Modern Periodic Law & Modern Periodic Table | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Moseley's Periodic Table
- He studied (1909) the frequency of the X-ray produced by the bombardment of a strong beam of electrons on 'metal target.
- He found that the square root of the frequency of X-rays (
) is directly proportional to number of effective nuclear charge (z) of metal i.e. to atomic number and not to atomic mass of the atom of that metal.(as nuclear charge of metal atom is equal to atomic number)
i.e. () = a (z - b)
- Where 'a' is the proportionality constant and 'b' is a constant for all the lines in a given series of X-rays.
- Therefore, he, concluded that atomic number was a better fundamental property of an element than its atomic weight He suggested that the atomic number (z) instead of atomic weight should be basis of the classification of the elements.
Modern Periodic Law (Moseley's Periodic Law)
Physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic number . If the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic number, after a regular interval ,element with similar properties are repeated.
Periodicity
The repetition of the properties of elements after regular intervals when the elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic number is called periodicity.
Cause of Periodicity:
The periodic repetition of the properties of the elements is due to the recurrence of similar valence shell electronic configuration after certain regular intervals. For example, alkali metals have same electronic configuration ns1, therefore, have similar properties.
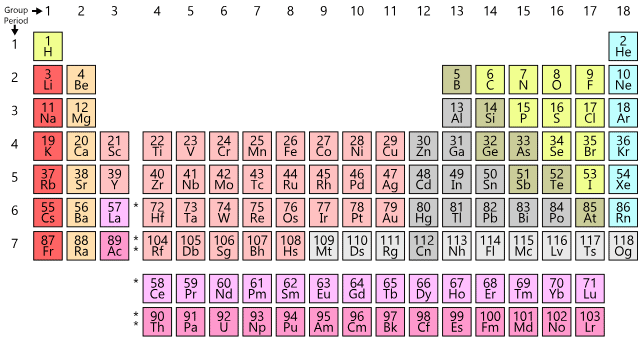
The long form of periodic table is the contribution of Range, Werner, Bohr and Bury
This table is also referred to as Bohr's table since it follows Bohr's scheme of the arrangements of elements into four types based on electronic configuration of elements
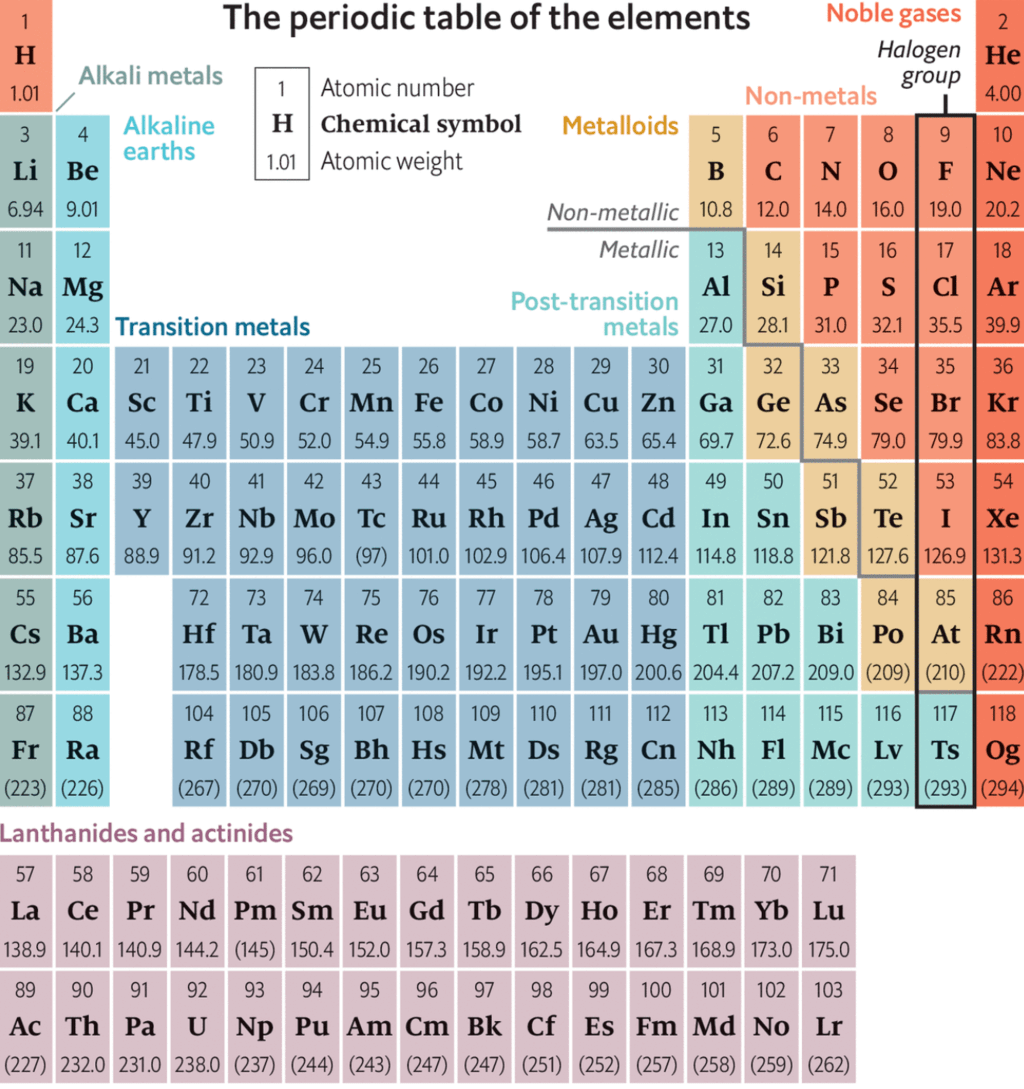
The modern periodic table consists of horizontal rows (periods) and vertical column (groups)
Periods:
There are seven periods numbered as 1, 2,3,4,5,6 and 7.
