Important Diagrams: Biomolecules | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
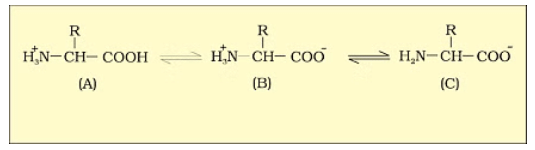
1. Zwitter Ion
A zwitter ion is a molecule or ion with both positive and negative regions of charge. In an aqueous solution, the carboxyl group of an amino acid can lose a proton, and the amino group can accept a proton, resulting in a dipolar ion called a zwitter ion.
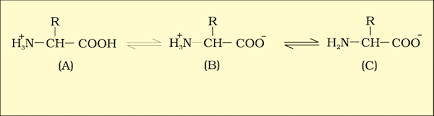 B is called zwitterionic form.
B is called zwitterionic form.
2. Carbohydrates, Amino acids, Lipids
Carbohydrates: Organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, primarily serving as a source of energy for living organisms. They can be simple sugars like glucose or complex molecules like starch and cellulose.
Amino Acids: Organic compounds with both amino and carboxyl groups attached to the same α-carbon. Their properties depend on the variable "R" group. Example: Glycine (R = H), Alanine (R = CH3).
Lipids: Hydrophobic molecules, often composed of glycerol and fatty acids. They can be fats, oils, or phospholipids. Examples include triglycerides and lecithin.
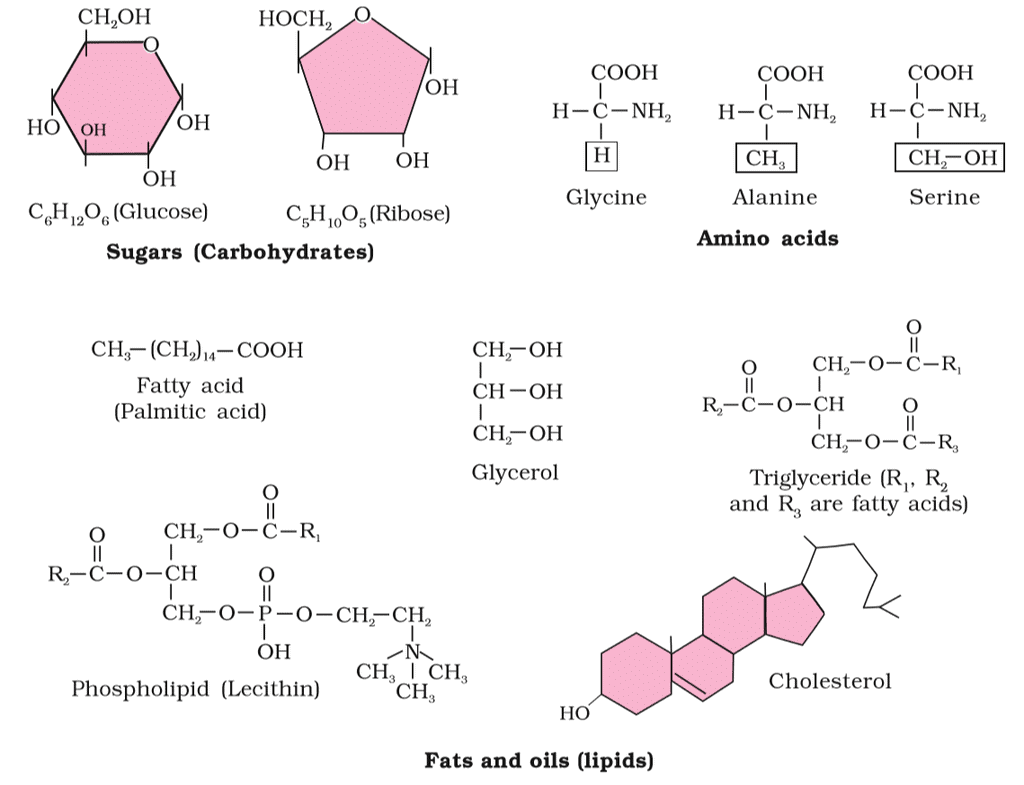 Carbohydrates, Amino acids and Lipids
Carbohydrates, Amino acids and Lipids
3. Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids: Polymers of nucleotides forming DNA and RNA, which store and transmit genetic information. DNA contains adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine bases.
