Spectrum Summary: Advent of the Europeans in India | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Portuguese In India |

|
| From Trading to Ruling |

|
| The Dutch-1596 |

|
| The English-1599 |

|
| The French-1667 |

|
Do you know that the Portuguese came to India 100 years before the British?
In this EduRev document, you will read about the advent of other European powers and how the British overpowered them and became a dominant power in India.
The Portuguese In India
The Quest for and Discovery of a Sea Route to India
- After the decline of the Roman Empire in the seventh century, the Arabs established dominance in Egypt and Persia, leading to a decline in direct contact between Europe and India.
- Easy accessibility to Indian commodities like spices, calicoes, silk, and precious stones was greatly affected.
- In 1453, Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks, making the Red Sea trade route a lucrative state monopoly for Islamic rulers.
- Arabs also controlled the land routes to India.
- The fifteenth-century spirit of the Renaissance in Europe led to increased prosperity and demand for oriental luxury goods.
- Prince Henry of Portugal, nicknamed the 'Navigator,' significantly promoted exploration.
- The Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 divided the non-Christian world between Portugal and Spain along an imaginary line in the Atlantic.
- Portugal could claim and occupy everything east of the line, while Spain could claim everything west of it.
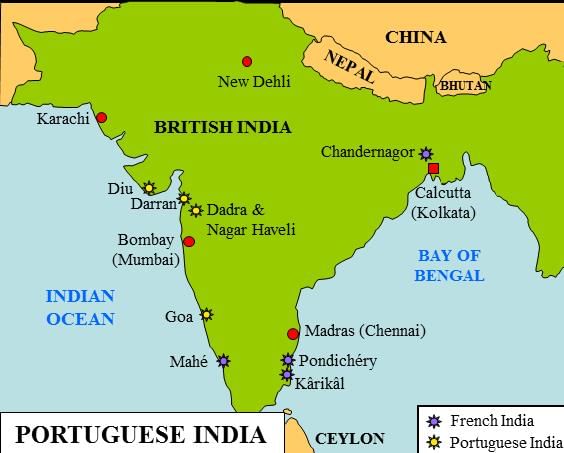
Francisco de Almeida
- The Viceroy of Portuguese possessions in India, Francisco de Almeida, opposed establishing a territorial empire in India, preferring that the Portuguese maintain supremacy at sea and limit their activities to purely commercial transactions. This is known as the Blue Water Policy.
- In order to protect Portuguese interests, King Ferdinand I of Portugal appointed a three-year governor in India and provided him with sufficient troops in 1505.
- By conquering Aden, Hormuz, and Malacca, the newly appointed governor, Francisco de Almeida, was tasked with strengthening the Portuguese position in India and obliterating the Muslim trade.
- Only 8 ships left when Francisco de Almeida arrived at Cochin on October 31, 1505.
- While he was there, he discovered that the Portuguese traders at Quilon had been massacred. He sent his son Lourenço with six ships to attack Quilon’s harbor, where they indiscriminately sank Calicut boats.
Policy of Blue Water – Implications in India
- Francisco de Almeida aimed to establish Portugal as a powerful maritime nation in the Indian Ocean region, focusing on expanding Portuguese influence and trade.
- He successfully took control of Goa from the Sultan of Bijapur in 1510 AD.
- Francisco de Almeida was succeeded by Alfonso de Albuquerque, who became the Portuguese Viceroy in India in 1509.
- Goa later became the headquarters of Portuguese settlements in India, and the Portuguese Navy's dominance and control over coastal regions played a pivotal role in building Portuguese power in India.
From Trading to Ruling
Vasco Da Gama
- Vasco Da Gama, led by a Gujarati pilot named Abdul Majid, arrived at Calicut in May 1498. The ruler of Calicut was Zamorin (Samuthiri) in 1498.
- Arab traders had a profitable business on the Malabar Coast, along with participants from India, Arabs, Africans from the east coast, Chinese, and Javanese. They dealt with Pedro Alvarez Cabral for the spice trade.
- After negotiations, the Portuguese established a factory at Calicut in September 1500.
- Vasco da Gama also set up trading factories at Cannanore and Cochin, which became important trade centers for the Portuguese.
Francisco de Almeida

- In 1505, the King of Portugal appointed a governor in India for a three-year term and equipped the incumbent with sufficient force to protect the Portuguese interests.
