Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th April 2025) - 2 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
Safeguarding the Taj Mahal
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Supreme Court (SC) of India has instructed the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) to evaluate the environmental impact of glass industrial units near the Taj Mahal. This directive arises from increasing concerns regarding industrial pollution in the Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ), an area sensitive to the world heritage site.
Key Takeaways
- The Taj Mahal was commissioned by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal.
- Construction began in 1632 AD and concluded in 1648 AD, with additional structures completed by 1653 AD.
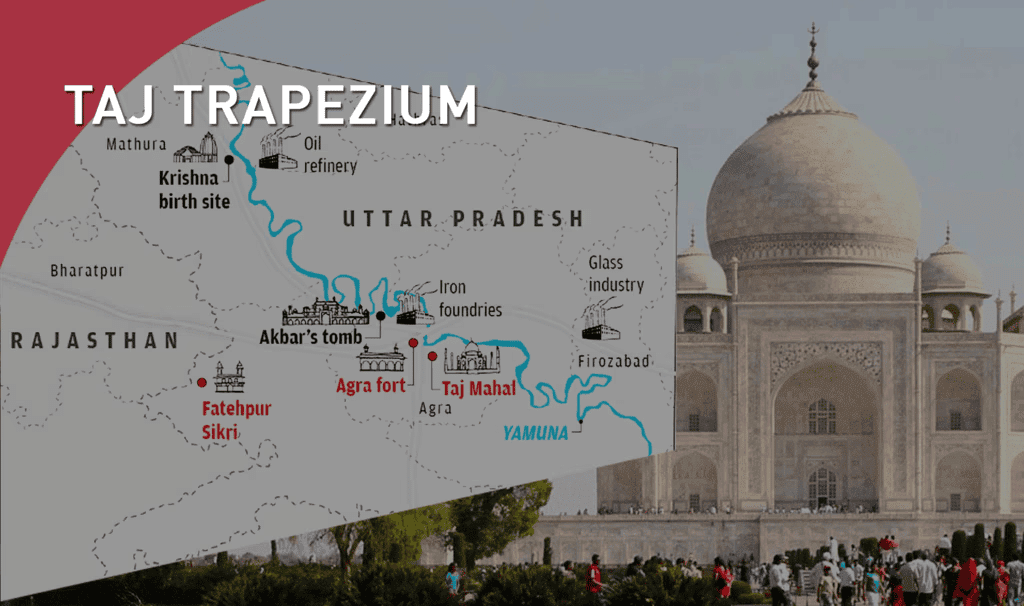
- It is located in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, surrounded by a 17-hectare Mughal garden.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983, it is celebrated as a masterpiece of human creativity.
Additional Details
- Historical Background: The Taj Mahal, designed by chief architect Ustad Ahmad Lahori, utilized artisans from the Mughal Empire, Central Asia, and Iran.
- Location & Layout: It is situated along the Yamuna River and features a Timurid-Persian Charbagh layout.
- Materials Used: Built primarily from white marble sourced from Makrana, Rajasthan, with intricate inlay work using various gemstones.
- Architectural Features: The tomb chamber is an octagon that includes cenotaphs of Shah Jahan and Mumtaz Mahal, with real graves located in a lower crypt.
- Protection and Management: The Taj Mahal has been a centrally protected monument since 1920, managed by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ): A defined area of 10,400 sq km established to mitigate pollution threats to the monument.
- The SC’s 1996 judgment mandated a ban on coal/coke usage in the TTZ and required a transition to cleaner fuels.
With various reports highlighting pollution sources, including vehicular emissions and industrial activities, the preservation of the Taj Mahal faces significant challenges. Addressing these threats involves strict regulatory measures and the adoption of cleaner technologies.
What are the Threats to the Taj Mahal?
- Hota Committee (2016): Identified local pollution sources contributing significantly to air quality degradation in Agra.
- 262 Parliamentary Report (2015): Highlighted operational inefficiencies within the TTZ Authority, including inadequate staffing and funding.
- NEERI Report (2016): Found that PM2.5 and PM10 levels exceeded permissible limits, with significant contributions from the Mathura Refinery.
