UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is the apex statutory body for disaster management in India.

- The NDMA was formally constituted on 27th September 2006, in accordance with the Disaster Management Act, 2005 with Prime Minister as its Chairperson and nine other members, and one such member to be designated as Vice-Chairperson.
- Mandate: Its primary purpose is to coordinate response to natural or man-made disasters and for capacity-building in disaster resiliency and crisis response. It is also the apex body to lay down policies, plans, and guidelines for Disaster Management to ensure a timely and effective response to disasters.
- Vision: To build a safer and disaster-resilient India by a holistic, proactive, technology-driven, and sustainable development strategy that involves all stakeholders and fosters a culture of prevention, preparedness, and mitigation.
Evolution of NDMA
- In recognition of the importance of Disaster Management as a national priority, the Government of India set up a High-Powered Committee (HPC) in August 1999 and a National Committee after the Gujarat earthquake (2001), for making recommendations on the preparation of Disaster Management plans and suggesting effective mitigation mechanisms.
- The Tenth Five-Year Plan document also had, for the first time, a detailed chapter on Disaster Management.
- On 23 December 2005, the Government of India enacted the Disaster Management Act, which envisaged the creation of NDMA, headed by the Prime Minister.Question for Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)Try yourself:The NDMA was formally constituted on ________.View Solution
Functions and Responsibilities of NDMA
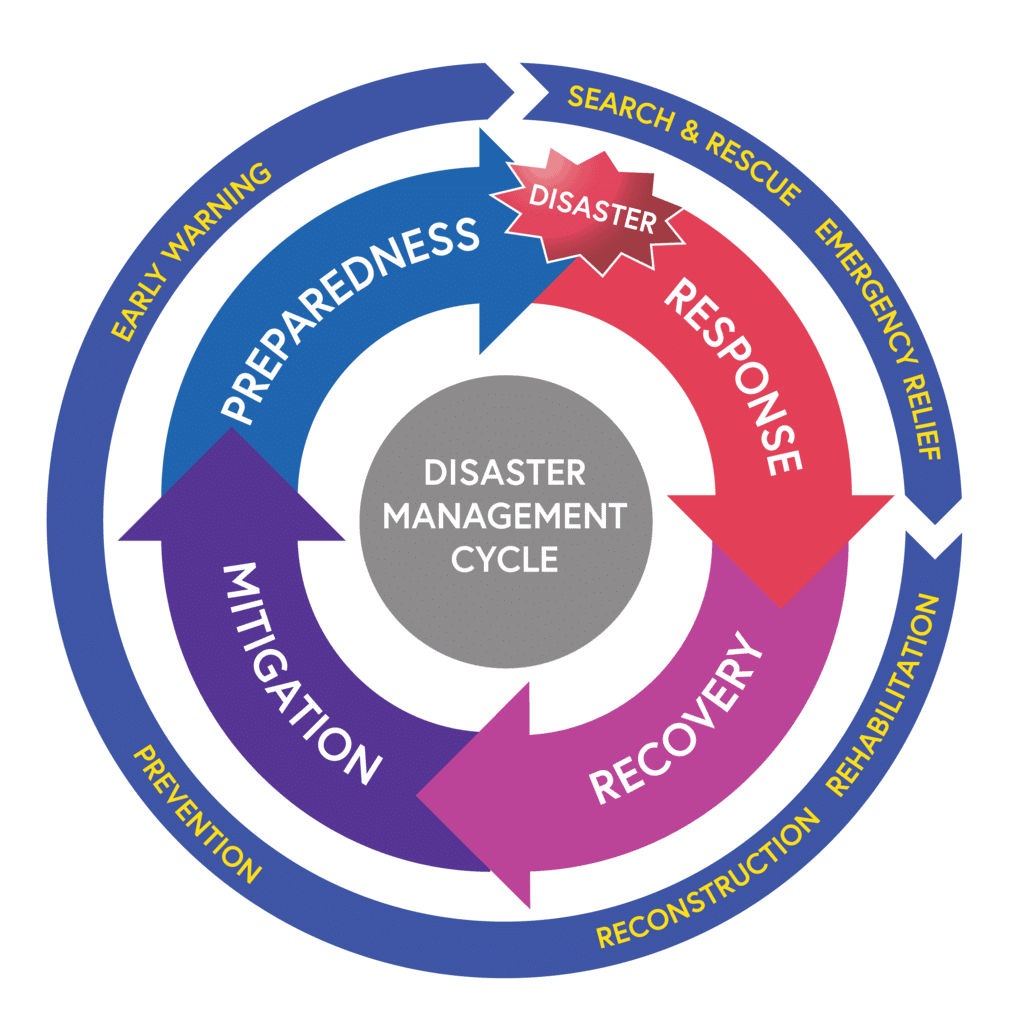 Disaster Management Cycle
Disaster Management Cycle
- Approve the National Disaster Plan
- Lay down policies on disaster management
- Approve plans prepared by Ministries or Departments of the Central Government in accordance with National Plan
- Lay down guidelines to be followed by State Authorities in drawing up State Plan
- Coordinate enforcement and implementation of disaster management policy and plan
- Recommend provision of funds for the purpose of mitigation
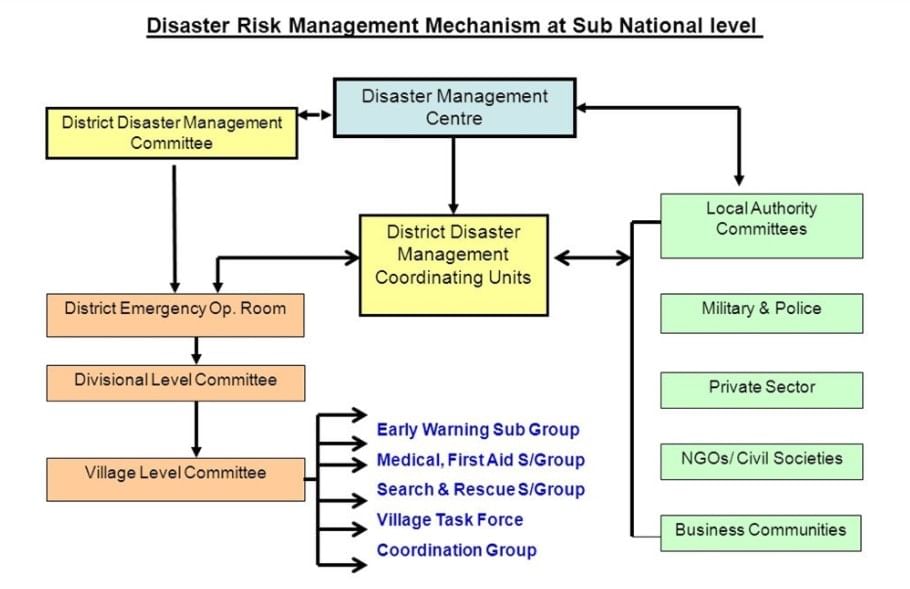
Institutional Framework for Disaster Management in India
- The Disaster Management Act, 2005 has provided the legal and institutional framework for disaster management in India at the national, state and district levels.
1. National Level Institutions
(i)
National Executive Committee (NEC)
