Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Q1: Define a solenoid. Compare the magnetic field produced by a solenoid with that of a bar magnet?
Ans: A coil of many circular turns of wire wrapped in the shape of a cylinder, is called a solenoid. The magnetic field lines in a solenoid, through which current is passed, is very similar to that of a bar magnet. One end of the coil acts like a magnetic north pole, while the other acts like a south pole. The magnetic field produced by a long solenoid has all the properties of the field produced by a bar magnet.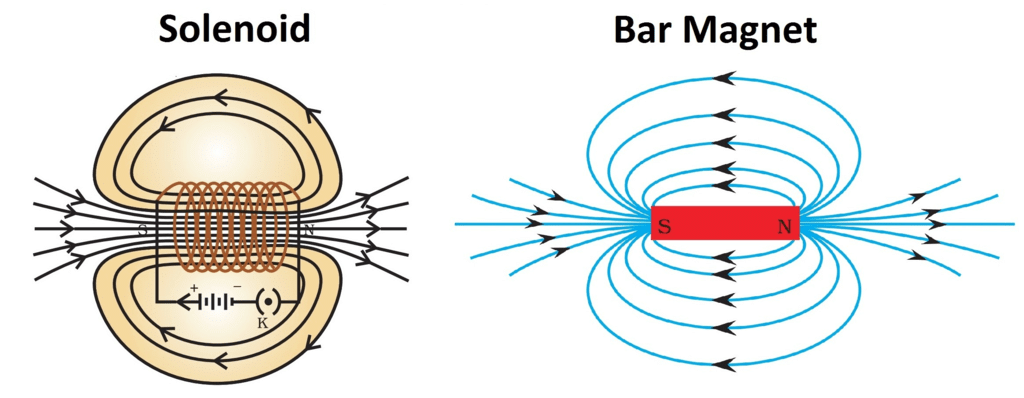
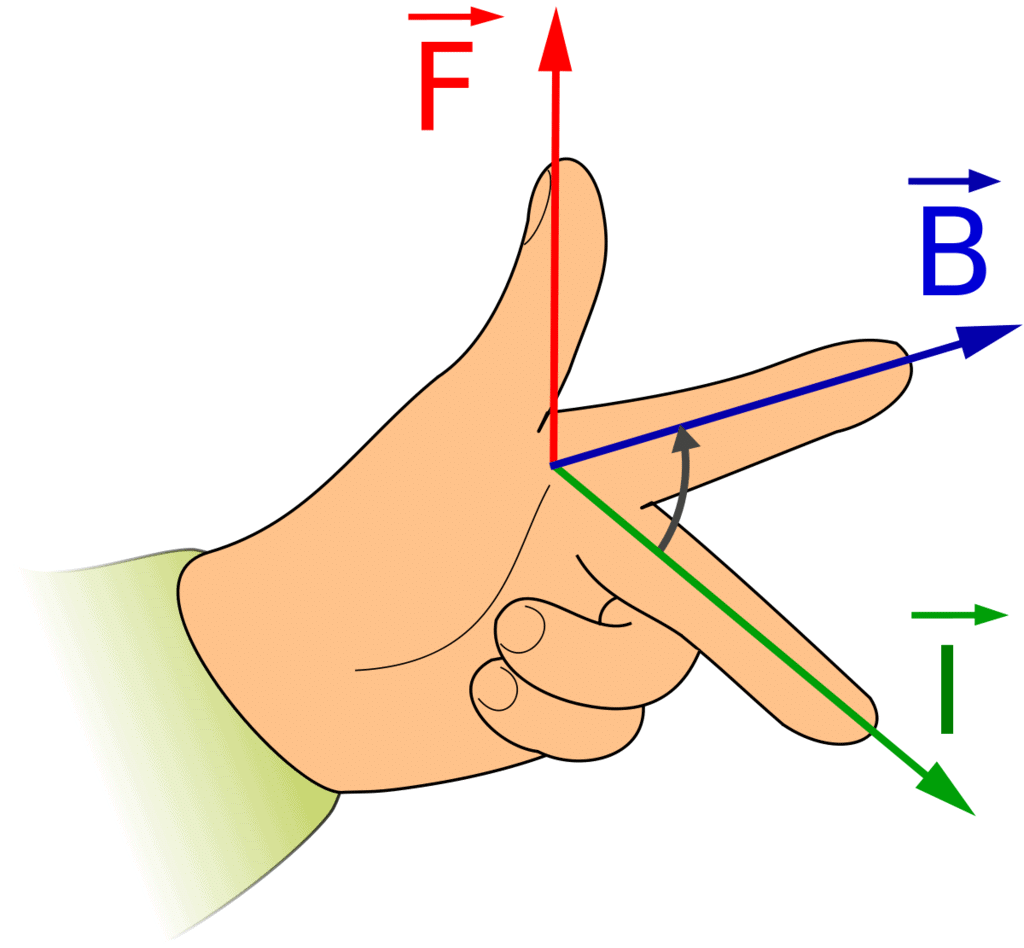
Q2: PQ is conductor × represents magnetic is ⊥ to the paper field and into the plane of the paper.