What Must Be Done to Safeguard the Taj Mahal?
- Adopt Flue Gas Recirculation (FGR): Recommended by NEERI to improve emission quality in the glass industry.
- Transition to Clean Energy: Industries in the TTZ should shift to cleaner fuels like piped natural gas (PNG).
- Integrated Traffic Management: Promote non-motorized transit and expand Agra Metro to reduce vehicular emissions.
- Institutional Strengthening: Empower the TTZ Authority with statutory powers and a dedicated budget for effective management.
- Relocate Polluting Industries: Accelerate the relocation of identified heavy polluters, as encouraged by the SC.
Ultimately, safeguarding the Taj Mahal requires a comprehensive approach that includes regulatory enforcement, technological upgrades, and community engagement to ensure the monument's preservation for future generations.
Climate Crisis and Gender-Based Violence
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- A recent report released by the UN Spotlight Initiative highlights a disturbing correlation between climate change and an increase in gender-based violence (GBV) against women, particularly in impoverished and vulnerable communities. The findings indicate that without immediate action, climate change could lead to one in ten cases of intimate partner violence (IPV) by the year 2100.
Key Takeaways
- A rise of 1°C in temperature correlates with a 4.7% increase in intimate partner violence (IPV).
- By 2090, 40 million additional women and girls may experience IPV annually if global warming reaches 2°C, with this number more than doubling at 3.5°C.
- Limiting warming to 1.5°C could reduce IPV rates from 24% to 14% by 2060.
Additional Details
- Disaster-Induced Violence: In 2023, 93.1 million individuals were affected by climate disasters, leading to 423 million cases of IPV. Notably, heatwaves contributed to a 28% increase in femicide, while post-disaster situations heightened risks of child marriage, human trafficking, and sexual exploitation, especially after floods and droughts.
- The report characterizes GBV as a "shadow pandemic," noting that one in three women worldwide has suffered from physical, sexual, or psychological abuse, with only 7% of survivors reporting these incidents.
- Vulnerable Groups: Women in poverty, those living in informal settlements, agricultural workers, Indigenous communities, individuals with disabilities, the elderly, and LGBTQ+ individuals face higher risks of GBV due to inadequate support systems.
- Women advocating for environmental rights are often subjected to harassment, violence, and even murder.
- Funding Gaps: A mere 0.04% of climate-related development assistance targets gender equality, reflecting a significant oversight in addressing GBV within climate action efforts.
The UN report outlines several key recommendations to combat GBV in the context of climate change:
- Integrate GBV in Climate Policy: It's essential to embed GBV prevention strategies into all climate policies at local, national, and global levels, ensuring increased funding focused on gender issues.
- Prioritize Women’s Safety and Leadership: Women should be integral to climate solutions as both leaders and beneficiaries. It is crucial to recognize GBV as a barrier to climate resilience, making it a priority in sustainable development initiatives.
- Support Civil Society Organizations: Strengthening organizations like the Pacific Feminist Community of Practice is vital for ensuring gender justice within global climate platforms such as COP27.
- Adopt Best Practices: Implementing gender-responsive programs, as seen in Vanuatu, Liberia, and Mozambique, can link gender justice with climate resilience. This includes retraining former female genital mutilation (FGM) practitioners in climate-smart agriculture and embedding GBV services in disaster response efforts.
In conclusion, the climate crisis is fundamentally a gendered issue. The findings from the UN report emphasize the urgent need for integrating gender equity and violence prevention into climate strategies. For both India and the global community, this requires a reevaluation of policy frameworks to ensure they are inclusive, responsive, and rights-centered. Only through such measures can we hope to build a climate-resilient future that is safe and just for all.
Mains Question:
- Examine the link between the climate crisis and gender-based violence. What measures can be taken to incorporate gender-responsive strategies in climate action?
Reviving the World Trade Organization

Why in News?
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) was established to promote rules-based global trade. However, challenges such as rising protectionism, the dysfunction of its dispute settlement mechanism, and an increase in preferential Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) have led to concerns about its continued relevance.
