NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biomolecules | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: The protein portion of an enzyme is called: (NEET 2025)
(a) Apoenzyme
(b) Prosthetic group
(c) Cofactor
(d) Coenzyme
Ans: (a)
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed in the process.
- Enzymes are composed of two main parts: the protein portion and the non-protein portion.
- The protein portion of an enzyme is called an Apoenzyme, and it is inactive by itself.
- The non-protein part, which can either be a cofactor or coenzyme, binds to the apoenzyme to form an active enzyme known as a holoenzyme.
Holoenzyme = Apoenzyme + Coenzyme
Q2: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2025)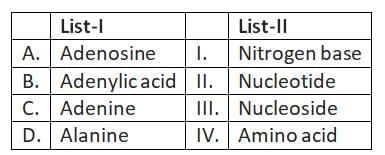
Choose the option with all correct matches.
(a) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
Ans: (a)
- A. Adenosine - III. Nucleoside: Adenosine is composed of adenine attached to a ribose sugar, making it a nucleoside.
- B. Adenylic acid - II. Nucleotide: Adenylic acid, also known as adenosine monophosphate (AMP), consists of three components: adenine (a nitrogenous base), ribose (a sugar), and a phosphate group.
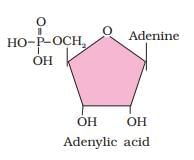
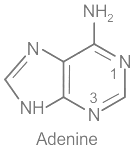
- C. Adenine - I. Nitrogen base: Adenine is one of the nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA.
- D. Alanine - IV. Amino acid: Alanine is an amino acid used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
Q3: Which one of the following enzymes contains 'Haem' as the prosthetic group? (NEET 2025)
(a) Succinate dehydrogenase
(b) Catalase
(c) RuBisCo
(d) Carbonic anhydrase
Ans: (b)
Catalase:
- Catalase is an enzyme that contains haem as its prosthetic group.
- It plays a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative damage by decomposing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
- The haem group in catalase contains iron, which is essential for the enzyme's catalytic activity.
- The reaction catalyzed by catalase is:
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 - This enzyme is highly efficient and critical for maintaining cellular health in aerobic organisms.
Other Options:
RuBisCo:
- RuBisCo (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase) is a key enzyme involved in the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis.
- It catalyzes the fixation of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into organic compounds in plants.
- It does not contain haem; instead, it is a protein enzyme with no metalloprotein or haem group association.
Carbonic anhydrase:
- This enzyme catalyzes the reversible conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into carbonic acid (H2CO3), which then dissociates into bicarbonate (HCO3⁻) and protons (H⁺).
- It contains zinc (Zn2+) as a cofactor
Succinate dehydrogenase:
- This enzyme is part of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and the electron transport chain in mitochondria.
- It facilitates the oxidation of succinate to fumarate and contains iron-sulfur clusters and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) as cofactors.
Q4: Name the class of enzyme that usually catalyze the following reaction: (NEET 2025)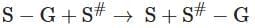
Where, G → a group other than hydrogen
S → a substrate
S# → another substate
(a) Transferase
(b) Ligase
(c) Hydrolase
(d) Lyase
Ans: (a)
Enzymes are divided into 6 classes, each with 4-13 subclasses and named accordingly by a four-digit number.
- Transferases: Enzymes catalysing a transfer of a group, G (other than hydrogen), between a pair of substrates S and S’
S - G + S' → S + S' - G
- Hydrolases: Enzymes catalysing hydrolysis of ester, ether, peptide, glycosidic, C-C, C-halide or P-N bonds.
- Oxidoreductases/dehydrogenases: Enzymes which catalyse oxidoreduction of two substrates S and S’.
- Lyases: Enzymes that catalyse removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds.
- Isomerases: Includes all enzymes catalysing inter-conversion of optical, geometric or positional isomers.
- Ligases: Enzymes catalysing the linking together of 2 compounds, e.g., enzymes which catalyse joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, P-O etc. bonds
2024
Q1: Lecithin, a small molecular weight organic compound found in living tissues, is an example of: (NEET 2024)
(a) Amino acids
(b) Phospholipids
(c) Glycerides
(d) Carbohydrates
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is option (b).
Some lipids have phosphorous and a phosphorylated organic compound in them. These are phospholipids. They are found in cell membrane. Lecithin is one example.
Option (c) is incorrect as glycerides are another group of lipids in which both glycerol and fatty acids are present.
Option (a) and (d) are incorrect as amino acids and carbohydrates are separate groups of biomolecules.
Q2: The cofactor of the enzyme carboxypeptidase is: (NEET 2024)
(a) Zinc
(b) Niacin
(c) Flavin
(d) Haem
Ans: (a)
The enzyme carboxypeptidase is well-known for its utilization of a zinc ion as a cofactor in its catalytic mechanism. The zinc ion plays a crucial role in the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, the reaction facilitated by carboxypeptidase. The presence of zinc allows for proper stabilization of water molecules which are necessary in the catalysis, making the hydrolysis of the peptide bond effective. This zinc dependency categorizes carboxypeptidase as a metalloenzyme.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option A: Zinc
Other options mentioned, such as Niacin, Flavin, and Haem, serve as cofactors for different enzymes. For example, Niacin is involved in the formation of NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) which acts as an electron carrier in many enzymatic reactions. Flavins (like FMN and FAD) are involved in a myriad of oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Haem, found in hemoglobin and cytochromes, also plays crucial roles primarily in electron transfer processes and oxygen transport. These are not associated with the functioning of carboxypeptidase, which specifically requires zinc for its enzymatic activity.
