Mnemonics: Biomolecules | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Secondary Metabolites |

|
| 2. Some Proteins and their Functions |

|
| 3. Polysaccharides |

|
| 4. Nucleic Acids |

|
| 5. Classification of Enzymes |

|
Master Biomolecules with Ease! These memory tricks are sure to enhance your learning experience. Get ready to remember more and stress less! Happy learning!
1. Secondary Metabolites
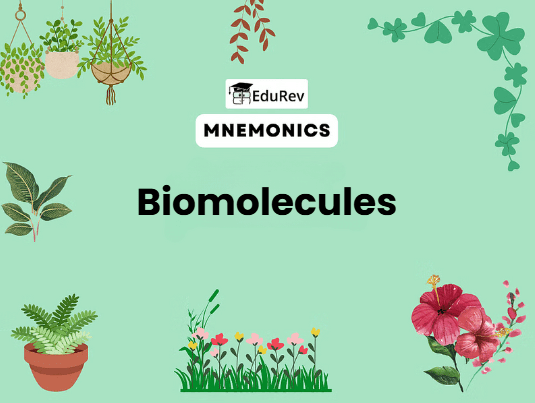
Mnemonic: Pigs And Tigers Eat Tasty Large Dishes Potatoes
Mnemonic Explanation:
- Pigments: Carotenoids, Anthocyanins, etc.
- Alkaloids: Morphine, Codeine, etc.
- Terpenoides: Monoterpenes, Diterpenes, etc.
- Essential oils: Lemon grass oil, etc.
- Toxins: Abrin, Ricin
- Lectins: Concanavalin A
- Drugs: Vinblastin, Curcumin, etc.
- Polymeric substances: Rubber, Gums, Cellulose
2. Some Proteins and their Functions
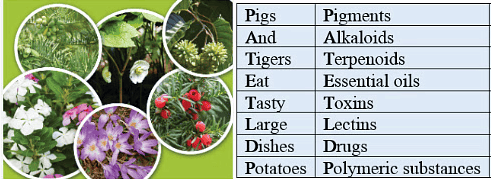
Mnemonic: Cool Tigers Instantly Attack Red Grapes
Mnemonic Explanation:
Collagen: Intercellular ground substance
Trypsin : Enzyme
Insulin: Hormone
Antibody:Fights infectious agents
Receptor: Sensory reception (smell, taste, hormone, etc.)
GLUT-4: Enables glucose transport into cells
3. Polysaccharides
Mnemonic: "Cats Sing Great Inspiring Chants Always"
- Cats = Cellulose: Forms plant cell walls and paper
- Sing = Starch: Energy storage in plants, forms helices
- Great = Glycogen: Energy storage in animals
- Inspiring = Inulin: Polymer of fructose
- Chants = Chitin: Found in exoskeletons of arthropods
- Always = Amino-sugars and chemically modified sugars (e.g., glucosamine, N-acetyl galactosamine)
4. Nucleic Acids
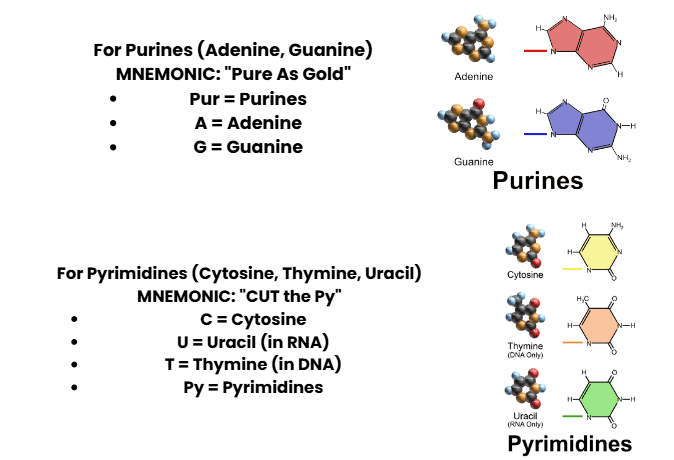
5. Classification of Enzymes
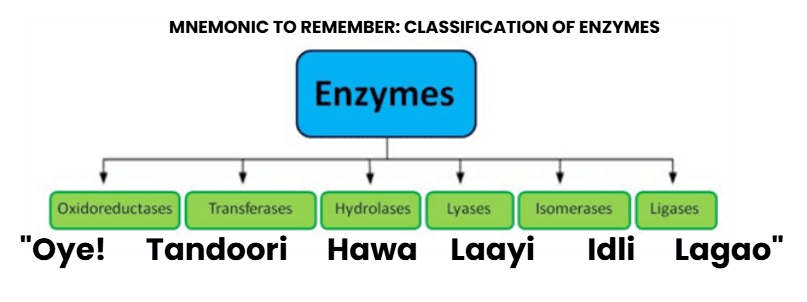 Mnemonic Explanation:
Mnemonic Explanation:
Oxidoreductases/Dehydrogenases:
Enzymes which catalyse oxidoreduction between two substrates S and S’.
Example:
S reduced + S’ oxidised → S oxidised + S’ reduced.
Transferases:
Enzymes catalysing a transfer of a group, G (other than hydrogen), between a pair of substrates S and S’.
Example:
S - G + S’ → S + S’ - G.
Hydrolases:
Enzymes catalysing hydrolysis of ester, ether, peptide, glycosidic, C-C, C-halide, or P-N bonds.
Lyases:
Enzymes that catalyse the removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis, leaving double bonds.
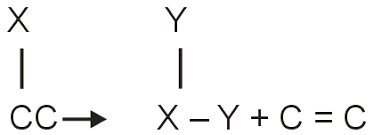
Isomerases:
Includes all enzymes catalysing inter-conversion of optical, geometric, or positional isomers.
Ligases:
Enzymes catalysing the linking together of two compounds.
Example:
Enzymes which catalyse joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, P-O, etc. bonds.
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Biomolecules - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are secondary metabolites and why are they important in plants? |  |
| 2. What are some key functions of proteins in biological systems? |  |
| 3. How are polysaccharides classified and what are their functions? |  |
| 4. What are the main types of nucleic acids and their functions? |  |
| 5. How are enzymes classified and what is their significance in biochemistry? |  |
















