NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure | Chemistry Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: A hypothetical diatomic molecule with bond order zero is quite stable.
Statement II: As bond order increases, the bond length increases.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Ans: (d)
Bond Order and Bond Stability
- Bond Order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. It can be determined using Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT).
- A bond order of zero means that there are equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons, resulting in no net bond formation.
- A molecule with a bond order of zero is considered unstable and cannot exist under normal conditions.
Bond Order and Bond Length
- Bond order is inversely related to bond length. As bond order increases, the bond strength increases, and the bond length decreases.
- Higher bond order indicates stronger bonds, which are shorter in length.
Explanation
- Statement I: "A hypothetical diatomic molecule with bond order zero is quite stable." This statement is false. A bond order of zero implies no bond formation, and the molecule would not exist as a stable entity.
- Statement II: "As bond order increases, the bond length increases." This statement is also false. As bond order increases, bond strength increases, and bond length decreases.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option d: Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
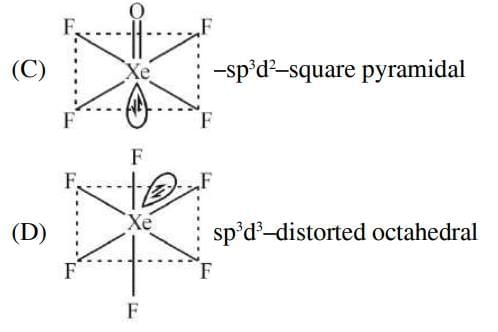
Q2: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2025)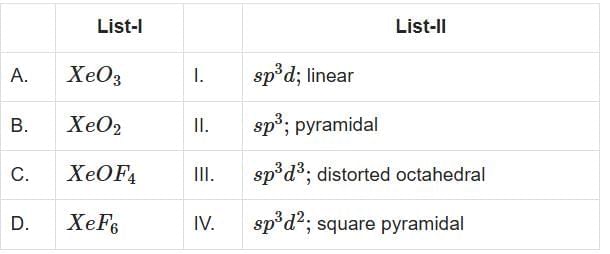 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
Ans: (c)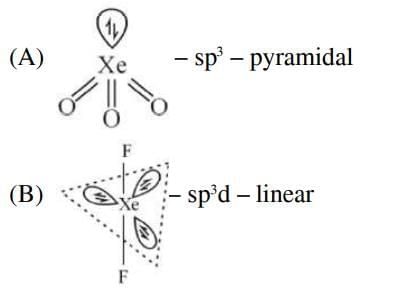
Q3: Identify the correct orders against the property mentioned (NEET 2025)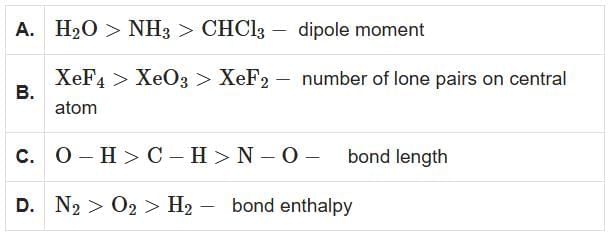
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B and C only
(c) A and D only
(d) B and D only
Ans: (c)
H₂O > NH₃ > CHCl₃ – Dipole Moment
- H₂O has the highest dipole moment due to its bent shape and high electronegativity difference.
- NH₃ has a lower dipole moment than H₂O, as it is pyramidal and less polar.
- CHCl₃ has the lowest dipole moment because its geometry partially cancels out dipoles.
- This order is correct.
XeF₄ > XeO₃ > XeF₂ – Number of Lone Pairs on Central Atom
- XeF₄: Xenon has 4 bonds and 2 lone pairs.
- XeO₃: Xenon has 3 bonds and 1 lone pair.
- XeF₂: Xenon has 2 bonds and 3 lone pairs.
- The correct order of lone pairs is XeF₂ > XeF₄ > XeO₃, so this option is incorrect.
O–H > C–H > N–O – Bond Length
- O–H has the shortest bond length due to high bond strength and small atomic size.
- C–H is longer than O–H but shorter than N–O.
- N–O has the longest bond length due to weaker bond strength and larger atomic size.
- This order is correct.
N₂ > O₂ > H₂ – Bond Enthalpy
- N₂ has the highest bond enthalpy due to the strong triple bond.
- O₂ has a lower bond enthalpy than N₂ due to its double bond.
- H₂ has the lowest bond enthalpy due to its single bond.
- This order is correct.
Therefore, the correct answer is A, D only.
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II.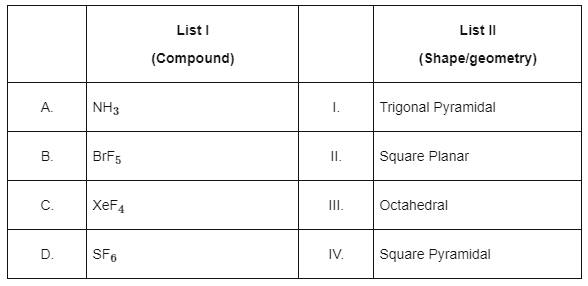 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(b) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
NH3 ⇒ sp3 hybridised with 1 lone pair.
Structure will be Trigonal Pyramidal.
BrF5 ⇒ sp3d2 hybridised with 1 lone pair.
Structure will be Square Pyramidal.
XeF4 ⇒ sp3d2 with two lone pairs.
Structure will be Square Planar.
SF6 ⇒ sp3d2 with no lone pair.
Structure will be Octahedral.
A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Q2: Identify the correct answer.
(a) Three resonance structures can be drawn for ozone
(b) BF3 has non-zero dipole moment
(c) Dipole moment of
(d) Three canonical forms can be drawn for CO32- ion (NEET 2024)
Ans: (d)
(1) In ozone; there are two resonating structures.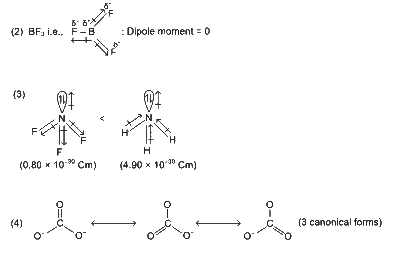
Q3: Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is present in: (NEET 2024)
(a) 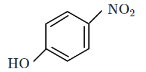
(b) 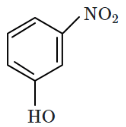
(c) HF
(d) 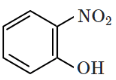
Ans: (d)
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs within the same molecule when a hydrogen donor (–OH) and an acceptor (–NO2) are positioned appropriately.
