torture: Involves threats, humiliation, sleep deprivation, solitary confinement, and mock executions.
- Custodial Deaths in India: Between 2016 and 2022, there were 490 recorded custodial deaths, with significant numbers in southern states and a disproportionate impact on Scheduled Castes.
- Constitutional and Legal Safeguards: Provisions in the Indian Constitution and various laws aim to protect against custodial torture, including Articles 14, 21, 20(1), and 20(3).
- Challenges: Include lack of specific anti-torture legislation, weak enforcement, institutional impunity, and fear of reprisal among victims.
Custodial torture remains a pressing human rights violation in India, exacerbated by legal gaps and systemic failures. Urgent reforms and stringent measures are necessary to address this issue effectively.
Blocking of AI Web Crawler
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- In a significant development, leading publishers in the US and UK have begun to block Artificial Intelligence (AI) web crawlers to safeguard their content from unauthorized use. This has sparked renewed discussions in India regarding the need for consent-based copyright protections and equitable revenue distribution, highlighting vital issues in digital governance, copyright enforcement, and the ethical application of AI.
Key Takeaways
- AI Web Crawlers: Automated tools that collect content from the internet to train AI models.
- Regulatory Challenges: India's current lack of a framework for overseeing AI access to web content.
- Copyright Issues: Use of content for training AI without proper consent or compensation.
- Ethical Concerns: The need for transparency in data usage by AI developers.
Additional Details
- What is an AI Web Crawler? An AI web crawler is a type of automated software or bot that scans and collects content from the internet primarily for training AI models, such as Large Language Models (LLMs), or to aid in real-time information retrieval for AI assistants.
- Types of AI Web Crawlers:
- Model Training Crawlers: These extract data from websites to train generative AI models. Examples include GPTBot from OpenAI and Amazonbot from Amazon.
- Live Retrieval Crawlers: These bots gather real-time data from websites to enhance pre-trained models during user interactions, ensuring accurate and updated responses. They are utilized by platforms like Bing and ChatGPT.
- Lack of Regulatory Framework: India currently has no specific regulations governing how AI companies can access and utilize online content. This results in larger tech companies profiting from Indian content without consent, leaving smaller publishers vulnerable.
- Copyright Enforcement: The existing Copyright Act of 1957 does not adequately address AI-specific scenarios, such as the rights associated with derivative outputs or training data. There is ambiguity surrounding the concepts of fair use versus unlicensed training.
- Ethical Use of AI: Many AI developers do not disclose the data sources used, denying original creators recognition or compensation. Additionally, using outdated or unverified material for training can lead to biases and misinformation, eroding public confidence in AI technologies.
- Path Forward for India: India should consider global frameworks like the EU's AI Act of 2024, which addresses issues of copyrighted data in AI training. Establishing a consent-based licensing framework and defining unauthorized data scraping is crucial.
These challenges highlight the urgent need for India to create a digital ecosystem that respects creators' rights while fostering innovation. The Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) and the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting (I&B) should work together to implement technical safeguards and provide tools to help publishers protect their digital content.
NITI Aayog Report on Chemical Industry
Why in News?
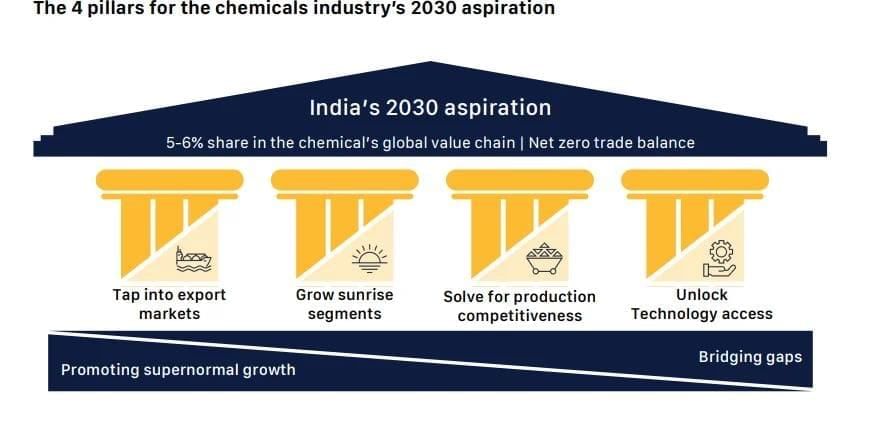
- The NITI Aayog has released its report titled ‘Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains’, which outlines an ambitious roadmap for India to emerge as a global chemical manufacturing powerhouse. The report aims for India to achieve a 12% share in global chemical value chains (GVC) and reach a USD 1 trillion output by 2040.
Key Takeaways
- India ranks as the 6th largest chemical producer globally, contributing over 7% to the manufacturing GDP.
- The sector supports critical industries: pharma, textiles, agriculture, and construction.
- India holds only a 3.5% share in global chemical value chains, with a USD 31 billion trade deficit in 2023.
- There is a significant shortage of skilled professionals (30%) in the chemical sector.
Additional Details
- Global Standing: India is a major player in the global chemical market, but it has a fragmented sector primarily dominated by MSMEs, with growth concentrated in states like Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
- Import Dependence: Over 60% of critical Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are sourced from China, highlighting the sector's vulnerability.
- Opportunities: Rising domestic demand in agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and construction is expected to drive growth, along with expected job creation of 7 lakh skilled jobs by 2030.
- Policy Interventions: Proposed measures include establishing world-class chemicals hubs, enhancing port infrastructure, and fast-tracking environmental clearances.
In conclusion, the chemical industry is poised to be a significant driver of GDP growth in India. With effective policy interventions, including the establishment of chemical hubs and an emphasis on research and development, India aims to transform into a global manufacturing leader by 2030. However, addressing challenges such as import dependency and regulatory hurdles is crucial for realizing this potential.
