Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Practice Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Carbon forms covalent bonds primarily because it has _____ valence electrons in its outermost shell.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 4
Q2: The process of conversion of vegetable oils into solid fats is called ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Hydrogenation
Q3: Ethanol and methanol belong to the class of ______ alcohols.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Monohydric
Q4: The functional group present in carboxylic acids is ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: -COOH (Carboxyl)
Q5: Polymers are formed by the repeated attachment of ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Monomers
Short Answer Questions
Q6: How is the property of catenation related to carbon?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The property of catenation allows carbon atoms to form long chains, branched structures, and rings due to its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.
Q7: Give an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon and explain its structure.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ethene is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a double bond between two carbon atoms, allowing for rotation around the single bonds and restricted rotation around the double bond.
Q8: Why is ethanol considered a renewable source of energy?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ethanol is considered renewable because it can be produced from biomass such as sugarcane or corn, which are renewable resources. This makes ethanol a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Q9: Define isomerism and provide an example involving carbon compounds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Isomerism is the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. An example is butane and isobutane, both having the molecular formula C4H10 but different arrangements of carbon atoms.
Q10: How does the presence of a functional group affect the properties of organic compounds?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The presence of a functional group determines the chemical behavior and properties of organic compounds. For instance, the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group makes alcohols polar and capable of hydrogen bonding, affecting their solubility and boiling points.
Long Answer Questions
Q11: Describe the process of polymerization with an example of a synthetic polymer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Polymerization is the chemical reaction in which small molecules called monomers join together to form long chains known as polymers. For instance, in the polymerization of ethene, multiple ethene monomers undergo addition reactions, forming a polyethylene chain.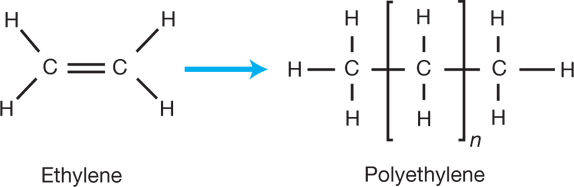