- Francisco de Almeida, the newly appointed governor, was asked to consolidate the Portuguese position in India and destroy Muslim trade by seizing Aden, Ormuz, and Malacca. He was also advised to build fortresses at Anjadiva, Cochin, Cannanore, and Kilwa.
Alfonso de Albuquerque

- The real founder of the Portuguese power in the East.
- In East Africa, Portuguese strongholds off the Red Sea, at Ormuz, in Malabar, and at Malacca.
- The principal port of the sultan of Bijapur became the first bit of Portuguese territory in India.
Nuno da Cunha

- Nuno da Cunha assumed the governor of Portuguese interests in India in November 1529 and almost one year later shifted the headquarters of the Portuguese government in India from Cochin to Goa.
- Bahadur Shah of Gujarat, during his conflict with the Mughal emperor Humayun, secured help from the Portuguese by ceding to them in 1534 the island of Bassein with its dependencies and revenues. He also promised them a base in Diu.
- However, Bahadur Shah’s relations with the Portuguese became sour when Humayun withdrew from Gujarat in 1536. Favorable Conditions for Portuguese.
- Favorable Conditions for Portuguese
(i) Gujarat, ruled by the powerful Mahmud Begarha (1458-1511).
(ii) The Portuguese had cannons placed on their ships.
Portuguese State
- Sixty miles of coast around Goa, The Portuguese established military posts and settlements on the east coast at San Thome (in Chennai) and Nagapattinam (in Tamil Nadu)
- Treaties were signed between Goa and the Deccan Sultans in 1570.
- The Portuguese always had a role to play in successive battles for the balance of power between Vijayanagara and the Deccan sultans, between the Deccan and the Mughals, and between the Mughals and the Marathas.
Portuguese Administration in India
- The Vedor da Fazenda is responsible for revenues and the cargos and dispatch of fleets.
Religious Policy of the Portuguese
- Intolerant toward the Muslims
- Zeal to promote Christianity
Portuguese Lose Favor with the Mughals
- In 1608, Captain William Hawkins with his ship Hector reached Surat. Jahangir appointed him as a mansabdar of 400 at a salary of Rs 30,000.
- In November 1612, the English ship Dragon under Captain Best and a little ship, the Osiander successfully fought a Portuguese fleet.
Capture of Hooghly
- Based on an imperial Farman circa 1579, the Portuguese had settled down on a riverbank which was a short distance from Satgaon in Bengal and later migrated to Hooghly.
- On June 24, 1632 - Hooghly was seized. Bengal governor becomes Qasim Khan.
Decline of the Portuguese
- The emergence of powerful dynasties in Egypt, Persia, and North India and the rise of the turbulent Marathas as their immediate neighbors.
- The union of the two kingdoms of Spain and Portugal in 1580-81, dragging the smaller kingdom into Spain's wars with England and Holland, badly affected India's Portuguese monopoly of trade.
- The religious policies of the Portuguese gave rise to political fears and, Dishonest trade practices.
- They earned notoriety as sea pirates.
- Goa which remained with the Portuguese had lost its importance as a port after the Vijayanagara empire's fall.
- Marathas invaded Goa-1683.
- Rise of Dutch and English commercial ambitions.
- Diversion to the west due to the discovery of Brazil.
Significance of the Portuguese
- Marked the emergence of naval power.
- Portuguese ships carried cannons.
- The Portuguese onshore's significant military contribution was the system of drilling groups of infantry, on the Spanish model, introduced in 1630.
- Masters of improved techniques at sea.
The Dutch-1596
Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutchman to reach Sumatra and Bantam in 1596. Cornelis de Houtman
Cornelis de Houtman
Dutch Settlements
- The Dutch founded their first factory in Masulipatnam (in Andhra) in 1605.
- Captured Nagapatam near Madras (Chennai) from the Portuguese and made it their main stronghold in South India.
- The Dutch established factories on the Coromandel coast, in Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Bengal, and Bihar.
- In 1609, they opened a factory in Pulicat, north of Madras. Their other principal factories in India were at Surat (1616), Bimlipatam (1641), Karaikal (1645), Chinsura (1653), Baranagar, Kasimbazar (near Murshidabad), Balasore, Patna, Nagapatnam(1658), and Cochin (1663).
