Olympiad Notes: How do Organisms Reproduce? | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
Reproduction is a vital biological process that ensures the continuity of life on Earth. It enables organisms to produce offspring resembling their parents, thus maintaining population stability and genetic diversity.
- Reproduction is essential for sustaining species.
- It involves the transfer of genetic material, primarily DNA, to offspring.
- Variations during reproduction play a crucial role in adaptation and survival.
Do Organisms Create Exact Copies of themselves?
- Organisms reproduce to create new individuals of their kind, which is necessary for the survival of species.
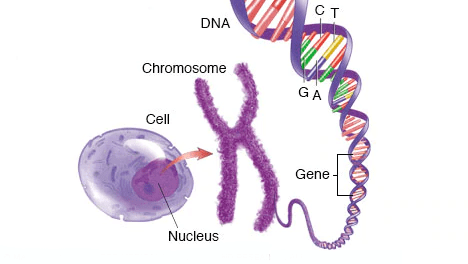
- The information needed for passing on traits from parents to offspring is found in chromosomes as DNA.
 DNA and Chromosome
DNA and Chromosome
- DNA is an information source for making proteins, which if changes will change the original body design.
- Thus, for reproduction, each organism must first make copies of its DNA, so that the daughter cell produced can have its copy of DNA. However, this DNA copying mechanism is not always foolproof.
- Any minor change in DNA, during copying, results in variation, which is the basis for evolution.
Importance of Variation
- DNA copying during reproduction ensures the preservation of body designs.
- Variations arise due to imperfections in DNA copying mechanism, allows adaptation to environmental changes.
- Example: Heat-resistant bacterial variants surviving global warming.
Modes of Reproduction used by Single Organisms
Two Modes of Reproduction:
Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent, no gamete formation.
- Produces genetically identical offspring (clones).
- Examples:Binary Fission, Budding, Vegetative Propagation, Regeneration, Spore Formation.
Sexual Reproduction
- Involves two parents, gamete formation occurs.
- Produces genetically varrying organisms.
- Examples: Reproduction in humans and other mammals.
Asexual Reproduction
- Subdivided into different methods.
- Examples: Binary Fission, Multiple Fission, Budding, Vegetative Propagation, Regeneration, Spore Formation.
Binary Fission
- Occurs in unicellular organisms.
- The parent cell divides into two daughter cells, each with a nucleus.
- Examples: Amoeba.
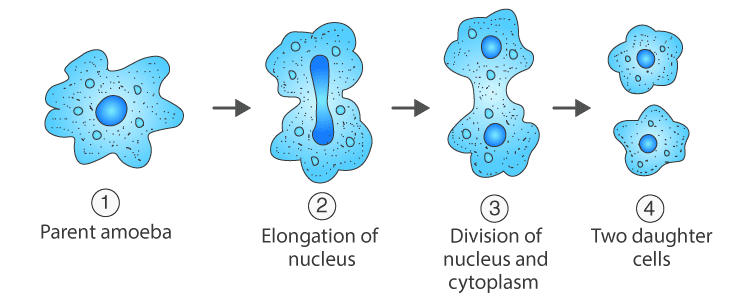 Binary Fission in Amoeba
Binary Fission in Amoeba
Multiple Fission
- Seen in organisms like Plasmodium when conditions are unfavourable.
- Organism forms a cyst, then releases daughter nuclei when conditions improve.
- Examples: Plasmodium, Entamoeba.