In the given options, option (4) contains ortho-nitrophenol, where the hydroxyl (-OH) and nitro (-NO2) groups form a strong intramolecular hydrogen bond.
Other options either involve intermolecular hydrogen bonding or lack the correct functional groups for intramolecular bonding. Conclusion: The correct option is (D)
Q4: Which one of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2024)
(a) BF₃ has non-zero dipole moment.
(b) The dipole moment of NF₃ is greater than that of NH₃.
(c) Three canonical forms can be drawn for CO₃²⁻ ion.
(d) Three resonance structures can be drawn for ozone.
Ans: (c)
(a) BF₃ has non-zero dipole moment: BF₃ has a trigonal planar geometry with boron at the center and three fluorine atoms at the corners. The molecule is symmetrical, and the dipole moments of the B-F bonds cancel out due to the 120° bond angles. Thus, BF₃ has a zero dipole moment. This statement is incorrect.
(b) The dipole moment of NF₃ is greater than that of NH₃: In NF₃, the nitrogen atom is bonded to three fluorine atoms with a lone pair, resulting in a pyramidal geometry. The dipole moments of the N-F bonds partially cancel the lone pair’s contribution, leading to a smaller net dipole moment. In NH₃, the nitrogen is bonded to three hydrogen atoms with a lone pair, also in a pyramidal geometry, but the dipole moments of the N-H bonds add to the lone pair’s contribution, resulting in a larger net dipole moment. Experimentally, NH₃ has a dipole moment of about 1.47 D, while NF₃ has a dipole moment of about 0.23 D. Thus, the dipole moment of NF₃ is less than that of NH₃, making this statement incorrect.
(c) Three canonical forms can be drawn for CO₃²⁻ ion: The carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻) has a central carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, with two of the oxygens carrying a negative charge that can delocalize. Resonance structures (canonical forms) can be drawn by shifting the double bonds and charges, resulting in three equivalent structures where the double bond is with each oxygen in turn. This is a well-known property of CO₃²⁻, making this statement correct.
(d) Three resonance structures can be drawn for ozone: Ozone (O₃) has a bent structure with a central oxygen atom bonded to two other oxygens. It exhibits resonance, with two main resonance structures where the double bond alternates between the two O-O bonds, and the negative charge is delocalized. A third structure is less common and not typically considered a major contributor. Standard chemistry texts recognize two primary resonance structures for ozone, making this statement incorrect (it should be two, not three).
The correct answer is (c).
Q5: Which one of the following molecules is paramagnetic? (NEET 2024)
(a)H2
(b)Li2
(c)C2
(d) O2
Ans: (d)
A molecule is paramagnetic if it has unpaired electrons, which can be determined by examining its molecular orbital (MO) configuration.
(a) H₂: The molecular orbital configuration is (σ₁s)². All electrons are paired, so H₂ is diamagnetic.
(b) Li₂: The molecular orbital configuration is (σ₂s)² (σ₂s*)² (σ₂p)². All electrons are paired, so Li₂ is diamagnetic.
(c) C₂: The molecular orbital configuration is (σ₂s)² (σ₂s*)² (π₂p)⁴. All electrons are paired, so C₂ is diamagnetic.
(d) O₂: The molecular orbital configuration is (σ₂s)² (σ₂s*)² (σ₂p)² (π₂p)⁴ (π₂p*)². The two electrons in the π₂p* orbitals are unpaired (one in each π₂p* orbital due to Hund’s rule), so O₂ is paramagnetic.
The correct answer is (d) O₂.
Q6: Arrange the following hydrides in the order of decreasing bond angle: (NEET 2024)
A. SbH₃
B. AsH₃
C. PH₃
D. NH₃
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B > A > D > C
(b) B > A > C > D
(c) D > C > B > A
(d) A > C > B > D
Ans: (c)
To arrange the hydrides in the order of decreasing bond angle, we need to understand the factors affecting bond angles. The bond angles in these hydrides are influenced by:
- The size of the central atom (larger atoms tend to have smaller bond angles due to more electron repulsion in larger orbitals).
- The lone pair on the central atom (the lone pair causes more repulsion, reducing the bond angle).
Bond Angles and Size of Central Atom:
- NH₃ (Ammonia) has the largest bond angle because nitrogen is small, and the lone pair of electrons causes a greater repulsion, maintaining a bond angle of 107°.
- PH₃ (Phosphine) has a smaller bond angle than NH₃ because phosphorus is larger than nitrogen, leading to a decrease in the bond angle.
- AsH₃ (Arsine) has a smaller bond angle than PH₃ for a similar reason: arsenic is larger than phosphorus, leading to an even smaller bond angle.
- SbH₃ (Stibine) has the smallest bond angle because antimony is the largest atom, and the bond angle is further reduced.
Conclusion: The order of bond angles is: NH₃ > PH₃ > AsH₃ > SbH₃.
Correct Answer: (c) D > C > B > A.
Q7: The correct shape and hybridisation of BrF₅ is: (NEET 2024)
(a) Square pyramidal and sp³d²
(b) Square pyramidal and d²sp³
(c) Trigonal bipyramidal and sp³d²
(d) Trigonal bipyramidal and d²sp³
Ans: (a)
To determine the correct shape and hybridization of BrF₅, let's go through the steps:
Step 1: Determine the Lewis Structure
BrF₅ consists of one bromine (Br) atom and five fluorine (F) atoms.
Bromine has 7 valence electrons and each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
The total number of valence electrons is:
7 (Br) + 5 × 7 (F) = 42 valence electrons.
The bromine atom is the central atom, and it forms five single bonds with the fluorine atoms.
