Acids, Bases and Salts - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 2
Q.1. Name the acid present in ant sting. (1 Marks)
Ans. Formic acid (Methanoic acid), HCOOH.
 Ant Sting
Ant Sting
Q.2. Answer the following:
(a)
(b) What causes tooth decay? (1 Marks)
Ans. A lower pH below 5.5 leads to tooth decay. At this pH, the calcium phosphate of the teeth' enamel gets corroded.
(c) The nature of toothpastes commonly used to protect tooth decay is ______. (1 Marks)
Ans. The toothpaste commonly used is basic so that the extra acid formed during tooth decay is neutralized and prevents tooth decay.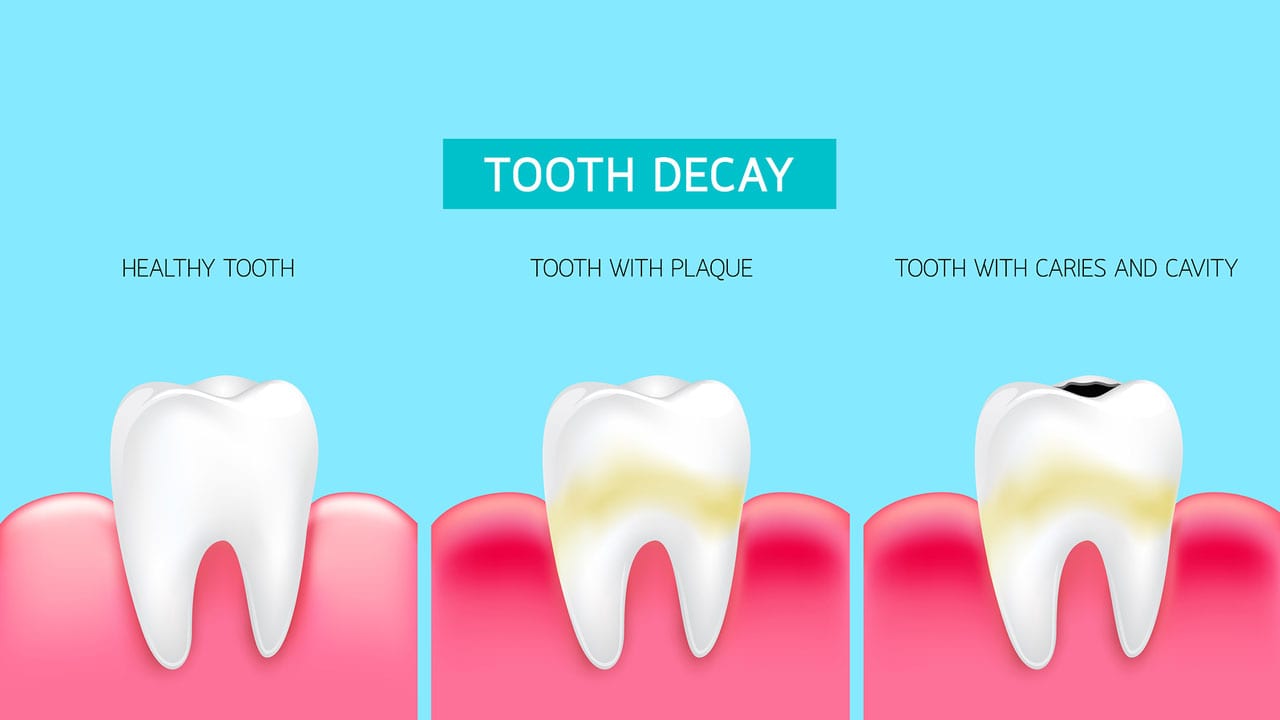
Q.3. You are provided with 90 mL of distilled water and 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid to prepare to dilute sulphuric acid.
(a) What is the correct way of preparing dilute sulphuric acid? Give reason.
(b) How will the concentration of H3O+ ions change on dilution? (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Add 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid slowly to 90 mL of water with constant stirring. Dilution of acid is a highly exothermic process. If water is added to concentrated sulphuric acid, heat generated causes the mixture to splash, leading to burns, and the glass container can break.
(b) Decreases per unit volume.
Q.4. (i) Define pH scale. Draw a figure showing the variation of pH with the change in concentration of H+(aq) and OH–(aq) ions.
(ii) Mention the range of pH of acidic solution, basic solution, and neutral solution, respectively. (5 Marks)
Ans. (i) The scale for measuring [H+] concentration in a solution is called a pH scale.
Refer to the below figure: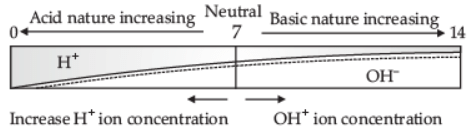
(ii) the pH of the Neutral solution is 7.
the pH of the Acidic solution is 0 to below 7.
the pH of the Basic solution is 7 to 14.
Q.5. 2 ml of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a few pieces of granulated zinc metal taken in a test tube. When the contents are warmed, a gas evolves bubbled through a soap solution before testing. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved and the test to detect the gas. Name the gas that will evolve when the same metal reacts with the dilute solution of a strong acid. (3 Marks)
Ans. Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
When a burning splinter is brought near the gas, it burns with a Pop Sound.
