Light - Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Worksheet Science
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which phenomenon is responsible for allowing us to see our reflection in a shiny surface?
(a) Refraction
(b) Absorption
(c) Reflection
(d) Diffraction
Ans: (c)
Sol: Reflection is the phenomenon where light bounces off a surface and changes direction, allowing us to see objects and ourselves.
Q2: Which type of mirror has a reflecting surface curved inwards?
(a) Convex Mirror
(b) Concave Mirror
(c) Plane Mirror
(d) Spherical Mirror
Ans: (b)
Sol: Concave mirrors have a reflecting surface curved inwards.
Q3: In a plane mirror, the image is:
(a) Real and inverted
(b) Virtual and erect
(c) Virtual and inverted
(d) Real and erect
Ans: (b)
Sol: The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect.
Q4: What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
(a) 3 x 107 m/s
(b) 3 x 108 m/s
(c) 3 x 106 m/s
(d) 3 x 109 m/s
Ans: (b)
Sol: The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 3 x 108 m/s.
Q5: What is the relationship between focal length and radius of curvature for spherical mirrors?
(a) f = R
(b) f = R/2
(c) f = 2R
(d) f = 2/R
Ans: (b) f = R/2
Sol: The focal length (f) of a spherical mirror is half of its radius of curvature (R).
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The word "AMBULANCE" is written in reverse direction so that it can be read correctly in the rear-view mirror of vehicles going in front of it. This is an application of ________________.
Ans: Lateral Inversion
Lateral inversion is the phenomenon where the right side of the object appears on the left side of the image and vice versa.
Q2: The point on the principal axis where all parallel light rays actually meet or appear to meet after reflection is called the ____________.
Ans: Focus
The focus is the point where parallel rays converge or appear to converge after reflection from a spherical mirror.
Q3: The bending of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another is called ______________.
Ans: Refraction
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, resulting from a change in its velocity.
Q4: The line joining the pole and center of curvature of a spherical mirror is called the ____________.
Ans: Principal Axis
The principal axis is the line passing through the pole and center of curvature of a spherical mirror.
Q5: The point for a given lens through which any ray passes undeviated is known as the ____________. Ans: Optical Centre
The optical centre is a point on a lens through which any ray passes undeviated.
True/False
Q1: The image formed by a concave mirror is always virtual.
Ans: False
The image formed by a concave mirror can be real or virtual depending on the position of the object.
Q2: The magnification of a convex lens is always positive.
Ans: False
The magnification of a convex lens can be positive or negative, depending on the relative positions of the object and image.
Q3: In refraction, when light passes from a denser to a rarer medium, the ray bends towards the normal.
Ans: False
In refraction, when light passes from a denser to a rarer medium, the ray bends away from the normal.
Q4: The focal length of a concave lens is positive.
Ans: False
The focal length of a concave lens is negative.
Q5: The magnification of a plane mirror is always +1.
Ans: True
The magnification of a plane mirror is always +1, indicating that the image is of the same size as the object and virtual.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Ans: R = 20 cm
R = 2f
f = R/2, f = 20/2
= 10 cm.
Focal length is 10 cm.
Q2: Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Ans: Convex mirror can cover a wider range and give erect and diminished image. Hence convex mirror is used as a rear-view mirror to get wider field of view.
Q3: A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Ans: Object distance u = –10 cm (concave mirror)
Magnification m = –3
m = −v/ u
∴ ν= –mu = –(–3) (–10) = –30 cm.
Image formed ν = 30 cm in front of the concave mirror.
Q4: Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m/s.
Ans: The speed of light in vacuum is = 3 × 108 m/s
Refractive index of glass ng = 1.50
ng = c/v
Speed of light in glass νg = c/ng = 3 × 108/1.50
= 2 × 108 m/s.
Q5: You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given in table above.
Ans: Refractive index of kerosene = 1.44
Refractive index of turpentine = 1.47
Refractive index of water = 1.33
Lower the refractive index faster is the speed of light in that medium. Hence light will travel fastest in water.
Q6: Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
Ans: 1 dioptre is the power of a lens whose focal length is 1 metre.
1 D = 1 m–1
Q7: Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Ans: Focal length of concave lens f = –2 m
Power of concave lens P = 1/f
∴ P = 1/–2
= –0.5 D.
Q8: Is it possible that a convergent lens in one medium becomes divergent, when placed in another medium?
Ans: Yes it's possible that convergent lens in one medium acts divergent in another medium . If a lens acts as convergent in a medium having refractive index less than that of lens material, then it will act as divergent in medium having greater refractive index and vice versa.
Q9: Out of convex mirror and a concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror?