Q3: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)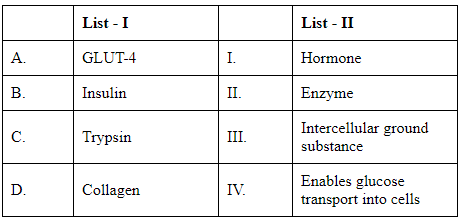 Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: (a)
To solve this matching question, we need to correctly identify what each item in List I represents and match it with its corresponding description in List II:
- GLUT-4 is a glucose transporter protein that allows glucose to be absorbed into cells when insulin is present. Hence, it should be matched with "Enables glucose transport into cells."
- Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues. It should be matched with "Hormone."
- Trypsin is an enzyme that aids in the digestion of proteins in the digestive system. It should be matched with "Enzyme."
- Collagen is a primary structural protein that forms connective tissues throughout the body, including the extracellular matrix. It should be matched with "Intercellular ground substance."
Here's how we match each term with the correct description from List II:
A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
This corresponds to:
- A (GLUT-4) - IV (Enables glucose transport into cells)
- B (Insulin) - I (Hormone)
- C (Trypsin) - II (Enzyme)
- D (Collagen) - III (Intercellular ground substance)
Therefore, the answer is Option A
Q4: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)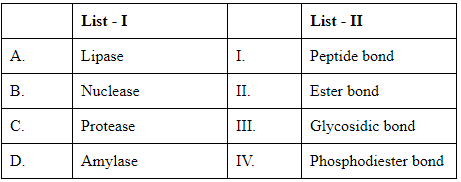 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(b) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(d) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
Ans: (c)
The task here is to correctly match the enzymes listed in List I with their corresponding type of bond they hydrolyze or act on, as listed in List II. To do this, we need to understand the function of each enzyme:
- Lipase: This enzyme catalyzes the breakup of fats (lipids), primarily working on the ester bonds in triglycerides. Thus, Lipase corresponds to Ester bond (II).
- Nuclease: Nucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bonds within the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. Therefore, Nuclease corresponds to Phosphodiester bond (IV).
- Protease: These enzymes hydrolyze proteins by breaking peptide bonds between amino acids. Thus, Protease matches with Peptide bond (I).
- Amylase: Amylase acts on starches, breaking down the glycosidic bonds in carbohydrate molecules to produce simple sugars. Hence, Amylase corresponds to Glycosidic bond (III).
Matching these to the given options:
- A - Lipase corresponds to Ester bond (II).
- B - Nuclease corresponds to Phosphodiester bond (IV).
- C - Protease corresponds to Peptide bond (I).
- D - Amylase corresponds to Glycosidic bond (III).
This matches with Option C, hence the correct response is: Option C
Q5: Regarding catalytic cycle of an enzyme action, select the correct sequential steps : (NEET 2024)
A. Substrate enzyme complex formation.
B. Free enzyme ready to bind with another substrate.
C. Release of products.
D. Chemical bonds of the substrate broken.
E. Substrate binding to active site.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) E, A, D, C, B
(b) A, E, B, D, C
(c) B, A, C, D, E
(d) E, D, C, B, A
Ans: (a)
The correct order of the steps in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action involves the following key events:
- Substrate binding to the active site: Before any reaction can take place, the substrate must bind to the enzyme's active site. This is where the substrate is correctly positioned for the reaction.
- Formation of the substrate-enzyme complex: Once the substrate binds to the active site, a substrate-enzyme complex is formed. This complex stabilizes the transition state of the reaction and lowers the activation energy required for the reaction.
- Chemical bonds of the substrate broken : Within the substrate-enzyme complex, the specific chemical reaction occurs, leading to the breaking of bonds within the substrate. This step often involves changes to the chemical structure of the substrate, turning it into the product(s) of the reaction.
- Release of products: After the reaction occurs, the product(s) of the reaction are released from the enzyme, leaving the enzyme unchanged.
- Free enzyme ready to bind with another substrate: Once the product is released, the enzyme is free again to bind with another substrate, repeating the cycle.
Given the correct sequence and your provided options, the correct answer is: Option A
This sequence correctly describes the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action, from substrate binding to the release of products and the readiness of the enzyme to start a new cycle.
Q6: Inhibition of Succinic dehydrogenase enzyme by malonate is a classical example of: (NEET 2024)
(a) Cofactor inhibition
(b) Feedback inhibition
(c) Competitive inhibition
(d) Enzyme activation
Ans: (c)
Sol: The inhibition of the enzyme succinic dehydrogenase by malonate is a classic example of competitive inhibition. To understand why this is the case, let's explore the mechanism and dynamics of this specific type of inhibition in the context of the given enzyme and inhibitor.
Competitive Inhibition: This type of enzyme inhibition occurs when an inhibitor compound resembles the substrate's structure and competes with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme. If the inhibitor binds to the active site, it prevents the substrate from binding, temporarily blocking the enzyme’s activity. Importantly, competitive inhibition can typically be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate, as this can displace the inhibitor from the active site.