Step 2: Determine the Electron Geometry
Bromine has 5 bonding pairs of electrons around it (from the 5 F atoms).
The electron geometry for a molecule with 5 bonding pairs of electrons is trigonal bipyramidal.
Step 3: Determine the Molecular Shape
Since there are no lone pairs on the bromine atom (only bonding pairs), the shape of BrF₅ is square pyramidal.
Step 4: Hybridization
For a trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry, the hybridization is sp³d².
Conclusion: The correct shape of BrF₅ is square pyramidal, and the hybridization is sp³d².
Correct Answer: (a) Square pyramidal and sp³d².
Q8: Which pair of the following compounds has one lone pair of electrons on the central atom? (NEET 2024)
(a) SF₄, BrF₅
(b) SF₄, ClF₃
(c) ClF₃, XeF₄
(d) XeF₄, BrF₅
Ans: (a)
Step 1: Analyze each compound
SF₄ (Sulfur Tetrafluoride)
- Central atom: Sulfur (S)
- Valence electrons: S has 6 valence electrons; each F has 7. Total = 6 + (4 × 7) = 34 electrons.
- Lewis structure: Sulfur forms 4 single bonds with 4 fluorine atoms (8 electrons used for bonding). Remaining electrons: 34 − 8 = 26, with 24 used for lone pairs on the 4 fluorines (3 lone pairs per F). This leaves 2 electrons for sulfur, forming 1 lone pair.
- Electron domains: 4 bonding pairs + 1 lone pair = 5 electron domains.
- Electron geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal (5 domains).
- Molecular geometry: Seesaw (4 bonding pairs, 1 lone pair).
- Lone pairs on central atom: 1.
BrF₅ (Bromine Pentafluoride)
- Central atom: Bromine (Br)
- Valence electrons: Br has 7 valence electrons; each F has 7. Total = 7 + (5 × 7) = 42 electrons.
- Lewis structure: Bromine forms 5 single bonds with 5 fluorine atoms (10 electrons used for bonding). Remaining electrons: 42 − 10 = 32, with 30 used for lone pairs on the 5 fluorines (3 lone pairs per F). This leaves 2 electrons for bromine, forming 1 lone pair.
- Electron domains: 5 bonding pairs + 1 lone pair = 6 electron domains.
- Electron geometry: Octahedral (6 domains).
- Molecular geometry: Square pyramidal (5 bonding pairs, 1 lone pair).
- Lone pairs on central atom: 1.
ClF₃ (Chlorine Trifluoride)
- Central atom: Chlorine (Cl)
- Valence electrons: Cl has 7 valence electrons; each F has 7. Total = 7 + (3 × 7) = 28 electrons.
- Lewis structure: Chlorine forms 3 single bonds with 3 fluorine atoms (6 electrons used for bonding). Remaining electrons: 28 − 6 = 22, with 18 used for lone pairs on the 3 fluorines (3 lone pairs per F). This leaves 4 electrons for chlorine, forming 2 lone pairs.
- Electron domains: 3 bonding pairs + 2 lone pairs = 5 electron domains.
- Electron geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal (5 domains).
- Molecular geometry: T-shaped (3 bonding pairs, 2 lone pairs).
- Lone pairs on central atom: 2.
XeF₄ (Xenon Tetrafluoride)
- Central atom: Xenon (Xe)
- Valence electrons: Xe has 8 valence electrons; each F has 7. Total = 8 + (4 × 7) = 36 electrons.
- Lewis structure: Xenon forms 4 single bonds with 4 fluorine atoms (8 electrons used for bonding). Remaining electrons: 36 − 8 = 28, with 24 used for lone pairs on the 4 fluorines (3 lone pairs per F). This leaves 4 electrons for xenon, forming 2 lone pairs.
- Electron domains: 4 bonding pairs + 2 lone pairs = 6 electron domains.
- Electron geometry: Octahedral (6 domains).
- Molecular geometry: Square planar (4 bonding pairs, 2 lone pairs).
- Lone pairs on central atom: 2.
Step 2: Evaluate the pairs
We need a pair where both compounds have one lone pair on the central atom.
- (a) SF₄, BrF₅
- SF₄: 1 lone pair.
- BrF₅: 1 lone pair.
- Result: Both have 1 lone pair.
- (b) SF₄, ClF₃
- SF₄: 1 lone pair.
- ClF₃: 2 lone pairs.
- Result: ClF₃ does not have 1 lone pair.
- (c) ClF₃, XeF₄
- ClF₃: 2 lone pairs.
- XeF₄: 2 lone pairs.
- Result: Neither has 1 lone pair.
- (d) XeF₄, BrF₅
- XeF₄: 2 lone pairs.
- BrF₅: 1 lone pair.
- Result: XeF₄ does not have 1 lone pair.
Step 3: Conclusion
Only option (a) SF₄, BrF₅ has both compounds with one lone pair on the central atom.
Final Answer: (a) SF₄, BrF₅
Q9: Which of the following molecules has "NON ZERO" dipole moment value? (NEET 2024)
(a) CCl₄
(b) HI
(c) CO₂
(d) BF₃
Ans: (b)
To determine which molecule has a non-zero dipole moment, we need to evaluate the polarity of each molecule. A molecule has a non-zero dipole moment if it is polar, which occurs when there is an uneven distribution of electron density due to electronegativity differences between atoms and an asymmetric molecular geometry that does not cancel out the individual bond dipoles.
Step 1: Analyze each molecule
(a) CCl₄ (Carbon Tetrachloride)
- Structure: Carbon (C) is the central atom, bonded to four chlorine (Cl) atoms in a tetrahedral geometry.
- Electronegativity: Cl (3.16) is more electronegative than C (2.55), so each C–Cl bond is polar, with the dipole moment directed toward Cl.
- Symmetry: Tetrahedral geometry is highly symmetric. The four C–Cl bond dipoles are equal in magnitude and point toward the vertices of the tetrahedron, canceling each other out.
- Dipole moment: Zero (non-polar due to symmetry).
- Conclusion: Zero dipole moment.
(b) HI (Hydrogen Iodide)
- Structure: A diatomic molecule with a single H–I bond.