- They carried indigo manufactured in the Yamuna Valley and Central India, textiles and silk from Bengal, Gujarat, and the Coromandel, saltpeter from Bihar, and opium and rice from the Ganga Valley.
Anglo-Dutch Rivalry
- This posed a severe challenge to the commercial interests of the Dutch by the English.
- The climax of the enmity between the Dutch and the English in the East was reached at Amboyna (a place in present-day Indonesia, which the Dutch had captured from the Portuguese in 1605) where they massacred ten Englishmen and nine Japanese in 1623.
- 1667- Dutch retired from India and moved to Indonesia.
- They monopolized the trade in black pepper and spices. The most important Indian commodities the Dutch traded were silk, cotton, indigo, rice, and opium.
- The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 AD facilitated the restoration of Dutch Coromandel and Dutch Bengal to Dutch rule, but they were returned to British rule as a result of the clause and provisions of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 AD.
- This required the Dutch to ensure all property and establishment transfers until March 1, 1825 AD.
- As a result, by the middle of 1825 AD, the Dutch had lost all of their commercial sites in India.
- The obvious happened as a result of the compromise. In 1667 AD, all parties reached an agreement in which the British committed to withdrawing fully from Indonesia in exchange for the Dutch withdrawing from India to trade in Indonesia, based on a give-and-take formula.
Decline of the Dutch in India
- The Dutch got drawn into the trade of the Malay Archipelago.
- Third Anglo-Dutch War (1672-74), links between Surat and the new English town of Bombay were disrupted, resulting in the Dutch forces capturing three homebound English ships in the Bay of Bengal.
- The English retaliation resulted in the defeat of the Dutch, in the battle of Hooghly (November 1759), thereby ending Dutch ambitions in India.
- Their concerns were trade.
- Commercial interest lay in the Spice Islands of Indonesia.
- Battle of Biderra (Bidara) 1759 the English defeated Dutch.
The English-1599
Charter of Queen Elizabeth I Queen Elizabeth I
Queen Elizabeth I
- Francis Drake's voyage around the world in 1580 and the English victory over the Spanish Armada in 1588. In 1599 'Merchant Adventurers' formed a company.
- On December 31, 1600, Queen Elizabeth I issued a charter with exclusive trading rights to the company named the 'Governor and Company of Merchants of London trading into the East Indies'.
Progress of the English Company
Foothold in West and South
- In 1611, the English started trading at Masulipatnam on the southeastern coast of India and later established a factory in 1616.
- Establish a factory at Surat under Thomas Aldworth-1613.
- In 1615, Sir Thomas Roe came as an accredited ambassador of James I to Jahangir's court.
- Secure permission to set up Agra, Ahmedabad, and Broach factories.
- Bombay had been gifted to King Charles II by the King of Portugal as a dowry when Charles married the Portuguese princess Catherine in 1662. Bombay was given over to the East India Company on an annual payment of ten pounds only in 1668.
- Bombay was made the headquarters by shifting the Western Presidency's seat from Surat to Bombay in 1687.
- 'Golden Farman' was issued by the Sultan of Golconda in 1632. On payment of 500 pagodas a year, they earned the privilege of trading freely in the ports of Golconda.
- The British merchant Francis Day, in 1639 received from the ruler of Chandragiri permission to build a fortified factory at Madras which later became Fort St. George and replaced Masulipatnam as the headquarters of the English settlements in south India.
- English extended their trading activities to the east and started factories at Hariharpur in the Mahanadi delta and Balasore (in Odisha) in 1633.
Foothold in Bengal
- Shah Shuja, the subahdar of Bengal in 1651, allowed the English to trade in Bengal in return for an annual payment of Rs 3,000.
- Factories in Bengal were started at Hooghly (1651) and other places like Kasimbazar, Patna, and Rajmahal.
- William Hedges, the first agent and governor of the Company in Bengal, and Shaista Khan, the Mughal governor of Bengal in August 1682.
- The English retaliated by capturing the imperial forts at Thana (modern Garden Reach), raiding Hijli in east Midnapur, and storming the Mughal fortifications at Balasore.
- On February 10, 1691, the English factory was established the day an imperial Farman was issued permitting the English to "continue contentedly their trade-in Bengal" on payment of Rs 3000 a year instead of all dues.
