Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th June 2025) - 1 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
National Alcohol Control Policy: A Necessity
Why in News?
- India is experiencing a continuous increase in alcohol consumption, despite its well-known associations with health risks, violence, crime, suicides, and financial difficulties. This situation highlights the urgent need for a cohesive National Alcohol Control Policy and Programme since there currently is no unified national strategy regulating alcohol consumption.
Key Takeaways
- 14.6% of individuals aged 10-75 consume alcohol in India, with rates of 23% among men and 1% among women.
- India ranks high globally for heavy episodic drinking, leading to significant health issues and societal costs.
- States like Bihar, Gujarat, Nagaland, and Mizoram enforce prohibition, but others have inconsistent regulations.
Additional Details
- Alcohol Consumption Statistics: According to NFHS-5, approximately 16 crore individuals in India consume alcohol. The societal cost of alcohol-related issues is around Rs 6.24 trillion (2021).
- Key Driving Factors: Psychological stress relief, social acceptance through urban lifestyles, peer pressure, and attractive product innovations contribute to increasing alcohol consumption.
- Policy Gaps: Regulatory inconsistencies arise due to state control over alcohol, leading to varied legal drinking ages and pricing regulations.
- Challenges: Issues such as a lack of public awareness, revenue dependency of states on alcohol taxation, and a political nexus complicate regulation efforts.
Addressing India’s rising alcohol crisis requires comprehensive measures. These should include raising excise duties, limiting accessibility, banning surrogate advertising, and launching public awareness campaigns that focus on the health risks associated with alcohol consumption. Effective coordination at the national level, with a focus on public health over fiscal interests, is crucial to combatting this growing issue.
Unique Stellar Chemistry of Star A980
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru have made a groundbreaking discovery of a rare helium-rich star, designated as Star A980. This star's unique chemical composition challenges existing theories related to stellar evolution and nucleosynthesis.
Key Takeaways
- Star A980 is located in the Ophiuchus constellation, approximately 25,800 light-years away from Earth.
- This star marks the first recorded detection of singly-ionized germanium (Ge II) in an Extreme Helium (EHe) star, with germanium levels found to be eight times greater than those in the Sun.
Additional Details
- About Star A980: Star A980 is classified as a cool Extreme Helium (EHe) star, a rare category of evolved stars predominantly composed of helium, with minimal to no hydrogen present. These stars typically form through the merger of a helium-rich white dwarf and a carbon-oxygen rich white dwarf.
- Stellar Models and Star A980: Current stellar models describe the formation and evolution of stars, suggesting that heavy elements are produced in supernovae or AGB stars, not in EHe stars. However, the unusually high germanium levels in Star A980 indicate that element formation may also occur during white dwarf mergers, a phenomenon that current models do not adequately address. This finding implies a potential need to revise our understanding of stellar evolution.
- The Indian Institute of Astrophysics is a premier research institution under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), focusing on astronomy, astrophysics, and related physical and engineering sciences. It has its roots in the Madras Observatory established in 1786, which was relocated to Kodaikanal in 1899, later renamed IIA in 1971, and its headquarters moved to Bengaluru in 1975.
The discovery of Star A980 not only enriches our understanding of stellar chemistry but also opens new avenues for research in astrophysics, highlighting the complexities of stellar evolution and the formation of elements in the universe.
Organ Transplantation Programme in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- A recent report by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has exposed severe gaps in India’s organ transplantation programme, raising concerns over the country’s ability to meet the growing demand for life-saving procedures. With only 13,476 kidney transplants performed in 2024—far below the recommended 1 lakh—the findings underscore an urgent need for systemic reforms to improve access to organ transplants for thousands of patients.
Key Takeaways
- India performed only 13,476 kidney transplants in 2024.
- There is a significant gap in organ availability compared to the demand.
Additional Details
- What is Organ Transplantation: Organ transplantation is a life-saving procedure where a failing organ (kidney, liver, heart, lung) is replaced with a healthy organ from a living donor or a deceased donor to restore function in end-stage organ failure. Common transplants include lungs, pancreas, and intestines.
- Status: India ranks third in the world after the USA and China in terms of the total number of transplants done in a year.
- Growing Demand and Persistent Shortage: Of 1.8 lakh renal failure cases annually, only 6,000 transplants occur, with a donation rate under 1 per million versus a need for 65 per million.
