NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Excretory Products & their Elimination | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which of the following diagrams is correct with regard to the proximal (P) and distal (D) tubule of the Nephron.
(a) 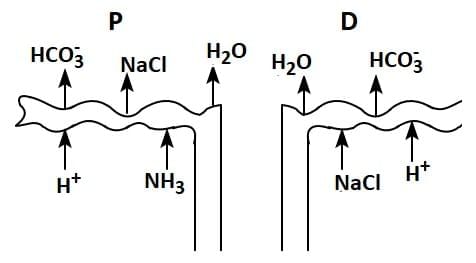
(b) 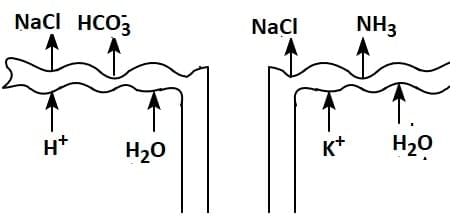
(c) 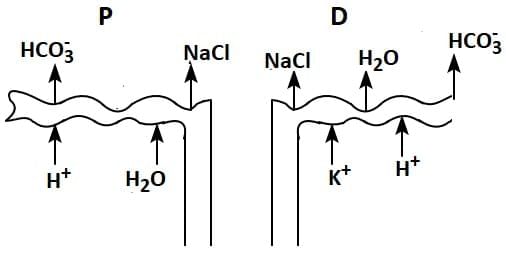
(d) 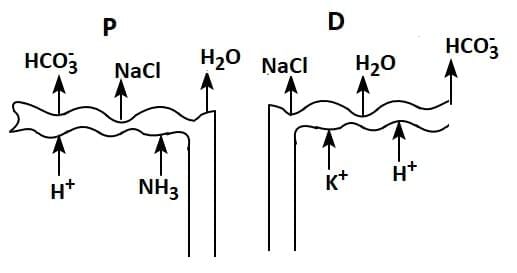
Ans: (d)
- The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is responsible for filtering blood, reabsorbing essential nutrients, and excreting waste as urine.
- The nephron consists of various parts:
- Bowman's capsule
- Proximal tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal tubule.
- Collecting duct.
- The proximal tubule (P) is closer to Bowman's capsule and is primarily involved in reabsorbing water, ions, glucose, and amino acids.
- The distal tubule (D) is farther along the nephron and plays a role in the selective reabsorption of ions and water, influenced by hormones like aldosterone and ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
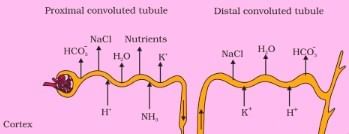
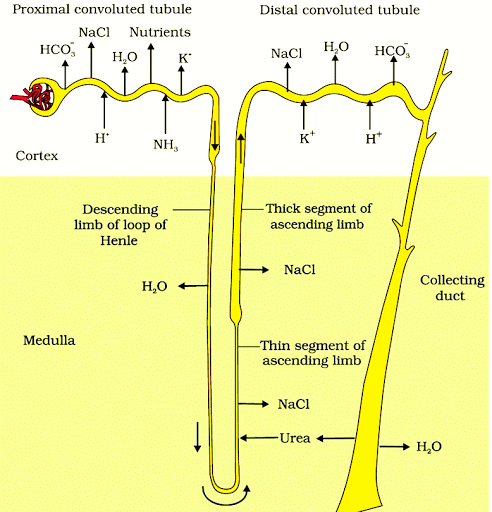
PCT is lined by simple cuboidal brush border epithelium which increases the surface area for reabsorption.
- Nearly all of the essential nutrients, and 70-80 per cent of electrolytes and water are reabsorbed by this segment.
- PCT also helps to maintain the pH and ionic balance of the body fluids by selective secretion of hydrogen ions and ammonia into the filtrate and by absorption of HCO3 – from it.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): Conditional reabsorption of Na+ and water takes place in this segment. DCT is also capable of reabsorption of HCO3 – and selective secretion of hydrogen and potassium ions and NH3 to maintain the pH and sodium-potassium balance in blood.
