NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - Human Environment Interactions The Tropical and
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Answer the following questions. |

|
| 2. Tick the correct answer. |

|
| 3. Match the following. |

|
| 4. Give reasons. |

|
| 5. Map skills. |

|
| 6. For fun. |

|
| 7. Activity |

|
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) Name the continent in which the Amazon Basin is located.
Ans: The Amazon Basin is located in South America.
(ii) What are the crops grown by the people of the Amazon Basin.
Ans: The people of the Amazon Basin primarily cultivate the following crops:
- Tapioca
- Pineapple
- Sweet potato
- Manioc (also known as cassava)
- Cocoa
- Coffee
These crops are essential for their diet and are often grown using a method called slash and burn agriculture. This technique involves clearing land by cutting down trees and burning the remains to enrich the soil.
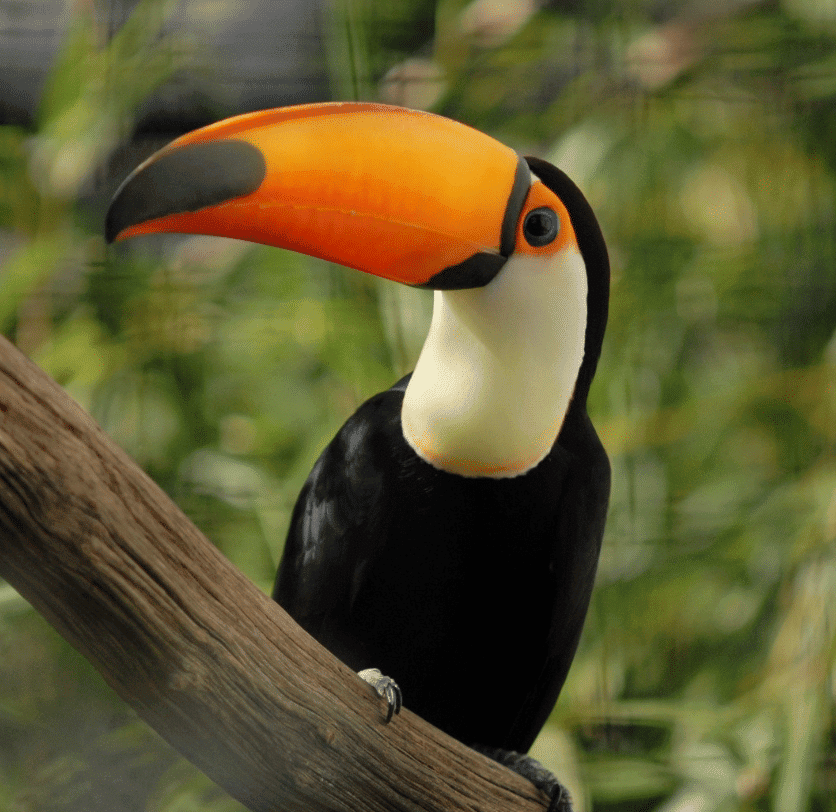
(iii) Name the birds that you are likely to find in the rainforests of the Amazon.
Ans: Toucans, hummingbirds, and macaws are commonly found in the Amazon rainforests. These birds are notable for their vibrant colours and distinctive features:
- Toucans: Known for their large, colourful bills.
- Hummingbirds: Recognised for their small size and rapid wing beats.
- Macaws: Famous for their brilliant plumage and social behaviour.
These birds play a vital role in the rich biodiversity of the Amazon rainforest.
(iv) What are the major cities located on the River Ganga?
Ans: The major cities located along the River Ganga include:
- Allahabad
- Kanpur
- Varanasi
- Patna
- Kolkata
All these cities have a population of over ten lakhs and play a significant role in the region.
(v) Where is the one-horned rhinoceros found?
Ans: The one-horned rhinoceros is mainly found in the Brahmaputra plain. This area is notable for its:
- Rich biodiversity
- Home to various wildlife species
