Class 10 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 5 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Class-X
Science-086
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2019-20
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions:
1. The question paper comprises three sections - A, B and C. Attempt all the sections.
2. All questions are compulsory.
3. Internal choice is given in each section.
4. All questions in Section A are one - mark questions comprising MCQ, VSA type and
assertion-reason type questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
5. All questions in Section B are three - mark, short - answer type questions. These are to be answered in about 50 - 60 words each.
6. All questions in Section C are five - mark, long - answer type questions. These are to be answered in about 80 - 90 words each.
7. This question paper consists of a total of 30 questions.
Section A
Q.1. Ankit told his sister that the electronic configuration of fluorine (F) is 2,7. Then, asked her to identify what type of bond is present in the F2 molecule. (1 Mark)
Ans: The bond present in F2 molecule is formed by sharing of electrons, hence, it is a covalent bond.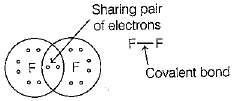
Q.2. The range of vision of a normal human eye is from (1 Mark)
(a) 100 m to 25 cm
(b) infinity to 25 m
(c) 1 km to 25 cm
(d) infinity to 25 cm
Ans: (d) The normal range of vision for a human eye is from infinity to 25 cm.
Q.3. Answer question numbers 3(a) - 3(d) on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts.
Another traditional source of energy was the kinetic energy of flowing water or the potential energy of water at a height. Hydro power plants convert the potential energy of falling water into electricity. Since there are very few waterfalls, which could be used as a source of potential energy, hydro power plants are associated with dams. In the last century, a large number of dams were built all over the world. Hydropower plants meet a quarter (25%) of our energy requirement in India.
In order to produce hydel electricity, high-rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water and thereby collect water in larger reservoirs.
The water level rises and in this process the kinetic energy of flowing water gets transformed into potential energy. The water from the high level in the dam is carried through pipes, to the turbine, at the bottom of the dam. Since the water in the reservoir would be refilled each time it rains (hydro power is a renewable source of energy) we would not have to worry about hydroelectricity sources getting used up the way fossil fuels would get finished one day. But, constructions of big dams have certain problems associated with it. The dams can be constructed only in a limited number of places, preferably in hilly terrains. Large areas of agricultural land and human habitation are to be sacrificed as they get submerged. Large eco-systems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dams. The vegetation which is submerged rots under anaerobic conditions and gives rise to large amounts of methane which is also a green-house gas. It creates the problem of satisfactory rehabilitation of displaced people. Opposition to the construction of Tehri Dam on the river Ganga and Sardar Sarovar project on the river Narmada are due to such problems.
(a) What percentage of our energy requirements is met by hydroelectric power? (1 Mark)
(b) What sort of transformation in energy occurs in a hydroelectric plant? (1 Mark)
(c) What problems are associated with construction of dams? (1 Mark)
(d) What type of energy is hydro power? (1 Mark)
Ans: (a) 25 %.
(b) The kinetic energy of running water is converted into electrical energy.
(c) The dams can be constructed only in a limited number of places, preferably in hilly terrains. Large areas of agricultural land and human habitation are to be sacrificed as they get submerged. Large eco-systems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dams.
(d) Renewable.
Q.4. For Q. Nos. 4(i)-4(iv) are based on the table given below. Study these table related to answer the questions that follow :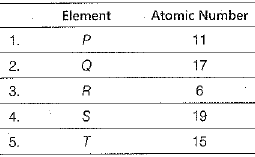
Answer the questions given below :
(i) Which of the given elements can be cut with a knife? (1 Mark)
(ii) Which element can form an ionic compound with Q? (1 Mark)
(iii) The allotrope of which of these elements is a good conductor of electricity? (1 Mark)
(a)P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
(iv) Which pair of elements are stored in kerosene? (1 Mark)
(a) P and S
(b) Q and R
(c) R and T
(d) Q and T
Ans: (i) Element P (Na) can be cut with a knife.
(ii) Element P (Na) can form an ionic compound with Q (Cl).
(iii) (c) The allotrope of element R(C), that is graphite, is a good conductor of electricity.
(iv) (a) The elements P and S (Na and K) are stored in kerosene.
Q.5. The most important safety method used in domestic electrical circuit so as to protect home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is (1 Mark)
(a) earthing.
(b) use of fuse of appropriate rating.
(c) use of voltage stabilisers.
(d) use of an electric meter.
Ans: (b) The most important safety device used in domestic electrical circuit so as to protect home appliances from short circuiting or over loading, is a fuse of appropriate current reading connected in the beginning of the circuit after the electric meter.
