Solutions: Mixtures & Types of Solutions | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What are Mixtures?
When two or more chemically non-reacting substances are mixed, they form mixtures. A mixture may be heterogeneous or homogeneous.
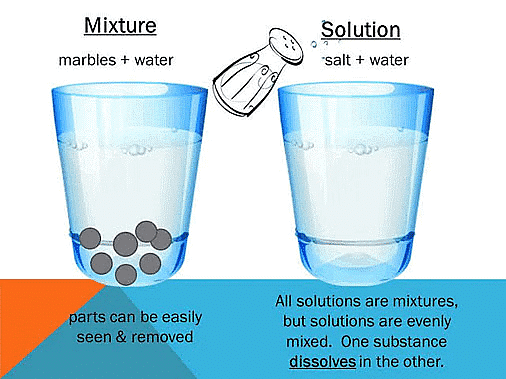
- A heterogeneous mixture consists of distinct phases and the observed properties are just the sum of the properties of individual phases. However, a homogeneous mixture consists of a single-phase which has properties that may differ drastically from those of the individual components.
- A homogeneous mixture whose composition can·be varied within certain limits is termed a true solution.
- The constituents of a solution cannot be separated by filtration, settling or centrifugal action. All solutions are characterised by
(i) Homogeneity
(ii) Absence of settling
(iii) The molecular or ionic state of sub-division of the components. When the solution is composed of only two chemical substances, it is termed a binary solution. - Similarly, it is called ternary and quaternary if it is composed of three and four . components, respectively. thus; a solution may be regarded as a single phase containing more than one component.
Examples
- A mixture of salt and sugar.
- A mixture of oxygen and nitrogen.
- A mixture of sugar in water.
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixture
1. Homogeneous Mixture:
A mixture of two or more components having no distinguish phase is called a homogeneous mixture.The homogeneous mixture is generally referred to as a solution.
Example: When two spoons of salt are mixed in a glass of water, the mixture so obtained has no distinguish phase and this is called a solution.
 Sugar Solution
Sugar Solution
Air is a mixture of different gases with no distinguish phase, thus, the air is often referred to as the solution.
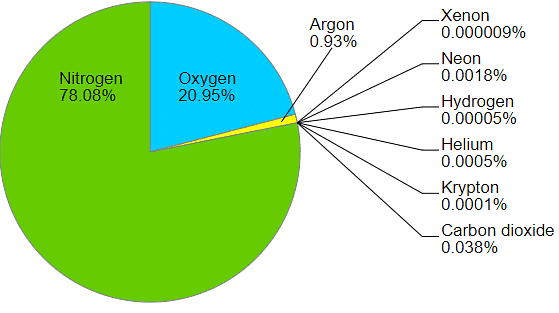 Air: Mixture of Gases
Air: Mixture of Gases
In a homogeneous mixture, i.e. solution, the composition, and properties of the solution are uniform throughout.
2. Heterogeneous Mixture:
A mixture of two or more components with distinguish phase is called a heterogeneous mixture.Example: A mixture of mustard oil and water, in this mixture phases of water and mustard oil, can be seen and distinguished clearly, and hence called heterogeneous mixture.
 Heterogeneous Mixture: Oil and Water
Heterogeneous Mixture: Oil and Water
Examples of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Solutions: Some examples of homogeneous and heterogeneous solutions include:
What is a Solution?
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm.
Common examples of solutions are sugar in water and salt in water solutions, soda water, etc. In a solution, all the components appear as a single phase. There is particle homogeneity i.e. particles are evenly distributed. This is why a whole bottle of soft drink has the same taste throughout.