- Regional Variations: States like Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat, and Maharashtra lead in organ donation, while Delhi-NCR, Kerala, and West Bengal report the most living donors.
Regulatory Framework
- Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994: It regulates organ and tissue transplantation in India, covering post-death donation and setting rules for healthcare providers.
- National Organ Transplant Program (NOTP): Implemented by the Central Government to promote organ transplantation across all states and union territories.
- National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO): Established to coordinate procurement and distribution of organs and maintain the registry of organ and tissue donation in India.
Gaps in India’s Organ Transplantation Programme
- Infrastructural Deficiencies: Many government hospitals lack dedicated infrastructure for organ retrieval and face a severe shortage of ICU beds.
- Shortage of Skilled Transplant Professionals: Critical shortage of trained transplant surgeons and other medical professionals disrupts continuity and lowers motivation.
- Procedural Bottlenecks: Delays in approval and formation of Brain-Stem Dead (BSD) Committees remain major hurdles.
- Financial Strain: Insufficient funding and high costs of immunosuppressant drugs limit access for poor patients.
- Ethical and Legal Challenges: Issues such as organ trafficking and consent problems undermine legitimate donation processes.
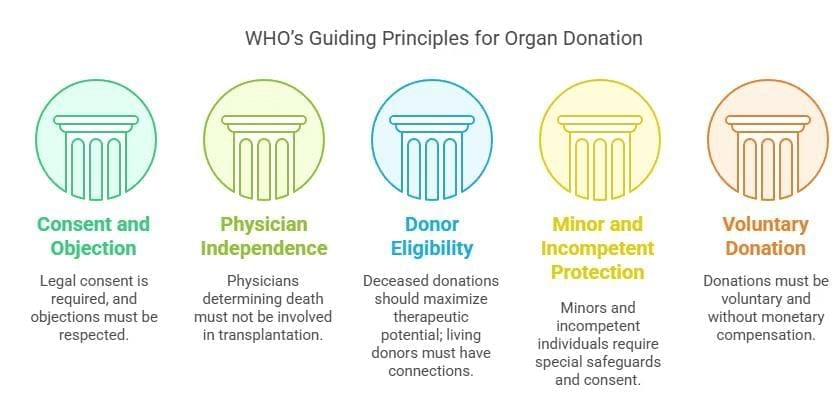
Strategies to Enhance the Organ Transplantation Framework in India
- Enhancing Infrastructure: Upgrade ICU and transplant facilities with dedicated Transplant ICUs and operation theatres.
- Financial Support and Policy Reforms: Include funding for liver and heart transplants and lifelong immunosuppressant costs.
- Addressing Manpower Shortages: Implement recruitment and retention policies for transplant specialists and ensure program continuity.
- Promoting Research and Ethical Practices: Invest in bioengineered organs and develop ethical guidelines for organ allocation.
- Strengthening Public Awareness: Launch nationwide awareness campaigns to dispel myths and encourage organ donation.
India’s organ transplantation crisis demands urgent attention—boosting accessibility while addressing procedural gaps. Expanding coverage, incentivizing specialists, and leveraging technology can bridge the demand-supply gap. A multi-stakeholder approach is vital to save lives and build an ethical transplant ecosystem.
Mains Question:
- "India’s organ transplantation programme faces systemic challenges, from infrastructural deficits to ethical concerns." Critically analyse the issues and suggest reforms to strengthen the ecosystem.
Zonal Councils
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation recently chaired the 25th Central meeting in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh. This meeting was organized by the Inter-State Council Secretariat in collaboration with the Uttar Pradesh Government, highlighting the ongoing significance of Zonal Councils in fostering cooperative federalism.
Key Takeaways
- Zonal Councils are statutory bodies established under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956.
- They serve as high-level advisory forums to promote cooperative working among states and improve inter-State and Centre-State relations.
- They have become instrumental in addressing various regional issues and enhancing mutual understanding.
