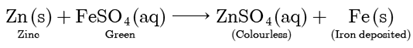Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Assertion and Reason Questions - Metals and Non-metals
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Question 1:
Assertion: When zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate, no change is observed.
Reason: Zinc is less reactive than iron
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true. Both Assertion and Reason are false. Zinc being more reactive than iron displaces iron from iron (II) sulphate solution.
Thus, the green colour of the solution fades and iron metal gets deposited.
Question 2:
Assertion: Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc.
Reason: Zinc is more reactive than tin.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A). Food cans are coated with tin not with zinc because zinc is more reactice than tin, it can react with organic acids present in food.
Tin coated food cans
Question 3:
Assertion: Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
Reason: Platinum, gold and silver are least reactive metals.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion(A). Platinum, gold and silver are highly malleable lustraus and least reactive, i.e. noble metals, so they are not corroded by air and water easily.
Question 4:
Assertion: Iron is found in the free state n nature.
Reason: Iron a highly reactive element.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Iron is found in free state in nature but is mildly reactive towards atmospheric oxidation.
Question 5:
Assertion: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide which is an acidic oxide.
Reason: Non-metals form acidic oxides.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true explanation of assertion (A). Carbon being a non-metal form acidic oxides, i.e., their aqueous solution turns blue litmus solution red.
Question 6:
Assertion: Coke and flux are used in smelting.
Reason: The phenomenon in which ore is mixed with suitable flux and coke is heated to fusion is known as smelting.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A). Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore in order to extract a base metal. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals.
Question 7:
Assertion: Leaching is a process of reduction.
Reason: Leaching involves treatment of the ore with a suitable reagent so as to make it solube while impurities remains insoluble.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Leaching is the process of concentration of ores in which metal is made soluble in a solvent while the impurities remain insoluble and get separated out. It does not involve any redox reaction.
Question 8:
Assertion: Lead, tin and bismuth are purified by liquation method.
Reason: Lead, tin and bismuth have low m.p. as compared to impurities.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Liquation process is used when the impurity is less fusible than the metal itself. lead, tin and bismuth have low m.p. as compared to impurities.Hence, lead, tin and bismuth are purified by liquation method.
Question 9:
Assertion: Leaching is a process of reduction.
Reason: Leaching involves treatment of the ore with a suitable reagent so as to make it soluble while impurities remains insoluble.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true. Leaching is a process where ore is soluble and impurities are insoluble, widely used extractive metallurgy technique which converts metals into soluble salts in aqueous media.
Question 10:
Assertion: Levigation is used for the separation of oxide ores from impurities.
Reason: Ore particles are removed by washing in a current of water.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false. Levigation method is commonly used for oxide ores such as haematite, tin stone and native ores of Au, Ag, etc.
|
80 videos|662 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Assertion and Reason Questions - Metals and Non-metals
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of metals? |  |
| 4. What are the physical properties of non-metals? |  |
| 5. How do metals and non-metals react with acids? |  |