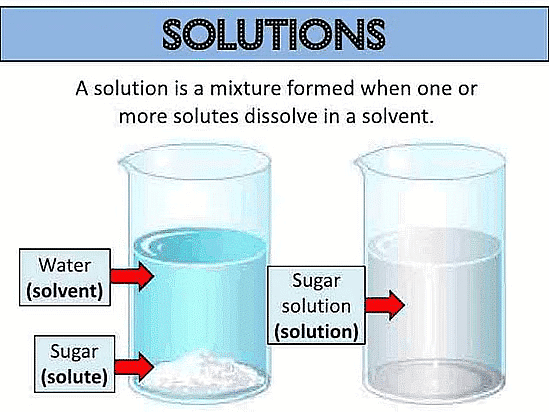
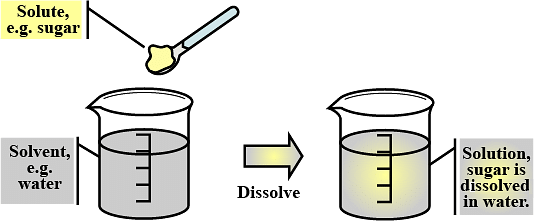
Solute and Solvent
- Solvent: The substance which is present in the largest quantity in a solution; is generally referred to as a solvent.
Example: In the solution of salt in water, since water is present in larger quantity, thus, water is called the solvent. It is the solvent that decides the phase of a solution. - Solute: The substance which is present in lesser quantity in a solution is generally called the solute.
In other words, one or more components present in a solution other than the solvent are is called the solute.
Example: In the solution of salt in water, salt is called the solute. The solute may be more than one.
Note: Physical state of solvent and solution is same.
Different Types of Solutions
Solutions can be classified on various basis. Let us have a look at them.
1. On the basis of number of components dissolved:
- Binary Solution: Solutions which contain only two components are called a binary solution. For example, a solution of salt in water is a type of binary solution, as it contains only two components.
Binary Solution = Solute + Solvent
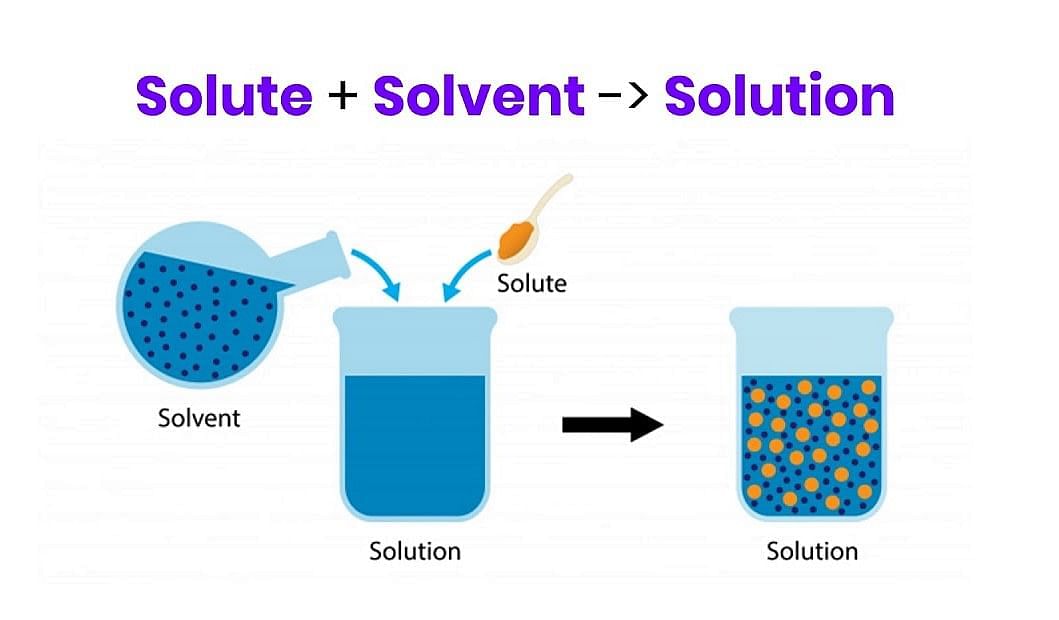 Binary SolutionSimilarly, it is called ternary and quaternary if it is composed of three and four components, respectively.
Binary SolutionSimilarly, it is called ternary and quaternary if it is composed of three and four components, respectively.
Thus; a solution may be regarded as a single-phase containing more than one component.