Key Takeaways
- The Appellate Body, crucial for resolving trade disputes, has been non-functional since 2019 due to the US blocking new judge appointments.
- The Doha Development Round has stalled, especially on agriculture, highlighting conflicts between developed and developing nations.
- The Most-Favoured-Nation (MFN) principle is being undermined by the proliferation of FTAs.
- Protectionist measures, notably the US-China trade war, challenge WTO principles.
- The WTO struggles to address new trade issues like digital economy and climate change.
- Geopolitical rivalries and disagreements over the classification of developing countries hinder consensus.
Additional Details
- Paralysis of the Dispute Settlement Mechanism: The Appellate Body's inactivity has weakened global trade rule enforcement, leading to a state of "appeals into the void."
- Negotiation Deadlock (Doha Round Failure): Initiated in 2001, the Doha Round aimed to enhance global trade equity for developing countries but has faced significant barriers, particularly concerning agricultural subsidies.
- Erosion of the MFN Principle: The rise of FTAs, which often bypass MFN obligations, has fragmented trade regulations and diminished the WTO’s multilateral approach.
- Rise of Protectionism: The use of national security exceptions to justify protectionist policies undermines the principles of the WTO.
- Power Asymmetry Among Members: Developed countries' push for aggressive reforms contrasts with developing nations' needs for equitable treatment in trade negotiations.
The WTO's significance cannot be understated. Established in 1995, it replaced the GATT and has played a crucial role in liberalizing global trade, with 166 member countries representing 98% of world trade. The organization has seen trade volumes increase significantly, with average tariffs halving since its inception. However, the current geopolitical climate and internal challenges necessitate a revival of the WTO to ensure it can adapt to modern trade dynamics.
How WTO Can Be Revived in a Multipolar World?
- Move Beyond Trade Liberalization: The WTO should evolve to support equitable globalization by crafting enforceable rules in emerging sectors like digital trade and green technology.
- Restore the Dispute Settlement System: Address US concerns to restore the Appellate Body to ensure effective dispute resolution.
- Redefining Special and Differential Treatment (SDT): Eligibility for SDT should be based on dynamic criteria rather than self-declaration to ensure fair treatment.
- Institutionalizing Trade-Climate Linkages: Develop a framework that aligns trade with climate objectives to prevent new forms of protectionism.
- Creating a Permanent WTO Reform Council: Establish a council to propose systemic reforms every five years, adapting to new global realities.
In conclusion, revitalizing the WTO in a multipolar world requires a shift towards inclusivity and adaptability, addressing both developmental needs and emerging global challenges, while upholding the fundamental principles of fair and rules-based trade.
Contributions of Dr. K. Kasturirangan
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Dr. K. Kasturirangan, who served as the chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) from 1994 to 2003, has passed away in Bengaluru. His contributions to space science and technology have left a lasting legacy in India.
Key Takeaways
- He was instrumental in the development of Chandrayaan-1, India's first lunar mission.
- Oversaw the launch of key satellite programs, including IRS and INSAT series.
- Contributed significantly to remote sensing and national development initiatives.
- Played a vital role in drafting the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Awarded prestigious honors such as Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Vibhushan.
Additional Details
- Leadership in ISRO: Dr. Kasturirangan was pivotal in launching Chandrayaan-1 in 2008, marking India's entry into lunar exploration. He also managed key satellite programs, including the operationalization of the IRS and INSAT series.
- Role in Remote Sensing: He contributed to the National Natural Resource Management System (NNRMS), which provided satellite-based services to sectors such as agriculture, forestry, and health.
- Pioneering Space Applications: He initiated various thematic space missions like EDUSAT for tele-education and INSAT/GSAT for telemedicine, which significantly impacted social and economic development in India.
- Policy Contributions: After his tenure at ISRO, he served as a member of the Rajya Sabha and the Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog). He chaired the committee responsible for the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Recognition and Awards: His contributions earned him numerous accolades, including Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Vibhushan, along with international recognition for his advancements in space science.
Dr. K. Kasturirangan's legacy in space exploration and education continues to inspire future generations, reflecting his profound impact on India's scientific landscape.
Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha

Why in News?
- The position of Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha, which is crucial for maintaining impartiality and continuity within the House, has remained unfilled since the 17th Lok Sabha and continues to be vacant in the 18th Lok Sabha. Although the Constitution does not specify a timeline for this appointment, the language used in Articles 93 and 178 indicates that an election is obligatory.
Key Takeaways
- The Deputy Speaker is essential for ensuring the Lok Sabha functions smoothly, especially in the absence of the Speaker.
- The election process for the Deputy Speaker is governed by parliamentary rules, requiring a simple majority of those present and voting.
- The office plays a vital role in maintaining legislative order and impartiality.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 93: Mandates the Lok Sabha to elect a Speaker and Deputy Speaker from its members.
- Article 94: Outlines the procedures for vacation, resignation, and removal of the Deputy Speaker.
- Article 95(1): States that the Deputy Speaker performs the Speaker's duties in their absence.
- Article 178: Contains provisions for the Speaker and Deputy Speaker in State Assemblies.
- Election Process: The Deputy Speaker is elected by a simple majority of Lok Sabha members present and voting, and the Speaker sets the election date.
- The position has alternated between parties, with the opposition holding it on various occasions as a convention, though not mandated by law.
- No separate oath is required for the Deputy Speaker; the MP's oath under the Third Schedule is sufficient.
- Tenure & Removal: The Deputy Speaker serves during the Lok Sabha's life but can vacate the office under specific conditions such as resignation or removal by a majority vote.
The significance of the Deputy Speaker's role extends beyond mere procedural duties. It ensures legislative continuity, upholds constitutional authority, and reinforces impartiality in parliamentary proceedings. The post is traditionally offered to opposition members, fostering bipartisan cooperation and reinforcing democratic values.
What Safeguards are Required for Effective Functioning of the Deputy Speaker’s Office?
- Clear Time Frame for Election: Amendments or rules should mandate the election of the Deputy Speaker within a specific period, such as 30 days after the new Lok Sabha's first sitting.
- Regular Delegation of Authority: Regularly delegating presiding duties to the Deputy Speaker can enhance the office's efficiency and relevance.
- Clear Role Codification: Defining the Deputy Speaker’s powers through detailed rules or statutory frameworks can help reduce ambiguity and safeguard against executive influence.
In conclusion, the Office of the Deputy Speaker is a fundamental component of India's parliamentary democracy. It not only facilitates legislative processes but also exemplifies respect for governance and institutional integrity. It is essential for Parliament to act swiftly in line with constitutional principles to uphold this vital office.
Mains Question: Discuss the constitutional and functional importance of the Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha.
Cucumber Mosaic Virus and RNA Silencing
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- A research team from Germany has made significant advancements in plant immunity by developing an effective double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) enriched with potent small interfering RNA (siRNA). This innovative method has been shown to reduce the viral load of the Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV) by up to 80%, surpassing traditional methods. The approach utilizes RNA silencing, a natural defense mechanism in plants, to accurately detect and eliminate the virus.
Key Takeaways
- CMV is a widespread plant virus affecting over 1,200 species.
- The new dsRNA technology significantly enhances plant immunity against CMV.
- RNA silencing is a key natural defense mechanism in plants.
Additional Details
- What is Cucumber Mosaic Virus? CMV is one of the most common plant viruses worldwide, belonging to the genus Cucumovirus in the Bromoviridae family. It affects a vast range of plants, including vegetables, cereals, ornamentals, and medicinal plants.
- Symptoms: Infected plants exhibit yellow mottling, distorted leaves, and stunted growth. Symptoms are prevalent in cucumbers, melons, bananas, and pumpkins.
- Transmission: The virus is primarily spread by sap-sucking insects such as aphids, with around 90 species capable of transmitting CMV, complicating containment efforts.
- Impact on India: In India, CMV results in yield losses of 25-30% in bananas and up to 70% in pumpkins, cucumbers, and melons, leading to noticeable mosaic discoloration and deformed fruits, with no known cure available.
What is RNA Silencing in Plants?