Additional Details
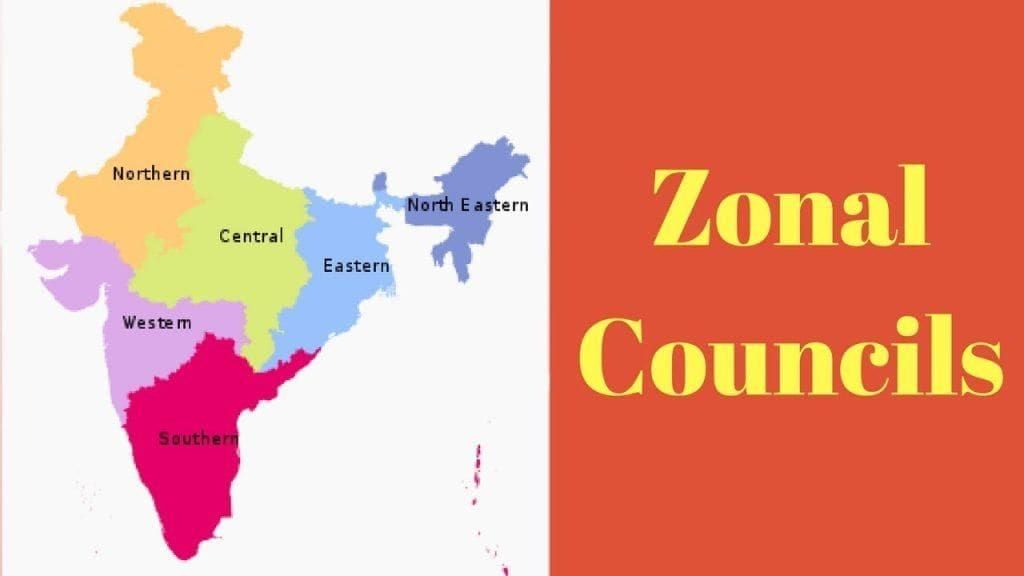
- Zonal Councils: Proposed by former Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru, these councils were established following the recommendations of the States Reorganisation Commission (Fazal Ali Commission, 1953). They consist of five councils, with a separate North Eastern Council created in 1972 to address specific regional needs.
- Composition:
- Northern Zonal Council: Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Delhi, Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, Sikkim.
- Western Zonal Council: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, and Daman & Diu.
- Southern Zonal Council: Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry.
- Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: Union Home Minister (ex-officio for all Zonal Councils).
- Vice-Chairman: Chief Minister of one member state (by annual rotation).
- Members: Chief Ministers, Lieutenant Governors, Administrators of member states and Union Territories, and two nominated ministers from each member state.
- Advisors: NITI Aayog representative, Chief Secretaries, and Development Commissioners from member states.
- Objectives and Functions:Zonal Councils aim to facilitate dialogue and coordination on inter-state issues, enhancing cooperative federalism. They address various matters, including:
- Investigation of sexual offenses and the implementation of Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs).
- Financial inclusion through expanded banking services in rural areas.
- Implementation of the Emergency Response Support System (ERSS-112).
- Regional concerns such as nutrition, education, health, and urban planning.
In conclusion, Zonal Councils play a crucial role in strengthening the relationship between states and the Centre, fostering a collaborative approach to governance and regional development.
Croatia: An Overview
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Prime Minister of India recently met with the President of Croatia during his three-nation tour, which included visits to Cyprus and Canada, following his participation in the 2025 G7 Summit held in Canada.
Key Takeaways
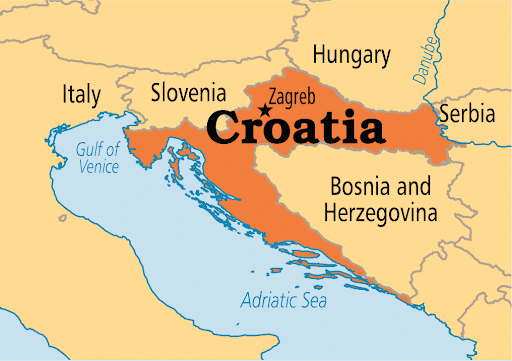
- Croatia is located at the intersection of Central and Southeast Europe along the Adriatic Sea.
- The country shares borders with Slovenia, Hungary, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and has a maritime boundary with Italy.
- Croatia gained independence from Yugoslavia in 1991, subsequently undergoing reconstruction and democratic reforms.
Geography & Climate
- Geography: Croatia features a diverse landscape that includes fertile plains, hills, and mountainous regions such as the Dinaric Alps, with the Dinara Peak reaching an elevation of 1,831 meters.
- Climate: The country experiences a continental climate inland, characterized by hot summers and cold winters, whereas the coastal region enjoys a Mediterranean climate with mild winters and dry summers.