- Ternary Solution: A ternary solution consists of three different components or substances mixed together. These solutions are more complex than binary solutions because they involve three different substances interacting.
For example, an alcohol-water-acetone mixture is a ternary solution, where each component may have its own concentration. - Quaternary Solution:
A quaternary solution is even more complex, as it contains four different components or substances dissolved in one another.
An example of a quaternary solution is a mixture of ethanol, water, acetone, and acetic acid. The properties and behavior of quaternary solutions can be quite intricate, as there are more interactions and possibilities among the components.
Note: In this chapter, we will focus on only Binary Solutions.
2. On the basis of the dissolving capacity of the solvent, the types of solutions can be classified as:
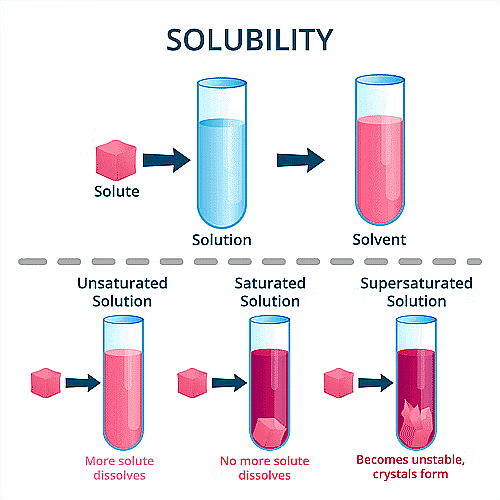
- Supersaturated Solution: A solution is known as supersaturated when it contains more than the maximum amount of the solute that can be dissolved in the solvent at a given temperature. The excess solute is separated at the bottom of the solution known as the crystals.
- Saturated Solution: A solution is known as saturated when it cannot further dissolve any more solute particles in the solvent at a given temperature.
- Unsaturated Solution: A solution is known as an unsaturated solution when the solute particles can still be added to the solvent at a given temperature.
3. On the basis of solute added to the solvent in a particular solution, the following can be classified:
- Dilute Solution: A solution in which relatively a small amount of solute is dissolved in a large amount of solvent is called a dilute solution.
- Concentrated Solution: A solution in which relatively a large amount of the solute is present is called a concentrated solution.
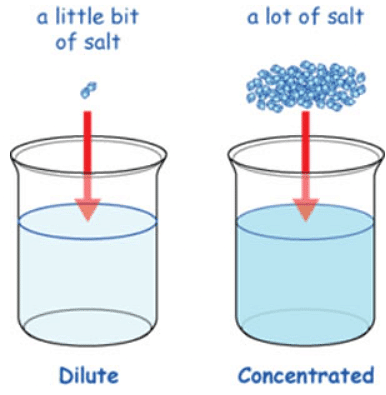 Dilute and Concentrated Solution
Dilute and Concentrated Solution
4. On the basis of the type of solvent, the following can be classified:
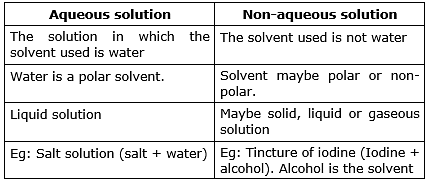
- Aqueous Solution: A solution is known as an aqueous solution when the solvent used is water only.
- Non-aqueous Solution: A solution is known as a non-aqueous solution when the solvent used is other than water.