Succinic Dehydrogenase and Malonate: Succinic dehydrogenase is an enzyme that plays a critical role in the citric acid cycle, an essential metabolic pathway for energy production. It catalyzes the oxidation of succinate into fumarate. The structure of malonate is closely similar to that of succinate, the natural substrate of succinic dehydrogenase. Because of its structural similarity, malonate competes with succinate for the active site on succinic dehydrogenase. When malonate binds to the active site, it effectively inhibits the enzyme from catalyzing the reaction to convert succinate into fumarate.
Conclusion: Considering these points, Option C, Competitive inhibition, is correct for describing the inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate, as it directly competes with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme.
Other options such as cofactor inhibition, feedback inhibition, and enzyme activation do not accurately describe the situation with malonate and succinic dehydrogenase. Cofactor inhibition involves inhibition by substances that affect the enzyme's cofactors, feedback inhibition generally pertains to the regulation of biochemical pathways by their product, and enzyme activation is a process that increases the enzyme's activity, none of which apply in this context.
Q7: Which of the following statement is incorrect about enzymes? (NEET 2024)
(a) They are highly substrate specific
(b) In thermophilic organisms, enzymes can catalyze reaction at high temperatures, i.e. 90°C
(c) All enzymes are proteinaceous in nature
(d) Some enzymes have metal ions
Ans: (c)
(a) They are highly substrate specific: This is true. Enzymes are highly specific to the substrate they act upon, meaning they catalyze reactions with particular molecules.
(b) In thermophilic organisms, enzymes can catalyze reactions at high temperatures, i.e. 90°C: This is true. Thermophilic organisms have enzymes that can function at extremely high temperatures, even up to 90°C or more.
(c) All enzymes are proteinaceous in nature: This is incorrect. While most enzymes are proteins, some are made of RNA molecules, known as ribozymes.
(d) Some enzymes have metal ions: This is true. Many enzymes require metal ions (such as zinc, magnesium, or iron) to function properly as cofactors.
Therefore, the incorrect statement is (c).
Q8: The following can be found as a zwitter ion: (NEET 2024)
(a) Fatty acid
(b) Monosaccharide
(c) Amino acid
(d) Nucleic acid
Ans: (c)
- (a) Fatty acid: Fatty acids do not typically exist as zwitterions. They are usually in their ionized form at physiological pH.
- (b) Monosaccharide: Monosaccharides (simple sugars) do not form zwitterions. They generally have hydroxyl groups and do not carry both positive and negative charges on the same molecule.
- (c) Amino acid: This is correct. Amino acids, at physiological pH, exist as zwitterions. They contain both a positively charged amino group (—NH₃⁺) and a negatively charged carboxyl group (—COO⁻), making them neutral overall but having both positive and negative charges.
- (d) Nucleic acid: Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, do not exist as zwitterions. They contain acidic phosphate groups but are not zwitterions.
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Amino acid.
Q9: Which of the following is not a complex polysaccharide? (NEET 2024)
(a) Inulin
(b) Chitin
(c) Glucosamine
(c) N-acetyl galactosamine
Ans: (a)
- (a) Inulin: Inulin is a type of carbohydrate, specifically a fructan, that is a polysaccharide but is not considered a "complex" polysaccharide. It consists of fructose units and is typically used by plants as a storage carbohydrate.
- (b) Chitin: Chitin is a complex polysaccharide made of N-acetylglucosamine, found in the exoskeletons of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi. It is a complex polysaccharide.
- (c) Glucosamine: Glucosamine is not a polysaccharide itself but is an amino sugar that forms part of larger polysaccharides such as glycosaminoglycans (e.g., in cartilage).
- (d) N-acetyl galactosamine: This is an amino sugar that forms part of complex polysaccharides, such as glycosaminoglycans.
Therefore, Inulin is not a complex polysaccharide, making (a) the correct answer.
Q10: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)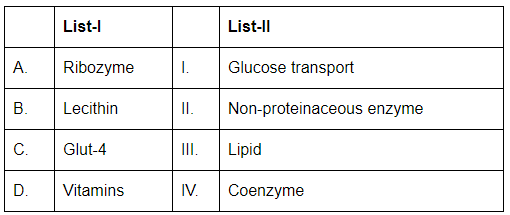 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
Ans: (d)
- A. Ribozyme (II. Non-proteinaceous enzyme): A ribozyme is a non-proteinaceous enzyme, meaning it is made of RNA and not protein.
- B. Lecithin (III. Lipid): Lecithin is a type of lipid, specifically a phospholipid, commonly found in cell membranes.
- C. Glut-4 (I. Glucose transport): GLUT-4 (Glucose transporter type 4) is involved in glucose transport in cells, particularly in muscle and fat cells.
- D. Vitamins (IV. Coenzyme): Vitamins often act as coenzymes or precursors to coenzymes in various metabolic reactions.
Therefore, the correct matching is A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV.
Q11: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
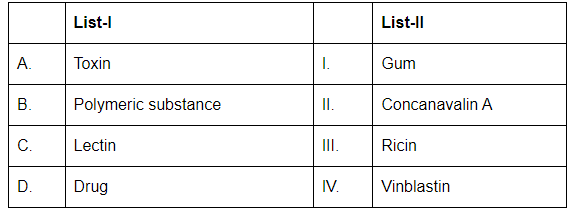 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(b) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(c) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
Ans: (c)
- A. Toxin (III. Ricin): Ricin is a toxic protein derived from castor beans. It is a well-known toxin.