Q.6. Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit? (1 Mark)
(a) I2R
(b) IR2
(c) VI
(d) V2/R
Ans: (b)
Q.7. Vegetative propagation refers to the production of new plants from (1 Mark)
(a) roots, stems and leaves
(b) roots, stems and flowers
(c) flowers, fruits and stems
(d) flowers, leaves and stems
Ans: (a) Vegetative propagation refers to the production of new plants from roots, stems and leaves. The property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses and grapes.
Q.8. In the process of anodising the (1 Mark)
(a) article is made the anode
(b) an oxide layer is formed on the article
(c) the oxide layer can be dyed
(d) all the above
Ans: (d) all the above
Q.9. Which of the fallowing is not an advantage of vegetative propagation? (1 Mark)
(a) Plants which produce non-viable seeds can be grown.
(b) Easier method than sowing seeds.
(c) Such plants produce seeds and fruits much earlier than plants produced from other methods.
(d) Best method to introduce new genetic traits in the species.
Ans: (d)
Q.10. Which of the following pairs of animals belong to the same trophic level? (1 Mark)
(a) Lizard and snake
(b) Lizard and hawk
(c) Mouse and snake
(d) Rabbit and hawk
Or
In a food chain, the first trophic level will always be occupied by
(a) consumers
(b) producers
(c) decomposers
(d) secondary consumers
Ans: (a) Lizard and snake belong to the same trophic level in a grassland ecosystem. In a food web of a grassland ecosystem, two possible food chains are as follows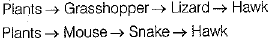
So, snake and lizard belong to the same trophic level, i.e, third trophic level.
Or
(b) Producers are plants that prepare food using sunlight and other raw materials. Hence, they always occupy first level in food chains.
Q.11. The junction of optic nerve and the retina in the eye is called __________ and __________ is possible here. (1 Mark)
Ans: blind spot, no vision
Q.12. Structural formula of ethyne is: (1 Mark)
(a) H - C ≡ C - H
(b) H3 - C ≡ C - H
(c) 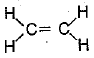
(d) 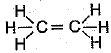
Or
The name of the compound
CH3 - CH2 - CHO is:
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethana
Ans: (a) or (a)
For question numbers 13 and 14, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below
(i) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation o f the assertion.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A is false but R is true.
Q.13. In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given by the corresponding statement of Reason. Of the statements, mark the correct answer as (1 Mark)
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Assertion Evolution is impossible without variations.
Reason Only useful variations are transmitted to the next generation.
Ans: (c) Variations are the basic pre-requisite and progressive factor for evolution because without variations, no change could occur in individuals and evolution would have been impossible. According to the natural selection theory, only useful variations are transmitted to the next generation, but sometimes small variations which are not useful for organisms are also inherited.
Q.14. One lim itation of Mendeleev’s classification is that it could not assign a position to hydrogen. (1 Mark)
Ans: True
SECTION B
Q.15. The diagram shown below is of electrolytic refining of copper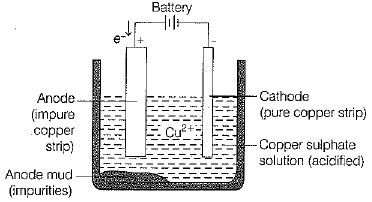
In this process, a thick block of impure metal is used as anode and a thin strip of pure metal is used as cathode. A solution of metal is used as an electrolyte.
Draw your own conclusion from the given figure and information and describe it stepwise. (3 Mark)
Ans: (i) When electric current is passed, copper ions from the electrolyte are reduced as copper which get deposited on the cathode.
(ii) An equivalent amount of pure copper from the anode get oxidised to copper ion and goes into the solution and from there, it goes to cathode and gets deposited.
(iii) Copper is refined. The reactions takes place as follows:
At cathode 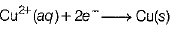
At anode 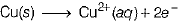
This cycle is repeated until whole of the copper ion from impure block is dissolved and deposited on cathode.
Q.16. Two circular coils P and Q are kept close to each other, of which coil P carries a current. What will you observe in the galvanometer connected across the coil Q
(а) if current in the coil P is changed?
(b) if both the coils are moved in the same direction with the same speed?
Give reason to justify your answer in each case. (3 Mark)
Ans: (a) When current in the coil P is changed, the magnetic field developed in neighbouring coil Q changes. As a result, an induced current is produced in coil Q and the galvanometer connected across it gives a deflection.