2024
Q1: Given below are two statements :
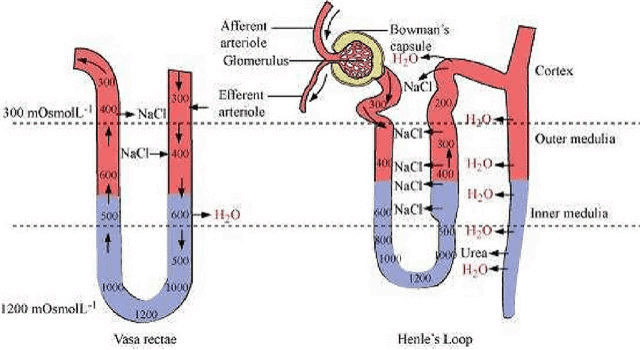
Statement I : In the nephron, the descending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water and permeable to electrolytes.
Statement II : The proximal convoluted tubule is lined by simple columnar brush border epithelium and increases the surface area for reabsorption.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the option given below :
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: (b)
Correct answer is option (B) because Statement I is false as the descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water and almost impermeable to electrolytes.
Statement II is false as proximal convoluted tubule is lined by simple cuboidal brush border epithelium which increases the surface area for reabsorption.
Q2: Choose the correct statement given below regarding juxta medullary nephron.
(a) Juxta medullary nephrons are located in the columns of Bertini.
(b) Renal corpuscle of juxta medullary nephron lies in the outer portion of the renal medulla.
(c) Loop of Henle of juxta medullary nephron runs deep into medulla.
(d) Juxta medullary nephrons outnumber the cortical nephrons.
Ans: (c)
The juxta medullary nephrons are one of the two types of nephrons found in the kidneys, specifically in mammals, including humans. These nephrons have distinctive characteristics and play crucial roles in the process of urine concentration, which is essential for water conservation and the regulation of blood pressure.
Q3: Which part of the human nephron is impermeable to water? (NEET 2024)
(a) Proximal convoluted tubule
(b) Distal convoluted tubule
(c) Ascending limb of loop of Henle
(d) Descending limb of loop of Henle
Ans: (c)
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water. In this part of the nephron, sodium and chloride ions are actively transported out of the filtrate into the surrounding interstitial fluid, but water cannot follow due to the lack of aquaporin channels. This helps in creating a high osmotic gradient in the kidney's medulla, which is important for the kidney's ability to concentrate urine.
In contrast:
- The proximal convoluted tubule is permeable to water and reabsorbs a significant amount of water along with solutes.
- The distal convoluted tubule is selectively permeable to water, especially under the influence of hormones like antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to water, which allows water to be reabsorbed as the filtrate moves down the loop into the increasingly hypertonic medulla.
Thus, the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is the part of the nephron that is impermeable to water.
Q4: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). (NEET 2024)
Assertion (A): Juxta Glomerular Apparatus (JGA) plays an important role in regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Reason (R): A fall in GFR can activate the J.G. cells to release renin which can stimulate the glomerular blood flow and thereby bringing the GFR to normal level.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is True but (R) is False.
(d) (A) is False but (R) is True.
Ans: (a)
- Assertion (A): Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) plays an important role in the regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This statement is true. The JGA, located where the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerular afferent arteriole meet, monitors the blood pressure and the sodium concentration in the filtrate. It helps regulate the GFR through various mechanisms.
- Reason (R): A fall in GFR can activate the JGA cells to release renin, which in turn stimulates the glomerular blood flow, thereby bringing the GFR back to normal. This statement is also true. When GFR decreases (due to a drop in blood pressure or reduced blood flow), the juxtaglomerular (JG) cells release renin, which leads to the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Renin ultimately causes vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole, which increases glomerular blood pressure and restores the GFR to normal levels.
Since both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) provides a correct explanation for (A), the correct answer is A.