5. On the basis of the ability to conduct electricity, the following can be classified:
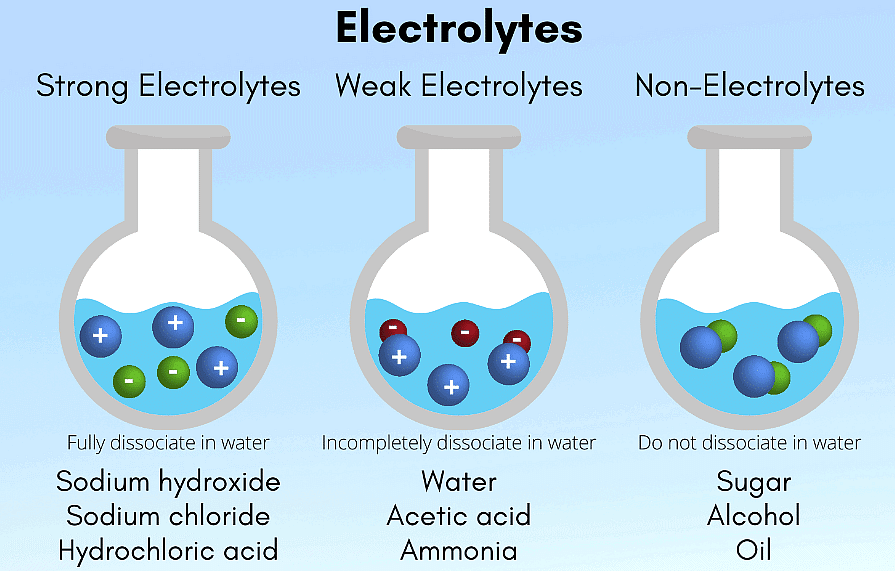
The solutions in which the solute gets dissolved in the solvent and then breaks into ions, which help in conducting the electricity are known as electrolytes. This ion – formation depends on the ability of the component to break down into ions. On the basis of the ability to conduct electricity, the following can be classified:
(i) Strong Electrolytes: These substances completely ionize (or dissociate) into ions when dissolved in water. This means they break apart into ions, which are charged particles. Common examples include:
- Strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3).
- Strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- Salts like sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium nitrate (KNO3), and calcium chloride (CaCl2).
(ii) Weak Electrolytes: These substances only partially ionize in solution. They exist in equilibrium between their molecular form and their ionized form. Common examples include:
- Weak acids like acetic acid (CH3COOH) and citric acid (found in citrus fruits).
- Weak bases like ammonia (NH3) and organic amines.
- Some salts, such as ammonium acetate (NH4CH3COO).
Properties of a Solution
- A solution consists of a single-phase i.e. it is a monophasic system.
- A solution is uniform throughout, such as uniform properties such as density, refractive index, etc.
- The components of a solution cannot be easily separated by physical methods.
- The composition of a solution is not definite but can vary within certain limits.
- Certain properties of solution such as density, viscosity, surface tension, boiling point, freezing point etc. vary with the composition of the solution.
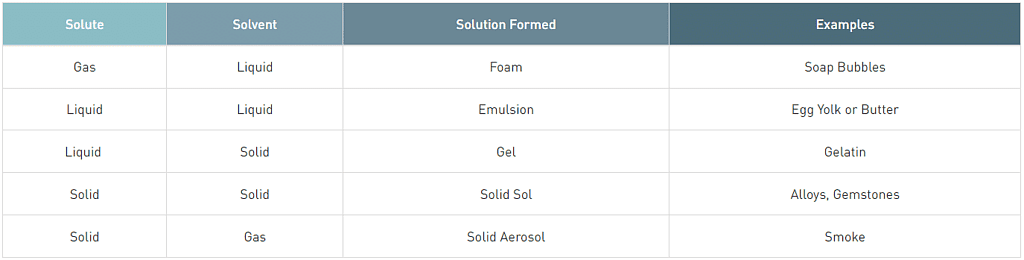
In a solution, components may be solid, liquid or gas.
Gaseous, Liquid & Solid Solutions
Gaseous, liquid, and solid solutions are three different types of mixtures in which one or more substances are combined together. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures where the components are evenly distributed at a molecular level. The difference between these solutions lies in the physical state of the solvent and solute.