Rivers and Lakes
- Major Rivers: Notable rivers include the Danube, Sava, Drava, Krka, Kupa, and Una.
- Major Lakes: Significant lakes include the Plitvice Lakes, which are designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and Lake Vrana.
- Capital: The capital city, Zagreb, is situated on the Sava River and serves as the administrative and economic center of the country.
Membership and International Relations
- Croatia is a member of the European Union and NATO.
In summary, Croatia's strategic location, rich history, and natural beauty make it a significant player in both regional and international relations, further emphasized by its recent interactions with India.
10th Sustainable Development Report 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- According to the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network's 10th report, India ranks within the top 100 in the SDG Index for the first time out of 167 countries, achieving a score of 67. This score measures progress on a scale from 0 to 100, where 100 indicates full achievement of all 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and 0 signifies no progress. This reflects a significant improvement from India's previous rankings: 109 in 2024 and 112 in 2023.
Key Takeaways
- Only 17% of SDG targets are on track to be met by 2030, indicating a slowdown in global progress.
- Nordic countries dominate the top SDG rankings, with Finland, Sweden, and Denmark leading.
- India has improved its ranking but still trails behind several South Asian nations.
Additional Details
- Global SDG Progress Status: Projections show significant stagnation in global progress due to conflicts, structural vulnerabilities, and limited fiscal space.
- Top Performers: Nordic countries lead the rankings, with 19 out of the top 20 being European. India ranks above Bangladesh (114th) and Pakistan (140th) but below Bhutan (74th) and Nepal (85th).
- Successes & Setbacks: Strong progress in basic services like mobile broadband and electricity access; however, five targets have seen reversals, including obesity rates and press freedom.
- Ranking on Multilateralism: Barbados, Jamaica, and Trinidad & Tobago are leading in UN multilateralism commitment.
- Strong Commitment to SDGs: 190 out of 193 UN member states have participated in the Voluntary National Review process.
- Global Financial Architecture: The report critiques the imbalanced flow of capital, favoring rich nations over emerging economies.

What are Sustainable Development Goals?
- About: The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) consist of 17 interconnected goals with 169 targets, addressing global challenges such as poverty, inequality, and climate change. Adopted in 2015 by 193 UN Member States as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Aim: To promote peace, prosperity, and sustainability by 2030 through global cooperation.
- Historical Background: The concept of sustainable development was defined in the 1987 Brundtland Commission Report, evolving through various global agreements.
Initiatives Contributing to India's Improved Ranking
Factors Responsible for Slow Progress in Achieving SDGs
- Global Conflicts: Ongoing conflicts have led to significant displacement, undermining progress on SDG 16.
- Climate Finance Gap: Developing nations need USD 6 trillion by 2030 for climate goals, but face severe funding shortfalls.
- Pandemic Setback: COVID-19 has reversed gains in poverty eradication, healthcare, and education access.
- Environmental Pressures: Biodiversity loss and deforestation threaten ecosystems, impacting SDG 14.
- Disasters: Natural disasters disproportionately affect LDCs and LLDCs, worsening poverty and vulnerability.
Strategies to Achieve SDGs
- Strengthen Global Governance: Reform multilateral institutions to enhance SDG financing and policy alignment.
- Increase Financing for SDGs: Expand mechanisms like blended finance and provide debt relief to developing nations.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promote regenerative farming and reduce global food waste.
- Localize the SDGs: Empower local governments to adopt and execute SDG-linked plans with proper funding.
India's entry into the top 100 of the SDG Index highlights its progress in poverty reduction. However, challenges such as climate finance gaps and pandemic setbacks threaten this progress. Achieving the SDGs requires urgent multilateral cooperation, financing reforms, local engagement, and focused implementation strategies.
Mains Question:
- Evaluate the role of India’s flagship schemes in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). What more can be done to accelerate progress?
India’s Mining Sector Reforms
Why in News?
- In May 2025, India auctioned its first potash block, marking a milestone in reforms aimed at transforming India’s mining sector and driving economic growth.
Key Takeaways
- Reforms introduced auction-based allocation to replace discretionary systems.
- The 2021 Amendment allowed commercial coal mining and increased lease terms.
- The National Mineral Policy (NMP) 2019 promotes sustainable mining and private sector participation.
- Technological advancements such as satellite imagery monitor illegal mining.
