NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - The Earth in the Solar System
Q1. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) How does a planet differ from a star?
Ans: A planet is different from a star in these ways:
- Planets do not emit their own light, while stars generate light through nuclear reactions.
- Planets shine by reflecting the light of a nearby star, such as the Sun.
- Stars are generally much larger and hotter compared to planets.
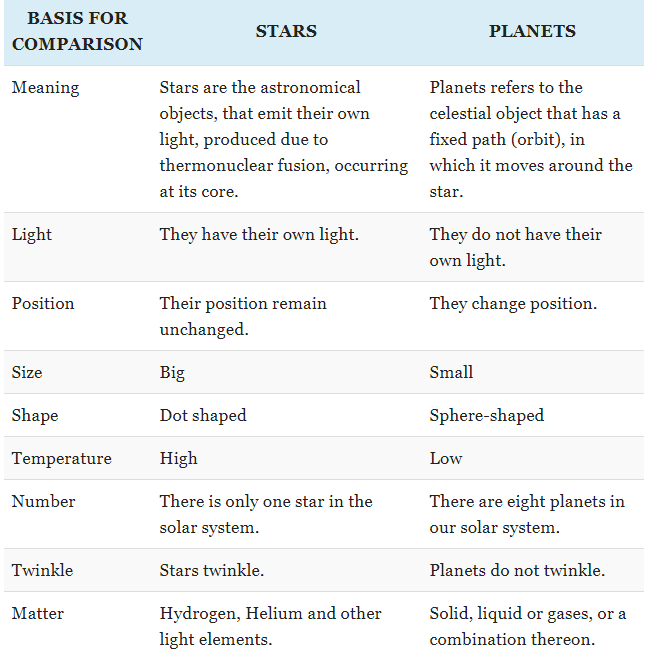 Detailed difference between Stars and Plantes
Detailed difference between Stars and Plantes
(b) What is meant by the ‘Solar System’?
Ans: The term Solar System refers to the collective system centered around the Sun. It comprises the Sun, eight planets, their natural satellites, and other celestial bodies such as asteroids, comets, and meteoroids, all orbiting the Sun.
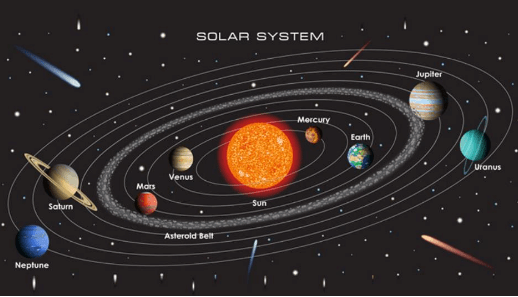 Solar System
Solar System
(c) Name all the planets according to their distance from the sun.
Ans: The planets, listed in order of their distance from the Sun, are:
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune.
(d) Why is the Earth called a unique planet?
Ans:
- Earth is considered a unique planet because it is the only known celestial body that supports life.
- It has favorable conditions for life, including a moderate temperature range, the presence of water, and an atmosphere containing essential gases like oxygen.
(e) Why do we see only one side of the moon always?
Ans:
- The Moon takes approximately 27 days to orbit the Earth and requires the same time to complete one rotation.
- Due to this synchronous rotation, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth.
(f) What is the Universe?
Ans:
- The Universe encompasses all of existence, including billions of galaxies, each containing vast numbers of stars, dust, and gases.
- These galaxies collectively make up the expanse of the Universe.
 UniverseQ2. Tick the correct answer.
UniverseQ2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) The planet known as the “Earth’s Twin” is
(i) Jupiter
(ii) Saturn
(iii) Venus
Ans: (iii) Venus
 View Answer
View Answer 
This is because Venus has a similar size, mass, and composition to Earth, although it has a very different atmosphere and surface conditions.