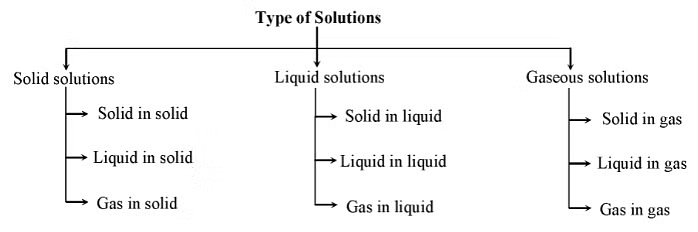
1. Gaseous Solution
Solutions in which solvent is present is a gaseous state is called Gaseous solution. Gaseous solutions can be divided into following three types on the basis of phases of solute and solvent:
- Gas - Gas Solution: Solutions in which solute and solvent both are gases; are called Gas-gas Solutions.
Example: solution (mixture) of nitrogen and oxygen, solution (mixture) of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, solution (mixture) of carbon dioxide and oxygen, etc. - Liquid Gas Solution: Solutions, in which solute is in a liquid state and solvent is in a gaseous state, are called Liquid-Gas Solution.
Example: solution (mixture) of chloroform in nitrogen gas. - Solid Gas Solution: Solutions, in which solute is in solid-state and solvent is in a gaseous state, are called Solid-Gas Solutions.
Example: Solution (mixture) of camphor in nitrogen gas.
2. Liquid Solution
Solutions, in which solvent is present in a liquid state, are called Liquid solutions.
Liquid solutions can be classified into the following three types:
- Gas-Liquid Solution: Solutions having solute in gaseous state and solvent in the liquid state are called Gas-Liquid Solutions.
Example: Solution (mixture) of oxygen in water, a mixture of carbon dioxide in water. Coca-cola, a beverage, is an example of a gas-liquid solution, as it has carbon dioxide dissolved in water. - Liquid - Liquid Solution: Solutions, in which solute and solvent both are present in a liquid state, are called liquid liquid solutions.
Example: Vinegar solution, vinegar is the mixture of ethanoic acid and water. Solution of ethanol in water, etc. - Solid-Liquid Solution: Solutions, in which solutes present in solid-state and solvent is in a liquid state, are called solid-liquid solutions.
Example: Solution of salt in water, solution of glucose in water, etc. Glucose in Water
Glucose in Water
3. Solid Solution
Solutions having solvent in the solid-state, are called solid solutions.
The solid solution can be divided into the following three categories:
- Gas-Solid Solution: Solutions having solvent in solid-state and solute in the gaseous state are called gas-solid solutions.
Example: solution of hydrogen in palladium. - Liquid-Solid Solution: Solutions having solvent in solid-state and solute in the liquid state are called liquid-solid solutions.
Example: an amalgam of mercury with sodium. - Solid-solid solution: Solutions having solvent and solute both in the solid-state are called solid-solid solutions.
Example: Solution of gold and copper.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the components of solution?
Ans: Solutions are made up of two parts: a solvent and a solute.
Solvent: The component that dissolves the other component is called the solvent.
Solute: The component that is dissolved in the solvent is called solute.
Q2. What are some common examples of mixtures and solutions?
Ans: Air is a homogeneous mixture that contains oxygen, nitrogen, argon and other gases; iron filings with sulfur powder is a commonly used heterogeneous mixture; salty water is a solution that contains particles of salt mixed with particles of water.
Q3. Is coffee a mixture?
Ans: Coffee is a solution, not a compound or mixture, as it includes a solute that dissolves into a solvent. At times, coffee can also be considered a mixture since it involves two mixed substances, but this is too vague.
Q4. Is chocolate a mixture?
Ans: Chocolate is a solid mixture. In its basic form it is composed of cacao powder, cocoa butter, and some type of sweetener such as sugar; however, modern chocolate includes milk solids, any added flavors, modifiers, and preservatives.
Q5. Are eggs a mixture?
Ans: An egg is neither a pure substance nor a mixture. If you crack open an egg, you see eggshells, egg whites, and egg yolks. This means that even macroscopically, an egg is not a mixture, it is an unmixed combination of egg shell, egg white, and egg yolk.
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Solutions: Mixtures & Types of Solutions - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the different types of solutions? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of a solution? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture? |  |
| 4. How are solutions different from mixtures? |  |
| 5. What is a solution and how is it formed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|



















