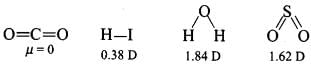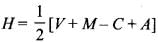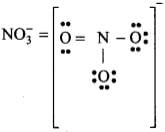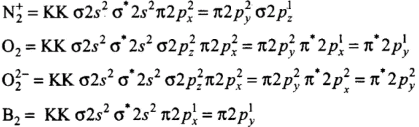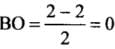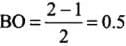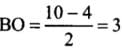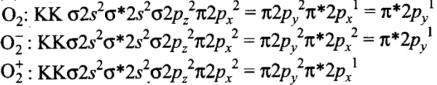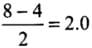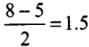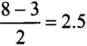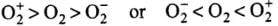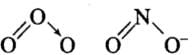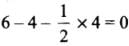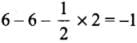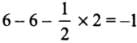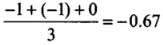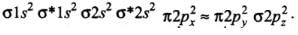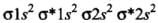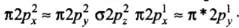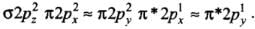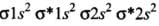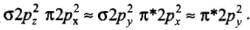NCERT Exemplar: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download

Single Correct Answer Questions
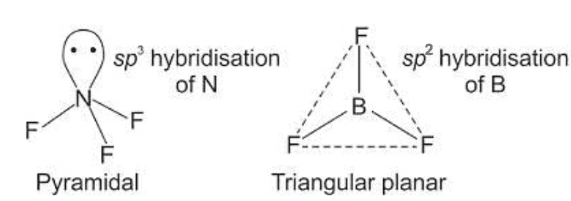
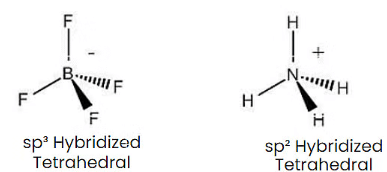
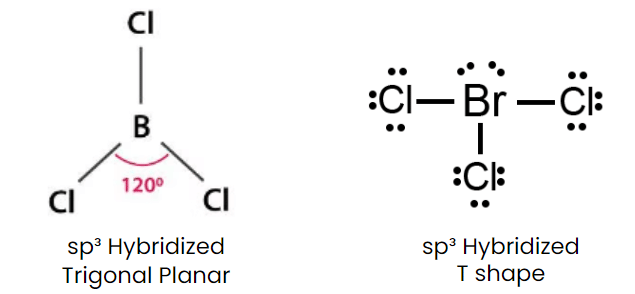
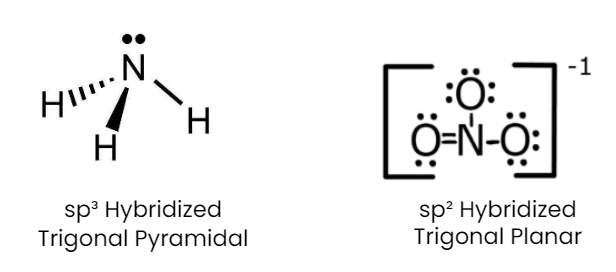
Q1: Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridization. Among the given species identify the isostructural pairs.
(a) [NF3 and BF3]
(b) [BF4– and NH+4 ]
(c) [BCl3 and BrCl3]
(d) [NH3 and NO3– ]
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- NF3 is pyramidal whereas BF3 is planar triangular.
- BF4– and NH+4 ions both are tetrahedral.
- BCl3 is triangular planar whereas BrCl3 is T Shape.
- NH3 is pyramidal whereas NO3- is triangular planar.
Q2: Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on the electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
(a) CO2
(b) HI
(c) H2O
(d) SO2
Correct Answer is Option (c)
H2O will have the highest dipole moment due to the maximum difference in electronegativity of H and O atoms.
