UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation > Mindmap: India After Independence
Mindmap: India After Independence | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation PDF Download
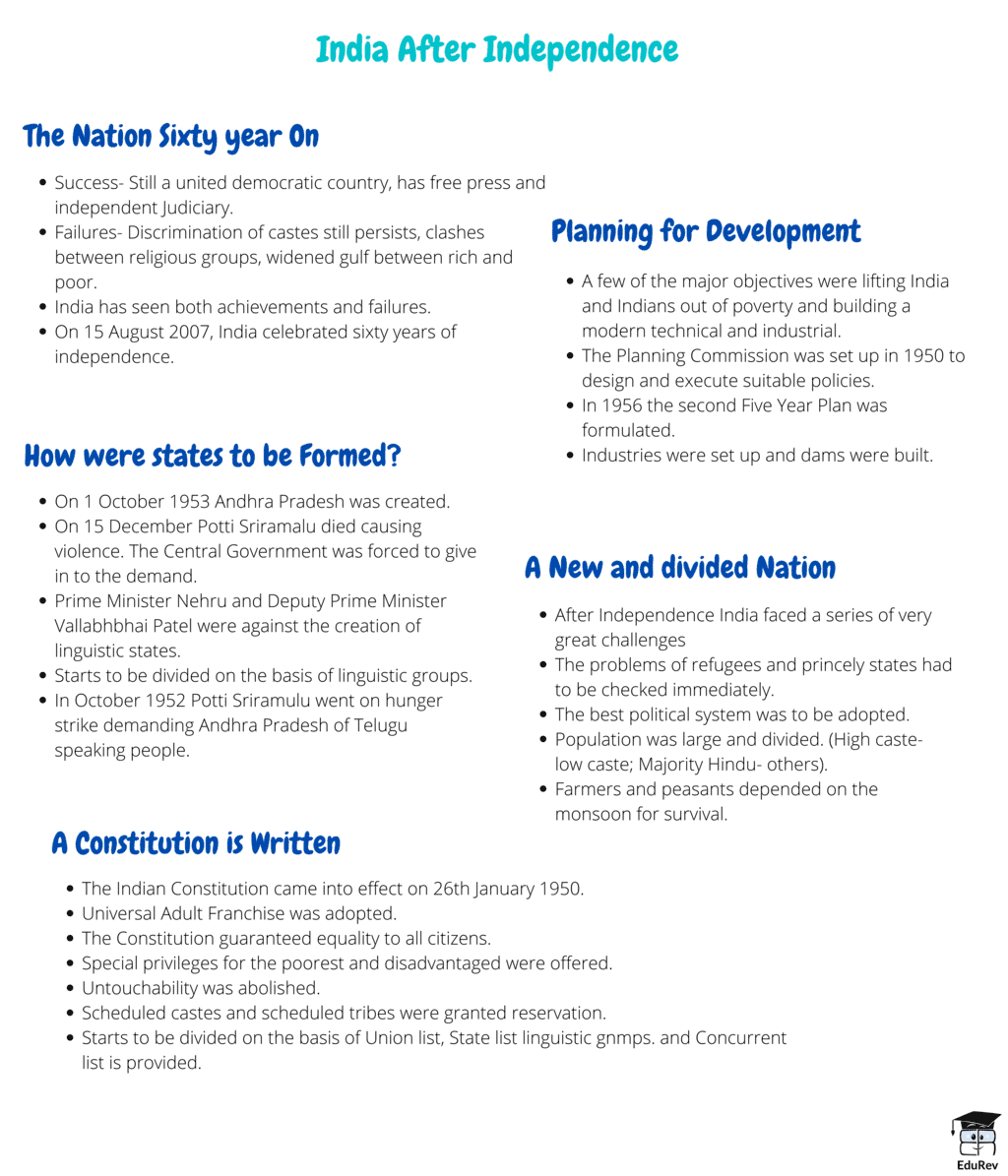
The document Mindmap: India After Independence | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation is a part of the UPSC Course Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Mindmap: India After Independence - Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation
| 1. How did India achieve independence from British rule? |  |
Ans. India achieved independence from British rule through a long and non-violent struggle led by Mahatma Gandhi and various other freedom fighters. The Indian National Congress played a crucial role in organizing protests, civil disobedience movements, and mass movements that ultimately led to the British granting independence to India on August 15, 1947.
| 2. What were the major challenges faced by India after independence? |  |
Ans. After independence, India faced several major challenges. These included the partition of the country leading to communal violence, mass migration, and the need to establish two separate nations, India and Pakistan. Other challenges included widespread poverty, illiteracy, inadequate infrastructure, religious and linguistic diversity, and the task of building a democratic nation from scratch.
| 3. How did India's economy evolve after independence? |  |
Ans. After independence, India adopted a mixed economy model, combining elements of socialism and capitalism. The government focused on industrialization, agricultural reforms, and the establishment of public sector industries. The Five-Year Plans were introduced to prioritize economic growth and development. However, the economy initially faced challenges such as low productivity, a large informal sector, and limited foreign investment.
| 4. What were the major political developments in India after independence? |  |
Ans. After independence, India adopted a parliamentary system of democracy with a federal structure. The Constitution of India was drafted and adopted in 1950, providing a framework for governance. The country witnessed several political developments, including the formation of political parties, the introduction of reservation policies for marginalized communities, the abolition of princely states, and the implementation of affirmative action programs.
| 5. How did India address social issues and promote social equality after independence? |  |
Ans. India made significant efforts to address social issues and promote social equality after independence. The government implemented various policies and programs to uplift marginalized communities, such as Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. Affirmative action policies, such as reservation in education and employment, were introduced. Initiatives were taken to eradicate social evils like untouchability and child marriage, and promote gender equality through legal reforms, education, and awareness campaigns.
Related Searches


