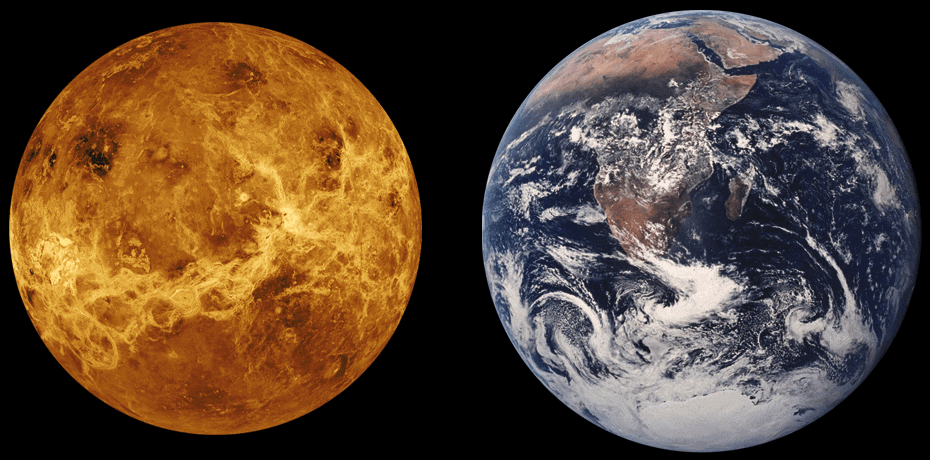 Earth and its Twin Venus
Earth and its Twin Venus
(b) Which is the third nearest planet to the sun?
(i) Venus
(ii) Earth
(iii) Mercury
Ans: (ii) Earth
 View Answer
View Answer 
Earth is the third nearest planet to the Sun, following Mercury and Venus in the order of planets in our solar system.
(c) All the planets move around the sun in a
(i) Circular path
(ii) Rectangular path
(iii) Elongated path
Ans: (iii) Elongated path
 View Answer
View Answer 
All the planets move around the sun in an elongated path, meaning it is slightly stretched out, though it is nearly circular for most planets.
(d) The Pole Star indicates the direction to the
(i) South
(ii) North
(iii) East
Ans: (ii) North
 View Answer
View Answer 
The Pole Star, also known as the North Star, is almost directly above the North Pole, making it a reliable guide for finding north.
 Pole Star
Pole Star
(e) Asteroids are found between the orbits of
(i) Saturn and Jupiter
(ii) Mars and Jupiter
(iii) The Earth and Mars
Ans: (ii) Mars and Jupiter
 View Answer
View Answer 
Asteroids are primarily found in the Asteroid Belt, a region located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This belt contains numerous rocky bodies that orbit the Sun, ranging in size from small rocks to large asteroids.
 Asteroids
Asteroids
Q3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) A group of ______ forming various patterns is called a ______.
Ans: Stars, constellation
 View Answer
View Answer 
A constellation is a collection of stars that appear to form a recognizable shape or pattern when viewed from Earth. These patterns often represent mythological figures, animals, or objects and are used by astronomers for identifying specific regions in the night sky.
(b) A huge system of stars is called______.
Ans: Galaxy
 View Answer
View Answer 
A galaxy is an enormous system composed of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter, all bound together by gravity. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains billions of stars, including our Sun.
 Galaxy
Galaxy
(c) ______ is the closest celestial body to our earth.
Ans: The Moon
 View Answer
View Answer 
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite and the nearest celestial object to us in space. Its proximity to Earth makes it a prominent feature in our night sky and has significant effects, such as tides.
(d) ______ is the third nearest planet to the Sun.
Ans: Earth
 View Answer
View Answer 
In our solar system, the planets are arranged in order of distance from the Sun. Earth is the third planet from the Sun, following Mercury and Venus.
(e) Planets do not have their own ______ and ______.
Ans: Heat, Light
 View Answer
View Answer 
Planets are not sources of light or heat; instead, they reflect the light of nearby stars, like our Sun. They are visible because they reflect sunlight and do not generate energy like stars do.
|
75 videos|322 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - The Earth in the Solar System
| 1. What is the solar system and what does it consist of? |  |
| 2. How do planets differ from stars in the solar system? |  |
| 3. What are the names of the eight planets in our solar system? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Earth in the solar system? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a comet and an asteroid? |  |






