Q3: The types of hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in NO+2, NO–3, and NH+4 respectively are expected to be
(a) sp, sp3, and sp2
(b) sp, sp2, and sp3
(c) sp2, sp, and sp3
(d) sp2, sp3, and sp
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The number of orbitals involved in hybridization can be determined by the application of formula:
where H = number of orbitals involved in hybridization- V= valence electrons of central atom
- M= number of monovalent atoms linked with central atom
- C = charge on the cation
- A = charge on the anion
- NO+2 : H = 1/2 [5 + 0 - 1 + 0] = 2 or sp
- NO+3 : H = 1/2 [5 + 0 - 0 + 0] = 3 or sp2
- NO4+ : H = 1/2 [5 + 4 - 1 + 0] = 4 or sp3
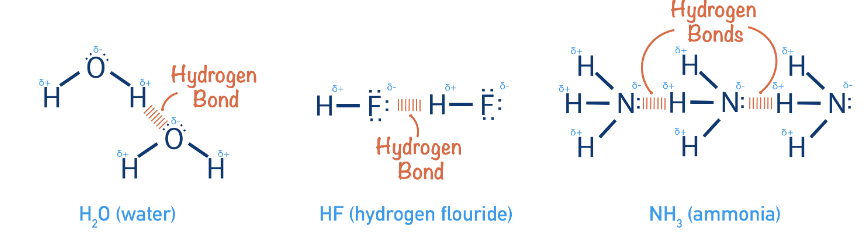
Q4: Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds, e.g., H2O, HF, NH3. The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bonds and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of the above compounds is:
(a) HF > H2O > NH3
(b) H2O > HF > NH3
(c) NH3 > HF > H2O
(d) NH3 > H2O > HF
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The strength of H-bonding depends on the electronegativity of the atom, which follows the order: F > O > N.
Strength of H-bond is in the order:
H……. F > H…….. O > H…….. N
- But each H2O molecule is linked to 4 other H2O molecules through H-bonds whereas each HF molecule is linked only to two other HF molecules.
Hence, the correct decreasing order of the boiling points is H2O > HF > NH3.
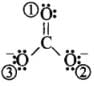
Q5: In PO3–4 ion, the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P – O bond is
(a) + 1
(b) – 1
(c) – 0.75
(d) + 0.75
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The formal charge of the atom in the molecule or ion = (Number of valence electrons in a free atom) – (Number of lone pair electrons + 1/2 Number of bonding electrons)
For charge on oxygen = 6 -
= 6 -7 = - 1
Q6: In NO–3 ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom is
(a) 2, 2
(b) 3, 1
(c) 1, 3
(d) 4, 0
Correct Answer is Option (d)
In N-atom, number of valence electrons = 5
- Due to the presence of one negative charge, number of valence electrons = 5 + 1 = 6.
- One O-atom forms two bonds (= bond) and two O-atom are shared with two electrons of N-atom.
- Thus, 3 O-atoms are shared with 8 electrons of N-atom.
- Number of bond pairs (or shared pairs) = 4
Number of lone pairs = 0
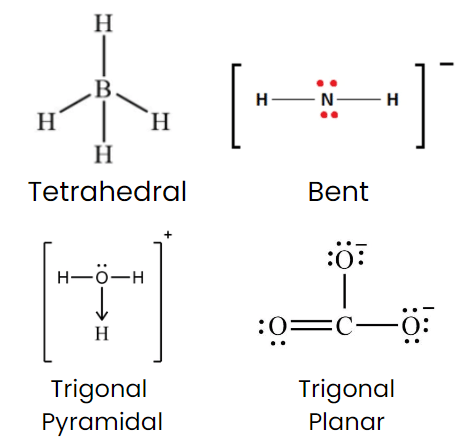
Q7: Which of the following species has tetrahedral geometry?
(a) BH–4
(b) NH–2
(c) CO2–3
(d) H3O+
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Boron is surrounded by 4 bonded pairs only.
- In BH-4 = no. of bond pair = 4
- No. of lone pair = 0
- sp3 hybridised, so have tetrahedral geometry
- NH-2 = Bent shape
- H3O+ = Trigonal Pyramidal
- CO-23= Trigonal Planar
Q8: Number of π bonds and σ bonds in the following structure is–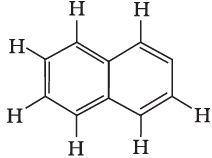
(a) 6, 19
(b) 4, 20
(c) 5, 19
(d) 5, 20
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Each C atom is sp2 hybridized and surrounded by 3 sigmas and 1 pi bond between two C atoms. Structure to be rectified.
- 8 C - H + 11 C - C bonds = 19 σ bonds.
- There are 5π -bonds and 19 σ bonds.
Q9: Which molecule/ion out of the following does not contain unpaired electrons?
(a) N+2
(b) O2
(c) O2–2
(d) B2
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Thus, O22-has no unpaired electrons.
Q10: In which of the following molecule/ion, all the bonds are not equal?
(a) XeF4
(b) BF4–
(c) C2H4
(d) SiF4
Correct Answer is Option (c)
C2H4 has one double bond and four single bonds. The bond length of a double bond (C = C) is smaller than a single bond (C – H).
Q11: In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
(a) HCl
(b) H2O
(c) HI
(d) H2S
Correct Answer is Option (b)
HCl, HI, and H2S do not form H-bonds. Only H2O forms hydrogen bonds. One H2O molecule forms four H-bonding.