SC Upholds Legislative Authority of State
Why in News?
- The Supreme Court ruling in the Nandini Sundar vs. State of Chhattisgarh case from 2011 emphasizes the legislative power of state assemblies in India and their interaction with judicial decisions within the democratic framework.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court directed the Chhattisgarh government to stop using Special Police Officers (SPOs) due to their inadequate training and violations of constitutional rights.
- In response, the state passed the Chhattisgarh Auxiliary Armed Police Forces Act to establish a new auxiliary force.
- The Supreme Court rejected a contempt plea, affirming the state's legislative authority as long as laws are constitutional.
- The ruling reaffirmed the doctrine of separation of powers, allowing legislatures to enact laws that may alter the basis of previous judgments.
Additional Details
- Background of the Case: The Supreme Court found that the use of SPOs in anti-Maoist operations violated Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution, prompting legislative action.
- Legislative Authority: The Court clarified that state legislatures can enact new laws to remove the basis of a judgment or to validate previously struck down laws.
- Similar Judicial Pronouncements: In the Indian Aluminium Co. vs. State of Kerala (1996) case, the Supreme Court upheld legislative power to amend or enact laws retrospectively to remove the basis of a judgment.
- Salwa Judum & Koya Commandos: This was a state-backed anti-Maoist initiative launched in 2005, involving tribal youth, primarily from the Koya tribe, to combat Maoist insurgency.
This ruling reinforces the balance of power between the judiciary and the legislature in India, ensuring that while courts can issue orders, state legislatures retain the authority to legislate within constitutional limits.
India - Trinidad and Tobago Relations

Why in News?
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi's recent visit to Trinidad and Tobago marks a significant milestone, being the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister since 1999. During this visit, he was honored with the country's highest civilian award, the Order of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, in recognition of his global leadership, strong engagement with the diaspora, and humanitarian efforts during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Key Takeaways
- Trinidad and Tobago joined India's initiatives on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure and Biofuels.
- India will provide funding for up to five grassroots development projects annually.
- An MoU was signed to enhance cooperation in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Training programs for Trinidad and Tobago diplomats in India were agreed upon.
- The OCI card facility will now extend to the sixth generation of the Indian diaspora.
- Collaboration on digital solutions, including India Stack initiatives, was established.
- India provided USD 1 million in agro-machinery to support local agriculture.
- Both nations committed to strengthening counterterrorism efforts and regional ties.
- Cultural exchanges through the establishment of ICCR Chairs and training for Hindu priests were announced.
Additional Details
- Historical Ties: The relationship between India and Trinidad and Tobago dates back to 1845, when the first Indian indentured laborers arrived. Today, their descendants account for 40-45% of the population, significantly influencing the socio-economic landscape.
- Bilateral Relations: Formal diplomatic relations were established in 1962, characterized by a warm and evolving partnership.
- Economic Cooperation: A trade agreement granting Most Favoured Nation status was signed in 1997, fostering trade growth post-pandemic.
- Development Initiatives: A USD 1 million project implemented during the pandemic included advanced healthcare technology in Trinidad and Tobago.
Overall, the evolving relations between India and Trinidad and Tobago reflect a commitment to mutual cooperation across various sectors, including culture, economy, and disaster resilience, highlighting India's broader strategy in the Global South.
Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The 62nd annual session of the Bonn Climate Change Conference was held in Bonn, Germany. This mid-year meeting sets the stage for important climate negotiations leading up to the 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which will take place in Belem, Brazil.
Key Takeaways
- Progress on the Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA) was noted, but disagreements over finance and Means of Implementation (MoI) hindered consensus. A draft list of 100 indicators is anticipated at COP30.
- Significant advancements were made on the Just Transition Work Programme (JTWP), with negotiators agreeing to establish a Belém Action Mechanism for sharing fair transition strategies.
- Most nations failed to meet the February 2025 deadline for updating their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which affects efforts to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
- Intense discussions on climate finance, with developing nations pressing for the fulfillment of financial pledges, particularly the mobilization of USD 1.3 trillion annually until 2030.
- The Loss and Damage Fund remains underfunded, with only USD 768 million pledged against the required USD 1 trillion.
Additional Details
- Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA): Initiated in the Paris Agreement (2015), the GGA aims to enhance adaptive capacity and climate resilience. Concrete actions were delayed until COP28 in Dubai, where a framework for its implementation was adopted.
- Just Transition Work Programme (JTWP): Launched at COP27 (2022), the JTWP aims to ensure that climate actions are equitable and aligned with national development goals while supporting communities affected by the transition from fossil fuels.
- National Climate Plans: Brazil has called on nations to submit stronger NDCs by September 2025 to meet the 1.5°C target, as current submissions are insufficient.
- Climate Finance: Disputes arose as developing countries emphasized the need for public grants, while wealthier nations suggested private finance as a solution.
- Loss and Damage Fund: Only USD 321 million has been paid into the fund, highlighting the gap between pledges and actual contributions.
The Bonn Climate Change Conference serves as a critical platform for advancing global climate negotiations and addressing urgent environmental challenges. The outcomes of this conference will significantly influence the direction of future climate policies and commitments at COP30.
|
287 docs|142 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th July 2025) - 2 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What is the role of UN Women in promoting the global gender agenda? |  |
| 2. What are the implications of custodial torture in India on human rights? |  |
| 3. How does the blocking of AI web crawlers impact internet accessibility and innovation? |  |
| 4. What insights does the NITI Aayog report on the chemical industry provide regarding its growth and sustainability? |  |
| 5. How does the Indian Supreme Court uphold the legislative authority of the state in recent rulings? |  |
