RNA silencing is a natural defense mechanism that helps plants combat viral infections. When a virus infects a plant, it introduces double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), triggering the plant's immune system to respond.
Working of RNA Silencing
- The plant activates Dicer-like enzymes (DCLs) in response to viral infection.
- DCLs cut the dsRNA into small fragments known as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
- These siRNAs guide the plant's defense system to identify and eliminate the viral RNA, preventing further spread of the infection.
Limitations of RNA Silencing
- Not all siRNAs produced by the plant are effective against the virus.
- CMV can mutate rapidly, often escaping the plant's natural defense mechanisms, which limits the reliability of this process.
Human Developed RNA Silencing Technologies
- Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS): This method involves genetically modifying plants to produce virus-fighting dsRNA, providing ongoing protection. However, its application is hindered by regulatory issues, high costs, and potential for viral resistance.
- Spray-Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS): This flexible approach involves treating plants with RNA sprays to stimulate their immune responses without genetic modification. Although SIGS is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, its effectiveness is limited due to the traditional dsRNA formulations producing a random mix of siRNAs, many of which may not effectively silence the virus.
In conclusion, advancements in RNA silencing technologies, particularly the recent developments using dsRNA and siRNA, represent a promising avenue for enhancing plant immunity against Cucumber Mosaic Virus and potentially other viral threats.
World Bank’s Poverty & Equity Brief Report
 Why in News?
Why in News?
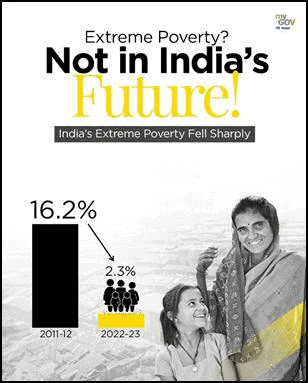
- The World Bank's Spring 2025 Poverty and Equity Brief report commended India for successfully lifting 171 million people out of extreme poverty between 2011-12 and 2022-23. This achievement lowered the extreme poverty rate from 16.2% to 2.3%, underscoring India's commitment to inclusive development through various welfare schemes and enhanced access to essential services.
Key Takeaways
- Extreme poverty in India has significantly decreased, with rural poverty falling from 18.4% to 2.8% and urban poverty from 10.7% to 1.1% during the same period.
- The five most populous states accounted for 65% of India's extreme poor in 2011-12 and contributed to two-thirds of the decline in extreme poverty by 2022-23.
- India's Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) decreased from 53.8% in 2005-06 to 16.4% in 2019-21, indicating improvements in living conditions.
Additional Details
- Employment Growth: Employment rates are on the rise, particularly for women, with urban unemployment at its lowest since 2017-18. However, only 23% of non-farm paid jobs are formal.
- Despite achieving a 31% female employment rate, significant gender gaps remain, with 234 million more men in paid work.
- Lower-Middle-Income Level Progress: The poverty rate at the USD 3.65 per day line dropped from 61.8% to 28.1%, lifting 378 million people out of poverty.
These statistics reflect that the benefits of economic growth have reached lower-middle-income groups in both rural and urban areas.
Social Issues Related to Poverty
- Marginalization of Vulnerable Communities: Poverty exacerbates the marginalization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs), limiting their access to education, healthcare, and employment.
- Health Disparities: Inadequate access to nutritious food and healthcare leads to widespread health issues in impoverished areas.
- Water Stress: Limited access to clean drinking water in rural communities results in waterborne diseases and poor sanitation.
- Energy Poverty: Lack of affordable energy in rural areas restricts educational and economic opportunities.
- Mental Poverty: Chronic stress and anxiety due to financial insecurity hinder productivity and social participation.
- Gender Disparity: Early marriage and domestic violence in impoverished communities perpetuate the cycle of poverty, with significant disparities in economic participation for women.
- Environmental Degradation: Reliance on unsustainable practices worsens poverty by reducing agricultural productivity and increasing vulnerability to climate change.
Measures to Address Social Issues Linked to Poverty
- Social Welfare and Economic Empowerment: Strengthening affirmative action and welfare schemes is essential for improving access to healthcare, education, and employment.
