Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| Table of contents |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
| Questions for Self-Practice |

|
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q 1. Define nutrition.
Ans: Nutrition is a method in which food is consumed by the organisms in the body and utilizing the nutrients from the food.
Q 2. Name the enzymes present in the stomach.
Ans: Pepsin is an enzyme that is present in the stomach.
Q 3. Which part of the body secretes bile? Where is bile stored?
Ans: Bile is secreted only by the liver and is stored in the gall bladder.
Q 4. Define peristalsis.
Ans: Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food to different processing stations in the digestive tract.
Q 5. What is the emulsification of fat?
Ans: Emulsification is the process that involves the breakdown of large fat globules into smaller globules that are soluble in water.
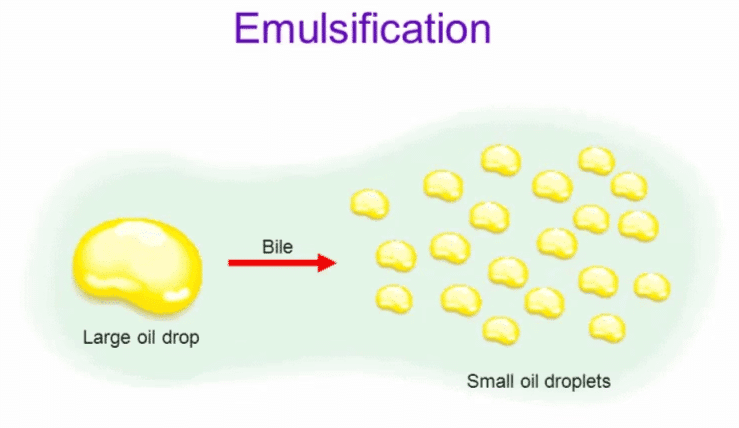 Q 6. Name the enzyme present in human saliva. What type of food material is digested by this enzyme?
Q 6. Name the enzyme present in human saliva. What type of food material is digested by this enzyme?
Ans: The enzyme found in human saliva is ptyaline. Ptyaline is also known as salivary amylase. Secreted ptyaline in the mouth causes starch digestion in the mouth itself.
Q 7. Give the function of guard cells.
Ans: Guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomata by intake of potassium ions and water. It helps in the exchange of gases.
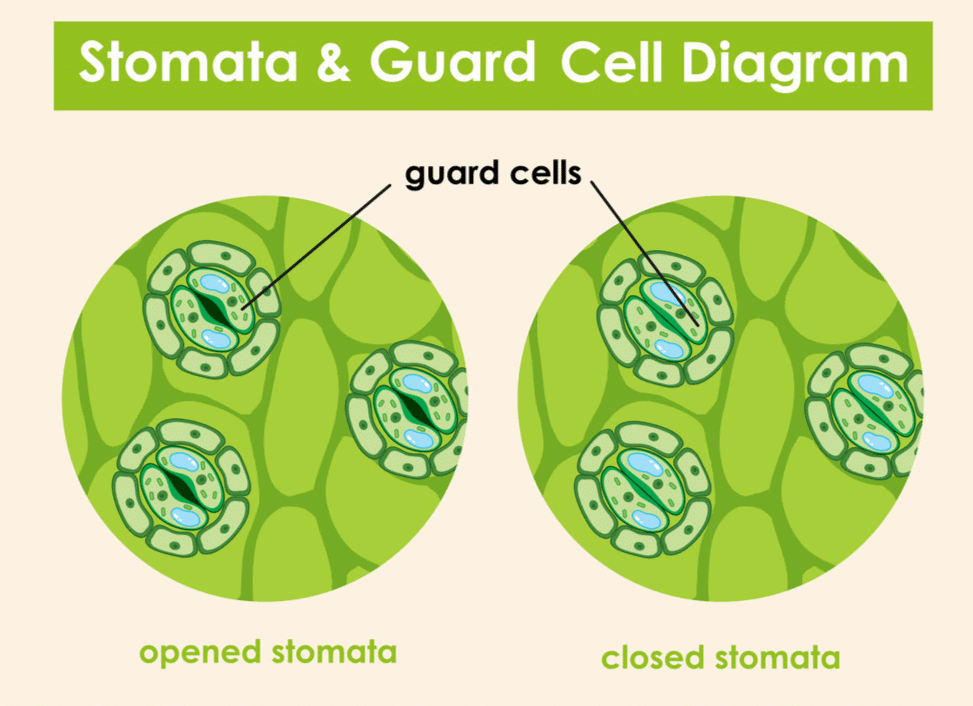 Q.8. Write the complete reaction of photosynthesis.