Ans: Fleming’s left-hand rule gives the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field. According to it, when the thumb, first finger and second finger of the left hand are kept perpendicular to each other such that the first finger points towards the direction of magnetic field, the central finger is along the direction of current, then the thumb shows the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
Q3: Define Electromotive force.
Ans: The motion of a magnet, with respect to the coil, produces an induced potential difference. This induced potential difference is called electromotive force which sets up an induced electric current in the circuit. The motion of a magnet, with respect to the coil, produces an induced potential difference.
Q4: What is meant by earthing? Why should electrical appliances be earthed?
Ans: The metal body of appliances like fridge, cooler, mixer etc. are connected to a an earth wire so that any leakage of current to the body of the appliance goes to the earth and does not give electric shock. This is called earthing. It is used as a safety measure in order to prevent electric shocks to the users.
Q5: What is a solenoid?
Ans: A solenoid is a long cylindrical conductor coil, having a large number of turns of insulated copper wire.
Q6 : What is a magnetic field?
Ans: The region around a magnet, in which the magnetic force of attraction and repulsion is felt, is called a magnetic field.
Q7: Distinguish between a solenoid and a bar magnet. Draw the magnetic lines for both
Ans:
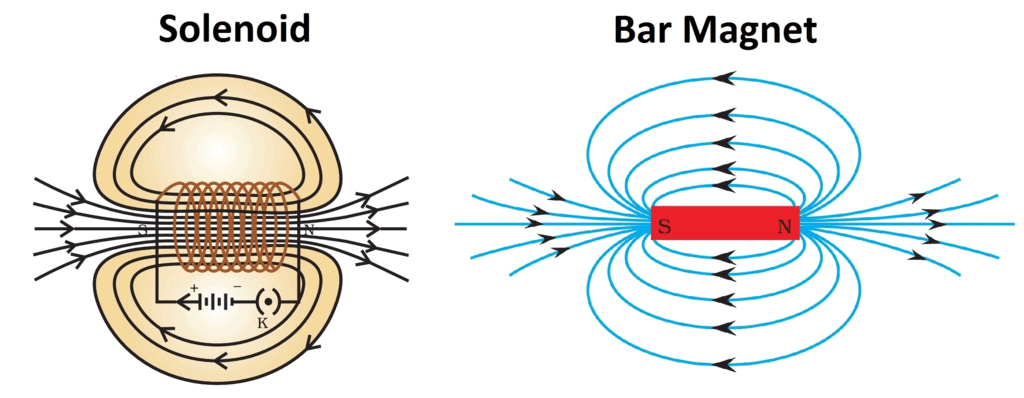 The solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced by the current carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. A solenoid is used for making electromagnets.Differences between a bar magnet and solenoid:
The solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced by the current carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. A solenoid is used for making electromagnets.Differences between a bar magnet and solenoid:
Bar magnet
It is a permanent magnet.
The strength of a bar magnet cannot be changed.
The polarity (North-South) of a bar magnet cannot be changed.
Solenoid
It is a temporary magnet. It acts as a magnet only as long as the current passes through it.
The strength of a solenoid can be changed by changing the number of turns in its coil or by changing the current passing through it.
The polarity of a solenoid can be changed by changing the direction of current in its coil.
Q8: What is electromagnetic induction? Explain how the movement of a magnet towards or away from a coil carrying a galvanometer produce current? Write the rule to find the direction of current in this above coil.
Ans: Whenever the magnetic field through a conductor changes, and induced current and e. m. f. is set up in the conductor. This is known as electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic induction is a process where a conductor placed in a changing magnetic field causes the production of a voltage across the conductor.
The rule being applied is Fleming's right-hand rule. Fleming’s right-hand rule is used to determine the direction of current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field. When the magnet is moved towards the coil, there is a change in the magnetic field which induces a current in the coil. The same thing will happen when the magnet is moved away.
Q9: Which effect of electric current is utilized in the working of an electric fuse?
Ans: An electric fuse works on the heating effect of current.
Q10: Name an instrument in which the directive property of a magnet is used.
