Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
Q1: With the help of an example, explain the process of hydrogenation.
Mention the essential conditions for the reaction and state the change in physical property with the formation of the product.
Ans: Process of hydrogenation: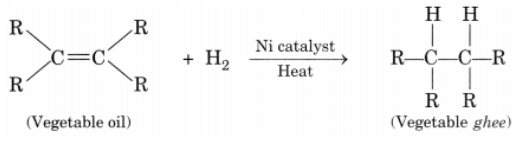 The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation.
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation.
Essential conditions for the reaction are:
- Presence of an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- Presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or palladium.
Changes observed:
- Change observed in the physical property is the change of unsaturated compound from the liquid state to saturated compound in the solid state.
- The boiling or melting points of a product is increased.
Q2: Name the oxidising agent used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid. Distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid on the basis of (i) litmus test, (ii) reaction with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Ans: Alkaline KMnO4 or acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) are used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Ethanol:
- Ethanol has no effect on red or blue litmus solution.
- No gas evolved when ethanol is treated with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Ethanoic acid:
- Ethanoic acid turns blue litmus solution red.
- Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate to evolve carbon dioxide along with the formation of salt and water.
- CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Q3: List four differences between soaps and detergents.
Ans: Soaps:
- Soaps are sodium salts of higher fatty acids.
- Biodegradable.
- Soaps cannot be used in acidic medium.
- Soaps cannot be used in hard water.
Synthetic Detergents:
- Detergents are sodium alkyl sulphates or sodium alkyl benzene sulphonates with alkyl group having more than ten carbon atoms.
- Non-biodegradable.
- They can be used in acidic medium.
- Detergents can be used even in hard water.
Q4: Give any four uses of ethanoic acid.
Ans:
- Ethanoic acid is used in making synthetic vinegar.
- Ethanoic acid is used as a reagent in chemistry laboratory.
- Ethanoic acid is used for making dyes, perfumes and esters.
- Ehanoic acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex and casein from milk.
Q5: What are substitution reactions? Justify your answer with a suitable example.
Ans: A chemical reaction in which atom(s) or group of atoms of an organic compound is/are replaced by other atom(s) or group of atoms without any change in the rest of the molecule is called a substitution reaction.
For example,
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
In this chemical reaction Cl atom substitutes one hydrogen atom from methane.
Q6: List two main points of difference between organic and inorganic compound.
Ans: Organic compounds:
- They are made up of few elements (C, H, O, N, S) through covalent bonds.
- They are combustible.
Inorganic compounds:
- They are made up of all the known elements, which involve ionic bond.
- They are generally non-combustible.
Q7: Give two uses each of methyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol.
Ans: Uses of ethyl alcohol:
- It is used in the manufacture of dyes, perfumes, antiseptics, etc.
- It is used in alcoholic drinks.
Uses of methyl alcohol:
- It is used as a solvent
- It is used as an antifreeze
Q8: Ethane, Ethene, Ethanoic acid, Ethyne, Ethanol
From the box given above, name:
(i) The compound with —OH as a part of its structure.
(ii) The compound with —COOH as a part of its structure.
(iii) Gas used in welding.
(iv) Homologue of the homologous series with general formula CnH2n+2.
Ans: (i) Ethanol
(ii) Ethanoic acid
(iii) Ethyne
(iv) Ethane
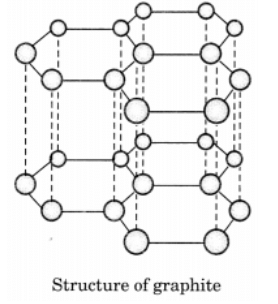
Q9: Draw the structures of diamond and graphite.
Ans: In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three dimensional structure.
In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. One of these bonds is a double bond.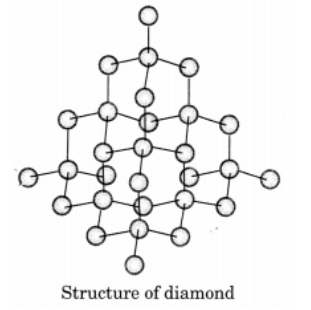
Q10: List the common physical properties of carbon compounds.
Ans:
- They have covalent bonds between their atoms therefore they do not form ions. So they are poor conductors of electric current.
- These compounds have low melting and low boiling points.
- They are generally insoluble in water but soluble in the organic solvents like ether, carbon- tetrachloride, etc.
Q11: Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Ans: Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons in their valence shell, it needs to gain or lose 4 electrons to attain the noble gas configuration.
(i) It could gain four electrons forming C4- anion. But it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
(ii) It could lose four electrons forming C4+ cation. But it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons from its outermost shell.
Therefore, carbon shares its valence electrons to complete its octet with other atoms to form covalent bonds.
Q12: Give the general formula of alkanes. Write the name, structural formula and physical state of the compound containing:
(i) 3-carbon atoms
(ii) 8-carbon atoms.
Ans: (a) General formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2
n = 1, 2, 3…
(i) Propane, CH3—CH2—CH3
or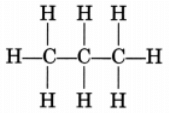
Propane is a gas.
(ii) CH3—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH3
or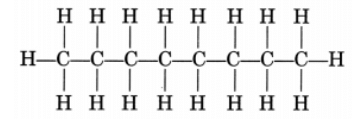 Octane is a liquid
Octane is a liquid
Q13: Draw the electron dot structure of O2 and N2 molecules.
