NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 12 > Mind Map: Electric Charges and Fields
Mind Map: Electric Charges and Fields | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
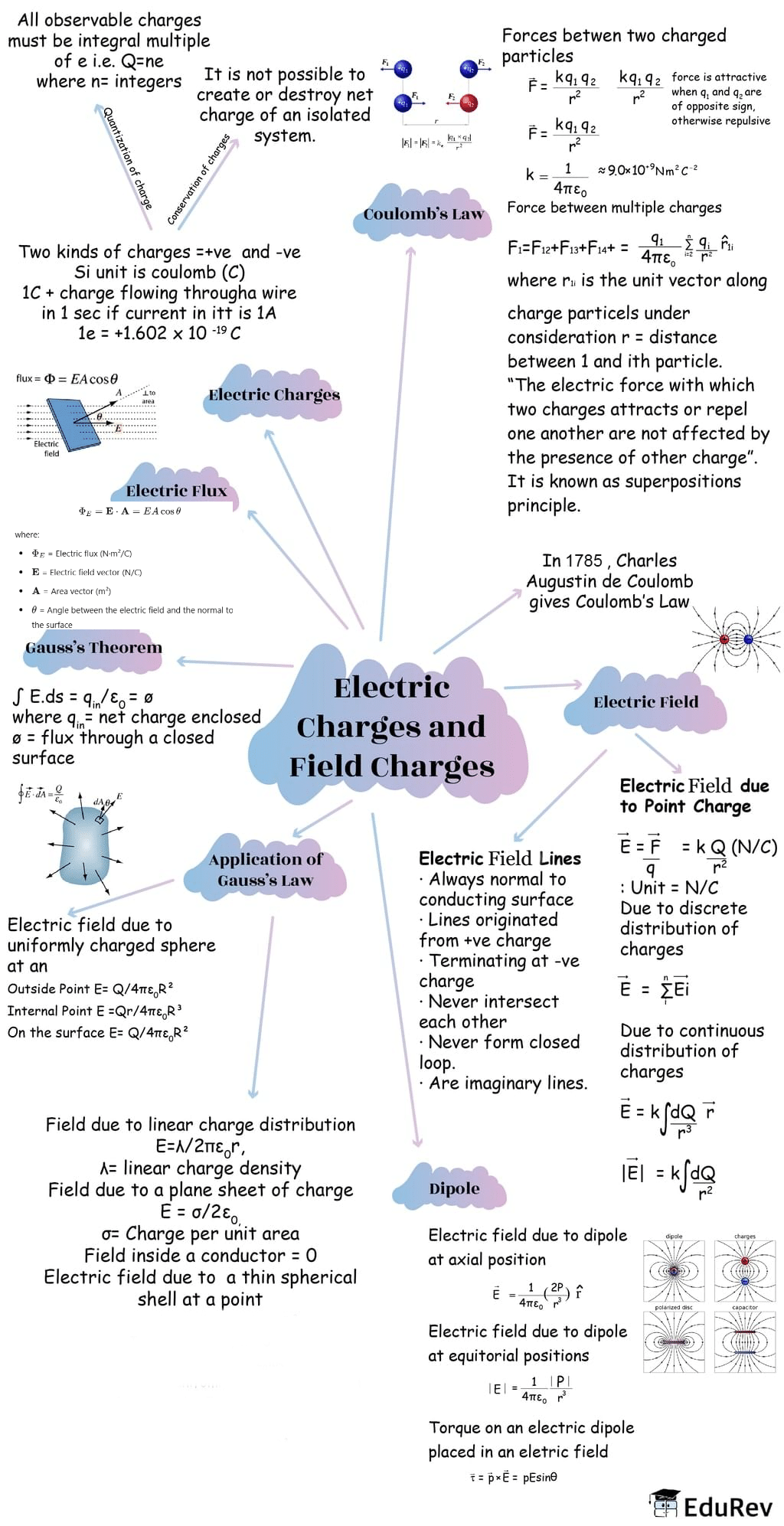
The document Mind Map: Electric Charges and Fields | Physics Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Electric Charges and Fields - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are electric charges and how do they interact with each other? |  |
Ans. Electric charges are fundamental properties of matter that determine how particles interact electromagnetically. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract. This interaction is described by Coulomb's Law, which quantifies the force between two charges based on their magnitudes and the distance between them.
| 2. What is an electric field and how is it related to electric charges? |  |
Ans. An electric field is a region around a charged object where other charges experience a force. It is represented by electric field lines that show the direction and strength of the field. The strength of the electric field (E) created by a point charge (Q) at a distance (r) is given by the formula E = k * |Q| / r², where k is Coulomb's constant. This means that the electric field is directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge.
| 3. What is the concept of electric field lines and what do they represent? |  |
Ans. Electric field lines are graphical representations of electric fields. They illustrate the direction of the electric field and the strength of the force that a positive charge would experience in that field. The lines emanate from positive charges and terminate at negative charges. The density of the lines indicates the strength of the field; closer lines represent a stronger field, while farther lines depict a weaker field.
| 4. How do conductors and insulators differ in terms of electric charge distribution? |  |
Ans. Conductors are materials that allow electric charges to flow freely, such as metals. In conductors, electric charges redistribute themselves in response to an electric field, allowing them to conduct electricity. Insulators, on the other hand, do not allow the free flow of electric charges. In insulators, such as rubber or glass, charges are fixed in place and cannot move freely, preventing the conduction of electricity.
| 5. What is Gauss's Law and how is it applied in electrostatics? |  |
Ans. Gauss's Law states that the electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed within that surface. Mathematically, it is expressed as ∮E · dA = Q_enc/ε₀, where E is the electric field, dA is the differential area vector, Q_enc is the enclosed charge, and ε₀ is the permittivity of free space. This law is used to calculate electric fields for symmetrical charge distributions, simplifying complex problems in electrostatics.
Related Searches






