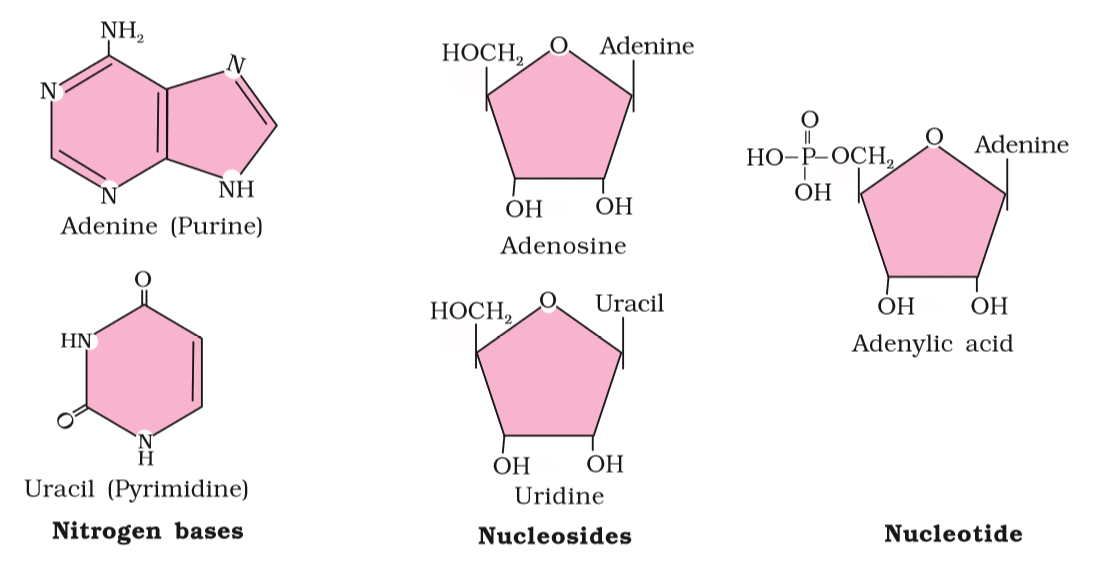
4. Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are long chains of sugars that function as energy storage or structural components in organisms. Examples include cellulose (a homopolymer of glucose), starch (energy storage in plants), and glycogen (energy storage in animals).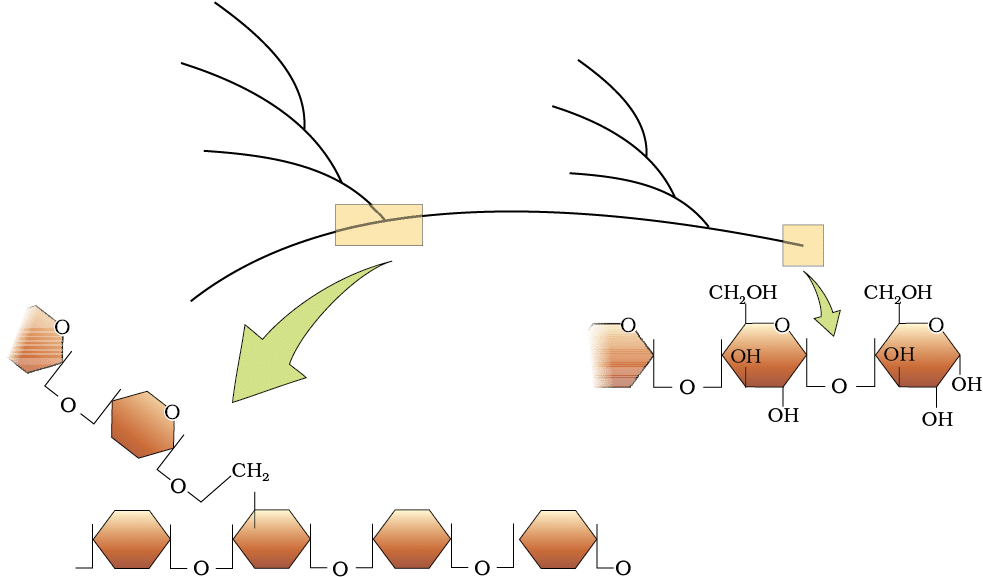 Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides
5. Various levels of Protein Structure
Primary Structure: The sequence of amino acids in a protein, determining the order from the N-terminal to the C-terminal.