Q.8. Write the complete reaction of photosynthesis.
Ans: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Q 9. Name pigment present in plants that can absorb sunlight energy.
Ans: Chlorophyll is the pigment present in plants that can absorb sunlight energy. Therefore, chlorophyll is crucial for photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert sunlight into energy.
Q 10. Name the cellular organelle where the photosynthesis process occurs.
Ans: The chloroplast is the cellular organelle where the photosynthesis process occurs.
Q 11. Which part of the alimentary canal is adapted for complete digestion and absorption of food?
Ans: The small intestine is adapted for complete digestion and absorption of food.
Q 12. Name the largest gland of the human body.
Ans: The liver is the largest gland of the human body.
 Q 13. Name the protein-digesting enzymes present in the pancreatic juice of man.
Q 13. Name the protein-digesting enzymes present in the pancreatic juice of man.
Ans: Trypsin is the protein-digesting enzyme present in man's pancreatic juice.
Q 14. What are the end-products of fat digestion?
Ans: Fats are digested in the small intestine. The complete digestion of one fat molecule (a triglyceride) results in three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The liver produces bile that helps you digest fats and certain vitamins.
Q 15. Which structure prevents the entry of food particles into the windpipe?
Ans: The epiglottis moves back and forth through the windpipe to prevent the passage of food and liquids into the lungs.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q 1. Why is nutrition necessary for the human body?
Ans: Human body continuously require energy for their life activities like respiration, circulation, excretion, etc. Energy is required even we are sleeping because a number of biological processes keep on occurring. All these processes require energy and this energy is obtained from nutrition. Nutrition is also needed for growth and repair of human body.
Q 2. Mention various steps of nutrition in Amoeba.
Ans: Amoeba obtains its nutrition through a process called holozoic nutrition, which involves taking in solid or liquid food. This process occurs in several steps:
- Ingestion: The amoeba surrounds and engulfs food using its temporary extensions called pseudopodia.
- Digestion: The food is enclosed in a food vacuole where it is broken down into simpler substances.
- Absorption: Nutrients from the digested food diffuse into the cytoplasm of the amoeba.
- Assimilation: The absorbed nutrients are used for energy and growth.
- Egestion: Undigested material is expelled from the cell.
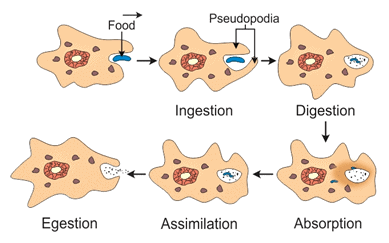
Q 3. Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Ans: Herbivores eat plants which is rich in cellulose. Cellulose takes longer time for complete digestion by the enzymes present in symbiotic bacteria. Therefore, they have longer small intestine. Carnivores, feed on flesh which is easier to digest and do not contain cellulose also. Therefore, they have shorter intestine for digestion of food eaten by them.
Q 4. What is the role of hydrochloric acid in our stomach?
Ans: Hydrochloric acid makes the environment in the stomach acidic, kills the microbes in the stomach that enter with the food, and provides a desired acidic medium so that the enzyme pepsin can act on the food.
Q 5. State two functions of the large intestine of man.
Ans: Functions of the large intestine are:
- It stores the waste food materials.
- It reabsorbs water and salts that were left after digestion.