Gas – Hydrogen / H2
Q.6
Q.7. Identify the acid and the base from which sodium chloride is obtained. Which type of salt is it? When is it called rock salt? How is rock salt formed? (3 Marks)
Ans.
- Acid – Hydrochloric acid / HCl
- Base – Sodium hydroxide / NaOH
- Neutral Salt
- When it forms brown crystals combined with impurities.
- Drying up of seas. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Q.8. Identify the acid and base which form sodium hydrogen carbonate. Write a chemical equation in support of your answer. State whether this compound is acidic, basic, or neutral. Also, write its pH value. (3 Marks)
Ans.
- Acid — H2CO3
- Base — NaOH
- NaOH + H2CO3 → NaHCO3 + H2O (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Detailed Answer:
The compound is basic (weak). Its pH is more than 7.
Q.9. (i) A white powder is an active ingredient of antacids and is used to prepare baking powder. Name the compound and explain how it is manufactured. Give chemical equations.
(ii) Write a chemical equation to show the effect of heat on this compound. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Compound is NaHCO3/baking soda/sodium hydrogen carbonate
Manufacture : NH3 + NaCl + H2O + CO2 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3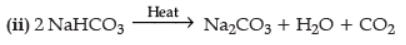
Q.10. Write the chemical name and formula of common salt. List two main sources of common salt in nature. Write any three uses of common salt. How is it connected to our struggle for freedom? (5 Marks)
Ans. Sodium chloride NaCl. Common salt from seawater and Rock salt.
Uses of common salt :
(i) As a raw material for making many useful chemicals in the industry as sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, hydrochloric acid.
(ii) Used in cooking food. It is essential in our food for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
(iii) Used as a preservative in pickles.
(iv) Used in the manufacture of soap. (Any three)
Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March was for the common salt procurement for the commoner. It is the essential product of daily use.
Q.11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd (Yogurt), will its pH value increase or decrease? Why? (1 Marks)
Ans. When milk changes into curd, its pH will decrease. Because curd contains lactic acid, so H+ ion concentration increases to decrease.
Q.12. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? (1 Marks)
Ans. Hydrogen gas.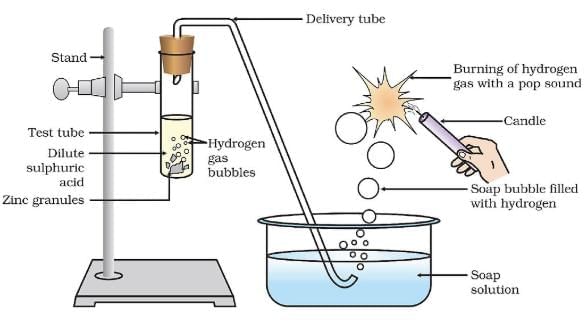
Q.13. Which is a stronger acid, with pH = 5 or with pH = 2? (1 Marks)
Ans. pH = 2 (lower the pH, stronger the acid).
Q.14. Explain the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on the following with chemical equation:
(i) Magnesium ribbon
(ii) Sodium hydroxide
(iii) Crushed eggshells (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Hydrogen gas is produced.
(ii) HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Neutralization reaction
(iii) 2HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O + CO2
Calcium chloride is formed.
Detailed Answer:
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium to form magnesium chloride, and H2 gas is liberated.
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(ii) Reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide is a neutralization reaction. Sodium chloride salt and water are formed.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
(iii) Eggshells are made of calcium carbonate, CaCO3. Dilute hydrochloric acid dissolves the CaCO3 and makes the shell soft.
CaCO3(s) + HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(Crushed egg shell)
Q.15. (a) While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid be added to water and not water to the acid?
(b) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not change the color of dry litmus paper. Why? (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Diluting an acid is an exothermic process. When water is added to an acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and may cause serious burns. Therefore, it is recommended that acid should be added to water carefully with constant stirring.
(b) Presence of ions like hydrogen (H+) ions or hydronium (H3O+) ions change the color of litmus paper. HCl can produce these ions only in the form of an aqueous solution. Hence, dry hydrogen chloride gas does not change the color of dry litmus paper.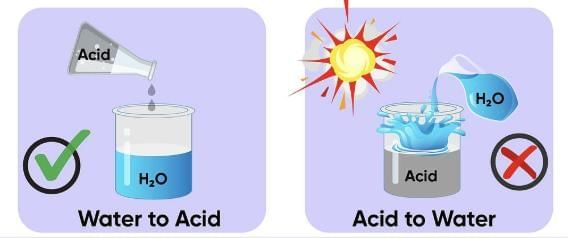
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Acids, Bases and Salts - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 2
| 1. What are acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 2. How do acids, bases, and salts affect pH levels? |  |
| 3. What are the common uses of acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 4. How can I identify acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 5. What are the health and environmental effects of acids, bases, and salts? |  |

















