Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Carbon And Its Compounds, Solutions- 3 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page No - 241)
Question 29:
(a) Write the formula of the functional group present in carboxylic acids.
(b) Name the functional group present in CH3—C ≡ CH.
(c) Name the functional groups present in the following compounds :
(i) CH3CHO (ii) CH3CH2COOH (iii) CH3COCH3 (iv) CH3CH2CH2OH
Solution :
Question 30:
(a) Write the IUPAC name and common name of CH3CI
(b) Draw the structure of chlorobutane.
(c) Draw the structure for bromopentane. Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane ?
Solution :
(a) IUPAC name: Chloromethane
Common name: Methyl chloride
(b) Chlorobutane:
(c)Bromopentane.
Question 31:
(a) Write the name and formula of an organic compound containing a ketone functional group.
(b) Write the names and formulae for the first three members of the homologous series of chloroalkanes.
(c) How would you name the following compound ?
CH3—CH2—Br
Solution :
(a) Acetone – CH3COCH3
(b) (i) Chloromethane – CH3Cl
(ii) Chloroethane – C2H5Cl
(iii) Chloropropane – C3H7Cl
(c) Ethylbromide
(a) Ketones
(b) CH3COOH
(c) Formaldehyde
Question 33:
(a) Define a homologous series. Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of the following :
CH3OH
(b) Write the molecular formula of the third member of the homologous series of carbon compounds with general formula CnH2n+1OH.
(c) Name any two fossil fuels.
Solution :
(a) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Ethyl alcohol : C2H5OH
(b) C3H7OH
(c) Coal and petroleum
Question 34:
(a) Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(a) Propanone (b) Butanone
(b) Write the IUPAC names of the following :
(i) HCHO (ii) CH3CHO (Hi) CH3CH2CHO (iv) CH3CH2CH2CHO
(c) Which functional group is likely to be present in an organic compound having the molecular formula C4H10O ? Write the formula of the organic compound.
Solution :
(a) (i) Propanone
(ii) Butanone
(b) (i) Methanal (ii) Ethanal (iii) Propanal (iv) gutanal
(c) Alcohol group, -OH; C4H9O
Question 35:
(a) Match the formulae in group A with appropriate names from group B :
Group A : CH3COOH, CH3CHO, CH3OH
Group B : Ethanol, Methanol, Ethanal, Ethanoic acid
(b) Draw the structure of butanoic acid.
(c) What is the IUPAC name of acetic acid ?
Solution :

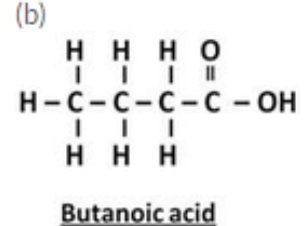
(c) Ethanoic acid
Question 36:
(a) Which functional group do you think can be present in an organic compound having the molecular formula C5H10O2 ? Write the formula of the organic compound.
(b) Give one example each of the compounds having the following functional groups :
(i) Aldehyde group (ii) Alcohol group (iii) Carboxylic acid group (iv) Halo group
(c) Give one example each of the compounds having the following functional groups :
(i) Alkene group (ii) Alkyne group
Solution :
(a) Carboxylic acid group, -COOH; C4H9COOH
(b) (i) Ethanal - CH3CHO
(ii) Methanol - CH3OH
(iii) Ethanoic acid - CH3COOH
(iv) Chloromethane - CH2 = CH2
(c) (i) Ethene:CH2 = CH2
(ii) Ethyne:
Question 37:
(a) What is the molecular formula and structure of the alcohol which can be thought to be derived from pentane ?
(b) Write the names of the following functional groups :
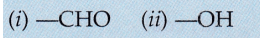

(c) What makes the candle flame yellow and luminous ?
Solution :
(a) C5H12O or C5H11OH
(b) (i) Aldehyde group
(ii) Alcohol group
(iii) Carboxylic acid group
(iv) Ketone group
(v) Halo group
(c) When a candle is lighted, the wax melts, rises up the wick and gets converted into vapours. In a candle, there is no provision for the proper mixing of oxygen (of air) for burning wax vapours. So, the wax vapours bum in an insufficient supply of oxygen (of air) which leads to incomplete combustion of wax. This incomplete combustion of wax produces small unburnt carbon particles. These solid carbon particles rise in the flame, get heated and glow to give out yellowish light. This makes the candle flame yellow and luminous.