- Electronegativity: I (2.66) is more electronegative than H (2.20), so the H–I bond is polar, with the dipole moment directed toward I.
- Symmetry: As a diatomic molecule, there is no cancellation of the bond dipole since there is only one bond.
- Dipole moment: Non-zero (polar due to the electronegativity difference).
- Conclusion: Non-zero dipole moment.
(c) CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide)
- Structure: Linear molecule with carbon (C) in the center, double-bonded to two oxygen (O) atoms (O=C=O).
- Electronegativity: O (3.44) is more electronegative than C (2.55), so each C=O bond is polar, with the dipole moment directed toward O.
- Symmetry: Linear geometry is symmetric. The two C=O bond dipoles are equal in magnitude and point in opposite directions, canceling each other out.
- Dipole moment: Zero (non-polar due to symmetry).
- Conclusion: Zero dipole moment.
(d) BF₃ (Boron Trifluoride)
- Structure: Boron (B) is the central atom, bonded to three fluorine (F) atoms in a trigonal planar geometry.
- Electronegativity: F (3.98) is more electronegative than B (2.04), so each B–F bond is polar, with the dipole moment directed toward F.
- Symmetry: Trigonal planar geometry is symmetric. The three B–F bond dipoles are equal in magnitude and arranged at 120° angles, canceling each other out.
- Dipole moment: Zero (non-polar due to symmetry).
- Conclusion: Zero dipole moment.
Step 2: Identify the molecule with a non-zero dipole moment
- CCl₄: Zero dipole moment (symmetric, non-polar).
- HI: Non-zero dipole moment (polar, asymmetric).
- CO₂: Zero dipole moment (symmetric, non-polar).
- BF₃: Zero dipole moment (symmetric, non-polar).
Only HI has a non-zero dipole moment due to its polar bond and lack of symmetry to cancel the dipole.
Final Answer: (b) HI
Q10: Match Column I (Molecule) with Column II (Bond enthalpy) and mark the correct option: (NEET 2024)z`
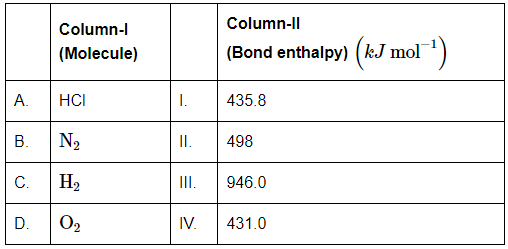 (a) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Ans: (d)
Step by Step Solution:
Step 1: Identify the bond enthalpy values for each molecule: HCl = 431.0 kJ mol−1, N2 = 946.0 kJ mol−1, H2 = 436.0 kJ mol−1, O2 = 498.0 kJ mol−1.
Step 2: Match HCl with its bond enthalpy: A. HCl matches with IV. 431.0 kJ mol−1.
Step 3: Match N2 with its bond enthalpy: B. N2 matches with III. 946.0 kJ mol−1.
Step 4: Match H2 with its bond enthalpy: C. H2 matches with I. 436.0 kJ mol−1 and O2 with II. 498.0 kJ mol−1.
Final Answer: (d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
2023
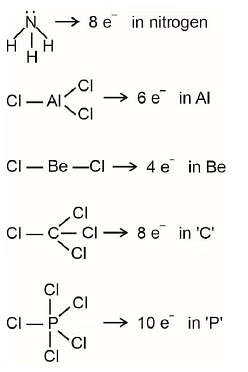
Q1: Amongst the following the total number of species NOT having eight electrons around central atom in its outermost shell, is (NEET 2023)NH3, AlCl3, BeCl2, CCl4, PCl5:
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 1
Ans: (a)
Q2: The correct order of energies of molecular orbitals of N₂ molecule, is (NEET 2023)
(a) σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < (π2pₓ = π2py) < σ2pz < (π*2pₓ = π*2py) < σ*2pz
(b) σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < σ2pz < (π2pₓ = π2py) < (π*2pₓ = π*2py) < σ*2pz
(c) σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < σ2pz < σ*2pz < (π2pₓ = π2py) < (π*2pₓ = π*2py)
(d) σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < (π2pₓ = π2py) < (π*2pₓ = π*2py) < σ2pz < σ*2pz
Ans: (a)
For molecules like B2, C2, N2 etc. the increasing order of energies of various molecular orbitals is
σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < (π2pₓ = π2py) < σ2pz < (π*2pₓ = π*2py) < σ*2pz
Q3: Taking stability as the factor, which one of the following represents correct relationship?
(a) InI
(b) AlCl > AlCl3
(c) TlI > TlI3
(d) TlCl
Ans: (c)
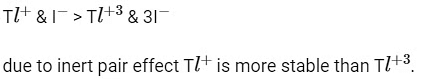
Q4: Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting particles that will include:
A. dipole - dipole forces.
B. dipole - induced dipole forces
C. hydrogen bonding
D. covalent bonding
E. dispersion forces
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) A, B, C, D are correct
(b) A, B, C, E are correct
(c) A, C, D, E are correct
(d) B, C, D, E are correct (NEET 2023)
Ans: (b)
Intermolecular forces means force of attraction between two or more molecules
dipole-dipole (attraction between two or more polar molecules).
Dipole induced dipole (attraction between polar and non polar molecules)
Hydrogen bonding (it is a special type of dipole-dipole and ion-dipole attraction)
Dispersion forces (mainly acts between non polar molecules).
Covalent bonding (acts between atom not between molecules )
Q5: The correct order of dipole moments for molecules NH₃, H₂S, CH₄, and HF is: (NEET 2023)
(a) CH₄ > H₂S > NH₃ > HF
(b) H₂S > NH₃ > HF > CH₄
(c) NH₃ > HF > CH₄ > H₂S
(d) HF > NH₃ > H₂S > CH₄
Ans: (d)
To determine the correct order of dipole moments for the molecules NH₃, H₂S, CH₄, and HF, we need to assess the polarity of each molecule. A dipole moment arises from an uneven distribution of electron density due to electronegativity differences between atoms and an asymmetric molecular geometry that does not cancel out the bond dipoles.