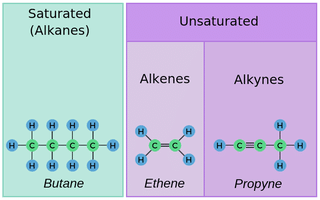
Q12: Compare and contrast the structures of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) have only single bonds between carbon atoms.
- They can have a straight chain or a branched chain structure.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes) have at least one double bond or triple bond between carbon atoms.
- These double or triple bonds limit the rotation of the carbon atoms.
- Due to this limitation, unsaturated hydrocarbons often have a planar structure.
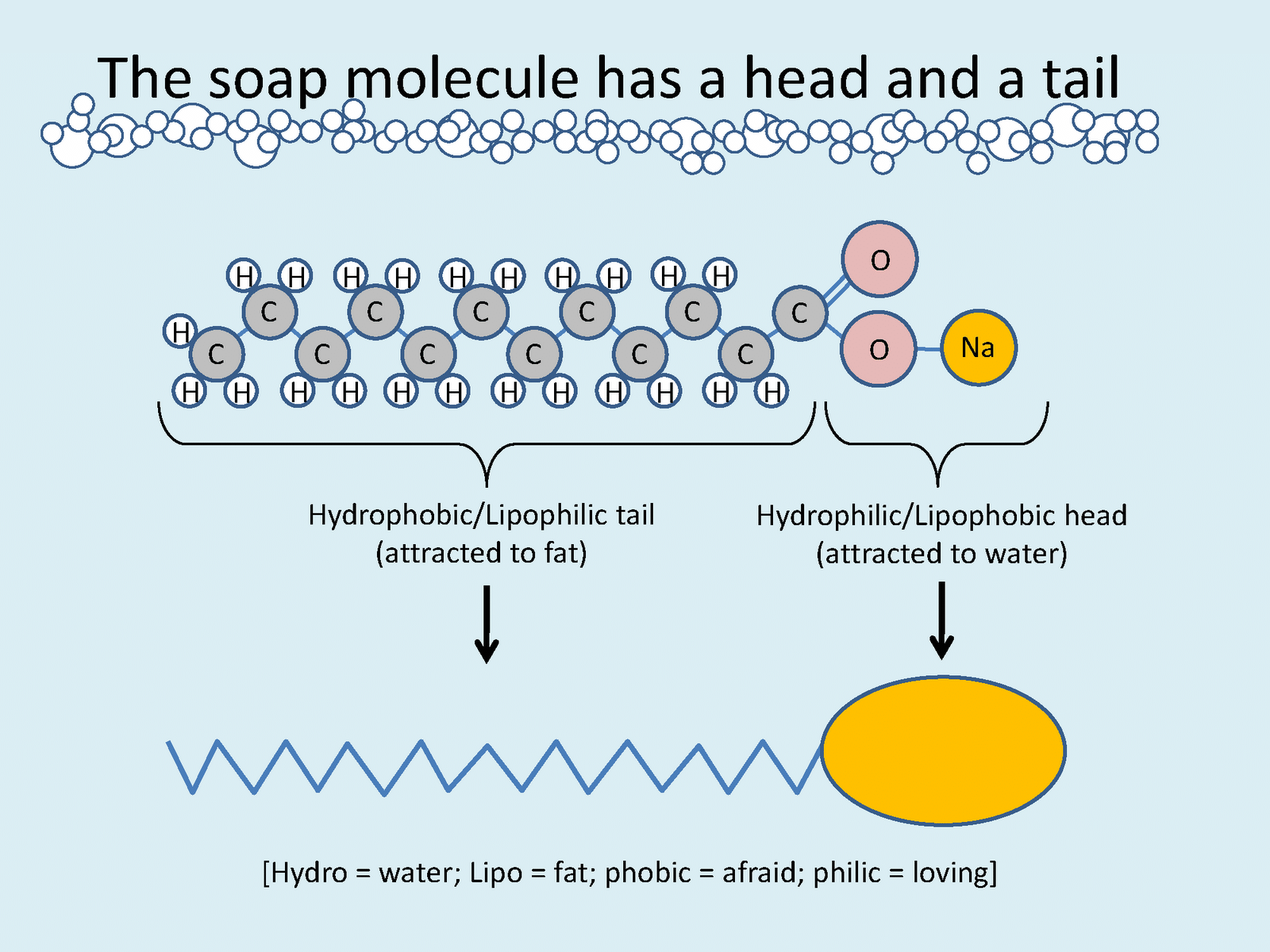
Q13: Explain the formation of a soap molecule using the process of saponification.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Saponification is a chemical reaction that occurs when fats and oils are hydrolyzed in the presence of an alkali, typically sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- This reaction involves the breaking of ester bonds present in triglycerides, which are the main components of fats and oils.
- The result of this process is the formation of soap molecules and glycerol as a byproduct.
- Soap molecules exhibit both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties, which enable them to effectively clean by emulsifying oils and fats in water.
- This dual nature of soap is what allows it to lift dirt and grease when mixed with water, making saponification a crucial process in soap-making and cleaning applications.
Q14: Define homologous series and provide an example from the carbon compounds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A homologous series is a group of organic compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties, but differing by a CH2 unit in their molecular formula. Example: Alkanes, where each member differs by -CH2 from the previous one.
Q15: Discuss the harmful effects of excessive carbon monoxide inhalation on human health.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, reducing their ability to transport oxygen. This can lead to oxygen deprivation in tissues, causing symptoms like headache, dizziness, and in severe cases, even death.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Practice Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
| 1. What are the main properties of carbon that make it essential for life? |  |
| 2. What are hydrocarbons, and what are their types? |  |
| 3. How does carbon form covalent bonds, and why is this important? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of carbon compounds in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of carbon compounds? |  |
