Secondary Structure: Local folding of the protein chain into structures like α-helices and β-pleated sheets, held by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary Structure: The overall 3D folding of a single protein chain, critical for its biological function.
Quaternary Structure: The arrangement of multiple protein subunits into a functional unit, such as in hemoglobin with its four subunits.
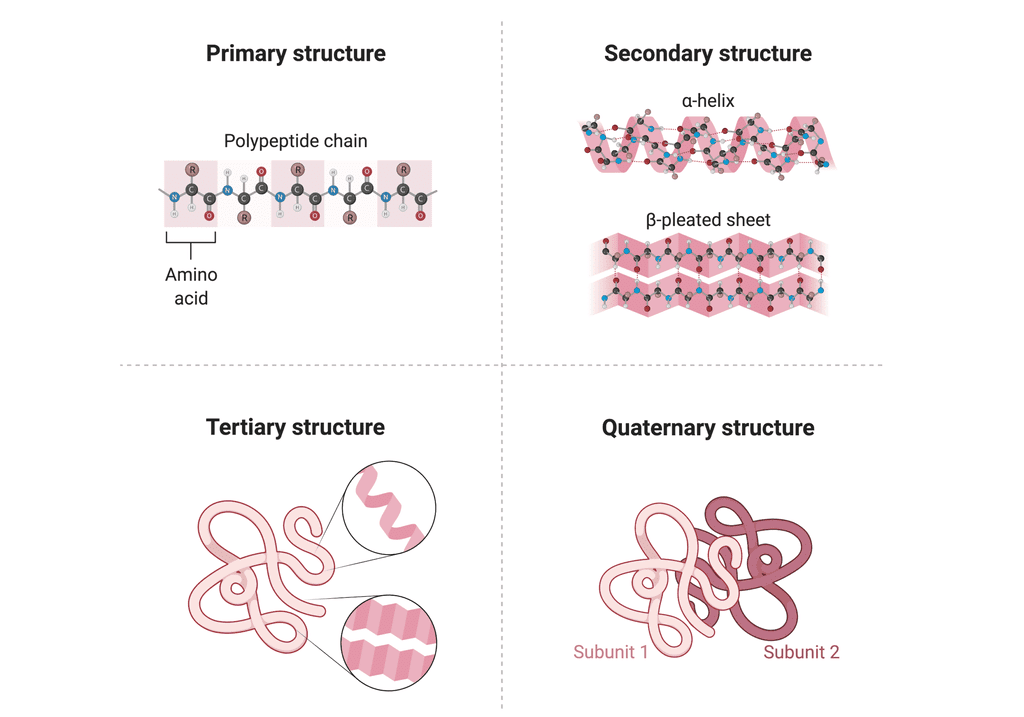 Various levels of Protein Structure
Various levels of Protein Structure
6. Concept of Activation Energy
The y-axis shows potential energy, and the x-axis represents the transformation of a reaction through a transition state. In exothermic reactions, the product (P) has lower energy than the substrate (S), and no extra energy is needed. Regardless of whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic, the substrate must pass through a high-energy transition state. The energy required to reach this state is called activation energy, which enzymes lower to make the reaction easier.