- B. Polymeric substance (I. Gum): Gums are polysaccharides or polymeric substances derived from plants that form gels when hydrated.
- C. Lectin (II. Concanavalin A): Concanavalin A is a type of lectin, which is a protein that binds to specific carbohydrate structures on cell surfaces.
- D. Drug (IV. Vinblastin): Vinblastine is a drug used in cancer treatment, particularly for its role in inhibiting cell division.
Therefore, the correct matching is A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV.
Q12: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
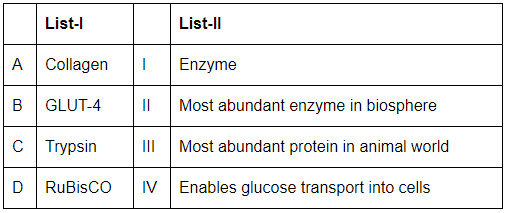
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (c)
- A. Collagen (III. Most abundant protein in animal world): Collagen is the most abundant protein in the animal world, providing structural support in tissues.
- B. GLUT-4 (IV. Enables glucose transport into cells): GLUT-4 is a glucose transporter that enables the transport of glucose into muscle and fat cells.
- C. Trypsin (I. Enzyme): Trypsin is a digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins in the small intestine.
- D. RuBisCO (II. Most abundant enzyme in biosphere): RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme on Earth, playing a key role in the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis.
Therefore, the correct matching is A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II.
Q13: Which of the following graphs explains the effect of pH on the enzyme activity? (NEET 2024)
(a) 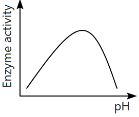
(b) 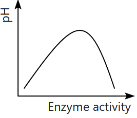
(c) 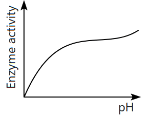
(d) 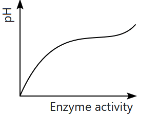
Ans: (a)
The graph that explains the effect of pH on enzyme activity typically shows that enzyme activity increases as the pH moves towards an optimal level, then decreases as the pH becomes too high or too low. This is a typical bell-shaped curve, where the enzyme activity is highest at a specific optimal pH, which matches the graph in option (a).
Q14: The catalytic cyclic of an enzyme action is described as: (NEET 2024)
A. Enzyme releases products of the reaction and gets free.
B. Substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape.
C. The substrate binds with the active site of the enzyme.
D. Enzymes-product complex is formed.
(a) C→B→A→D
(b) C→B→D→A
(c) B→C→D→A
(d) D→C→A→B
Ans: (b)
- C. The substrate binds with the active site of the enzyme: The substrate first binds to the enzyme's active site.
- B. Substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape: The binding of the substrate often induces a conformational change in the enzyme (induced fit model).
- D. Enzyme-product complex is formed: The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, forming the enzyme-product complex.
- A. Enzyme releases products of the reaction and gets free: Finally, the enzyme releases the products and returns to its original form, ready for the next cycle.
Therefore, the correct order is C → B → D → A.
Q15: Which of the following is a nucleotide? (NEET 2024)
(a) Uridine
(b) Adenylic acid
(c) Guanine
(d) Guanosine
Ans: (b)
- Adenylic acid is a nucleotide, which consists of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group.
- Uridine is a nucleoside, not a nucleotide, as it lacks the phosphate group.
- Guanine is a nitrogenous base, not a nucleotide.
- Guanosine is a nucleoside, as it consists of the base guanine and a sugar but lacks the phosphate group.
Q16: Enzymes that catalyse the removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds, are known as: (NEET 2024)
(a) Transferases
(b) Oxidoreductases
(c) Dehydrogenases
(d) Lyases
Ans: (d)
- Lyases are enzymes that catalyze the removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis, often leaving double bonds. Examples include dehydratases, decarboxylases, and other enzymes that break bonds without the use of water.
- Transferases catalyze the transfer of functional groups.
- Oxidoreductases are enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions.
- Dehydrogenases are a subclass of oxidoreductases that specifically catalyze the removal of hydrogen atoms.
Q17: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
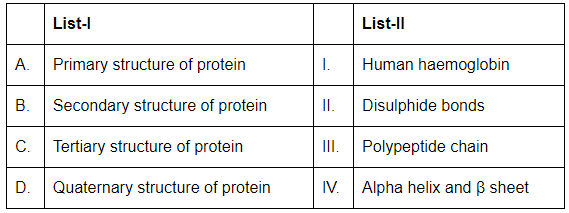
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III,B-IV,C-II,D-I
(b) A-III,B-II,C-I,D-IV
(c) A-I,B-III,C-II,D-IV
(d) A-IV,B-III,C-II,D-I
Ans: (a)
- A. Primary structure of protein (III. Polypeptide chain): The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
- B. Secondary structure of protein (IV. Alpha helix and β sheet): The secondary structure of a protein involves the regular folding of the polypeptide chain into structures like alpha helices and beta sheets.
- C. Tertiary structure of protein (II. Disulphide bonds): The tertiary structure refers to the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein, which is stabilized by interactions such as disulfide bonds.