- Bridging the Gender Gap: Expanding women’s access to education and financial independence is crucial, alongside ensuring equal pay and skill development.
- Improving Energy Access: Promoting solar-powered solutions will enhance energy access, particularly in remote areas.
- Universal Water Access: Prioritizing large-scale water conservation programs is vital for ensuring access to clean drinking water.
- Enhancing Mental Health Support: Scaling up mental health programs and training community health workers to address mental health issues at the grassroots level is necessary.
- Ensuring Transparency & Accountability: Implementing Aadhaar-based authentication in welfare schemes will help eliminate fraudulent beneficiaries.
Tackling poverty in India requires a multifaceted approach that addresses inequalities, resource access, and policy efficiency. By enhancing welfare schemes and empowering marginalized communities, India can make significant strides in poverty reduction. Sustained efforts and collaborative action will pave the way for a more inclusive and prosperous future for all.
Mains Question:
- Critically examine the impact of government welfare schemes on poverty alleviation and suggest effective measures to address the social issues linked to poverty in India.
Balancing AI Growth with Clean Energy
Why in News?
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has highlighted that the economic advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI) may surpass its environmental drawbacks related to rising energy demands in data centers, particularly in nations that are adopting renewable energy sources. As India's AI infrastructure develops, it is crucial to integrate renewable energy into AI advancements.
Key Takeaways
- AI has the potential to generate Rs 33.8 lakh crore in economic value in India by 2030.
- AI can significantly enhance productivity in various sectors including agriculture, manufacturing, and finance.
Additional Details
- Massive Economic Potential: According to a Google report, AI adoption could contribute 20% to India's GDP, aiding the nation in achieving its goal of a USD 1 trillion digital economy by 2028.
- Energy Consumption: Data centers that support AI models consume substantial electricity, primarily from fossil fuels. In 2024, data centers consumed 415 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity.
- Carbon Emissions: AI systems, especially those reliant on fossil fuel energy sources, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, with AI hardware accounting for 1% of global emissions, projected to double by 2026.
- Water Consumption: Training large AI models can use up to 700,000 liters of water, highlighting the pressure on freshwater resources.
AI can also be utilized to address environmental challenges through initiatives like pollution control, weather forecasting, and conservation efforts.
What is India's Approach in Integrating AI with Renewable Energy?
- Integration of AI with Renewable Energy: The IndiaAI Mission emphasizes the significance of merging AI with renewable energy to alleviate the energy costs associated with AI growth.
- Future Prospects: Exploring the use of small modular reactors for clean energy in AI data centers is underway.
Challenges in Integrating AI with Renewable Energy
- Limited Renewable Energy Capacity: India’s dependency on fossil fuels currently limits the potential for renewable energy in AI infrastructure.
- Insufficient Grid Infrastructure: The existing energy grid requires modernization to manage decentralized renewable sources effectively.
- Economic Barriers: High initial investments for renewable energy infrastructure can deter participation from the private sector.
Aligning AI Ambitions with Sustainable Energy Practices
- Massive Solar and Wind Capacity: India's climate is favorable for renewable energy, which can support AI data centers.
- Green Backup Power: Transitioning from diesel generators to green alternatives such as hydrogen fuel cells can reduce carbon footprints.
- AI-Powered Smart Grids: Implementing smart grid technologies can optimize energy distribution and enhance efficiency.
In conclusion, integrating renewable energy with AI development is essential for minimizing environmental impacts while maximizing economic benefits. As India aims for a sustainable future, innovative solutions and robust policies will be critical to achieving this balance.
|
287 docs|142 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th April 2025) - 2 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What are the main strategies for safeguarding the Taj Mahal from climate change effects? |  |
| 2. How does gender-based violence relate to the climate crisis? |  |
| 3. What are the key proposals for reviving the World Trade Organization (WTO)? |  |
| 4. What are the significant contributions of Dr. K. Kasturirangan to Indian science and education? |  |
| 5. How does the Cucumber Mosaic Virus affect agricultural productivity? |  |





