- A National Executive Committee is constituted under Section 8 of DM Act, 2005 to assist the National Authority in the performance of its functions. Union Home secretary is its ex-officio chairperson.
- NEC has been given the responsibility to act as the coordinating and monitoring body for disaster management, to prepare a National Plan, monitor the implementation of National Policy, etc.
(ii) National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM)

- NIDM has the mandate of human resource development and capacity building for disaster management within the broad policies and guidelines laid down by the NDMA.
(iii) National Disaster response force (NDRF)
- NDRF is the specialized force for disaster response which works under the overall supervision and control of NDMA.
2. State-level Institutions
(i) State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA)
- Headed by the Chief Minister of the respective state, SDMA lays down the policies and plans for disaster management in the state.
- It is responsible to coordinate the implementation of the State Plan, recommend the provision of funds for mitigation and preparedness measures and review the developmental plans of the different departments of the state to ensure integration of prevention, preparedness and mitigation measures.
(ii) State Executive Committee (SEC)
- Headed by the Chief Secretary of the state, SEC has the responsibility for coordinating and monitoring the implementation of the National Policy, the National Plan, and the State Plan as provided under the DM Act.
3. District level Institutions
(i) District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA)
- Section 25 of the DM Act provides for the constitution of DDMA for every district of a state.
- The District Magistrate/ District Collector/Deputy Commissioner heads the Authority as Chairperson besides an elected representative of the local authority as Co-Chairperson except in the tribal areas where the Chief Executive Member of the District Council of Autonomous District is designated as Co-Chairperson. Further in the district, where Zila Parishad exists, its Chairperson shall be the Co-Chairperson of DDMA.
- The District Authority is responsible for planning, coordination, and implementation of disaster management and to take such measures for disaster management as provided in the guidelines.
- The District Authority also has the power to examine the construction in any area in the district to enforce the safety standards and to arrange for relief measures and respond to the disaster at the district level.
Achievements of Disaster Planning in India
- Cyclone Fani was one of the worst cyclones to hit India in the last two decades.