Q5: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Concentrated urine is formed due to counter current mechanism in nephron.
Statement II: Counter current mechanism helps to maintain osmotic gradient in the medullary interstitium.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
- Statement I: Concentrated urine is formed due to countercurrent mechanism in nephron: This statement is correct. The countercurrent mechanism in the nephron, especially in the loop of Henle, plays a crucial role in concentrating urine. The arrangement of the ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle, along with the countercurrent exchange of ions and water, creates a high osmotic gradient in the kidney medulla, which allows the kidneys to produce concentrated urine.
- Statement II: Countercurrent mechanism helps to maintain osmotic gradient in the medullary interstitium: This statement is also correct. The countercurrent multiplier system, especially in the loop of Henle, helps maintain an osmotic gradient in the medullary interstitium. This gradient is critical for water reabsorption in the collecting ducts, contributing to the formation of concentrated urine.
Thus, both Statement I and Statement II are correct, making the answer (C).
2023
Q1: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R. (NEET 2023)
Assertion A: Nephrons are of two types: Cortical and juxta medullary, based on their relative position in the cortex and medulla.
Reason R: Juxta medullary nephrons have a short loop of Henle whereas, cortical nephrons have a longer loop of Henle.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (c)
- Assertion A is correct. In the kidney, nephrons, the functional units responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes, are indeed of two types: cortical and juxta-medullary. These types are classified based on their location within the kidney; cortical nephrons are primarily located in the cortex, while juxta-medullary nephrons are located near the junction between the cortex and medulla.
- However, Reason R is incorrect. The assertion that juxta-medullary nephrons have short loops of Henle, while cortical nephrons have longer loops of Henle is false. In fact, it's the opposite. Juxta-medullary nephrons have longer loops of Henle which extend deep into the medulla. This allows them to concentrate urine more effectively than cortical nephrons, whose loops of Henle are shorter and do not extend as deep into the medulla.
Q2: Which of the following statements are correct? (NEET 2023)
A. An excessive loss of body fluid from the body switches off osmoreceptors.
B. ADH facilitates water reabsorption to prevent diuresis.
C. ANF causes vasodilation.
D. ADH causes an increase in blood pressure.
E. ADH is responsible for the decrease in GFR.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B, C and D only
(c) A, B and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer because statements B, C and D are true statements. ADH facilitates water reabsorption from DCT of nephron to prevent diuresis, which causes increase in blood pressure. ANF which is secreted by the heart is a vasodilator.
Q3: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R) (NEET 2023)
Assertion (A): Ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water and allows transport of electrolytes actively or passively.
Reason (R): Dilution of filtrate takes place due to efflux of electrolytes in the medullary fluid.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) is True, (R) is False
(b) (A) is False, (R) is True
(c) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(d) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans: (d)
- Assertion (A): Ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water and allows transport of electrolytes actively or passively. This statement is true. The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water, but it actively transports sodium, potassium, and chloride ions out of the filtrate into the surrounding interstitial fluid, creating an osmotic gradient in the medulla.
- Reason (R): Dilution of filtrate takes place due to efflux of electrolytes in the medullary fluid. This statement is true. The efflux of electrolytes from the ascending limb into the medullary interstitium helps dilute the filtrate by reducing its osmolarity. This is important in the process of urine concentration and dilution.
However, Reason (R) does not fully explain Assertion (A). While the efflux of electrolytes helps in the dilution of the filtrate, the assertion specifically refers to the impermeability of water in the ascending limb, which is not directly explained by the dilution caused by electrolyte efflux.
Thus, (A) and (R) are both true, but (R) is not the correct explanation for (A), making the correct answer (D).
