Chemical Reactions and Equations - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science
Q.1.
Q.2. Read the given passage and answer the following questions.
The physical states of the reactants and products can be represented by using the symbols (s) for solids, (l) for liquids, (g) for gases, and (aq) for an aqueous solution along with their respective formulae. The word aqueous is written if the reactant or product is present as a water solution. Precipitation can also be represented using an arrow pointing downwards (↓) instead of using the symbol (s). Similarly, the gaseous state of an evolved gas can be represented by using an arrow pointing upward direction (↑) instead of using the symbol (g). The specific condition of the reaction, like temperature, pressure, catalyst, etc., is written above or below the arrow in the chemical equation.
(a) Write the balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the given reaction: Magnesium reacting with dilute sulphuric acid [1 Marks]
(b) To indicate a gaseous reactant or product, we use the _____ or ____ symbol. (1 Marks)
(c) Complete the missing variable given as X and Y in the following reaction: (1 Marks)
2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (X) + H2 (Y)
(d) Which of the following reactions is balanced? (1 Marks)
(i) 2NaCl + 2H2O → 2NaOH + 2Cl2 + H2
(ii) Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Ans. (a) Mg (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → MgSO4 (aq) + H2 ↑
(b) (g) or ↑
(c) X is (aq) and Y is (g)
(d) Reaction II is balanced.
Q.3. (a) Write two observations when lead nitrate is heated in a test tube. (1 Marks)
(b) Name the type of reaction. (1 Marks)
(c) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans. (a) It turns yellow due to lead oxide and reddish-brown fumes' formation.
(b) Thermal decomposition reaction.
(c) (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2020)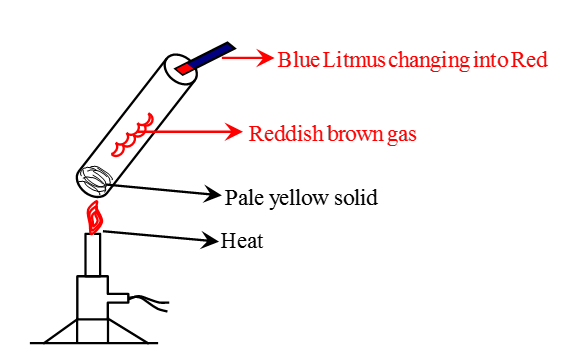 Observation after heating Lead Nitrate in a test tubeQ.4. Define a chemical reaction. State four observations help us determine that a chemical reaction has taken place. Write one example of each observation with a balanced chemical equation. (5 Marks)
Observation after heating Lead Nitrate in a test tubeQ.4. Define a chemical reaction. State four observations help us determine that a chemical reaction has taken place. Write one example of each observation with a balanced chemical equation. (5 Marks)
Ans. Process in which the rearrangement of atoms forms new substances with new properties.
(i) Evolution of gas: The chemical reaction between zinc and dilute H2SO4.
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) ↑
(ii) Change in color: The chemical reaction between potassium iodide and lead nitrate.
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(s) → 2KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s)
Colorless Yellow
(iii) Formation of precipitate: The chemical reaction between sulphuric acid and barium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → 2HCl(aq) + BaSO4(s)
White precipitate
(iv) Change in temperature: The chemical reaction between quicklime and water.
CaO(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Q.5.
Q.6. Why is hydrogen peroxide kept in colored bottles? (1 Marks)
Ans. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into H2O and O2 in the presence of sunlight, and hence to prevent decomposition, they are kept in colored bottles.

Q.7. 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish, and the china dish is placed in sunlight for some time. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction. (3 Marks)
Ans.
- White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight.

- Decomposition reaction/Photolytic decomposition. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Q.8. (i) Define corrosion.
(ii) What is corrosion of iron called?
(iii) How will you recognize the corrosion of silver?
(iv) Why is iron corrosion a serious problem?
(v) How can we prevent corrosion of iron? (1 Marks)
Ans. (i) Corrosion is a process in which metals are deteriorated by air, moisture, chemicals, etc.
(ii) Rusting.
(iii) Silver - black, copper green.
(iv) It destroys car bodies, bridges, railing, etc. (Any two)
(v) By Painting, alloying, greasing, etc. (Any two)
Detailed Answer :
(i) Corrosion is a process in which metals are deteriorated by the action of air, moisture, chemicals, etc.
(ii) Corrosion of iron is called rusting.
(iii) Silver turns black as it reacts with H2S present in the air and forms a layer of Ag2S.
(iv) Corrosion of iron is a serious problem because it leads to the wastage of tonnes of iron every year, and a lot of money is spent to repair or replace it.
(v) The iron articles should be painted to prevent corrosion. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2016)
Q.9. The following reaction is an example of a
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
(i) Displacement reaction
(ii) Combination reaction
(iii) Redox reaction
(iv) Neutralisation reaction (1 Marks)
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (c)
Solution. The given reaction is a redox reaction because oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously. Also, it is a displacement reaction because the hydrogen of NH3 has been displaced by oxygen.