Step 1: Analyze each molecule
CH₄ (Methane)
- Structure: Tetrahedral, with carbon (C) bonded to four hydrogen (H) atoms.
- Electronegativity: C (2.55) and H (2.20) have a small difference, and the symmetric tetrahedral geometry cancels out any bond dipoles.
- Dipole moment: Zero (non-polar).
H₂S (Hydrogen Sulfide)
- Structure: Bent, with sulfur (S) bonded to two hydrogen (H) atoms and two lone pairs (similar to H₂O but with a larger bond angle ~92° due to S's larger size).
- Electronegativity: S (2.58) is slightly more electronegative than H (2.20), creating a polar S–H bond. The bent shape results in a net dipole moment.
- Dipole moment: Non-zero, but small (~0.97 D) due to the small electronegativity difference and larger bond angle reducing the net effect.
NH₃ (Ammonia)
- Structure: Trigonal pyramidal, with nitrogen (N) bonded to three hydrogen (H) atoms and one lone pair.
- Electronegativity: N (3.04) is more electronegative than H (2.20), creating polar N–H bonds. The lone pair and asymmetric shape enhance the net dipole moment.
- Dipole moment: Non-zero, moderate (~1.47 D) due to the significant electronegativity difference and lone pair contribution.
HF (Hydrogen Fluoride)
- Structure: Linear diatomic molecule.
- Electronegativity: F (3.98) is highly electronegative compared to H (2.20), creating a strongly polar H–F bond. As a diatomic molecule, there is no cancellation of the dipole.
- Dipole moment: Non-zero, largest among these (~1.82 D) due to the large electronegativity difference.Step 2: Compare dipole moments
- CH₄: 0 D (non-polar).
- H₂S: ~0.97 D (polar, but small due to weak polarity and geometry).
- NH₃: ~1.47 D (polar, enhanced by lone pair).
- HF: ~1.82 D (polar, strongest due to large electronegativity difference).
The order of dipole moments from highest to lowest is: HF > NH₃ > H₂S > CH₄.
Step 3: Match with options
(a) CH₄ > H₂S > NH₃ > HF: Incorrect (CH₄ has zero dipole moment).
(b) H₂S > NH₃ > HF > CH₄: Incorrect (H₂S < NH₃ < HF).
(c) NH₃ > HF > CH₄ > H₂S: Incorrect (HF > NH₃).
(d) HF > NH₃ > H₂S > CH₄: Correct.
Final Answer: (d) HF > NH₃ > H₂S > CH₄
Q6: Which one of the following statements is incorrect related to Molecular Orbital Theory? (NEET 2023)
(a) The π∗ antibonding molecular orbital has a node between the nuclei.
(b) In the formation of a bonding molecular orbital, the two electron waves of the bonding atoms reinforce each other.
(c) Molecular orbitals obtained from 2Px and 2Py orbitals are symmetrical around the bond axis.
(a) A π−bonding molecular orbital has larger electron density above and below the internuclear axis.
Ans: (c)
Let's analyze each statement in relation to Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT):
(a) The π∗ antibonding molecular orbital has a node between the nuclei.
This statement is correct. In a π∗ antibonding molecular orbital, there is a node between the two nuclei where the probability of finding an electron is zero. This is typical for antibonding molecular orbitals.
(b) In the formation of a bonding molecular orbital, the two electron waves of the bonding atoms reinforce each other.
This statement is correct. In a bonding molecular orbital, the atomic orbitals overlap constructively, meaning the electron waves reinforce each other, leading to an increase in electron density between the nuclei and a stronger bond.
(c) Molecular orbitals obtained from 2Px and 2Py orbitals are symmetrical around the bond axis.
This statement is incorrect. The molecular orbitals formed from 2Px and 2Py orbitals (which are side-by-side overlaps) are not symmetrical around the bond axis. These orbitals form π-bonding and π-antibonding orbitals, and the electron density is distributed above and below the bond axis, not along it.
(d) A π−bonding molecular orbital has larger electron density above and below the internuclear axis.
This statement is correct. In a π-bonding molecular orbital, the electron density is larger above and below the internuclear axis, as the orbitals overlap side-by-side.
Conclusion: The incorrect statement is (c). The molecular orbitals obtained from 2Px and 2Py orbitals are not symmetrical around the bond axis.
Correct Answer: (c).
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R)
Assertion (A) : ICI is more reactive than I2
Reason (R) : I-CI bond is weaker than I-I bond.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct.
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct. (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (a)
In general, interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens (except fluorine). This is because X - X' bond in interhalogens is weaker than X - X bond in halogens excepts F - F bond. Therefore I-Cl is more reactive than I2 because of weaker I - Cl bond then I - I bond.
Q2: Amongst the following which one will have maximum ‘lone pair-lone pair’ electron repulsions? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(1) SF4
(2) XeF2
(3) ClF3
(4) IF5
Ans: b
In XeF2, the central atom Xe has 3 lone pairs around it.
Q3: Which amongst the following is incorrect statement? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) 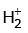 ion has one electron.
ion has one electron.
(b) 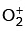 ion is diamagnetic.
ion is diamagnetic.
(c) The bond orders of 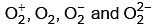 are 2.5, 2, 1.5 and 1, respectively.
are 2.5, 2, 1.5 and 1, respectively.
(d) C2 molecule has four electrons in its two degenerate π molecular orbitals.