- D. Quaternary structure of protein (I. Human haemoglobin): The quaternary structure is the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in a multi-subunit protein, like human hemoglobin.
Thus, the correct matching is A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I.
Q18: Which of the following graphs depicts the effect of substrate concentration on velocity of enzyme catalysed reaction? (NEET 2024)
(a) 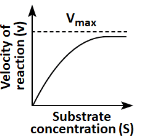
(b) 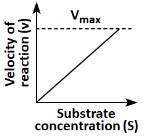
(c) 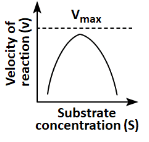
(d) 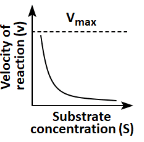
Ans: (a)
The graph in (a) depicts the typical effect of substrate concentration on the velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. As the substrate concentration increases, the reaction velocity increases proportionally until it reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax), at which point all enzyme active sites are occupied, and further increases in substrate concentration do not increase the reaction rate. This is a classic Michaelis-Menten kinetics graph.
Q19: Which of the following are not fatty acids? (NEET 2024)
A. Glutamic acid
B. Arachidonic acid
C. Palmitic acid
D. Lecithin
E. Aspartic acid
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, D and E only
(b) A and B only
(c) A, D and E only
(d) B and C only
Ans: (c)
- A. Glutamic acid: This is an amino acid, not a fatty acid.
- B. Arachidonic acid: This is a fatty acid. It is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid found in the cell membranes.
- C. Palmitic acid: This is a fatty acid. It is a saturated fatty acid found in animal fats and plant oils.
- D. Lecithin: Lecithin is a phospholipid, not a fatty acid. It is composed of fatty acids, but it itself is not a fatty acid.
- E. Aspartic acid: This is an amino acid, not a fatty acid.
Therefore, A, D, and E are not fatty acids, making (c) A, D, and E only the correct answer.
Q20: Ligases is a class of enzymes responsible for catalysing the linking together of two compounds. Which of the following bonds is not catalysed by it? (NEET 2024)
(a) C-C
(b) P-O
(c) C-O
(d) C-N
Ans: (a)
- Ligases are enzymes that catalyze the joining of two molecules, typically using energy derived from ATP or another nucleotide triphosphate. They are involved in forming various types of bonds, but not all bonds.
- (a) C-C: This is generally not catalyzed by ligases. C-C bond formation typically requires other mechanisms or enzymes.
- (b) P-O: Ligases can catalyze the formation of phosphodiester bonds (P-O), such as in the joining of DNA strands.
- (c) C-O: Ligases can catalyze the formation of C-O bonds, such as in the joining of alcohols and other molecules.
- (d) C-N: Ligases can also catalyze the formation of C-N bonds, for example, in the synthesis of peptides or other amide linkages.
Therefore, the bond that is not catalyzed by ligases is C-C.
2023
Q1: Cellulose does not form blue colour with Iodine because (NEET 2023)
(a) It is a disaccharide
(b) It is a helical molecule
(c) It does not contain complex helices and hence cannot hold iodine molecules
(d) It breaks down when iodine reacts with it
Ans: (c)
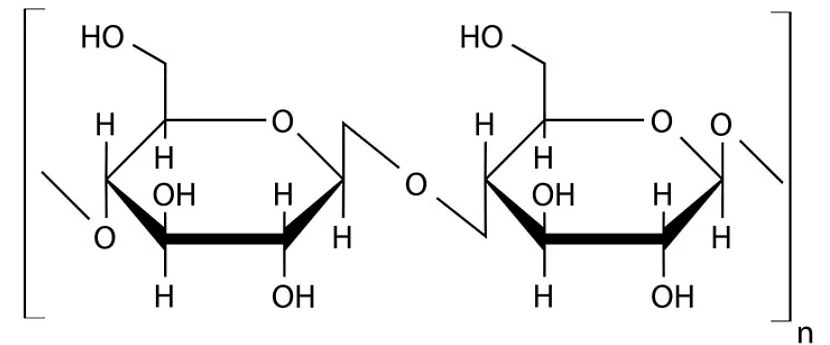
Option (c) is the correct answer because cellulose does not contain complex helices and hence cannot hold iodine molecules. Option (a), (b) and (d) are not correct
Q2: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: A protein is imagined as a line, the left end represented by first amino acid (C-terminal) and the right end represented by last amino acid (N-terminal).
Statement II: Adult human haemoglobin, consists of 4 subunits (two subunits of α type and two subunits of β type.)
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(b) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(c) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
Ans: (c)
Statement I is false - because the C-terminal represents the last amino acid in the protein chain, not the first. The N-terminal represents the first amino acid.
Statement II is true - Adult human hemoglobin consists of 4 subunits: two subunits of α-type and two subunits of β-type. These subunits come together to form a complex protein structure responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood.
The correct option is (C): Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: low temperature preserves the enzyme in a temporarily inactive state whereas high temperature destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
Statement II: when the inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the activity of enzyme, it is known as competitive inhibitor.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: (a)
- Statement I is true - Low temperatures can slow down enzymatic reactions by placing the enzyme in an inactive state, and high temperatures can denature proteins, including enzymes, which can lead to a loss of enzymatic activity.