It is an important habitat for this unique rhinoceros.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Toucans are a type of:
(a) birds
(b) animals
(c) crops
(d) trees
Ans: (a)
Toucans are colorful, tropical birds found in rainforests, particularly in Central and South America. They are known for their large, bright bills and are often associated with the Amazon Rainforest.
(ii) Manioc is the staple food of:
(a) Ganga Basin
(b) Africa
(c) Amazon
(d) Asia
Ans: (c)
Manioc, also known as cassava, is a root vegetable that serves as a staple food for people living in the Amazon Basin. It is well-suited to the tropical climate and is a significant source of carbohydrates.
(iii) Kolkata is located on the river:
(a) Orange
(b) Hooghly
(c) Bhagirathi
(d) Beas
Ans: (b)
Kolkata, the capital of West Bengal, is situated on the banks of the Hooghly River. This river is a distributary of the Ganges and is crucial for transportation and trade in the region.
(iv) are a type of:
(a) Coniferous trees
(b) Deciduous trees
(c) shrubs
(d) Herbs
Ans: (a)
Deodars and firs are evergreen trees that belong to the coniferous forest category. These trees are adapted to cold climates, with needle-like leaves and cones, and are commonly found in mountainous regions like the Himalayas.
(v) The Bengal tiger is found in:
(a) mountains
(b) delta area
(c) Amazon
(d) plains
Ans: (b)
The Bengal tiger is primarily found in the Sundarbans delta, which spans parts of India and Bangladesh. This delta area is formed by the confluence of the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers and is home to a unique mangrove ecosystem.
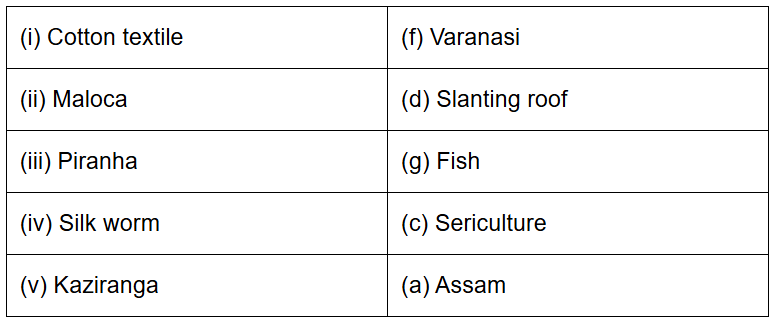
3. Match the following.
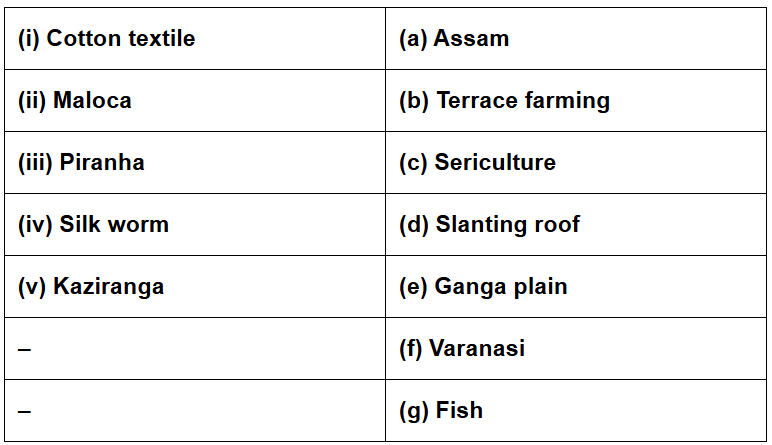
Ans:
4. Give reasons.
(i) The rainforests are depleting.
Ans: The rainforests are depleting due to several factors:
- Development and industrial activities are destroying large areas.
- Land is being cleared for agriculture and mining.
- Industrial operations require significant amounts of wood.
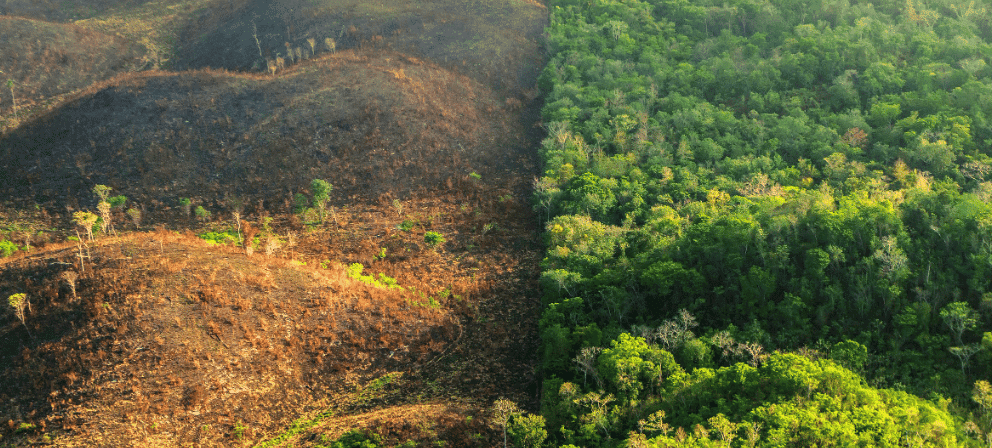