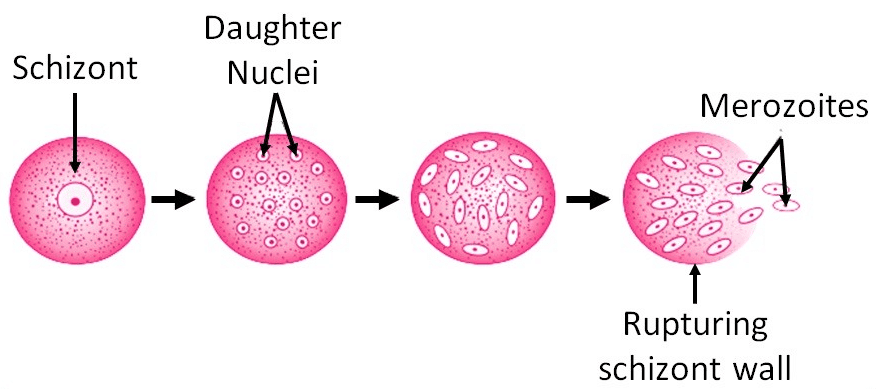 Multiple Fission in PlasmodiumBudding
Multiple Fission in PlasmodiumBudding
- Outgrowth produces a new organism attached to the parent.
- The bud detaches when mature, leaving scar tissue.
- Prominent in yeast and hydra.
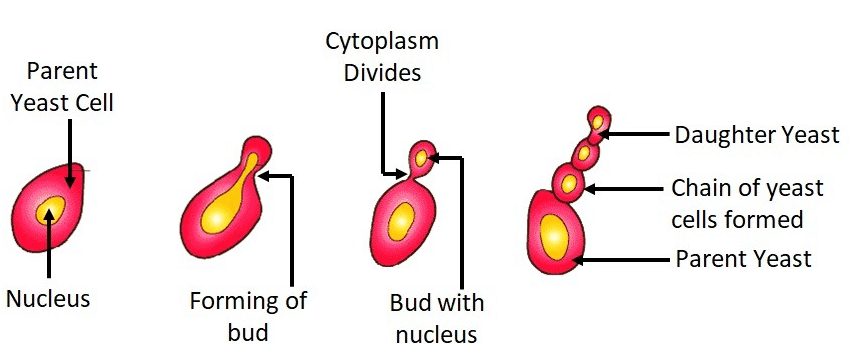 Budding in Yeast
Budding in Yeast
Vegetative Propagation
- New plant grows from fragments or specialized reproductive structures.
- This produces offspring are exact clones of the parent without DNA mixing.
- Methods: Grafting, layering, cutting, tuber, tissue culture, etc.
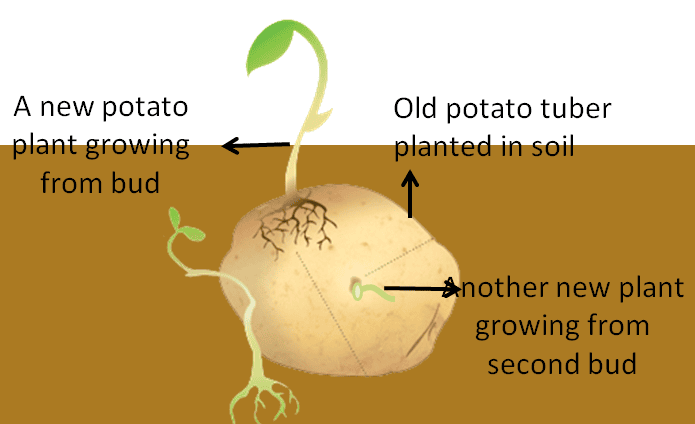 Vegetative Propagation in Potato
Vegetative Propagation in Potato
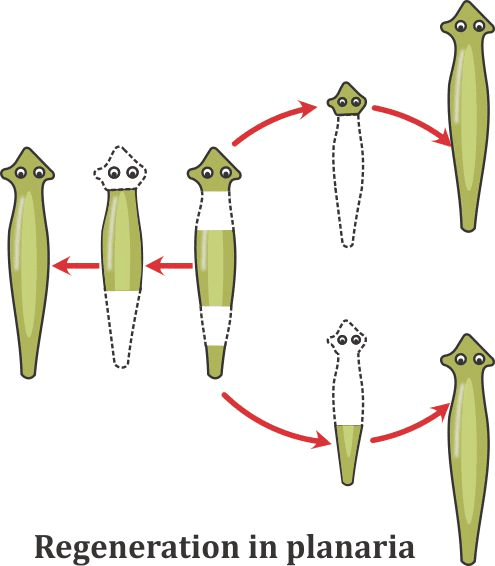
Regeneration
- Hydra and Planaria can regenerate when cut into pieces.