Q4: Arrange the events of Renin-Angiotensin mechanism in correct sequence: (NEET 2023)
(A) Activation of JG cells and release of renin
(B) Angiotensin II activated release of aldosterone
(C) Fall in glomerular blood pressure
(D) Reabsorption of Na+ and water from distal convoluted tubule
(E) Angiotensinogen is converted to Angiotensin I and then to Angiotensin II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C), (A), (E), (B), (D)
(b) (A), (D), (E), (C), (B)
(c) (A), (D), (C), (B), (E)
(d) (B), (A), (E), (D), (C)
Ans: (a)
The Renin-Angiotensin mechanism is a critical regulatory system for maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance. The sequence of events is as follows:
- (C) Fall in glomerular blood pressure: A decrease in blood pressure or blood volume is detected in the kidneys, leading to a drop in glomerular blood pressure.
- (A) Activation of JG cells and release of renin: In response to the low blood pressure, the juxtaglomerular (JG) cells of the kidneys are activated and release renin into the bloodstream.
- (E) Angiotensinogen is converted to Angiotensin I and then to Angiotensin II: Renin acts on angiotensinogen, a protein produced by the liver, converting it into angiotensin I, which is then converted into angiotensin II by the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), mostly found in the lungs.
- (B) Angiotensin II activated release of aldosterone: Angiotensin II stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
- (D) Reabsorption of Na+ and water from distal convoluted tubule: Aldosterone promotes the reabsorption of sodium and water from the distal convoluted tubule, which helps restore blood volume and pressure.
Thus, the correct sequence of events is: (C), (A), (E), (B), (D).
2022
Q1: Select the correct statements. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Angiotensin II activates the cortex of adrenal gland to release aldosterone.
(b) Aldosterone leads to increase in blood pressure.
(c) ANF acts as a check on renin-angiotensin mechanism.
(d) ADH causes vasodilation.
(e) Vasopressin is released from adenohypophysis.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) (a), (b) and (c) only
(b) (a), (b) and (e) only
(c) (c), (d) and (e) only
(d) (b), (c) and (d) only
Ans: (a)
The correct statements are (A), (B), and (C) only. (D) and (E) are incorrect.
A. Angiotensin II is a hormone that s produced as part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. It acts on the cortex of the adrenal gland to stimulate the release of aldosterone.
B. Aldosterone is a hormone that plays a key role in regulating sodium and water balance in the body. By increasing the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidneys, it leads to an increase in blood volume and, consequently, an increase in blood pressure.
C. ANF (Atrial Natriuretic Peptide) is a hormone that is released by the heart in response to increased blood volume and pressure. It acts as a check on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by promoting vasodilation and the excretion of sodium and water by the kidneys, thus reducing blood volume and blood pressure.
D. ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone), also known as vasopressin, actually causes vasoconstriction. It acts on blood vessels to constrict them, which helps to increase blood pressure.
E. Vasopressin, also known as ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone), is released from the neurohypophysis, which is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The adenohypophysis (anterior lobe) of the pituitary gland is responsible for releasing various tropic hormones, but not vasopressin.
Q2: Nitrogenous waste is excreted in the form of pellet or paste by: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Salamandra
(b) Hippocampus
(c) Pavo
(d) Ornithorlnychus
Ans: (c) Pavo
- Option (c) is the correct answer because birds (Pavo) excrete nitrogenous wastes as uric acid in the form of pellet or paste with minimum loss of water.
- Option (a) and (b) are incorrect because many bony fishes (like Hippocampus) and aquatic amphibians (like Salamandra) are ammonotelic in nature.
- Option (d) is incorrect because mammals (like Ornithorhynchus) mainly excrete urea and are called ureotelic animals.
2020
Q1: Presence of which of the following conditions in urine are indicative of Diabetes Mellitus? (NEET 2020)
(a) Ketonuria and Glycosuria
(b) Renal calculi and Hyperglycaemia
(c) Uremia and Ketonuria
(d) Uremia and Renal Calculi
Ans: (a) Ketonuria and Glycosuria
Presence of Ketone bodies in urine (Ketonuria) and presence of glucose in urine (Glycosuria) are indicative of Diabetes mellitus.