Question 38:
(a) What is a homologous series ? Explain with an example.
(b) State two characteristics of a homologous series.
(c) The molecular formula of an organic compound is C18H36. Name its homologous series.
(d) Select the hydrocarbons which belong to the same homologous series. Give the name of each series.
CH4, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, C4H10, C3H4, C3H6
(e) What is meant by ‘heteroatom’? Give examples. Write the names and formulae of two organic compounds containing different heteroatoms.
Solution :
(a) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Example of Homologous series: All the alkanes have similar structures with single covalent bonds and show similar chemical properties, so they can be grouped together in the form of a homologous series.
Homologous series of alkanes: Methane, CH4; Ethane, C2H6; Propane, C3H8; Butane, C4H10; Pentane, C5H12
(b) (i) All the members of the homologous series can be represented by the same general formula.
(ii) Any two adjacent homologues differ by 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms in their molecular formulae.
(c) Alkene, CnH2n
(d) Alkanes: CH4, C2H6, C4H10?
Alkenes :C2H4, C3H6
Alkynes : C2H2, C3H4
(e) In an organic compound, any atom other than carbon and hydrogen is called a heteroatom.
Example: Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Oxygen (O)
Chloromethane – CH3Cl and methanol – CH3OH
(Page No - 242)
Question 39:
(a) What is meant by a functional group ? Explain with an example.
(b) Write three common functional groups present in organic compounds. Give their symbols/formulae.
(c) Name the functional groups present in the following compounds :
(i) CH3COOH (ii) CH3CH2CHO (iii) C2H5OH (iv) CH3COCH2CH3
(d) Name the functional group which always occurs in the middle of a carbon chain.
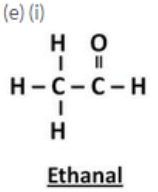
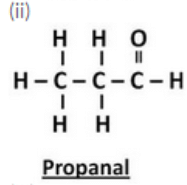
(e) Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(i) Ethanal (ii) Propanal (iii) Butanal (iv) Pentanal
Solution :
(a) An ‘atom’ or ‘a group of atoms’ which makes a carbon compound (or organic compound) reactive and decides its properties (or functions) is called a functional group. The alcohol group, -OH, present in ethanol, C2H5OH, is an example of a functional group.
(b) (i) Halo group: -X
(ii) Alcohol group: -OH
(iii) Aldehyde group: -CHO
(c) (i) Carboxylic acid group
(ii) Aldehyde group
(iii) Alcohol group
(iv) Ketone group
(d) Ketone group, -CO-
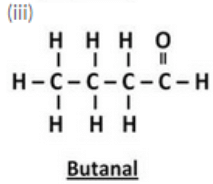
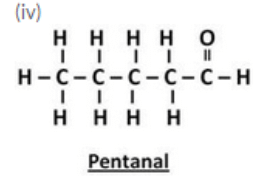
Question 40:
(a) What happens when carbon burns in air ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place.
(b) Why are coal and petroleum called fossil fuels ?
(c) Explain how coal was formed in the earth.
(d) Describe how petroleum was formed in the earth.
(e) Name a fossil fuel other than coal and petroleum.
Solution :
(a) When carbon is burned in air, it forms carbon dioxide gas and releases a large amount of heat and some light:
C +02 → C02 + Heat + Light
(b) Coal and petroleum are called as fossil fuels because they were formed by the decomposition of the remains of the pre-historic plants and animals (fossils) buried under the earth long, long, ago.
(c) Coal was formed by the decomposition of large land plants and trees buried under the earth millions of years ago. It is believed that millions of years ago, due to earthquakes and volcanoes, etc., the forests were buried under the surface of the earth and got covered with sand, clay and water. Due to high temperature and high pressure inside the earth, and in the absence of air, wood was converted into coal.
(d) Petroleum oil (and natural gas) was formed by the decomposition of the remains of extremely small plants and animals buried under the sea millions of years ago. It is believed that millions of years ago, the microscopic plants and animals which lived in seas, died. Their bodies sank to the bottom of the sea and were soon covered with mud and sand. The chemical effects of pressure, heat and bacteria, converted the remains of microscopic plants and animals into petroleum oil and natural gas just as they converted forest trees into coal. This conversion took place in the absence of oxygen or air. The petroleum thus formed got trapped between two layers of impervious rocks (non-porous rocks) forming an oil trap.