- Specialized cells multiply to form different cells and tissues and complete body of the plant.
Spore Formation
- Some plants develop knob-like structures (sporangia) form during unfavorable conditions.
- Spores inside sporangia develop into new individuals.
- These spores have protective walls; grow upon moisture contact.
Sexual Reproduction
This type of reproduction involves two individuals, male and female, to produce offspring.
Male and female gametes combine to form a new cell, making both sexes essential for creating new generations.
- Examples include flowering plants and humans.
- Processes: Pollination, fertilization, zygote formation, and embryo development.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
In angiosperms, both male and female reproductive organs exist.
Parts of flower
1. Sepals and petals protect the flower and attract pollinators but do not participate in reproduction.
2. The stamen is the male reproductive part, consisting of:
- Anther: Produces pollen grains containing male gametes.
- Filament: Supports the anther.
3. The pistil or carpel is the female reproductive part, consisting of:
- Stigma: Sticky surface for capturing pollen.
- Style: Tube connecting the stigma to the ovary.
- Ovary: Contains ovules, each with an egg cell.
- Unisexual: Containing either stamens or pistils (e.g., papaya, watermelon).
- Bisexual: Containing both stamens and pistils (e.g., hibiscus, mustard).
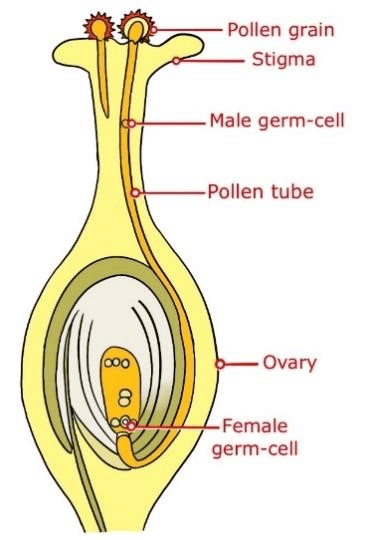
Pollination involves the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma and can be of two types:
- Self-Pollination: Occurs within the same flower.
- Cross-Pollination: Occurs between different flowers, aided by wind, water, or animals.
After pollination, pollen germinates on the stigma, forming a pollen tube that delivers male gametes to the ovule.
Fertilization occurs when male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an embryo.
The ovule matures into a seed, and the ovary develops into a fruit, while non-essential parts like petals and sepals fall off.
Seed formation ensures the continuation of plant species and allows germination under suitable conditions.
Reproduction in Human Beings
Human reproduction is a sexual process involving two parents.
Offspring result from the fusion of gametes from each parent.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of organs that produce and transport the male germ-cell or gamete, male hormone testosterone and the organs which facilitate the discharge of male germ-cells into the female reproductive system for fertilization.
Function of male reproductive system is to produces male gametes (sperms), which consist of a head, middle piece, and tail. 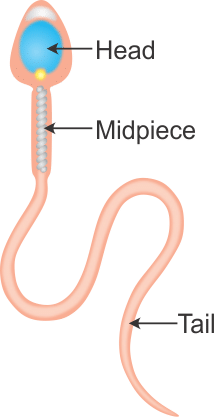 Parts of Male reproductive system are:
Parts of Male reproductive system are:
- Testicles (testes): Oval organs responsible for sperm production and testosterone.
- Scrotum: Sac-like organ housing the testes, maintaining optimal temperature.
- Vas Deferens: Tube for maturing sperm, leading to the urethra.
- Accessory Glands: Seminal vesicles, prostate gland their fluids form semen.
- Penis: Cylindrical tube acting as a reproductive and excretory organ, delivering sperm during intercourse.