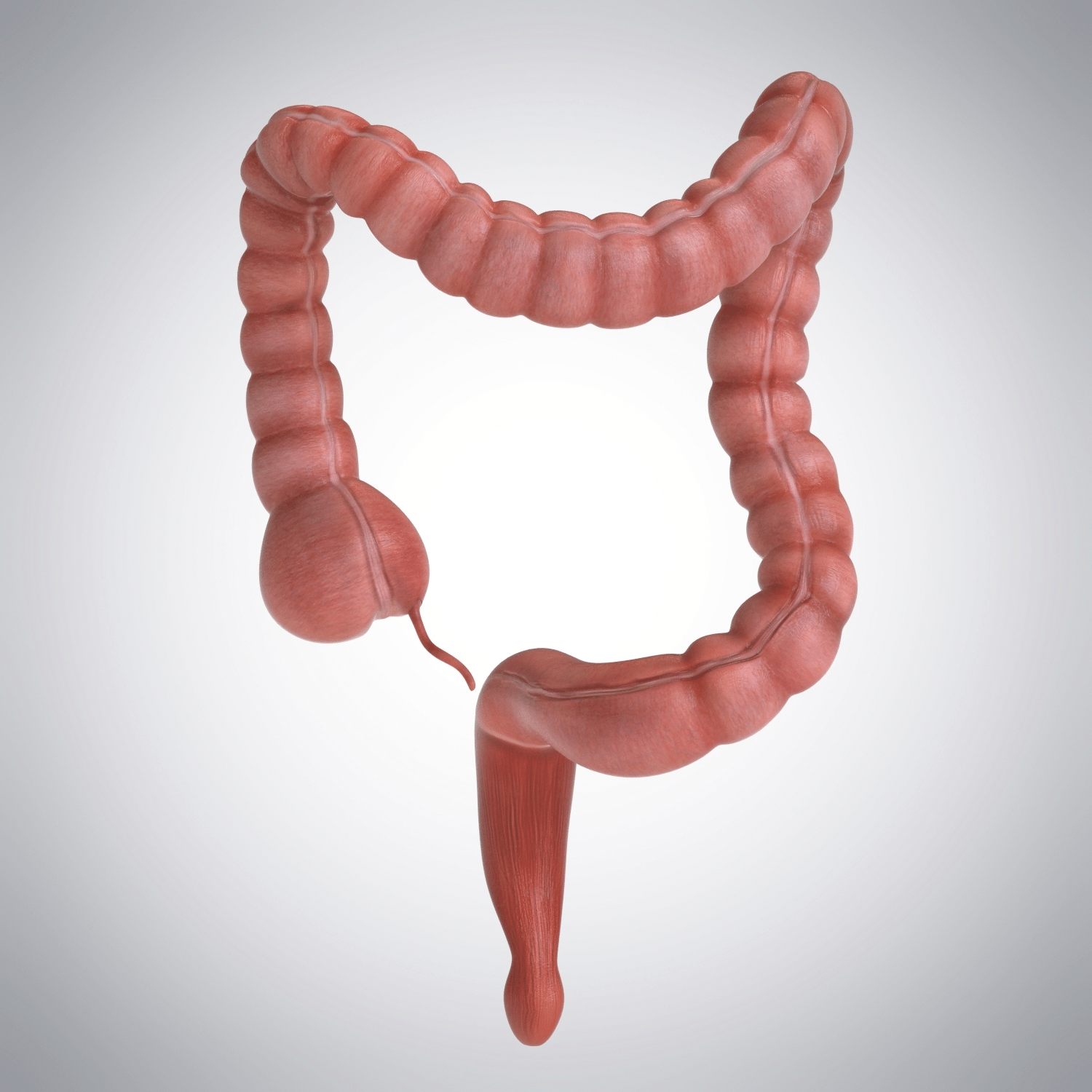
Long Answer Type Questions
Q 1. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans: All living organisms are made up of cells and show living characteristics by showing visible movement, such as walking, breathing, or growing. However, a living organism can also have movements that are not visible to the naked eye. But all living cells perform life processes like respiration, nutrition, reproduction, etc. Therefore, the presence of life processes is a fundamental criterion that can be used to decide whether something is alive or not.
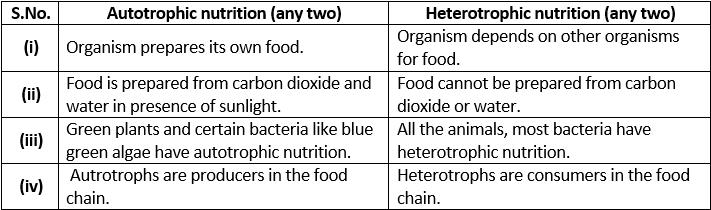
Q 2. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans:
Q 3. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Ans: The small intestine is the most important part of the alimentary canal for digestion and absorption of food.