- Statement II is also true - A competitive inhibitor is a molecule that closely resembles the substrate of an enzyme and competes for the active site, thus reducing the enzyme's activity. This type of inhibition is called competitive inhibition.
So, the correct answer is : Option A : Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
Q4: Malonate inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria by inhibiting the activity of: (NEET 2023)
(a) Dinitrogenase
(b) Succinic dehydrogenase
(c) Amylase
(d) Lipase
Ans: (b)
Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase. Succinic dehydrogenase is an enzyme in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) that helps in the conversion of succinate to fumarate. Malonate mimics succinate and competes for the same binding site on the enzyme, thereby inhibiting its activity and blocking the bacterial growth.
Q5: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2023)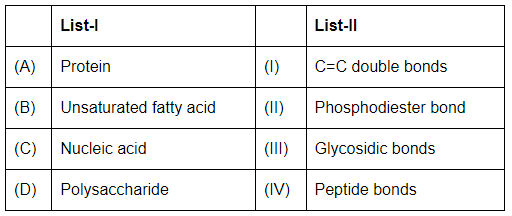 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)-II (B)-I (C)-IV (D)-III
(b) (A)-IV (B)-III (C)-I (D)-II
(c) (A)-IV (B)-I (C)-II (D)-III
(d) (A)-I (B)-IV (C)-III (D)-II
Ans: (c)
- Protein (A): Peptide bonds (IV) link amino acids in proteins.
- Unsaturated fatty acid (B): C=C double bonds (I) are present in unsaturated fatty acids, making them unsaturated.
- Nucleic acid (C): Phosphodiester bonds (II) join nucleotides in nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
- Polysaccharide (D): Glycosidic bonds (III) link monosaccharides in polysaccharides like starch and cellulose.
Q6: Inulin is a polymer of: (NEET 2023)
(a) Fructose
(b) Galactose
(c) Amino Acids
(d) Glucose
Ans: (a)
Inulin is a carbohydrate polymer made up of fructose units linked together. It is a type of fructan and is commonly found in plants like chicory and Jerusalem artichoke. Inulin is used as a dietary fiber and has various health benefits.
Q7: Which of the following is not a secondary metabolite? (NEET 2023)
(a) Curcumin
(b) Morphine
(c) Anthocyanin
(d) Lecithin
Ans: (d)
Curcumin, Morphine, and Anthocyanin are all secondary metabolites.
Curcumin is an active compound in turmeric and a secondary metabolite known for its medicinal properties.
Morphine is an alkaloid found in opium and is a secondary metabolite used for its analgesic properties.
Anthocyanin is a pigment found in plants and is a secondary metabolite responsible for the red, blue, and purple colors of many fruits and flowers.
Lecithin is not a secondary metabolite. It is a phospholipid, primarily involved in the structure and function of cell membranes, and is classified as a primary metabolite.
2022
Q1: When a carrier protein facilitates the movement of two molecules across the membrane in same direction, it is called
(a) Symport
(b) Uniport
(c) Transport
(d) Antiport (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
- A symport is the transport of two types of molecules across the membrane in same direction.
- Antiport is the transport of two different molecules in opposite directions.
- Uniport is transport of a molecule across the membrane independent of other molecule.
Q2: Match List-I with List-II
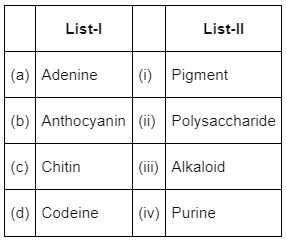
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) (a) - (i), (b) - (iv), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
(b) (a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iii)
(c) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(d) (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii) (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer as adenine is a purine, anthocyanin is a pigment, chitin is a polysaccharide and codeine is an alkaloid.
Q3: Primary proteins are also called as polypeptides because :
(a) They can assume many conformations
(b) They are linear chains
(c) They are polymers of peptide monomers
(d) Successive amino acids are joined by peptide bonds (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
- Option (4) is the correct answer because primary proteins are heteropolymers containing strings of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
- Option (1) and (2) are incorrect as primary proteins are called polypeptides due to the presence of many monomers linked via peptide bonds, not due to the presence of many conformations.
- Option (3) is incorrect because proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers.
Q4: Choose the incorrect enzymatic rection:
(a) 
(b) 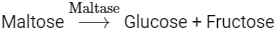
(c) 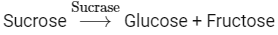
(d) 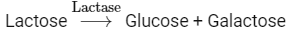 (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer because maltose is a disaccharide which on hydrolysis gives two molecules of glucose.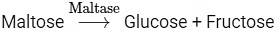
Options (a), (c) and (d) represent correct enzymatic reactions so they are not the answer.
Q6: Given below are two statements:
Statement I : Amino acids have a property of ionizable nature of −NH2 and −COOH groups, hence have different structures at different pH.
Statement-II : Amino acids can exist as Zwitterionic form at acidic and basic pH.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
Option (d) is the correct answer as statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
A particular property of amino acids is the ionizable nature of −NH2 and −COOH groups. Hence, in solutions of different pH, the structure of amino acid changes. Amino acid exists as a dipolar ion called a zwitterion at a particular pH called isoelectric point.