(e) Natural gas.
(Page No - 243)
Question 56:
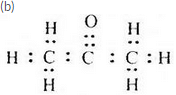
An organic compound having the molecular formula C2H60 can exist in the form of two isomers A and B having different functional groups. The isomer A is a liquid which is used as a solvent for nail polish. The isomer B is also a liquid. An aqueous solution of one of the lower homologues of B is used for preserving biological specimens in the laboratory
(a) What is compound A ?
(b) Write the electron-dot structure of A.
(c) What is compound B ?
(d) Write the electron-dot structure of B.
(e) Name the lower homologue of compound B which is used in preserving biological specimens.
Solution :
(a) Propanone (or Acetone)
(c) Propanal
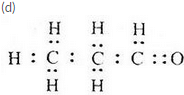
(e) Methanal (or Formaldehyde) is used in preserving biological specimens.
Question 57:
A hard material X which is mined from the earth is used as a household fuel and also for the generation of electricity at Thermal Power Stations. A soft material Y is also used as a fuel in the form of candles. A gaseous material Z which occurs along with petroleum is increasingly being used as a fuel in running vehicles in its compressed form.
(a) What are materials, X, Y and Z ?
(b) When materials X, Y and Z are burned separately :
(i) Which material burns by producing a yellow, luminous flame ?
(ii) Which material ultimately burns without producing a flame ?
(iii) Which material can burn in a gas stove by producing a blue flame ?
Solution :
(a) X is coal; Y is wax; Z is natural gas
(b)(i) Y (wax)
(ii) X (coal)
(iii) Z (natural gas)
Question 58:
Three organic compounds A, B and C have the following molecular formulae :
A C4H8O2
B C4H10O
C C4H8O
(a) Which compound contains an alcohol group ? Write its name and structural formula.
(b) Which compound contains a carboxyl group ? Write its name and structural formula.
(c) Which molecular formula can represent an aldehyde as well as a ketone ? Write the names and structural formulae of the aldehyde and ketone represented by this molecular formula.
Solution :
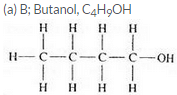
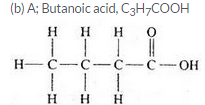
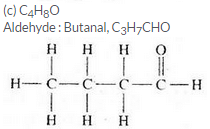
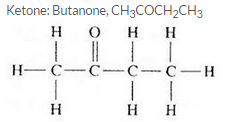
Question 59:
A colourless organic liquid X of molecular formula C2H402 turns blue litmus to red. Another colourless organic liquid Y of molecular formula C2H60 has no action on any litmus but it is used as a nail polish remover. A yet another colourless organic liquid Z of molecular formula C2H6O has also no action on litmus but it is used in tincture of iodine.
(a) Name the liquid X. To which homologous series does it belong ? Give the name of another member of this homologous series.
(b) Name the liquid Y. To which homologous series does it belong ? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
(c) Can you name an organic compound having the same molecular formula as liquid Y but which belongs to a different homologous series ? What is this homologous series ?
(d) Name the liquid Z. To which homologous series does it belong ? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
Solution :
(a) Liquid X is ethanoic acid; it belongs to homologous series of carboxylic acids. Methanoic acid is another member of this homologous series.
(b) Liquid Y is Propanone; it belongs to homologous series of ketones. Butanone is another member of this homologous series.
(c) Propanal; it belongs to homologous series of aldehydes.
(d) Liquid Z is ethanol; it belongs to homologous series of alcohols. Methanol is another member of this homologous series.
Question 60:
You are given an organic compound having the molecular formula C2H8. Give the name and formula of the compound formed :
(a) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a Cl atom.
(b) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by OH group.
(c) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a CHO group.
(d) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a COOH group.
(e) when two H atoms joined to the middle carbon atom of C3H8 are replaced by one O atom.
Solution :
(a) Chloropropane, CH3-CH2-CH2-Cl
(b) Propanol, CH3-CH2-CH2-OH
(c) Butanal, CH3-CH2-CH2-CHO
(d) Butanoic acid, CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH
(e) Propanone, CH3-CO-CH3
(Page No - 262)
Question 1:
Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid is added to sodium carbonate. How would you prove the presence of this gas ?