Ans: b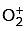 is paramagnetic, as it has one unpaired electron. (15e–)
is paramagnetic, as it has one unpaired electron. (15e–)
Q4: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
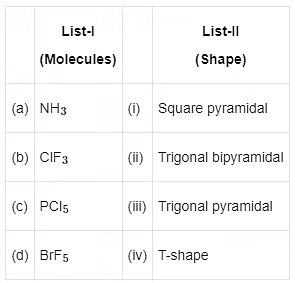
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
(b) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(c) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
Ans: (c)
Q5: The correct order of bond angles in the following compounds/species is :
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 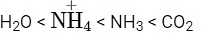
(d) 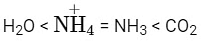 (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (b)

2021
Q1: BF3 is planar and electron deficient compound. Hybridization and number of electrons around the central atom, respectively are: (NEET 2021)
(a) Sp2 and 6
(b) sp2 and 8
(c) sp3 and 4
(d) sp3 and 6
Ans: (a)
Geometry of Molecules in which the Central Atom has No Lone Pair of Electrons
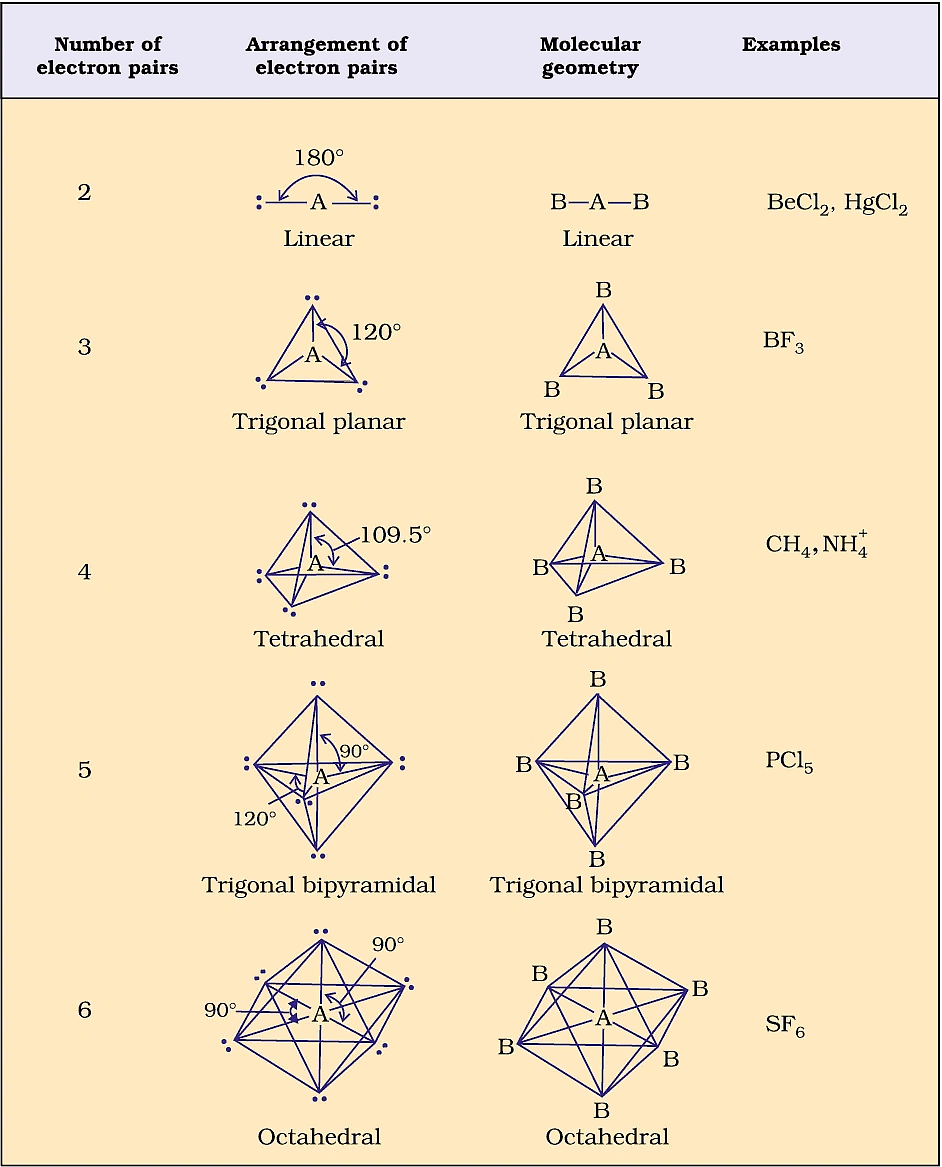
Hint: 1 bond pair means two electrons
BF3 = 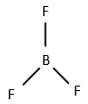 = 3σ band = sp2
= 3σ band = sp2
The number of bond pairs is three. One bond pair needs two electrons. So, the number of electrons for the three bond pairs is 6.
Q2: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2021)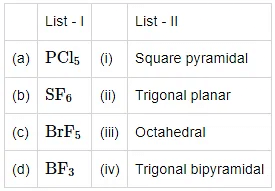
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
(b) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(c) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
(d) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
Ans: c
Hint: Sp3 = tetrahedral, sp3d = trigonal bipyramidal, and sp3d2 = octahedral
1. The hybridization of P in PCl5 is sp3d. The geometry of PCl5 is trigonal bipyramidal.
2. The hybridization of S in SF6 is sp3d2. The geometry of SF6 is octahedral.
3. The hybridization of Br in BrF5 is sp3d2. It contains 5 bond pairs and one lone pair. Hence, its shape is square pyramidal.
4. The hybridization of B in BF3 is sp2. The geometry of BF3 is square planar.
Hence, option third is the correct answer.
Q3: The correct sequence of bond enthalpy of 'C-X' bond is : (NEET 2021)
(a) CH3 - Cl > CH3 - F > CH3 - Br > CH3 - l
(b) CH3 - F < CH3 - Cl < CH3 - Br < CH3 - l
(c) CH3 - F > CH3 - Cl > CH3 - Br > CH3 - l
(d) CH3 - F < CH3 - Cl > CH3 - Br > CH3 - l
Ans: (c)
On moving down the group from F to I, the size of atom increases. Order of the size of halogen atoms is I > Br > Cl > F.
So, the bond length of C—X bond also increases from F to I and hence, the bond enthalpy decreases from F to I. Correct order of bond length of C—X bond is
H3C - I > H3C - Br > H3C - Cl > H3C - F.
Correct order of bond enthalpy is
H3C - F > H3C - Cl > CH3 - Br > H3C - I.
Q4: The non-polar nature molecule among the following is- (NEET 2021)
(a) SbCl5
(b) NO2
(c) POCl3
(d) CH2O
Ans: (a)
Dipole moment depends on the structure of the compound.