- Odisha's preparedness, efficient early warning system, timely action, and well-planned large-scale evacuation strategies helped 1.2 million people move safely into nearly 4,000 cyclone shelters, thereby saving the lives of vulnerable population in the sensitive coastal region.
- The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Deduction (UNIS DR) and other organizations have hailed government and volunteer efforts that have ensured the levels of destruction to keep minimum.
- Similarly, Andhra Pradesh demonstrated an equally excellent evacuation strategy for millions during cyclone Hudhud in 2014.
- There has been a significant reduction in mortality rate from the loss of over 10000 lives in 1999 during Super Cyclone in Odisha to a mortality of 16 in 2019 during cyclone Fani.
- NDMA runs intensive earthquake and extreme weather events awareness campaigns and provides guidelines regarding natural and man-made disasters.
- NDMA has released Guidelines on School Safety, Hospital Safety, and Minimum Standards for Shelter, Food, Water, Sanitation, and Medical Cover in Relief Camps.
Shortcomings and Challenges
- Questions were raised about the role of NDMA during Uttarakhand Flooding in 2013, where it failed to timely inform people about the flash floods and landslides. The post-disaster relief response had been equally poor.
- A CAG report noted that there were delays in the completion of projects under the flood management programs. It noted the projects were not taken up in an integrated manner and blamed NDMA for institutional failures for poor flood management.
- Devastations during Kerala Floods in 2018 and Chennai Floods in 2015 were eye-opening for the institutions regarding preparedness for the disaster situation.
- CAG report on 2015 Chennai Floods termed it to be a “man-made disaster'’ and holds Tamil Nadu government responsible for the catastrophe.
- The NDRF personnel lack sufficient training, equipment, facilities, and residential accommodation to tackle the crisis situation properly.
- Misutilization of Funds- The government constituted National Disaster Response Fund and State Disaster Response Fund to deal with the disasters.
Way Forward
- Policy guidelines at the macro level are needed that would inform and guide the preparation and implementation of disaster management and development plans across sectors.
- Building in a culture of preparedness and mitigation is the need of the hour.
- Operational guidelines should be framed for integrating disaster management practices into the development, and specific developmental schemes for prevention and mitigation of disasters.
- Robust early warning systems coupled with effective response plans at district, state, and national levels should be put in place.
- Community, NGOs, CSOs, and the media should be involved at all stages of disaster management.
- Climate risk management should be addressed through adaptation and mitigation.
- India should learn from best global practices.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)Try yourself:Which state demonstrated an equally excellent evacuation strategy for millions during cyclone Hudhud in 2014.
View Solution
The document Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|989 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)? |  |
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is a government agency in India responsible for disaster management at the national level. It was established in 2005 under the Disaster Management Act and operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
| 2. How has the NDMA evolved over time? |  |
The NDMA has evolved over time to strengthen disaster management in India. It has undergone institutional changes, such as the establishment of state-level and district-level institutions, to ensure effective coordination and response to disasters. The NDMA has also developed guidelines, policies, and plans for disaster management, and has played a crucial role in enhancing the country's preparedness and response capabilities.
| 3. What are the functions and responsibilities of the NDMA? |  |
The functions and responsibilities of the NDMA include:
- Formulating policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management.
- Coordinating and implementing measures for prevention, mitigation, and preparedness.
- Capacity building and training of various stakeholders involved in disaster management.
- Providing technical support and expertise to states and other agencies.
- Monitoring and evaluating the implementation of disaster management plans.
- Undertaking research and development activities in the field of disaster management.
| 4. What is the institutional framework for disaster management in India? |  |
The institutional framework for disaster management in India consists of three levels:
1. National Level Institutions: These include the NDMA, which is the apex body, and other national-level agencies involved in disaster management.
2. State-level Institutions: Each state in India has its own State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) responsible for disaster management at the state level. It coordinates with district-level institutions and implements disaster management plans.
3. District Level Institutions: These include the District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) responsible for disaster management at the district level. They coordinate with local administrations, NGOs, and other stakeholders for effective disaster response.
| 5. What are some achievements of disaster planning in India? |  |
Some achievements of disaster planning in India include:
- Development of national and state-level disaster management plans and policies.
- Enhanced coordination and collaboration among various stakeholders involved in disaster management.
- Improvement in early warning systems and disaster preparedness.
- Capacity building and training of personnel in disaster response.
- Implementation of measures for disaster mitigation and resilience.
- Successful response and recovery efforts during large-scale disasters such as cyclones, earthquakes, and floods.
Related Searches

