Q.10. Read the given passage and answer the following questions.
P, Q, and R are 3 elements that undergo chemical reactions according to the following equations:
(i) P2O3 + 2Q → Q2O3 + 2P
(ii) 3RSO4 + 2Q → Q2(SO4)3 + 3R
(iii) 3RO + 2P → P2O3 + 3R
(a) Which element is most reactive? (1 Marks)
(b) Which element is least reactive? (1 Marks)
(c) The type of reactions is (1 Marks)
(i) Displacement reaction
(ii) Combination reaction
(iii) Neutralisation reaction
(iv) Substitution reaction
(d) Define the reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans. (a) Q, as it has replaced both P and R from their compounds
(b) R, as it has been replaced by both P and Q
(c) (i) Displacement reaction
(d) Displacement reaction is a reaction in which a more active element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
Q.11. N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3, name the type of reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans. It is a combination reaction.
Q.12. On heating blue colored powder of copper (ii) nitrate in a boiling tube, black copper oxide, O2, and a brown gas X are formed.
(a) Identify the type of reaction and the gas X.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(c) Write the pH range of the aqueous solution of the gas X. (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Decomposition / Thermal decomposition,
The gas X is NO2 or (nitrogen dioxide)
(b) 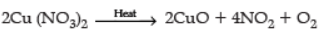
(c) Range less than 7 (or 0------6.9pH) (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Detailed Answer :
(a) Type of reaction: Thermal decomposition reaction. The gas X is nitrogen dioxide.
(b) 2Cu(NO3)2(s) → 2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Copper nitrate(II) Black Brown
(c) As oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature, an aqueous solution of nitrogen dioxide will have a pH range between 0 and 7.
Q.13. During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, the following observations were made by a change.
(a) Silver does not show any change.
(b) Some bubbles of gas are seen when the lead is reacted with the acid.
(c) The reaction of sodium is found to be highly explosive.
(d) The reaction mixture's temperature rises when aluminum is added to the acid.
Explain these observations giving appropriate reasons. (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Silver is placed below Hydrogen in reactivity series / among least reactive metal / Silver does not react with dil. Hydrochloric acid.
(b) Rate of reaction is slow / bubbles of Hydrogen gas are formed / lead lies above hydrogen in reactivity series.
(c) Sodium is highly reactive / reaction is highly exothermic, evolving Hydrogen gas, which catches fire.
(d) Reaction is exothermic
Detailed Answer :
(a) As silver is less reactive, it does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(b) Bubbles are seen due to the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Pb(s) + 2HCl (aq) → PbCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) As sodium is a highly reactive metal, it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid vigorously with heat evolution.
(d) The reaction between aluminum with dilute hydrochloric acid is exothermic; thus, the mixture's temperature rises with the addition of aluminum. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Q.14.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
(i) Displacement reaction
(ii) Combination reaction
(iii) Redox reaction
(iv) Neutralisation reaction
Q.15. Assertion and Reason:
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (a) is followed by a reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(i)
Reason (R): Metallic sodium melts when exposed to air.
(ii)
Reason (R): Specific heat of water is quite large.
Q.16. Decomposition reactions require energy either in heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light, and electricity. (3 Marks)
Ans.
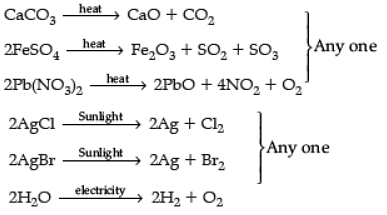
(or any other equation for the above decomposition reaction.)
Note: No marks to be deducted if equations are not balanced. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2018)
Q.17. In the reaction :
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(a) Name the compound (i) oxidized, (ii) reduced.
(b) Define oxidation and reduction on its basis. (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) (i) HCl is oxidized.
(ii) MnO2 is reduced.
(b) (i) Oxidation: Gain of Oxygen or loss of Hydrogen.
(ii) Reduction: Gain of Hydrogen or loss of Oxygen. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2018)
Q.18. Why do silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air? (1 Marks)
Ans. They get tarnished by reacting with atmospheric air to form silver sulphide.
Q.19. Give the reason why chip manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with a gas such as nitrogen? (1 Marks)
Ans. To prevent the chips' oil and fats from being oxidized or become rancid.
Q.20. Name the term used to indicate the development of unpleasant smell and taste in fats and oils containing food due to oxidation. What are antioxidants? Why are they added to fat and oil-containing food? (3 Marks)
Ans. Rancidity: Antioxidants are substances that prevent oxidation, are actually reducing agents. When added to food, the fats and oils present in the food do not get oxidized easily. Hence they do not turn rancid and remain good to eat for a longer time.
|
83 videos|438 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Reactions and Equations - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is a chemical reaction? |  |
| 2. How can we represent a chemical reaction? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. How can you determine if a chemical reaction has occurred? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to balance chemical equations? |  |
