Q7: In the enzyme which catalyses the breakdown of: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
H2O2 → H2O + O2
the prosthetic group is :
(a) Niacin
(b Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
(c) Haem
(d) Zinc
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because peroxidase is the enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen; haem is the prosthetic group of this enzyme.
- Option (a) and (b) are incorrect because co-enzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain the vitamin niacin.
- Option (d) is incorrect because zinc is a co-factor for the proteolytic enzyme carboxypeptidase.
Q8: Read the following statements on lipids and find out correct set of statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(A) Lecithin found in the plasma membrane is a glycolipid
(B) Saturated fatty acids possess one or more c = c bonds
(C) Gingely oil has lower melting point, hence remains as oil in winter
(D) Lipids are generally insoluble in water but soluble in some organic solvents
(E) When fatty acid is esterified with gIycerol, monoglycerides are formed
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (D) and (E) only
(b) (A), (B) and (D) only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) only
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because statements (c), (d) and (e) correct as oils have lower melting point and hence remain oil in winters. Lipids are generally insoluble in water but soluble in some organic solvents.
- Option (a), (b) and (d) are incorrect because statements (a) and (b) are incorrect. Lecithin is a type of phospholipid found in plasma membrane. Saturated fatty acids are without double bond.
2021
Q1: Which of the following are not secondary metabolites in plants? (NEET 2021)
(a) Vinblastin, curcumin
(b) Rubber, gums
(c) Morphine, codeine
(d) Amino acids, glucose
Ans: (d)
- Amino acids and glucose are included under the category of primary metabolites as they have identifiable functions and play known roles in normal physiological processes.
- Rubber, gums, morphine, codeine, vinblastin and curcumin are included under the category of secondary metabolites as their role or functions in host organisms is not known yet. However, many of them are useful to human welfare.
Q2: Match List -I with List - II. (NEET 2021)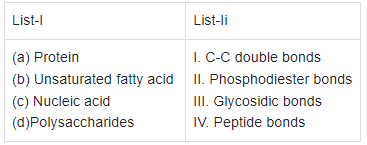
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(a) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
(b) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(c) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
(d) (i) (iv) (iii) (ii)
Ans: (c)
- In a polypeptide or a protein, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (−COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with amino (−NH2) group of the next amino acid with the elimination of a water moiety.
- Unsaturated fatty acids are with one or more C = C double bonds.
- In nucleic acids, a phosphate moiety links the 3'-carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 5'-carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide. The bond between the phosphate and hydroxyl group is an ester bond. As there is one such ester bond on either side, it is called phosphodiester bond.
- In a polysaccharide, the individual monosaccharides are linked by a glycosidic bond.
Q3: Following are the statements with reference to 'lipids'. (NEET 2021)
(a) Lipids having only single bonds are called unsaturated fatty acids.
(b) Lecithin is a phospholipid.
(c) Trihydroxy propane is glycerol.
(d) Palmitic acid has 20 carbon atoms including carboxyl carbon.
(e) Arachidonic acid has 16 carbon atoms.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b) and (c) only
(b) (b) and (e) only
(c) (a) and (b) only
(d) (c) and (d) only
Ans: (a)
- The correct option is (a) because lipids having only single bonds are called saturated fatty acids and lipids having one or more C = C double bonds are called unsaturated fatty acids.
- Palmitic acid has 16 carbon atoms including carboxyl carbon.
- Arachidonic acid has 20 carbon atoms including the carboxyl carbon.
- Lecithin is a phospholipid found in cell membrane.
- Glycerol has 3 carbons, each bearing a hydroxyl ( − OH) group.
2020
Q1: Identify the substances having glycosidic bond and peptide bond, respectively in their structure. (NEET 2020)
(a) Cellulose, lecithin
(b) Inulin, Insulin
(c) Chitin, cholesterol
(d) Glycerol, trypsin
Ans: (b)
Inulin is a mixture of linear fructose polymers with different chain length and a glucose molecule at each C2 end. Adjacent fructose units are linked through glycosidic bond. The inulin that is used for medicine is most commonly obtained by soaking chicory roots in hot water.
Insulin is a protein composed of 51 amino acids and acts as a hormone which is secreted by beta-cells of pancreas. Adjacent amino acids are attached through peptide bond.
Q2: Which one of the following is the most abundant protein in the animals? (NEET 2020)
(a) Lectin
(b) Insulin
(c) Haemoglobin
(d) Collagen
Ans: (d)
Collagen is the most abundant protein in animal world. Collagen is the major insoluble fibrous protein found in the extracellular matrix and in connective tissue. RuBisCO is the most abundant protein in the whole of the Biosphere.
Q3: Identify the basic amino acid from the following (NEET 2020)
(a) Lysine
(b) Valine
(c) Tyrosine
(d) Glutamic acid
Ans: (a)
Glutamic Acid - is an acidic amino acid.
Lysine - is a basic amino acid.
Valine - is an aliphatic amino acid.
Tyrosine - is an aromatic amino acid.