(b) If both the coils P and Q are moved in the same direction with the same speed, there is no relative motion between the two coils. So the magnetic field of coil Q remains unchanged and no current is induced in it. As a result the galvanometer does not show any deflection.
Q.17. The elements Be, Mg and Ca each having two electrons in their outermost shells are in periods 2, 3 and 4 respectively of the modem periodic table. Answer the following questions, giving justification in each case:
(i) Write the group to which these elements belotig.
(ii) Name the least reactive element.
(iii) Name the element having largest atomic radius. (3 Mark)
Ans: (i) Group 2 because they have same number of valence electrons.
(ii) Be, because chemical reactivity increases for metals in a group from top to bottom.
(iii) Ca, as the atomic size increases from top to bottom in a group/as Ca has four shells.
Q.18. What is meant by esterification and saponification reactions of organic compounds. Explain with the help of chemical equation for each. What is the use of
(i) esters and (ii) saponification process? (3 Mark)
Ans: Esterification It is a process in which alcohol and carboxylic acid combine in the presence of cone. H2SO4 to form an ester.
Saponification When an ester reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium salt of acid (soap) and alcohol is formed. This process for the preparation of soap is known as saponification.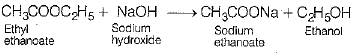
(i) Esters are used in cold drinks, ice creams, perfumes and as an artificial flavouring agents.
(ii) Saponification process is used in the manufacture of soaps.
Q.19. A white powder is added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking. (3 Mark)
Ans: The white powder (baking powder) is a mixture of sodium hydrogencarbonate and tartaric acid.
Sodium hydrogencarbonate releases carbon dioxide gas which makes the cake soft and fluffy. Tartaric acid neutralises th e bitter taste of the salt.
Equation for the reaction is given as under: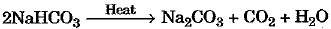
Q.20. Explain the terms analogous and homologous organs with examples. (3 Mark)
Ans: Homologous organs are those organs having similar basic structure but has been modified to perform different functions, e.g., forelimbs of reptiles, frog, lizard, bird and human (amphibians and mammals) are homologous organs. Such homologous characteristic helps to identify an evolutionary relationship between apparently different species. Analogous organs are those organs which are different in basic structure but perform same function, e.g., wings of bat and wings of birds.
Q.21. An electrical circuit is shown below: (3 Mark) 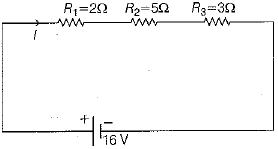
Find the potential difference across resistance R1, R2 and R3.
Ans: Equivalent resistance of the circuit,
Req = r1 + r2 + r3 [For series combination]
= 2 + 5 + 3 = 10Ω
Current, 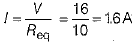
∴ Voltage across R1, R2 and R3 are V1, V2 and V5 respectively, then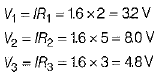
Alternate solution
Using voltage division rule,
Voltage or potential difference across resistance R1,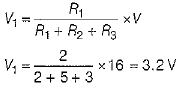
Voltage across resistance R2,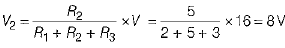
Voltage across resistance R3,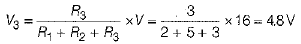
Q.22. (a) Write two water conducting tissues present in plants. How does water enter continuously into the root xylem?
(b) Explain why plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. (3 Mark)
Ans: (a) Water conducting tissue is xylem and its two components that conduct water are xylem tracheids and xylem vessels.
In xylem tissue, vessels and tracheids of the roots, stems and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant. The root hair which are in contact with the soil actively take up mineral ions. This creates a difference in the concentration of these ions between the root and the soil. Water, therefore, moves into the root from the soil to eliminate this difference. This means that there is steady movement of water into root xylem, creating a column of water that is steadily pushed upwards.
(b) Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals because -
(i) They are not mobile and hence do not require energy for locomotion.
(ii) They do not need to digest food.
(iii) Their waste products are fewer and either released through leaves or roots.
(iv) Most of their body is made of dead cells which provide rigidity and strength to the plant body.
Hence, their energy requirements are low.
Q.23. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near point A. In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through A and there is no change in the deflection of the compass? Under what condition is the deflection maximum and why? (3 Mark)
Ans: In the plane of the paper itself. The axis of the compass is vertical and the field due to the conductor is also vertical. It could result in a dip of compass needle which is not possible in this case (dips result only if axis of compass is horizontal). The deflection is maximum when the conductor through A is perpendicular to the plane of paper and the field due to it is maximum in the plane of the paper.