- In 1698, the English succeeded in getting permission to buy the zamindari of the three villages of Sutanuti, Gobindapur, and Kalikata (Kalighat) on payment of Rs 1,200.
- The fortified settlement was named Fort William in the year 1700 when it also became the seat of the eastern presidency (Calcutta) with Sir Charles Eyre as its first president.
Farrukhsiyar’s Farman
- In 1715, an English mission led by John Surman to the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar secured three famous farms, giving the Company many valuable privileges in Bengal, Gujarat, and Hyderabad. The Farman thus obtained were regarded as the Magna Carta of the Company. Their important terms were:
(i) Company’s Exports and imports are exempted from customs duties except for the annual payment of 3000 rupees in Bengal.
(ii) Issues of data (passes) for transportation.
(iii) East India Company was exempted from the levy of all duties in surat on an annual payment of 10000.
(iv) The coins of the Company minted at Bombay were to have currency throughout the Mughal empire. - Sir William Norris was its ambassador to the court of Aurangzeb (January 1701-April 1702).
- Under pressure from the Crown and the Parliament, the two companies were amalgamated in 1708 under the title of 'United Company of Merchants of England Trading to the East Indies.
Merging of Two English Companies
- After the 1688 English Revolution, the Whigs gained more influence and opposed the East India Company's exclusive trading rights (monopoly) with India.
- A new rival company was formed to challenge this monopoly.
- The rival company sent Sir William Norris as its ambassador to Emperor Aurangzeb's court in India from January 1701 to April 1702 to get trading privileges.
- The new company failed and couldn't succeed.
- In 1708, under pressure from the British Crown and Parliament, the two companies merged into the "United Company of Merchants of England Trading to the East Indies."
- This merged entity operated as the East India Company from 1708 to 1873 and helped establish British political power in India.
The French-1667
Foundation of French Centres in India
- Louis XIV, the king’s famous minister Colbert, laid the Compagnie des Indes Orientales (French East India Company) in 1664 the Compagnie des Indes Orientales was granted a 50-year monopoly.
- In 1667, Francois Caron headed an expedition to India, setting up a factory in Surat. Mercara, a Persian who accompanied Caron.
- Founded another French factory in Masulipatnam in 1669, In 1673 established a township at Chandernagore near Calcutta.
Pondicherry Nerve Centre of French Power in India
- In 1673, Sher Khan Lodi, the governor of Valikondapuram (under the Bijapur Sultan) granted Francois Martin, the Masulipatnam factory director.
- Pondicherry was founded in 1674. And Caron became the French governor.
- Mahe, Karaikal, Balasore, and Qasim Bazar were a few important trading centers of the French East India Company.
Early Setbacks to the French East India Company
- The Dutch captured Pondicherry in 1693.
- The Treaty of Ryswick concluded in September 1697 and restored Pondicherry to the French, the Dutch garrison held on to it for two more years.
- Francois Martin died on December 31, 1706.
- In 1720, the French company was reorganized as the 'Perpetual Company of the Indies’.
Reorganisation of the French Company
- In 1720, the French East India Company was reorganized and renamed the ‘Perpetual Company of the Indies’.
- This reorganization helped revive and strengthen the company's operations.
The Anglo-French Struggle for Supremacy: the Carnatic Wars First Carnatic War (1740-48) First Carnatic War
First Carnatic War
- Background - Carnatic-Coromandel coast and its hinterland, Extension of the Anglo-French War caused by the Austrian War of Succession.
- Immediate cause - France retaliated by seizing Madras in 1746, Thus beginning the First Carnatic War.
- The result - The treaty of Aix-La Chapelle was signed bringing the Austrian War of Succession to a conclusion.- Madras was handed back to the English. The French got their territories in North America.
First Carnatic War (1740-48)
- Carnatic was the European name for the Coromandel coast and its inland areas.
- The First Carnatic War (1740-48) was part of the larger Anglo-French conflict in Europe, caused by the Austrian War of Succession.
- Immediate cause: France avoided fighting in India due to weakness, but England provoked them by capturing French ships. France responded by taking Madras in 1746 with help from a fleet led by Admiral La Bourdonnais from Mauritius.
- This started the war.
- Result: The war ended in 1748 with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, returning Madras to England and giving France back its North American territories.