The structure of SbCl5, NO2, POCl3, and CH2O is as follows: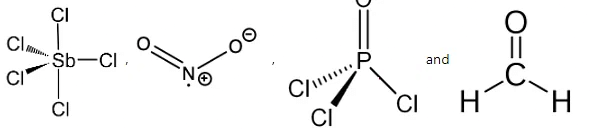 The SbCl5 is a non-polar compound because it has zero dipole moment. The SbCl5 is a symmetrical molecule thus it has a net dipole moment is zero.
The SbCl5 is a non-polar compound because it has zero dipole moment. The SbCl5 is a symmetrical molecule thus it has a net dipole moment is zero.
2020
Q1: Which of the following set of molecules will have zero dipole moment ? (NEET 2020)
(a) Nitrogen trifluoride, beryllium difluoride, water, 1,3-dichlorobenzene
(b) Boron trifluoride, beryllium difluoride, carbon dioxide, 1,4-dichlorobenzene
(c) Ammonia, beryllium difluoride, water 1,4-dichlorobenzene
(d) Boron trifluoride, hydrogen fluoride, carbon dioxide, 1,3-dichlorobenzene
Ans: (b)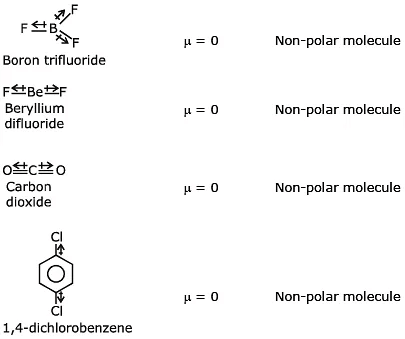
Q2: Identify a molecule which does not exist. (NEET 2020)
(a) C2
(b) O2
(c) He2
(d) Li2
Ans: c
Diatomic molecule for which bond order is zero or negative does not exist.
| Molecule | BO |
| C2 | 2 |
| O2 | 2 |
| He2 | Zero |
| Li2 | 1 |
2019
Q1: Which of the following diatomic molecular species has only π bonds according to Molecular Orbital Theory? (NEET 2019)
(a) O2
(b) N2
(c) C2
(d) Be2
Ans: (c)
MO configuration C2 is: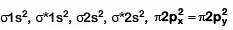
Q2: The number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in pent-2-en-4-yne is - (NEET 2019)
(a) 11 σ bonds and 2 π bonds
(b) 13 σ bonds and no π bonds
(c) 10 σ bonds and 3 π bonds
(d) 8 σ bonds and 5 π bonds
Ans: (c)
H–C
Here, 10 σ bonds and 3 π bonds are presents.
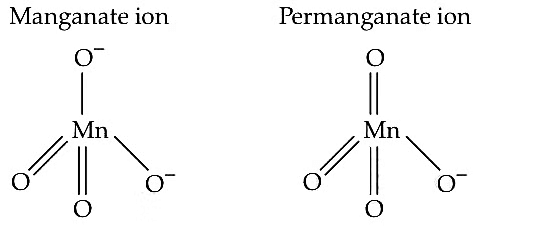
Q3: The manganate and permanganate ions are tetrahedral due to : (NEET 2019)
(a) The π-bonding involves overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with p-orbtials of manganese
(b) The π-bonding involves overlap of d-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese
(c) The π-bonding involves overlap of p-orbitals of oxygen with d-orbitals of manganese
(d) There is no π-bonding
Ans: (c)
Q4: Identify the incorrect statement related to PCl5 from the following: (NEET 2019)
(a) Three equatorial P–Cl bonds make an angle of 120° with each other
(b) Two axial P–Cl bonds make an angle of 180° with each other
(c) Axial P–Cl bonds are longer than equatorial P–Cl bonds
(d) PCl5 molecule is non-reactive
Ans: (d)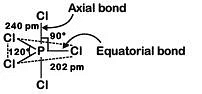
(1) True
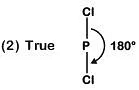
(3) TrueAxial bond : 240 pm
Equatorial bond : 202 pm
(4) False
Due to longer and hence weaker axial bonds, PCl5 is a reactive molecule.
2018
Q1: Consider the following species: CN+, CN–, NO and CN
Which one of these will have the highest bond order? (NEET 2018)
(a) NO
(b) CN–
(c) CN+
(d) CN
Ans: (b)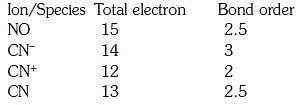
Q2: In the structure of ClF3 , the number of lone pairs of electrons on central atom ‘Cl’ is (NEET 2018)
(a) one
(b) two
(c) four
(d) three
Ans: (b)
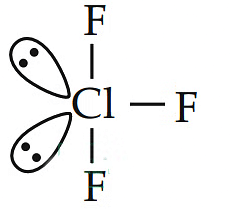
Hence, Cl has 2 lone pairs of electrons.
2017
Q1: Which of the following pairs of species have the same bond order? (NEET 2017)
(a) O2, NO+
(b) CN–, CO
(c) N2 , O2-
(d) CO, NO
Ans: (b)
Total no. of electrons in CN– is 14
Total no. of electrons in CO is also 14
Hence, B.O. of both CN– & CO is 3
Q2: The species, having bond angles of 120o is (NEET 2017)
(a) ClF3
(b) NCl3
(c) BCl3
(d) PH3
Ans: (c)
BCl3-Trigonal planar, sp2-hybridised, 120o angle
2016
Q1: Predict the correct order among the following : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Ione pair - bond pair > bond pair - bond pair > lone pair - lone pair
(b) lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair > bond pair - bond pair
(c) lone pair - lone pair > bond pair - bond pair > lone pair - bond pair
(d) bond pair - bond pair > lone pair - bond pair > lone pair - lone pair
Ans: (b)
The order of repulsion force according to VSEPR theory :
lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair > bond pair - bond pair
Q.20. Consider the molecules CH4, NH3 and H2O. Which of the given statement is false? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) The H-C-H bond angle in CH4 is larger than the H-N-H bond angle in NH3
(b) The H-C-H bond angle in CH4, the H-N-H bond angle in H2O are all greater than 90°.