Q12: If the electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2, the four electrons involved in chemical bond formation will be_____.
(a) 3p6
(b) 3p6, 4s2
(c) 3p6, 3d2
(d) 3d2, 4s2
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The electron involved in the formation of any chemical bond are the valence shell electrons. In the given electronic configuration, the valence shell electrons are in d- orbital and s-orbital.
Q13: Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridization?
(a) 90°
(b) 120°
(c) 180°
(d) 109°
Correct Answer is Option (b)
sp2 hybridization gives three sp2 hybrid orbitals which are planar triangular forming an angle of 120° with each other.
Directions: The electronic configurations of three elements A, B, and C are given below.
Answer the questions from 14 to 17 on the basis of these configurations.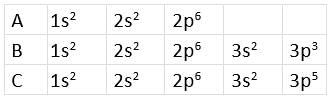
Q14: Stable form of A may be represented by the formula :
(a) A
(b) A2
(c) A3
(d) A4
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The given electronic configuration shows that A represents noble gas because the octet is complete. A is neon which has 10 atomic numbers.
Q15: Stable form of C may be represented by the formula :
(a) C
(b) C2
(c) C3
(d) C4
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The electronic configuration of C represents chlorine. Its stable form is dichlorine (Cl2), i.e., C2.
Q16: The molecular formula of the compound formed from B and C will be
(a) BC
(b) B2C
(c) BC2
(d) BC3
Correct Answer is Option (d)
B represents P, and C represents Cl. The stable compound is PCl3, i.e., BC3.
Q17: The bond between B and C will be
(a) Ionic
(b) Covalent
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Coordinate
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Both B and C are non-metals, and therefore, the bond formed between them will be covalent.
Q18: Which of the following order of energies of molecular orbitals of N2 is correct?
(a) (π2py) < (σ2pz) < (π*2px) ≈ (π*2py)
(b) (π2py) > (σ2pz) > (π*2px) ≈ (π*2py)
(c) (π2py) < (σ2pz) > (π*2px) ≈ (π*2py)
(d) (π2py) > (σ2pz) < (π*2px) ≈ (π*2py)
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Molecules like B2, C2 & N2 having 1 to 3 electrons in p orbital energy of σ2p molecular orbital is greater than that of π2px and π2py molecular orbitals.
Q19: Which of the following statement is not correct from the viewpoint of molecular orbital theory?
(a) Be2 is not a stable molecule.
(b) He2 is not stable, but He+2 is expected to exist.
(c) Bond strength of N2 is maximum amongst the homonuclear diatomic molecules belonging to the second period.
(d) The order of energies of molecular orbitals in N2 molecule is
σ2s < σ*2s < σ2pz < (π2px = π2py) < (π*2px = π*2py) < σ*2pz
Correct Answer is Option (d)
- (a) Be2 (4 + 4 = 8) = σ1s2, σ*1s2 ,σ1s2 ,σ*2s2
Bond order (BO) = 1/2 [Number of bonding electron (Nb) - Number of anti - bonding electrons Na]= (4-4)/2=0
- (b) Here, the bond order of He2 is zero. Thus, it does not exist.
He2 (2 + 2 = 4) = σ1s2 , σ*1s2
Here, the bond order of He2 is zero. Thus, it does not exist.
He+2 (2 + 2 - 1 = 3) = σ1s2, σ*1s1
Since the bond order is not zero, this molecule is expected to exist.- (c) N2 (7 + 7 = 14) = σ1s2, σ*1s2 ,σ2s2 ,σ*2s2 , (π2p2x ≈ π* 2p2y) < σ*2p2z
Thus, the dinitrogen (N2) molecule contains a triple bond, and no other molecule of the second period have more than a double bond. Hence, the bond strength of N2 is maximum amongst the homonuclear diatomic molecules belonging to the second period.- (d) It is incorrect. The correct order of energies of molecular orbitals in N2 molecule is
σ2s < σ* 2s < σ2pz < (π2px ≈ π2py) < (π* 2px ≈ π* 2py) < σ*2pz
Q20: Which of the following options represents the correct bond order :
(a) O–2 > O2 > O+2
(b) O–2 < O2 < O+2
(c) O–2 > O2 < O+2
(d) O–2 < O2 > O+2
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Bond order, O2
- Bond order, O2-
- Bond order, O2 +
∴
Q21: The electronic configuration of the outermost shell of the most electronegative element is
(a) 2s22p5
(b) 3s23p5
(c) 4s24p5
(d) 5s25p5
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The electronic configuration represents:
- 2s22p5= fluorine = most electronegative element
- 3s23p5 = chlorine
- 4s24p5 = bromine
- 5s25p5 = iodine
Q22: Amongst the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below, the one having the highest ionization enthalpy is
(a) [Ne]3s23p1
(b) [Ne]3s23p3
(c) [Ne]3s23p2
(d) [Ar]3d104s24p3
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(i), (iii), and (iv) have exactly half-filled p-orbitals but (ii) is smaller in size. Hence, (ii) has the highest ionization enthalpy.