(i) Each period consists of a series of elements having same valence shell.
(ii) Each period corresponds to a particular principal quantum number of the valence shell present in it.
(iii) Each period starts with an alkali metal having outermost electronic configuration ns1.
(iv) Each period ends with a noble gas with outermost electronic configuration ns2np6 except helium having outermost electronic configuration 1s2.
(v) Each period starts with the filling of new energy level.
(vi) The number of elements in each period is twice the number of atomic orbitals available in energy level that is being filled. To illustrate
1st period shortest period having only two elements. Filling of electron takes place in the first energy shell, for which,
n = 1, l. = 0 (s- subshell) and m = O.
Only one orbital (1s) is available and thus it contains only two elements. 3rd period short period having only eight elements. Filling of electrons takes place in the third energy level. For which,
n = 3, l = 0, 1,2 and no. of orbitals m = 0, 3, 5
no. of orbitals 1 3 5
(3s) (3p) (3d)
Total no. of orbitals 9
But the energy of 3d orbitals are higher than 4s orbitals. Therefore, four orbitals (one 3s and three 3p orbitals) corresponding to n = 3 are filled before filling in 4s orbital (next energy elevel). Hence 3rd period contains eight elements not eighteen elements.
Groups:
There are eighteen groups numbered as 1,2,3,4,5, ................ 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18.
Group consists of a series of elements having similar valence shell electronic configuration.
Periodic Properties
Helium belongs to s-block because last entered electron goes in s-block.
- Iridium is the most dense element followed by Osmium.
- Note:
- (1) Last entered electron (According to Aufbau's Principle) decides the block of the element.
- (2). The valence shell determines the period number.
General Properties of Periodic table
(1) There are Seventeen non-metals (including hydrogen) in periodic table.
(2) Five non - metals are solid C, P, S, Se, I
(3) One non - metal is liquid i.e. Br
(4) Eleven non-metals are gaseous.
(5) Six gases are monoatomic (noble gases) i.e. He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
(6) Five gases are diatomic, they are H, F, N, O, Cl
(7) There are eight metalloids in periodic table like, B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At
(8) Five elements are liquid at room temperature namely Cs, Fr, Ga, Hg, and Br,
(9) s - Block and p - Block together are called Representative elements.
(10) Five elements are radioactive amongst representative elements. They are Po, At, Rn, Fr and Ra
(11) There are seven periods in long - form of periodic table.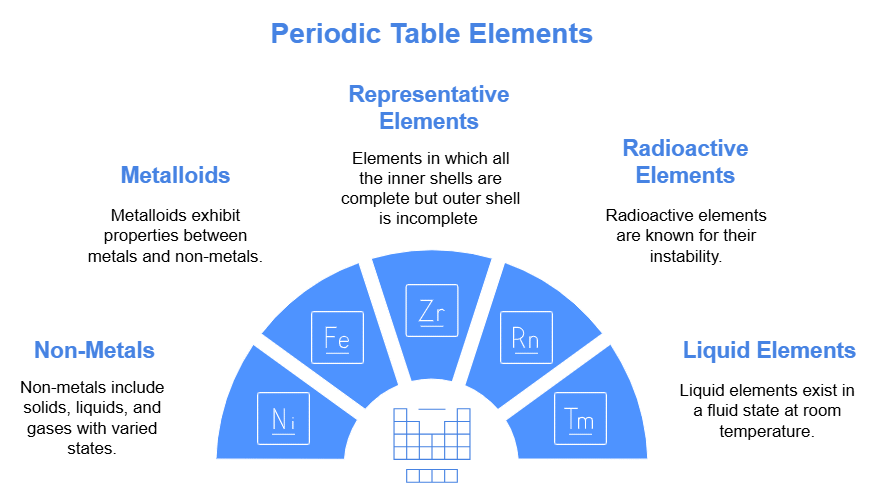
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Modern Periodic Law & Modern Periodic Table - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is Moseley's Periodic Law? |  |
| 2. How does Moseley's Periodic Law improve upon Mendeleev's Periodic Table? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of periodic properties that can be explained by Moseley's Periodic Law? |  |
| 4. How does Moseley's Periodic Law help predict the properties of unknown elements? |  |
| 5. What impact did Moseley's Periodic Law have on the development of the modern periodic table? |  |






