Q2: Which of the following would help in the prevention of diuresis? (NEET 2020)
(a) Atrial natriuretic factor causes vasoconstriction
(b) Decrease in the secretion of renin by JG cells
(c) More water reabsorption due to under-secretion of ADH
(d) Reabsorption of Na+ and water from renal tubules due to aldosterone
Ans: (d)
Adrenal cortex secretes mineralocorticoids like aldosterone which increase the reabsorption of Na+ and water from renal tubule that prevent diuresis. Diuresis is a condition in which the kidneys filter too much bodily fluid.
2019
Q1: Use of an artificial kidney during hemodialysis may result in
(A) Nitrogenous waste build-up in the body
(B) Non-elimination of excess potassium ions
(C) Reduced absorption of calcium ions from the gastrointestinal tract
(D) Reduced RBC production
Which of the following options is the most appropriate? (NEET 2019)
(a) (A) and (D) are correct.
(b) (A) and (B) are correct.
(c) (B) and (C) are correct.
(d) (C) and (D) are correct.
Ans: (d)
- Kidney produces erythropoietin which helps in RBC production
- Kidney also secretes calcitriol which allows absorption of calcium ion from gastrointestinal tract.
Q2: Which of the following factors is responsible for the formation of concentrated urine? (NEET 2019)
(a) Hydrostatic pressure during glomerular filtration.
(b) Low levels of antidiuretic hormone.
(c) Maintaining hyperosmolarity towards the medullary interstitium in the kidneys.
(d) Secretion of erythropoietin by Juxtaglomerular complex.
Ans: (c)
Maintaining hyperosmolarity towards inner medullary interstitium in the kidneys for the formation of concentrated urine.
2018
Q1: Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below. (NEET 2018)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Glycosuria | (i) Accumulation of uric acid in joints |
| B. Gout | (ii) Mass of crystallised salts within the kidney |
| C. Renal calculi | (iii) Inflammation in glomeruli |
| D. Glomerular nephritis | (iv) Presence of glucose in urine |
| A | B | C | D | |
| (a) | (iii) | (ii) | (iv) | (i) |
| (b) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
| (c) | (ii) | (iii) | (i) | (iv) |
| (d) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
Ans: (d)
- Glycosuria means there is sugar glucose in the urine, which is often seen in people with diabetes.
- Gout is a painful condition caused by the buildup of uric acid in the joints.
- Renal calculi are masses of crystallized salts that form in the kidney.
- Glomerular nephritis is when the glomerulus (a part of the kidney that helps filter blood) becomes inflamed.
Q2: Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below. (NEET 2018)
| Column I (Function) | Column II (Part of the excretory system) |
| A. Ultrafiltration | (i) Henle's loop |
| B. Concentration of urine | (ii) Ureter |
| C. Transport of urine | (iii) Urinary bladder |
| D. Storage of urine | (iv) Malpighian corpuscle |
| (v) Proximal convoluted tubule |
| A | B | C | D | |
| (a) | (iv) | (v) | (ii) | (iii) |
| (b) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
| (c) | (v) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| (d) | (v) | (iv) | (i) | (iii) |
Ans: (b)
- Ultrafiltration happens in the kidneys when blood is filtered to form urine in a part called Bowman's capsule, also known as the Malpighian corpuscle.
- The function of Henle's loop is to maintain the concentration of urine by reabsorbing water and sodium chloride from the urine.
- Urine is transported from the kidney to the bladder through a duct called the ureter. The bladder stores the urine until it is time for the body to release it through urination.
2017
Q1: A decrease in blood pressure/volume will not cause the release of (NEET 2017)
(a) Atrial natriuretic factor
(b) Aldosterone
(c) ADH
(d) Renin.
Ans: (a)
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is responsible for lowering of blood pressure and volume. The walls of the atria of the heart release ANF in response to an increase in blood volume and pressure. It opposes regulation by RAAS. It inhibits release of renin from JGA thereby inhibiting NaCl reabsorption by the collecting duct and reduces aldosterone release from adrenal gland.
Q2: Which of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2017)
(a) The descending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water.