As a result of deforestation:
- The topsoil is washed away.
- There is no space for new tree growth.
- This leads to a decrease in rainforest areas.
(ii) Paddy is grown in the Ganga-Brahmaputra plains.
Ans: The Ganga-Brahmaputra plains offer an excellent environment for growing paddy due to several factors:
- The plains have flat, rich terrain with alluvial soil.
- There is a significant amount of rainfall, which is essential for rice cultivation.
- The local climate is also well-suited for growing rice.

Therefore, paddy is widely cultivated in this region.
5. Map skills.
(i) On an outline map of the Indian Sub-continent, draw the rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra from the source to the mouth. Also, show the important tributaries of both rivers.
(ii) On the political map of South America, draw the equator and mark the countries it passes through.
For (i):
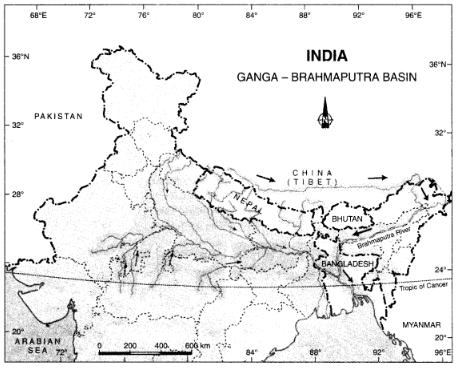
For (ii):
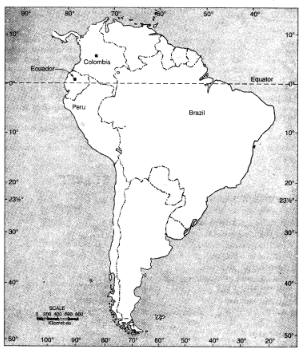
6. For fun.
Make a collage to show places of attractions in India. You can divide the class in different groups to show attractions based on mountain landscapes, coastal beaches, wildlife sanctuaries and places of historical importance.
Ans: Students are advised to try these questions independently.
7. Activity
Collect under mentioned material and observe how destruction of trees effect the soil cover.
Material
(i) Three small flowerpots or food cans (e.g., cold drinks tin cans),
(ii) one big can with holes punched in the bottom (this will act as a sprinkling can),
(iii) twelve coins or bottle caps
(iv) soil.
Steps
Take three small cans or pots. Fill them with soil till the top. Press the soil to make it level with the top of the can. Now put four coins or bottle caps on the soil of each can. Take the big can that has been punched with holes and fill it with water. You can also take the sprinkling can from your garden. Now, sprinkle water on the three cans. On the first can sprinkle water very slowly so that no soil splashes out. Let moderate amount of water be sprinkled on the second can. On the third can, sprinkle the water heavily. You will observe that unprotected soil splashes out. Where the ‘rain’ is heavy the amount of soil that splashes out is the maximum and least in case of the first can. The coins or caps represent the tree covers. It is clear that if the land is cleared completely of the vegetation, the soil cover will quickly disappear.
Ans: Students are advised to try these questions independently.
Steps:
- Fill the small cans with soil, level it at the top.
- Place four coins or caps on the soil in each can.
- Water the cans with varying amounts:
- First can: sprinkle slowly.
- Second can: moderate amount.
- Third can: heavy sprinkle.
- Observe how much soil splashes out. The first can will lose the least soil, demonstrating the importance of tree cover.
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - Human Environment Interactions The Tropical and
| 1. What are the main characteristics of the tropical and subtropical regions? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact the environment in tropical and subtropical regions? |  |
| 3. What adaptations do plants and animals have in tropical and subtropical climates? |  |
| 4. What role do tropical and subtropical regions play in global climate regulation? |  |
| 5. How can sustainable practices help preserve tropical and subtropical environments? |  |


