Solution :
Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas is evolved in the reaction. When passed through lime water, it turns lime water milky.
Question 2:
Which of the following will give brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogencarbonate and why ? CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH
Solution :
CH3COOH will give brick effervescence. Being acid, it reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas.
Question 3:
Name the functional group present in an organic compound which gives brisk effervescence with NaHC03.
Solution :
Carboxylic acid group, -COOH gives brisk effervescence with NaHCO3
Question 4:
Name the hydrocarbon formed when ethanol is heated with cone. H2S04 at 170°C ? What is this reaction known as ?
Solution :
Ethene is formed when ethanol is heated with conc. H2SO4 at 170oC. This reaction is called dehydration.
Question 5:
Why does ethyne (acetylene) burn with a sooty flame ?
Solution :
Ethyne (acetylene) burn with a sooty flame because ethyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon and the percentage of carbon in these hydrocarbons is comparatively higher which does not get oxidised completely in oxygen of air.
Question 6:
Name the product formed when hydrogen is added to ethene.
Solution :
Ethane is formed when hydrogen is added to ethene.
Question 7:
Explain why, ethene decolourises bromine water whereas ethane does not.
Solution :
Ethene decolourises bromine water because ethene is an alkene. And all alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated compounds which decolourise bromine water. On the other hand, ethane being an alkane is a saturated compound which does not decolourise bromine water.
Question 8:
Name two catalysts which can be used in the hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds.
Solution :
Nickel or palladium can be used as catalyst in the hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds.
Question 9:
State two disadvantages of incomplete combustion.
Solution :
Disadvantages of incomplete combustion:
(i) It leads to the formation of soot which is nothing but unburnt carbon which pollutes the atmosphere, blackens cooking utensils.
(ii) It leads to the formation of an extremely poisonous gas called carbon monoxide.
Question 10:
What happens when (give chemical equation) :
Sodium reacts with ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
Solution :
When Sodium reacts with ethanol (ethyl alcohol), hydrogen gas is evolved.
2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5O-Na+ + H2
Question 11:
Describe one reaction of ethanol.
Solution :
Ethanol reacts with sodium metal to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. This reaction is used as a test for ethanol. When a small piece of sodium metal is put into ethanol in a dry test tube, rapid effervescence is produced due to evolution of hydrogen gas.
2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5O-Na+ + H2
Question 12:
Name one liquid carbon compound which is being used as an additive in petrol in some countries.
Solution :
Ethanol is used as an additive in petrol.
Question 13:
What are the raw materials required for making soap in a laboratory (or at home) ?
Solution :
(i) Vegetable oil (like castor oil, cottonseed oil or soyabean oil)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
(iii) Sodium chloride (common salt)
Question 14:
Would you be able to check whether water is hard by using a detergent ? Why ?
Solution :
No, we would not be able to check the hardness of water by using a detergent because a detergent forms lather easily even with hard water.
Question 15:
Describe a test for carboxylic acids.
Solution :
Litmus test: Some blue litmus solution is added to the organic compound (to be tested). If the blue litmus solution turns red, it shows that the organic compound is acidic in nature and hence it is a carboxylic acid.
Question 16:
Why is the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction ?
Solution :
Oxidation means controlled combustion. When ethanol is heated with alkaline potassium permanganate solution (or acidified potassium dichromate solution), it gets oxidised to ethanoic acid. It is called an oxidation reaction because oxygen is added to it during this conversion.
Question 17:
Explain why, alkanes are excellent fuels.
Solution :
Alkanes burn in air to produce a lot of heat due to which they are known to be excellent fuels.
Question 18:
Name one chemical compound which can be used to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Solution :
Sodium hydrogencarbonate can be used to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Question 19:
Complete the following equations :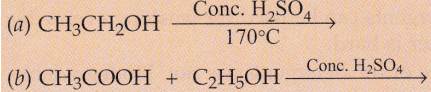
Solution :
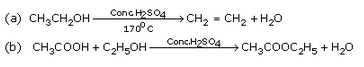
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Carbon And Its Compounds, Solutions- 3 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the properties of carbon and its compounds? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of carbon compounds in daily life? |  |
| 3. How do carbon compounds form covalent bonds? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of carbon compounds? |  |
| 5. How do carbon compounds contribute to climate change? |  |
