Ans: Compass needle makes use of the directive property of a magnet.
Q11: Name the elements of Earth’s magnetic field.
Ans: The elements of Earth’s magnetic field are angle of dip, declination and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field.
Q12: Explain why, two magnetic lines of force do not intersect.
Ans: The magnetic lines of force do not intersect one another due to the fact that the resultant force on a north pole at any point can be only in one direction. But if the two magnetic lines of force intersect one another, then the resultant force on a north pole placed at the point of intersection will be along directions, which is not possible.
Q13: State the right-hand thumb rule.
Ans: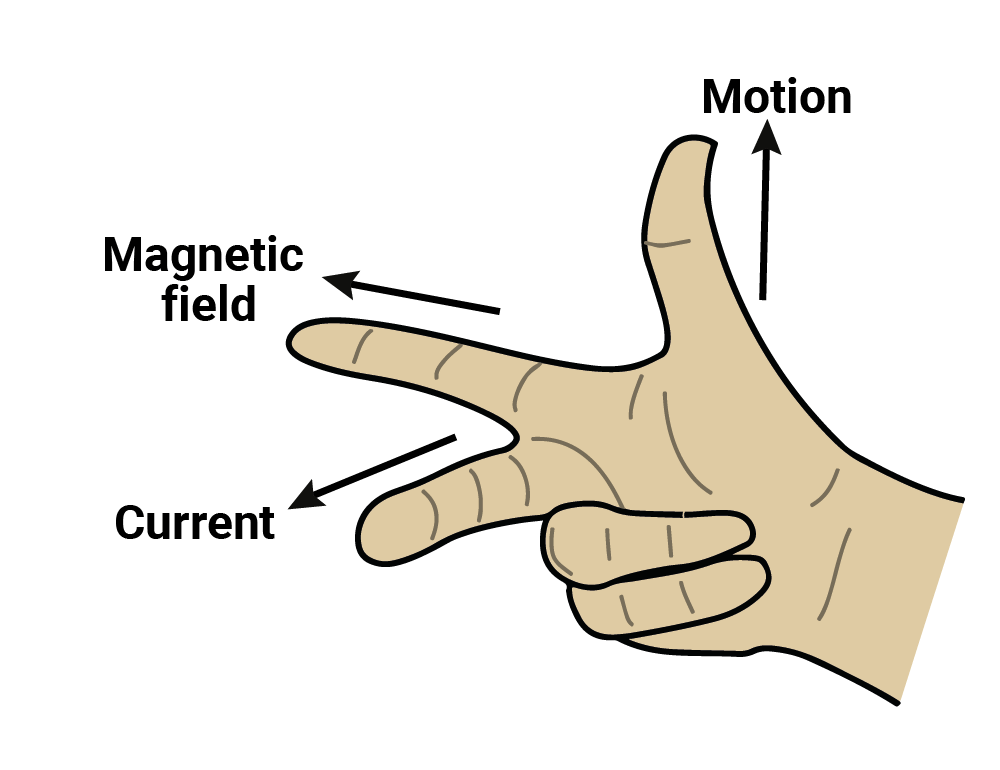
If you hold your right hand with the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger at right angles, you can determine the direction of induced current in a conductor.
- Point your forefinger in the direction of the magnetic field.
- Point your thumb in the direction of the motion of the conductor.
- The direction your middle finger points indicates the direction of the induced current.
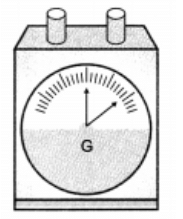
Q14: What is galvanometer?
Ans:
- A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit.
- The pointer remains at zero (the centre of the scale) for zero current flowing through it.
- It can deflect either to the left or to the right of the zero mark depending on the direction of current.
Q15: What is the role of fuse, used in series with any electrical appliance? Why should a fuse with defined rating not be replaced by one with larger rating?
Ans: Fuse is used for protecting appliances due to short-circuiting or overloading. The fuse is rated for a certain maximum current and blows off when a current more than the rated value flows through it. If a fuse is replaced by one with larger ratings, the appliances may get damaged while the protecting fuse does not burn off. This practice of using fuse of improper rating should always be avoided.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
| 1. What is the relationship between electric current and magnetism ? |  |
| 2. How can we demonstrate the magnetic effects of electric current in a simple experiment ? |  |
| 3. What are electromagnets and how are they used in everyday applications ? |  |
| 4. What is the right-hand rule in relation to magnetic fields generated by electric currents ? |  |
| 5. How does the strength of the magnetic field change with variations in electric current ? |  |

