Ans: Out of the two spherical mirrors convex and concave mirror, the convex mirror has the focus point situated behind the mirror as its centre of curvature lies behind the mirror due to which it forms virtual and erect image always
Q10: What is the unit of refractive index?
Ans: Refractive index has no units as it is a ratio of two similar physical quantities.
Q11: An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Ans: Convex mirror
f = +15 cm, u = – 10 cm.
1/f = 1/ν + 1/u
1/15 = 1/ν + 1 /(– 10)
1/v = 1/15 + 1/10
1/v = 5/30
ν = + 6 cm
The image is formed 6 cm behind the mirror, virtual image is formed.
Q12: An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Ans: f = R/2 = 30/2 = 15 cm
f = + 15 cm, u = – 20 cm, h = 5.0 cm
1 /v +1/u = 1/f
∴ 1/ ν + 1 /(– 20) = 1/15
1/v =1 /15 + 1/20
1/v = 7/60
∴ ν = 60/7 cm
The image is virtual behind the mirror and erect.
hi/ ho = ν / u
⇒ hi/5 = 8.57 / 20
hi = 3.33 cm
Q13: Find the focal length of a lens of power –2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
Ans: P = – 2.0 D
P = 1 /f
∴ f = 1/P
= 1/-2.0 D
= –0.5 m.
∴ The lens is concave lens as f = –ve.
Q14: An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Ans: u = - 27 cm, f = - 18 cm. h0= 7.0 cm
1/v = 1/f - 1/u
1/v = -1/18 + 1/27 = -1/54
v = - 54 cm
Screen must be placed at a distance of 54 cm from the mirror in front of it.
hi/ho = v/u
hi/7 = +54/-27
hi = -2 7 = -14 cm.
Thus, the image is of 14 cm length and is inverted image.
Q15: If a magnification of -1 is to be obtained using a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm, then what should be the position of the object?
Ans: Magnification of -1 means that the image is real and size of image is equal to the size of the object. This is possible when the object is placed at C of a concave mirror. Therefore, position of object = C = 2f = 12 cm in front of the concave mirror.
Q16: A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal- length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find the: (i) position (ii) nature (iii) size of the image formed.
Given object size = 5 cm
Object distance from lens u=−30𝑢=−30 cm
Focal length f=20𝑓=20 cm,
We have to find v=?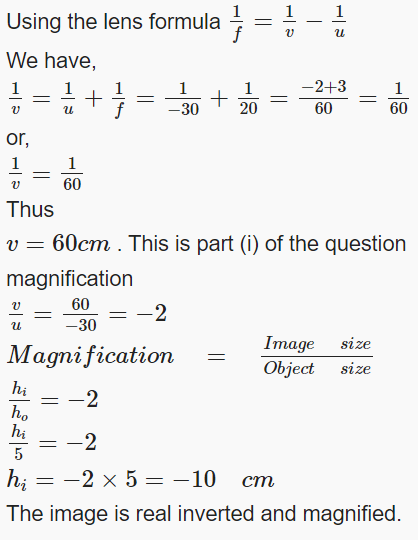
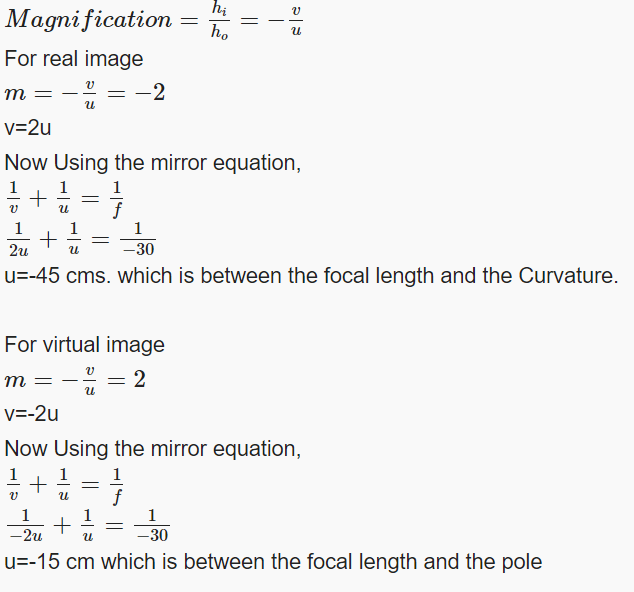
Q17: 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of image and magnification. Describe what happens to the image as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.

Q18: Rohit placed a pencil perpendicular to principal axis in front of a converging mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image formed is twice the size of the pencil. Calculate the distance of the object from the mirror.