Female Reproductive System
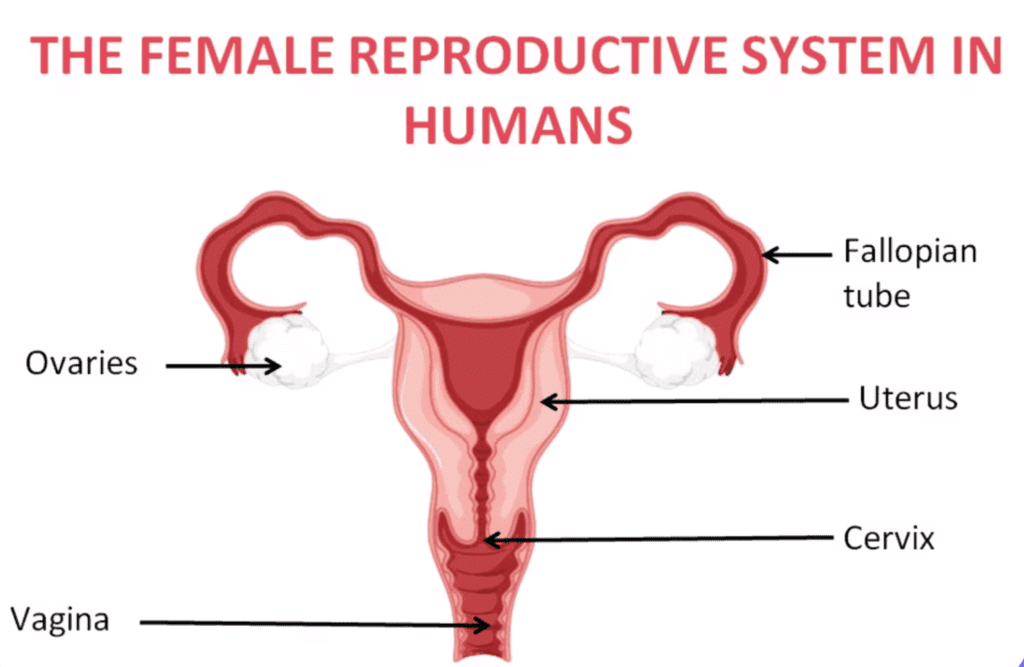
The female reproductive system functions before, during, and after fertilisation. It includes:
- Ovaries: Produce and store ova (eggs) and release the female hormone, estrogen.
- Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts): Site of fertilisation, connecting the ovaries and uterus.
- Uterus: The location where the embryo develops.
- Vagina: Connects the cervix to the external female body, serving as a passage for the penis during intercourse and for the fetus during birth.
Reproductive Health and Challenges
1. Reproductive Health
Reproductive Health refers to total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, including physical, emotional, social, and behavioral health.
2. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs):
Diseases like gonorrhea and syphilis (bacterial) and warts and HIV-AIDS (viral) can spread through sexual contact.
Using contraceptive methods can help prevent the transmission of these diseases to some extent.
3. Contraceptive Methods
- Physical Barriers: Prevent the union of sperm and egg using condoms, cervical caps, or diaphragms.
- Chemical Methods: Oral pills that alter hormonal balance to prevent egg release. These may have side effects.
- Intrauterine Devices: Devices like Copper-T or loops are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
- Surgical Methods: It includes vasectomy and tubectomy
- Vasectomy: Blocking the vas deferens in males to prevent sperm transfer.
- Tubectomy: Blocking the fallopian tubes in females to prevent egg transfer.
4. Female Foeticide
- Female foeticide is the practice of killing a female fetus inside the womb, which leads to an imbalanced sex ratio.
- Promoting education and awareness is essential to discourage this malpractice.
- Prenatal sex determination is legally prohibited to ensure a balanced sex ratio in society.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: How do Organisms Reproduce? - Science Class 10
| 1. Do organisms create exact copies of themselves during reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are the different modes of reproduction used by single organisms? |  |
| 3. How does sexual reproduction occur in plants? |  |
| 4. What are the stages of reproduction in human beings? |  |
| 5. What are some reproductive health challenges faced by individuals? |  |