(b) The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to water.
(c) The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to electrolytes.
(d) The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water.
Ans: (d)
Descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water but impermeable to electrolytes whereas ascending limb is impermeable to water but permeable to electrolytes.
2016
Q1: The part of the nephron involved in the active reabsorption of sodium is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Distal convoluted tubule
(b) Proximal convoluted tubule
(c) Bowman’s capsule
(d) Descending limb of Henle’s loop.
Ans: (b)
- From the Bowman’s capsule, a glomerular filtrate enters the proximal convoluted tubule. Absorption of selected materials takes place from the filtrate into the blood of the peritubular capillaries or vasa recta. It is termed the tubular reabsorption. Reabsorption involves both passive and active transport across the tubular epithelium.
- About 65 per cent of the glomerular filtrate is normally reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule before reaching the loop of Henle. Glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, sodium, potassium, chlorides, phosphates, bicarbonates, much of water and some urea from the filtrate are absorbed. Sodium and potassium are reabsorbed by primary active transport.
2015
Q1: Human urine is usually acidic because: (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015)
(a) Excreted plasma proteins are acidic
(b) Potassium and sodium exchange generates acidity
(c) Hydrogen ions are actively secreted into the filtrate.
(d) The sodium transporter exchanges one hydrogen ion for each sodium ion, in peritubular capillaries.
Ans: (c)
Urine has acidic nature because hydrogen ions(H+) are components of an acid which are secreted into the filtrate.
Q2: Which of the following does not favour the formation of large quantities of dilute urine? (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Caffeine
(b) Renin
(c) Atrial-natriuretic factor
(d) Alcohol
Ans: (b)
Angiotensinogen is an α-globulin protein produced by liver. Renin serves as an enzyme in the conversion of the plasma protein angiotensinogen into angiotensin. This protein stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce aldosterone which acts on the cells of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and increases the rate of reabsorption of Na+. Reabsorption of Na+ brings about the uptake of an osmotically equivalent amount of water. Absorption of sodium and water increases blood volume and pressure.
Q3: Removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron will result in: (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) More concentrated urine
(b) No change in quality and quantity of urine
(c) No urine formation
(d) More diluted urine
Ans: (d)
Removing the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) from the nephron would lead to more diluted urine because the PCT is responsible for reabsorbing a significant amount of water, glucose, amino acids, and other essential substances from the filtrate, and its absence would disrupt this reabsorption process.
- Function of the PCT:The PCT is a crucial part of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, where the process of urine formation takes place. The PCT is responsible for the reabsorption of a large portion of the glomerular filtrate, including water, glucose, amino acids, sodium, potassium, and other essential substances back into the bloodstream.
- Impact of PCT Removal:Reduced Reabsorption: If the PCT is removed, the reabsorption of these essential substances will be significantly reduced.More Dilute Urine: Consequently, the urine produced will contain a higher concentration of these substances and a greater volume of water, resulting in more diluted urine.Disruption of Electrolyte Balance: The lack of reabsorption of electrolytes like sodium and potassium can lead to imbalances in the body's fluid and electrolyte balance.
2014
Q1: Which of the following causes an increase in sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) Increase in aldosterone levels
(b) Increase in antidiuretic hormone levels
(c) Decrease in aldosterone levels
(d) Decrease in antidiuretic hormone levels
Ans: (a)
Aldosterone hormone, released by the adrenal cortex, helps the body regulate blood pressure. Aldosterone causes the tubules of the kidneys to increase the reabsorption of sodium and water into the blood. This increases the volume of fluid in the body, which also increases blood pressure.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Excretory Products & their Elimination - Biology Class 11
| 1. What are the main excretory products in humans? |  |
| 2. How do the kidneys help in the elimination of waste products from the body? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the liver in excretion? |  |
| 4. How does the skin contribute to the elimination of waste products? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of excretion in maintaining homeostasis in the body? |  |






