Q4: Match the following: (NEET 2020)
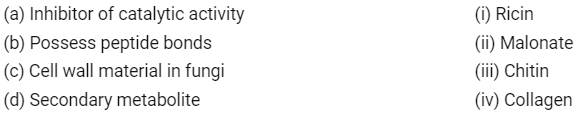
Choose the correct option from the following
(a) (A) → (ii), (B) → (iii), (C) → (i), (D) → (iv)
(b) (A) → (iii), (B) → (i), (C) → (iv), (D) → (ii)
(c) (A) → (ii), (B) → (iv), (C) → (iii), (D) → (i)
(d) (A) → (iii), (B) → (iv), (C) → (i), (D) → (ii)
Ans: (c)
Malonate is the competitive inhibitor of catalytic activity of succinic dehydrogenase, Collagen is proteinaceous in nature and possesses peptide bonds, Chitin is a homopolymer present in the cell wall of fungi and exoskeleton of arthropods, Abrin and Ricin are toxins, secondary metabolites.
2019
Q1: Concanavalin A is (NEET 2019)
(a) A pigment
(b) An alkaloid
(c) An essential oil
(d) A lectin
Ans: (d)
Concanavalin A is an example of lectin.
Q2: Consider the following statements.
(A) Coenzyme or metal ion that is tightly bound to enzyme protein is called prosthetic group.
(B) A complete catalytic active enzyme with its bound prosthetic group is called apoenzyme.
Select the correct option. (NEET 2019)
(a) (A) is false but (B) is true.
(b) Both (A) and (B) are true.
(c) (A) is true but (B) is false.
(d) Both (A) and (B) are false.
Ans: (c)
Coenzyme or metal ion that is tightly bound to enzyme protein is called prosthetic group while a complete catalytic active enzyme with its bound prosthetic group is called holoenzyme.
2018
Q1: The two functional groups characteristic of sugars are (NEET 2018)
(a) Hydroxyl and methyl
(b) Carbonyl and methyl
(c) Carbonyl and phosphate
(d) Carbonyl and hydroxyl
Ans: (d)
Sugar is a carbohydrate. These are polyhydroxy aldehyde, ketone or their derivatives, which means they have carbonyl and hydroxyl groups in its structure.
2017
Q1: Which of the following statements is correct with reference to enzymes? (NEET 2017)
(a) Holoenzyme = Apoenzyme + Coenzyme
(b) Coenzyme - Apoenzyme + Holoenzyme
(c) Holoenzyme = Coenzyme + Co-factor
(d) Apoenzyme = Holoenzyme + Coenzyme
Ans: (a)
Holoenzyme is the complete conjugate enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a cofactor. Cofactor may be organic or inorganic in nature. Organic cofactors are of two types-coenzyme and prosthetic group.
Q2: Which of the following are not polymeric? (NEET 2017)
(a) Proteins
(b) Polysaccharides
(c) Lipids
(d) Nucleic acids
Ans: (c)
– Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides
– Proteins are polymers of amino acids
– Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides
– Lipids are the tri-esters of fatty acids with glycerol.
2016
Q1: A non-proteinaceous enzyme is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Ribozyme
(c) Ligase
(d) Deoxyribonuclease
Ans: (b)
A ribozyme is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) enzyme that catalyses a chemical reaction in a similar way to that of a protein enzyme. These are found in ribosomes and are also called catalytic RNAs.
Q2: Which of the following is the least likely to be involved in stabilising the three-dimensional folding of most proteins?
(a) Hydrogen bonds
(b) Electrostatic interaction
(c) Hydrophobic interaction
(d) Ester bonds (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
Tertiary structure or three dimensional structure of protein is stabilised by several types of bonds-hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waal's interactions, covalent bonds and hydrophobic bonds.
Q3: Which of the following describes the given graph correctly? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)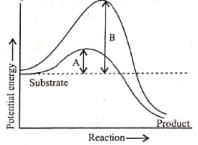
(a) Endothermic reaction with energy A in presence of enzyme and B in absence of enzyme.
(b) Exothermic reaction with energy A in presence of enzyme and B in absence of enzyme.
(c) Endothermic reaction with energy A in absence of enzyme and B in presence of enzyme.
(d) Exothermic reaction with energy A in absence of enzyme and B in presence of enzyme.
Ans: (b)
The graph shows the activation energies of catalyzed and uncatalyzed reations. A transition state is observed when the reactants are at the crest of the hump. At this state, they are ready to be converted to products. If the products are at a lower level than the reactants, the reaction is exothermic.
Q4: A typical fat molecule is made up of (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) One glycerol and one fatty acid molecule
(b) Three glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
(c) Three glycerol molecules and one fatty acid molecule
(d) One glycerol and three fatty acid molecules.
Ans: (d)
Neutral or true fats are triglycerides which are formed by esterification of three molecules of fatty acids with one molecule of trihydric alcohol, glycerol (glycerine or trihydroxy propane).
Q5: Which one of the following statements is wrong? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Uracil is a pyrimidine.
(b) Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid.
(c) Sucrose is a disaccharide.
(d) Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
Ans: (b)
Glycine (abbreviated as Gly or G) is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins, and indeed is the smallest possible (having a hydrogen substituent as its side-chain). The formula is NH2CH2COOH. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG of the genetic code.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biomolecules - Biology Class 11
| 1. What are the four major classes of biomolecules? |  |
| 2. What is the primary function of carbohydrates in living organisms? |  |
| 3. How are lipids different from other biomolecules? |  |
| 4. What is the role of proteins in living organisms? |  |
| 5. How do nucleic acids contribute to genetic information in cells? |  |






