Q.24. RBCs act as the carrier for oxygen. Analyse and evaluate the adaptations RBCs have for this function. (3 Mark)
Ans: Adaptations of RBCs to act as oxygen carrier are as follows
(a) They have biconcave shape, which increases their surface area over volume.
(b) They contain haemoglobin (Hb), which binds to oxygen for its efficient transport.
(c) They have no nucleus, which helps to make space for haemoglobin.
Section C
Q.25. Describe three industrial uses of caustic soda. What happens when caustic soda reacts with:
(i) ZnO
(ii) CO2
(iii) HCl
Or
State reason for the following statements:
(i) Tap water conducts electricity, whereas distilled water does not.
(ii) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas dilute hydrochloric acid does.
(iii) During summer season, a milk man usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(iv) The concentration of H3O+ ions decreases on diluting the acid.
(v) Curd and sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels. (5 Mark)
Ans: Caustic soda (sodium hydroxide, NaOH) is used
• for mercerizing cotton fabrics in textile industry.
• to manufacture the soap, paper, dyes etc.
• in petroleum refining.
Reaction of caustic soda with ZnO, CO2 and HCl takes place as follows:
(i) Reaction with ZnO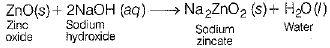
(ii) Reaction with CO2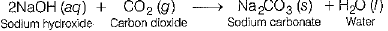
(iii) Reaction with HCl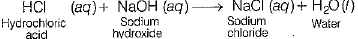
Or
(i) Tap water contains ions which conduct electricity. Distilled water does not contain any ions.
(ii) Dry HCI does not produce ions but dilute HCl gives H+ and Cl- , thus turns blue litmus red.
(iii) Baking soda does not allow milk to change into lactic acid, which makes milk sour.
(iv) An acid dissociates into hydronium ions (H3O+)an d anions when dissolved in water. On diluting an acidic solution, the volume of the solution increases but the number of ions remains the same and thus, the concentration of H3O+ ions per unit volume decreases.
(v) Curd and sour substances contain acid which react with Cu and brass to form certain salts that are poisonous in nature and can cause food poisoning.
Q.26. Compare the power used in 2Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: (5 Mark) 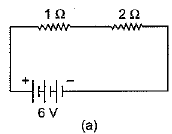
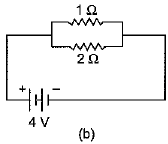
Or
A bulb is rated 40 W; 220 V. Find the current drawn by it, when it is connected to a 220 V supply. Also find its resistance. If the given bulb is replaced by a bulb of rating 25 W; 220 V, will there be any change in the value of current and resistance? Justify your answer and determine the change.
Ans: In the circuit (a), Voltage V = 6 V, resistances of R1 = 1Ω and R2 = 2Ω are connected in series, hence equivalent resistance R = R1 + R2 = 1 + 2 = 3Ω
∴ Current flowing through the circuit 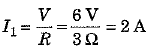
∴ Power used in resistance R2 = 2Ω, is given as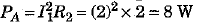
In the circuit (b), Voltage V = 4 V. Now resistances of R1 = 1 Ω and R2 = 2 Ω are connected in parallel. Hence, current flowing through 2 Ω resistance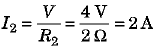
∴ Power used in resistance R2 = 2 Ω, is given as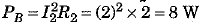
⇒ 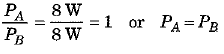
Or
Bulb A is rated as 40 W, 220 V. Thus, power of bulb A, PA = 40 W when voltage V = 220 V.
∴ Current drawn by bulb A, 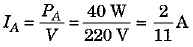
and resistance of bulb A, 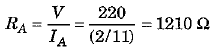
Since bulb B is rated as 25 W, 220 V, its power is PB = 25 W when voltage V = 220 V. Since power of bulb B is different from power of A, current drawn by it and its resistance will be different.
∴ Current drawn by bulb B, 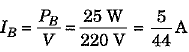
and resistance of bulb B, 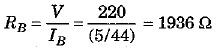
Q.27. (a) Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
(b) What is the role of the add in our stomach? (5 Mark)
Ans: (a) The raw materials for photosynthesis are : carbon dioxide and water. The plants get carbon dioxide (in gaseous form) horn the atmosphere (through stomata) while the water is obtained from soil (through roots). The energy required for this process is received by chlorophyll from sun in the form of light.
(b) The hydrochloric acid (secreted by gastric glands) in our stomach creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin (otherwise this enzyme is present in our stomach in its inactive form pepsinogen).
Q.28. The elements of second period are given below:
Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne
(i) Identify whether Be and O are metals or non-metals.