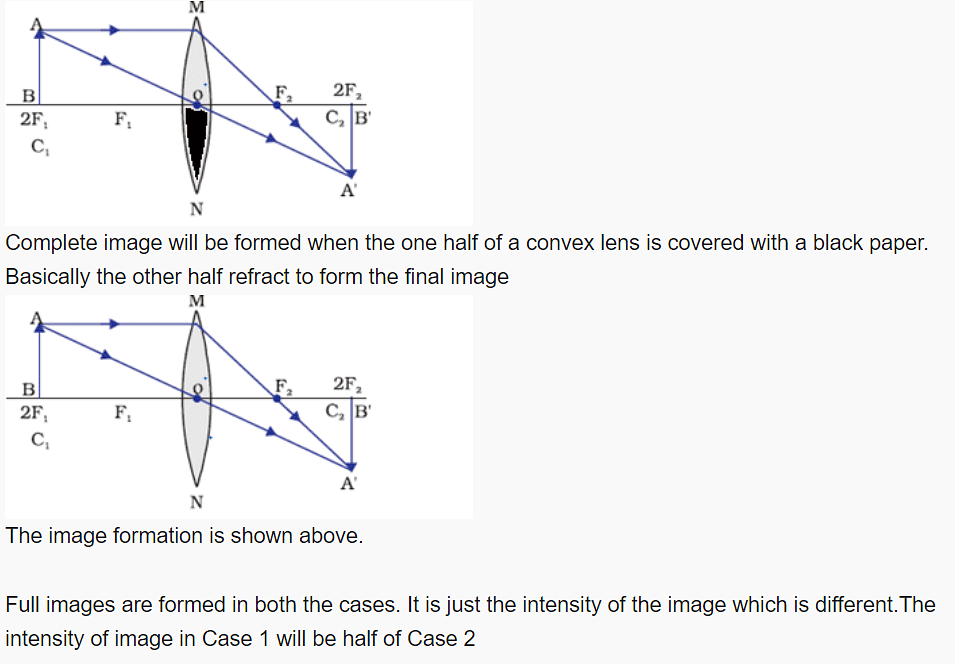
Q.19: One half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper.
(a)Show the formation of image of an object placed at 2F1, of such covered lens with the help of ray diagram. Mention the position and nature of image.
(b)Draw the ray diagram for same object at same position in front of the same lens, but now uncovered. Will there be any difference in the image obtained in the two cases? Give reason for your answer.
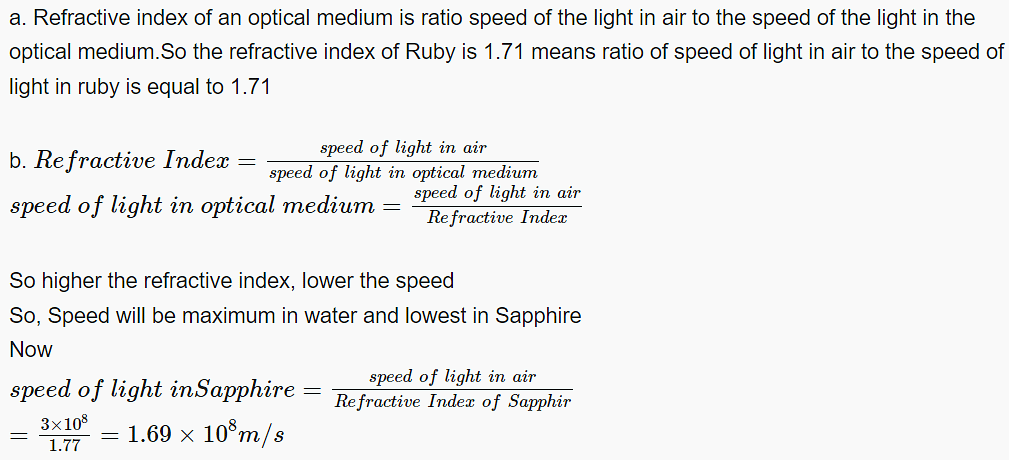
Q.20 (a) The refractive index of Ruby is 1.71. What is meant by this statement?
(b) The refractive index of some medium are given below:
Crown glass- 1.52
Water- 1.33
Sapphire- 1.77
In which of the medium is the speed of light
(i)maximum
(ii)minimum
(iii) Calculate speed of light in sapphire.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Light - Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is the difference between reflection and refraction of light? |  |
| 2. How does the angle of incidence affect the angle of reflection? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between regular and irregular reflection? |  |
| 4. How does refraction of light occur? |  |
| 5. What is the principle behind the formation of a rainbow? |  |

