Multiple Correct Answer Questions
In the following questions, two or more options may be correct.
Q23: Which of the following have an identical bond order?
(a) CN–
(b) NO+
(c) O2–
(d) O2–2
Correct Answer is Option (a) & (b)
- CN– (number of electrons = 6 + 7 + 1 = 14)
- NO+ (number of electrons = 7 + 8 – 1 = 14)
- O–2 (number of electrons = 8 + 8 + 1 = 17)
- O22- (number of electrons = 8 + 8 + 2 = 18)
Thus, CN and NO+ because of the presence of same number of electrons, have same bond order.
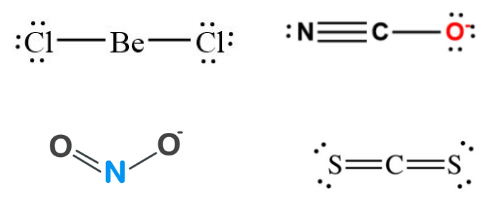
Q24: Which of the following attain the linear structure:
(a) BeCl2
(b) NCO+
(c) NO2
(d) CS2
Correct Answer is Option (a) & (d)
- BeCl2 (Cl – Be – Cl) and CS2 (S = C = S) both are linear, NCO+ is non-linear. However, remember that NCO(N = C = O) is linear because it is isoelectronic with CO2.
- NO2 is angular with bond angled 132° and each O – N bond length of 1.20A°(intermediate between single and double bond).
Q25: CO is isoelectronic with
(a) NO+
(b) N2
(c) SnCl2
(d) NO–2
Correct Answer is Option (a) & (b)
- Number of electrons in NO+ =14
- Number of electrons in N2 = 14
- Number of electrons in SnCl2 = 84
- Number of electrons in NO2– = 24
Q26: Which of the following species have the same shape?
(a) CO2
(b) CCl4
(c) O3
(d) NO2–
Correct Answer is Option (c) & (d)
CO2 →Linear, CCl4 → Tetrahedral, O3 →Angular (V-shaped), NO–2 →Angular (V-shaped)
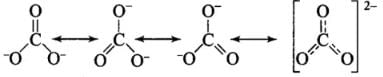
Q27: Which of the following statements are correct about CO2–3?
(a) The hybridization of the central atom is sp3.
(b) Its resonance structure has one C–O single bond and two C=O double bonds.
(c) The average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units.
(d) All C–O bond lengths are equal.
Correct Answer is Option (c) & (d)
All C - O bonds are equal due to resonance.
- Formal charge in O atom (1):
- Formal charge in O atom (2):
- Formal charge in O atom (3):
- The average formal charge on each oxygen atom:
Q28: Diamagnetic species are those which contain no unpaired electrons. Which among the following are diamagnetic?
(a) N2
(b) N22–
(c) O2
(d) O22–
Correct Answer is Option (a) & (d)
- (a) Electronic configuration of N2 =
It has no unpaired electron. This indicates it is a diamagnetic species.- (b) Electronic configuration of N2-2 ion =
It has two unpaired electrons, so it is paramagnetic in nature.- (c) Electronic configuration of O2 =
The presence of two unpaired electrons shows its paramagnetic nature.- (d) Electronic configuration of O22- ion =
It contains no unpaired electron. Therefore, it is diamagnetic in nature.
Q29: Species having the same bond order are:
(a) N2
(b) N2–
(c) F2+
(d) O2–
Correct Answer is Option (c) & (d)
The total number of electrons in F2+ and O2 -are the same, i.e. 17 electrons.
Q30: Which of the following statements are not correct?
(a) NaCl being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the solid state.
(b) In canonical structures, there is a difference in the arrangement of atoms.
(c) Hybrid orbitals form stronger bonds than pure orbitals.
(d) VSEPR Theory can explain the square planar geometry of XeF4.
Correct Answer is Option (a) & (b)
(a) Ionic compounds are good conductors only in molten state or aqueous solution since ions are not furnished in solid-state.
(b) In canonical structures, there is a difference in the arrangement of electrons.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of chemical bonds? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the polarity of a molecule? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of bond angles in molecular geometry? |  |
| 4. What is hybridization in the context of chemical bonding? |  |
| 5. How does the VSEPR theory help in predicting molecular shapes? |  |