Ans: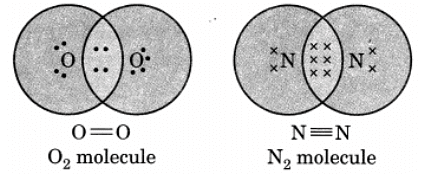
Q14: Which of the following hydrocarbons can undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C4H10, C3H6, C3H4, CH4, C2H2, C4H8
Ans: C3H6, C3H4, C2H2 and C4H8 because these compounds are unsaturated organic compounds and hence can undergo addition reactions.
Q15: Name the functional groups present in the following compounds:
(a) CH3 CO CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
(b) CH3 CH2 CH2 COOH
(c) CH3 CH2 OH
Ans:
(a) Ketone
(b) Carboxylic acid
(c) Aldehyde
Q16: Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula.
Ans: Ethyne, C2H2
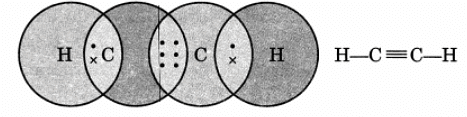
Q17: Write the general IUPAC names of alcohol, carboxylic acid, aldehyde and ketone.
Ans: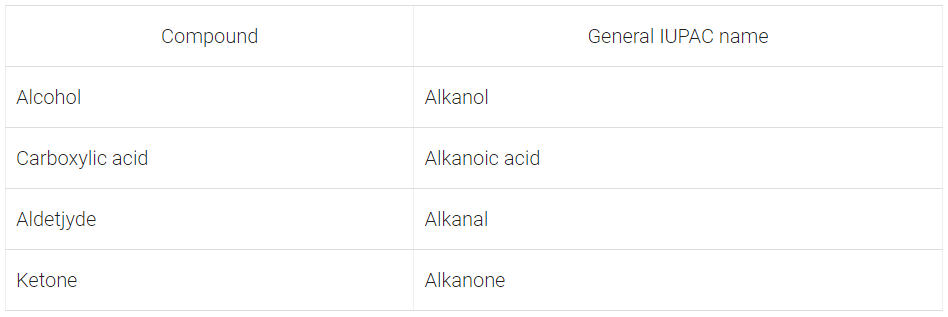
Q18: Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologous series of hydrocarbons: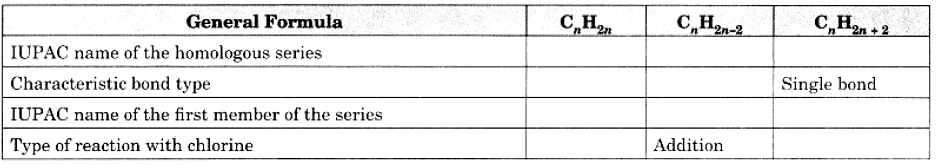 Ans:
Ans: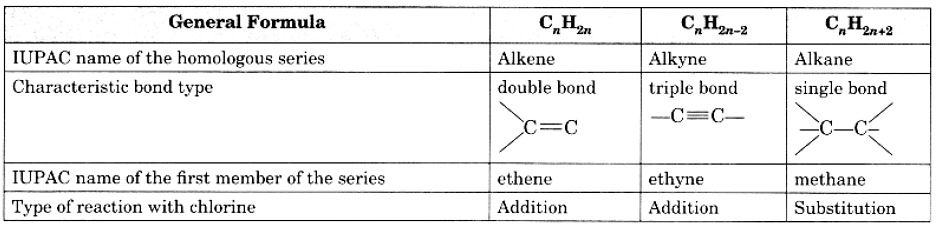
Q19: The list of some organic compounds is given below:
Ethanol, ethane, methanol, methane, ethyne, ethene
From the above list, name a compound:
(i) formed by the dehydration of ethanol by conc. H2SO4.
(ii) which will give red precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride solutions,
(iii) which forms ethanoic acid on oxidation with KMnO4.
(iv ) which has vapour density 14 and decolourises pink alkaline potassium permanganate.
(v) which forms chloroform on halogenation in the presence of sunlight.
(vi) which decolourises bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride.
Ans: (i) Ethene
(ii) Ethyne
(iii) Ethanol
(iv) Ethene
(v) Methane
(vi) Ethene
Q20: What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrow’s in the given chemical reactions?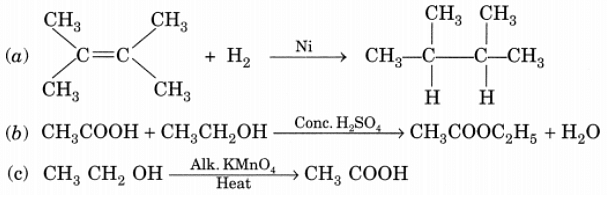 Ans:
Ans:
(a) Ni acts as a catalyst.
(b) Concentrated H2SO4 acts as a catalyst.
(c) Alkaline KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent.
|
666 docs
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
| 1. What is carbon and its compounds? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of carbon compounds? |  |
| 3. How do carbon compounds play a role in living organisms? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of carbon compounds? |  |
| 5. How is carbon dioxide related to carbon compounds? |  |





