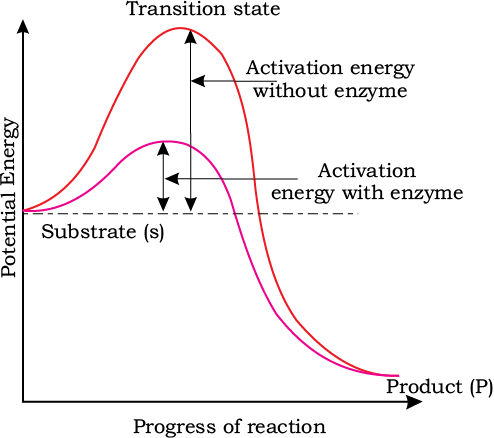 Concept of activation energy
Concept of activation energy
7. Effect of change in : (a) pH (b) Temperature and (c) Concentration of substrate on enzyme activity
Enzymes work best at specific temperatures and pH levels, with activity dropping outside of their optimal range. Increasing substrate concentration initially boosts reaction velocity, but it plateaus at Vmax once all enzymes are saturated. Enzyme activity can also be blocked by competitive inhibitors, which mimic the substrate and prevent binding.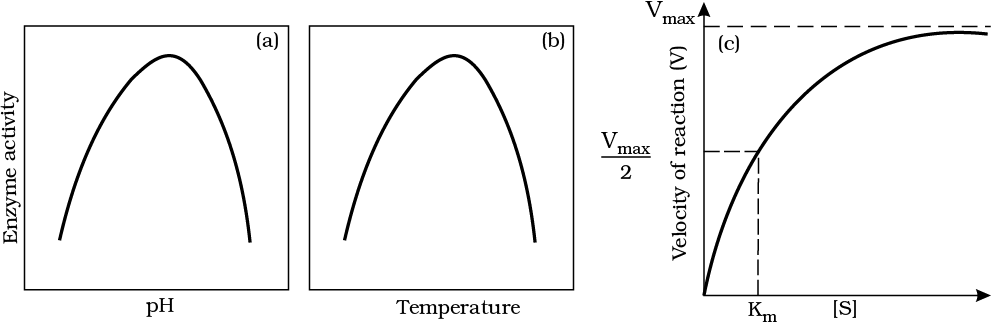 Effect of change in : (a) pH (b) Temperature and (c) Concentration of substrate on enzyme activity
Effect of change in : (a) pH (b) Temperature and (c) Concentration of substrate on enzyme activity
Diagram Based Questions NEET
Q1: Given below are two statements:
Statement I : Amino acids have a property of ionizable nature of −NH2 and −COOH groups, hence have different structures at different pH.
Statement-II : Amino acids can exist as Zwitterionic form at acidic and basic pH.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
Option (d) is the correct answer as statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
A particular property of amino acids is the ionizable nature of −NH2 and −COOH groups. Hence, in solutions of different pH, the structure of amino acid changes. Amino acid exists as a dipolar ion called a zwitterion at a particular pH called isoelectric point.
Q2: Which of the following describes the given graph correctly?
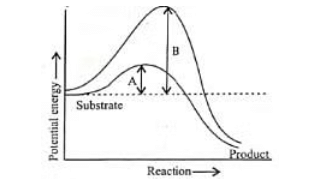
(a) Endothermic reaction with energy A in presence of enzyme and B in absence of enzyme.
(b) Exothermic reaction with energy A in presence of enzyme and B in absence of enzyme.
(c) Endothermic reaction with energy A in absence of enzyme and B in presence of enzyme.
(d) Exothermic reaction with energy A in absence of enzyme and B in presence of enzyme.
Ans: (b)
The graph shows the activation energies of catalyzed and uncatalyzed reations. A transition state is observed when the reactants are at the crest of the hump. At this state, they are ready to be converted to products. If the products are at a lower level than the reactants, the reaction is exothermic.
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Biomolecules - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the structure of an amino acid and how does it relate to its function in proteins? |  |
| 2. What is a zwitterion and how does it form in amino acids? |  |
| 3. What are nucleosides and nucleotides, and what is their significance in nucleic acids? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of bonds found in DNA and how do they contribute to its stability? |  |
| 5. What factors affect the activity of enzymes and how can they be manipulated in a laboratory setting? |  |






