- Exploration reforms have created opportunities for MSMEs and startups.
- Sustainable mining initiatives like the Star Rating System rate mining practices.
Additional Details
- Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Acts, 2015: Introduced auction-based allocation, ensuring automatic extensions for captive mines and a focus on local area development.
- National Mineral Policy (NMP) 2019: Aims for sustainable mining, private sector participation, and the adoption of new technologies such as AI and drones for transparency.
- Coal Sector Reforms: Allowed private players in the coal sector, promoting cleaner coal technologies and ensuring faster environmental approvals.
- Technological Advancements: Includes tools like the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) for public access to geological data and drone surveys to improve efficiency.
- Sustainable Mining Initiatives: Enforces mandatory mine closure plans for environmental rehabilitation and promotes the use of M-Sand to reduce river sand mining.
India's mining sector is crucial for economic growth, contributing 1.97% to GVA in 2023-24. It plays a vital role in generating revenue for states, supporting infrastructure, and creating jobs in mining-affected regions.
Challenges in India's Mining Sector
- Regulatory & Bureaucratic Hurdles: Delays in clearances and land acquisition issues slow down projects.
- Illegal & Unsustainable Mining: Rampant illegal mining leads to environmental degradation and corruption.
- Low Exploration: Only 10% of India’s geological potential has been explored, with low investment in new technologies.
- Logistics Bottlenecks: Poor transport connectivity and power shortages raise costs and disrupt operations.
- Dependence on Imports for Critical Minerals: Heavy reliance on imports for key minerals hampers self-reliance.
Steps Needed to Strengthen India's Mining Sector
- Boost Exploration & Geological Data: Increase funding for exploration and incentivize geological surveys.
- Infrastructure & Logistics Development: Improve connectivity and expand port capacities for efficient mineral transport.
- Technology & Automation Adoption: Invest in satellite imaging and create a national mineral database for better resource management.
- Sustainable & Responsible Mining: Enforce ESG norms and promote community-centric mining practices.
- Tackling Illegal Mining & Corruption: Strengthen surveillance and impose harsh penalties for illegal activities.
In conclusion, India's mining sector, revitalized by reforms and technological advancements, is essential for achieving national economic, energy, and food security. However, persistent challenges need to be addressed through strategic investments and sustainable practices to ensure its long-term viability.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the role of India’s mining sector in achieving national economic, energy, and food security. How can reforms strengthen its contribution?
State of Climate in Asia 2024 Report
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has published a report indicating that Asia has experienced unprecedented warming, nearly twice the rate of the global average. The year 2024 has been marked as the second-hottest year on record, highlighting the urgent need for climate action.
Key Takeaways
- Asia's temperature for 2024 was recorded at 1.04°C above the 1991–2020 average.
- Warming rates have doubled since the period from 1961 to 1990.
- Extreme heatwaves in India resulted in the loss of over 450 lives and temperatures soaring between 45°C to 50°C.
- Marine heatwaves affected approximately 15 million sq km, particularly in the northern Indian Ocean and waters near Japan and China.
- A total of 29 tropical cyclones occurred, with Cyclone Yagi being the deadliest.
Additional Details
- Heatwaves: In India, extreme heat conditions not only led to fatalities but also caused significant disruptions due to accompanying storms that resulted in around 1,300 deaths from lightning strikes.
- Tropical Cyclones: The Indian subcontinent faced severe impacts from cyclones such as Remal, Fengal, Dana, and Asna, affecting nations including the Philippines, Vietnam, Hong Kong, Macau, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar.
- Glacial Retreat: Loss of glacier mass continues, with 23 out of 24 glaciers in High Mountain Asia, including the Himalayas and Karakoram, showing a decline. Notably, Urumqi Glacier No. 1 in the Tian Shan region recorded its highest melt since 1959.
This report underscores the critical state of climate change in Asia and emphasizes the need for immediate global attention and action to mitigate its effects.
Overview of Parliamentary Committees
Why in News?
- The Lok Sabha Speaker recently addressed the National Conference of Estimates Committees, emphasizing that parliamentary committees are not adversaries but rather complementary to the government. He urged both government officials and members to treat committee recommendations seriously and implement them diligently.
Key Takeaways
- Parliamentary committees play a crucial role in governance.
- Recommendations made by these committees should be respected and acted upon.