(ii) Identify the elements that respectively has
(a) largest radius
(b) smallest radius
(iii) Give reason for the variation in atomic radii. (5 Mark)
Ans: (i) Be is a metal, whereas O is a non-metal.
(ii) (a) Li has the largest radius.
(b) Ne has the smallest radius.
(iii) Atomic radius decreases on moving from left to right along a period. This is due to an increase in nuclear charge, which tends to pull the valence electrons closer to the nucleus.
Q.29. (a) Distinguish between cross-pollination and self-pollination. Mention the site and product of fertilisation in a flower.
(b) Draw labelled diagram of a pistil showing the following parts:
Stigma, Style, Ovary, Female germ cell
Or
(a) Draw a diagram of human female reproductive system and label the parts:
(i) which produces an egg.
(ii) where fertilisation takes place.
(b) List two bacterial diseases which are transmitted sexually.
(c) What are contraceptive devices? Give two reasons for adopting contraceptive devices in humans. (5 Mark)
Ans: (a)
| Self-pollination | Cross-pollination |
| Transfer of pollen from anther of a flower to stigma of same flower. | Transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower; to the stigma of another flower- of same or different plants, of same species. |
| Only one flow er is involved. | Two flowers are involved. |
| No external agency required. | External agency like wind, water, insects, bird etc., are needed. |
Site of fertilisation is Ovary.
Product of fertilisation is Zygote
(b)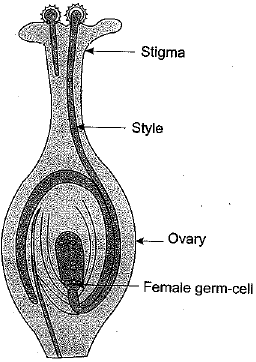
Or,
(a)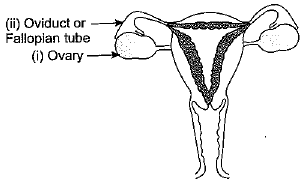
(i) Ovary - Produces egg
(ii) Oviduct - Site of fertilisation
(b) Two bacterial diseases that are sexually transmitted are - Syphilis and Gonorrhoea.
(c) Devices that are adopted to prevent pregnancy are the contraceptive devices. These may be chemicals or objects like hormonal pills, condoms, GuT etc.
Reasons for adopting contraceptive devices are:
• They help in spacing two children.
• Thus helps in maintaining a woman’s and child’s health.
• Better care and healthier society.
• Also prevention of sexually transmitted diseases on using condoms.
• More productivity and hence better economic status.
Q.30. An object 60 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens and its 30 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the object. What is the focal length of the lens?
Or
(i) If p, q and r denotes the object distance, image distance and the radius of curvature, respectively of a spherical mirror, then find out the relation between them.
(ii) Find the distance at which an object should be placed infront of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm to obtain an image of double its size. (5 Mark)
Ans: As, the image is formed on the screen, thus the image formed is real and inverted in nature.
Here, hi = 60 cm, h0=-30 cm
Let the object be kept at a distance x cm from the lens.
⇒ Image distance, v = (40 - x), f =?
As, we know, magnification, 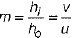
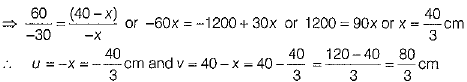
Substituting the values of u and v in the lens formula, we get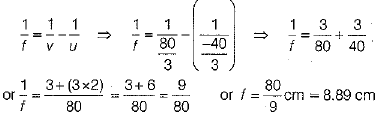
∴ Focal length of convex fens is 8.89 cm.
Or
(i) From mirror formula, 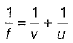
We have, 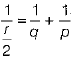
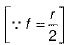
or 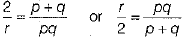
∴ 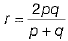
(ii) Focal length of lens, f = 10 cm
Distance of an object, u = ?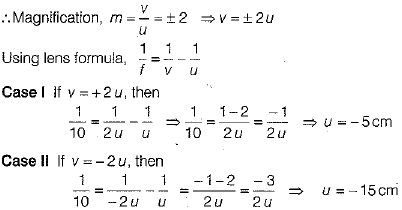
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 5 - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the format of the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Science (2019-20)? |  |
| 2. How can I access the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Science (2019-20)? |  |
| 3. Are the CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Science (2019-20) helpful for exam preparation? |  |
| 4. Can the CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Science (2019-20) be used as a study resource? |  |
| 5. How often are the CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Science (2019-20) updated? |  |
