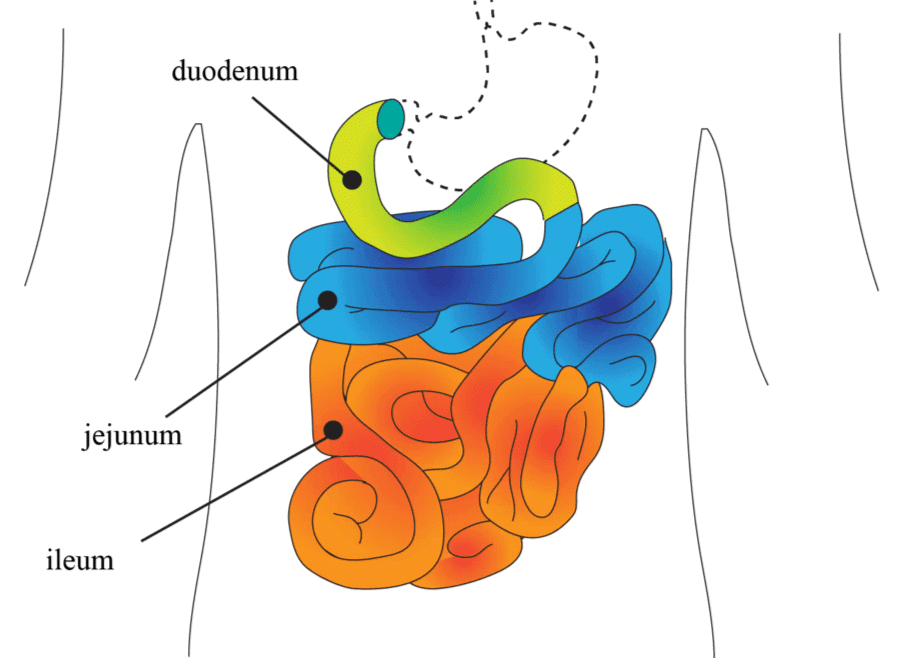
- It has three regions: a U-shaped duodenum, a long coiled middle portion jejunum, and a highly coiled ileum.
- The innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal is the mucosa. This layer forms irregular folds (rugae) in the stomach and small finger-like foldings called villi in the small intestine.
- These modifications increase the surface area for more absorption. Villi are supplied with a network of capillaries.
- It transports lipid molecules. The wall of the intestine is surrounded by blood vessels that assimilate food molecules to the different parts of the body.
Q 4. What will happen if mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
Ans: Gastric glands secrete HCl, mucus, and some other enzymes. Mucus protects the inner lining of stomach from the action of HCl and enzymes. In the absence of mucus, there would be erosion of inner lining of stomach leading to acidity and wounds.
Q 5. How can dental caries be prevented?
Ans: To prevent dental caries, consider the following steps:
- Avoid foods that are high in acidity.
- Brush your teeth regularly, especially after meals, to remove plaque.
- Use fluoride toothpaste, which helps strengthen tooth enamel.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks, as they contribute to acid production by bacteria.
- Visit the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
These practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing dental caries.
Questions for Self-Practice
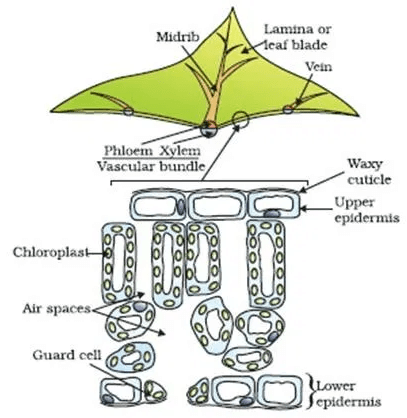
Q 1. Look at the figure and identify X. What is its role in plants?
Q 2. Which is the site of Photosynthesis? The given figure shows a section of the leaf as seen under a microscope. What is the role of the waxy layer on the upper epidermis?
Q 3. Look at the figure. Answer the following questions:
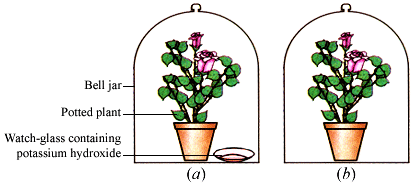
(a) What is the need to use potassium hydroxide?
(b) Why do we need two plants?
(c) Why do we cover both plants with polythene sheets or bell jars?
(d) What observation do you expect at the end of the experiment and why?
(e) What is the aim of the activity?
Q 4. If a plant is kept covered with a polythene sheet, we notice some water drops on the inner side of the sheet after some time. What are they due to? Name and define the process. What is the significance of this process in plants and nature? How does transpiration help in the upward movement of water from roots to leaves?

|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| 1. What are the main life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of respiration in living beings? |  |
| 4. How do organisms excrete waste? |  |
| 5. What role does growth play in the life cycle of an organism? |  |
