(c) The H-O-H bond angle in H2O is larger than the H-C-H bond angle in CH4.
(d) The H-O-H bond angle in H2O is smaller than the H-N-H bond angle in NH3.
Ans: (c)
The H-O-H bond angle in H2O is larger than the H-C-H bond angle in CH4.
According to VBT: lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than a bond pair -lone pair repulsion.
As the number of lone pair of electrons on central element increases, repulsion between that lone pair of electrons increases and therefore, bond angle decreases.
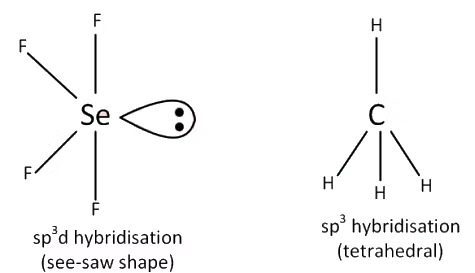
Q3: Among the following, which one is a wrong statement ? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) PH5 and BiCl5 do not exist.
(b) pπ-dπ bonds are present in SO2.
(c) SeF4 and CH4 have same shape.
(d) I3+ has bent geometry.
Ans: (c)
Q4: The correct geometry and hybridization for XeF4 are (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) octahedral, sp3d2
(b) trigonal bipyramidal, sp3d
(c) planar triangle, sp3d3
(d) square planar, sp3d2
Ans: (d)
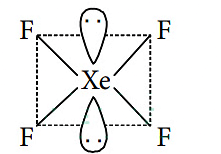
sp3d2 hybridisation (octahedral geometry, square planar shape)
Q5: The hybridizations of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in NO2+, NO3− and NH4+ respectively are
(a) sp, sp3 and sp2
(b) sp2, sp3 and sp3
(c) sp, sp2 and sp3
(d) sp2, sp and sp3 (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
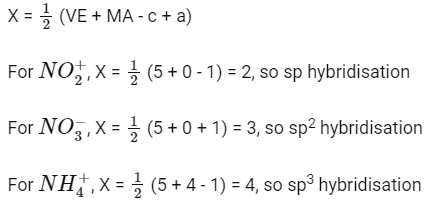
Q6: Which one of the following compounds shows the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bond?
(a) H2O2
(b) HCN
(c) Cellulose
(d) Concentrated acetic acid (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
H2O2, HCN and conc. CH3COOH form intermolecular hydrogen bonding while cellulose has intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
2015
Q1: The correct bond order in the following species is: (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(a)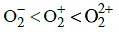
(b)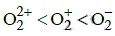
(c)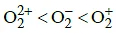
(d)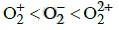
Ans: (a)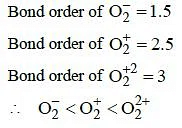
Q2: Maximum bond angle at nitrogen is present in which of the following ? (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(a) NO2+
(b) NO3 -
(c) NO2
(d) NO2-
Ans: (a)
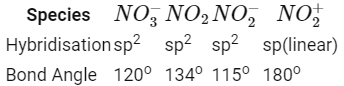
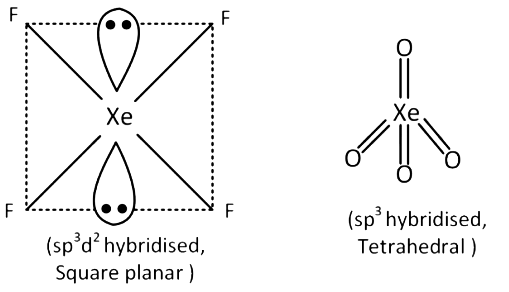
Q3: In which of the following pairs, both the species are not isostructural ? (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(a) Diamond, Silicon carbide
(b) NH3, PH3
(c) XeF4, XeO4
(d) SiCl4, PCl4+
Ans: (c)
Q4: Decreasing order of stability of O2, O2
(a) O22
(b) O2 > O2+ > O22
(c) O2
(d) O2+ > O2 > O2
Ans: (d)
According to molecular orbital theory as bond order decreases stability of the molecule decreases.
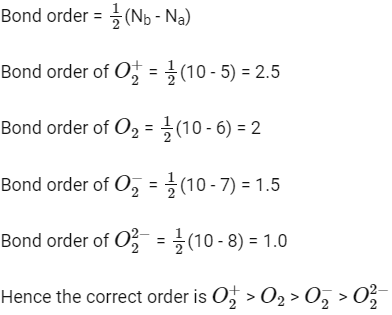
2014
Q1: Which one of the following species has plane triangular shape? (NEET / AIPMT 2014)
(a)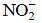
(b) CO2
(c) N3
(d)
Ans: (d)
Species with sp2 hybridisation are plane triangular in shape. Among the given species  is sp2 hybridised with no lone pair of electrons on central atom, N. Whereas, N3,
is sp2 hybridised with no lone pair of electrons on central atom, N. Whereas, N3,  and CO2 are sp hybridised with a linear shape.
and CO2 are sp hybridised with a linear shape.
Q2: Which of the following molecules has the maximum dipole moment ? (NEET / AIPMT 2014)
(a) NH3
(b) NF3
(c) CO2
(d) CH4
Ans: (a)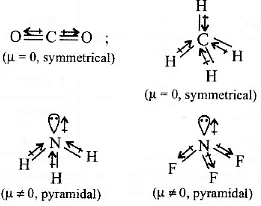
In NH3, H is less electronegative than N and hence dipoie moment of each N - H bond is towards N and create high net dipole moment whereas in NF3 ,F is more electronegative than N, the dipole moment of each N - F bond is opposite to that of lone pair, hence reducing the net dipole moment.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - Chemistry Class 11
| 1. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding? |  |
| 2. How does the VSEPR theory help predict the molecular geometry of a molecule? |  |
| 3. What is hybridization and how does it influence the bonding in a molecule? |  |
| 4. How does electronegativity play a role in determining the type of bond formed between two atoms? |  |
| 5. What is resonance in chemical bonding and how does it affect the stability of molecules? |  |

