What are Parliamentary Committees?
- Definition: Parliamentary committees are bodies formed by the Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha, or nominated by the Speaker/Chairman, to undertake functions delegated by Parliament.
- They operate under the direction of the presiding officer and present their findings to the House or the Speaker/Chairman.
- Serviced by Lok Sabha/Rajya Sabha Secretariat, they derive their authority from Article 105 and Article 118 of the Indian Constitution.
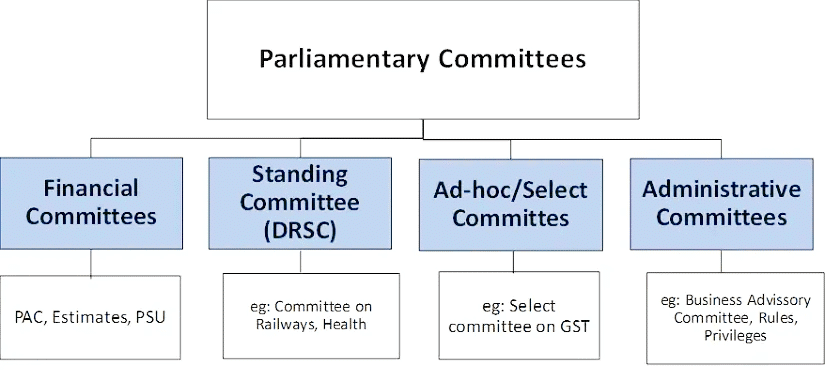
Types of Parliamentary Committees
- Standing Committees:These are permanent bodies reconstituted every year, functioning continuously. Examples include:
- Financial Committees
- Departmentally Related Standing Committees (DRSCs) that scrutinize grants, bills, and policies of various ministries.
- Other Standing Committees such as the Committee on Petitions and the Committee on Subordinate Legislation.
- Ad hoc Committees: These are temporary and formed for specific tasks, dissolving once the task is completed. Examples include Select Committees on GST and Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs) on specific Bills.
Significance of the Parliamentary Committee System
- Ensure Executive Accountability: Although committee recommendations are advisory and non-binding, they create a public record that enhances scrutiny of executive actions.
- Facilitate Informed & Inclusive Lawmaking: Committees provide a platform for expert consultations, ensuring evidence-based deliberation.
- Mini-Parliaments: Committees promote bipartisan representation and facilitate focused inquiries into specific issues.
- Capacity Building & Governance Reform: Committees offer insights that strengthen legislation and governance, acting as training grounds for new MPs.
Challenges Facing Parliamentary Committees
- Limited Powers: Committees lack enforcement powers, resulting in weak follow-up on recommendations.
- Resource Constraints: Insufficient staff and infrastructure limit their effectiveness.
- Low Participation: Average MP attendance in committee meetings is only around 50%, impacting the quality of discussions.
- Inadequate Parliamentary Time: A decline in parliamentary sittings restricts effective oversight.
- Political Influence: External pressures and political considerations can compromise the impartiality of committee functions.
Measures to Strengthen Parliamentary Committees
- Strengthen Institutional Support: Enhance research support and resources for committees to improve analysis and recommendations.
- Improve Accountability: Mandate ministries to submit Action Taken Reports (ATRs) and require justifications for the acceptance or rejection of committee recommendations.
- Enhance MP Engagement: Introduce measures to increase MP attendance in committee meetings and provide training for new MPs.
- Promote Transparency: Simplify committee reports for public access and leverage digital platforms for citizen engagement.
In conclusion, Parliamentary Committees are essential for ensuring legislative oversight, democratic accountability, and participatory governance. The call for greater respect for committee recommendations highlights the need for revitalization of these institutions to enhance their effectiveness in India’s governance framework.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the role of Parliamentary Committees in promoting transparency and accountability in governance. Why has their effectiveness waned recently, and what steps can be taken to restore their efficacy?
|
1452 docs|722 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th June 2025) - 1 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of a National Alcohol Control Policy? |  |
| 2. How does the unique stellar chemistry of stars like A980 contribute to our understanding of the universe? |  |
| 3. What are the challenges faced by the organ transplantation programme in India? |  |
| 4. What role do Zonal Councils play in India's governance? |  |
| 5. Why is the State of Climate in Asia report important for policy-making? |  |





