- Significance: Key event was the Battle of St. Thome in Madras, where a small French force under Captain Paradise defeated a large Indian army led by Mahfuz Khan (from Nawab Anwar-ud-din, allied with England) on the River Adyar.
- This showed that a small, disciplined European army could beat a bigger Indian one.
- It also proved the importance of naval power in Anglo-French fights in the Deccan region.
Second Carnatic War (1749-54)
- The background for the Second Carnatic War was provided by rivalry in India.
- Cause -
(i) The opportunity was provided by the death of Nizam-ul-Mulk, the founder of the independent kingdom of Hyderabad, in 1748, and the release of Chanda Sahib, the son-in-law of Dost Ali, the Nawab of Carnatic, by the Marathas.
(ii) The French supported Muzaffar Jang and Chanda Sahib's claims in the Deccan and Carnatic, respectively, while the English sided with Nasir Jang and Anwar-ud-din. - During the war
(i) The combined armies of Muzaffar Jang, Chanda Sahib, and the French defeated and killed Anwar-ud- din at the Battle of Ambur (near Vellore) in 1749.
(ii) Muzaffar Jang became the subahdar of Deccan, and Dupleix was appointed governor of all the Mughal territories to the south of the River Krishna.
(iii) In August 1751, with only a force of 210 men, Robert Clive attacked and captured Arcot.
Third Carnatic War (1758-63)
- Background - In 1758, the French army under Count de Lally captured the English forts of St. David and Vizianagaram in 1758.
- The course of the war in India - 'Battle of Wandiwash', The decisive battle of the Third Carnatic War was won by the English on January 22, 1760, at Wandiwash (or Vandavasi) in Tamil Nadu.
- The result - The Treaty of Peace of Paris (1763) restored India's French factories.
(I). Dutch had already been defeated in the Battle of Bidara in 1759.
(ii) The victory at Wandiwash left the English East India Company with no European rival in India.
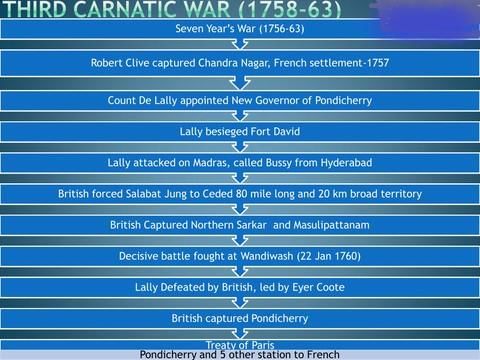
Causes for the English Success and the French Failure
- The English company was a private enterprise - With less governmental control over it, The French company, on the other hand, was a State concern. It was controlled and regulated by the French government.
- The English navy was superior to the French navy.
- The English held three important places: Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras, whereas the French had only Pondicherry.
- The French subordinated their commercial interest to territorial ambition, which made the French company short of funds.
- The superiority of the commanders in the British camp.
The Danes-1620
- They founded a factory at Tranquebar near Tanjore, on the eastern coast of India. Their principal settlement was at Serampore near Calcutta.
Why did the English succeed against Other European Powers?
- Structure and Nature of the Trading Companies - English East India Company, was controlled by a board of directors whose members were elected annually.
- Naval Superiority - The Royal Navy of Britain was not only the largest; it was the most advanced of its times. The victory against the Spanish Armada and the French at Trafalgar had put the Royal Navy at the European naval forces' peak.
- Industrial Revolution - The industrial revolution reached other European nations late, which helped England maintain its hegemony.
- Military Skill and Discipline - British soldiers were disciplined a lot and well-trained.
- Stable Government
- Lesser Zeal for Religion
- Use of Debt Market - The world’s first central bank (the Bank of England) was established to sell government debt to the money markets to promise a decent return on Britain’s defeating rival countries.
By now you got an idea about how Europeans came to India and how did they manage and trade with us. In the next Edurev document, you will read about how the condition in India was when the British arrived and how they benefitted from it.
To practice the questions of the topic "Advent of the Europeans in India", you just read, attempt the tests given below:
|
216 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Spectrum Summary: Advent of the Europeans in India - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What was the significance of the Blue Water Policy for the Portuguese in India? |  |
| 2. How did the arrival of the Dutch in 1596 impact the Portuguese trade in India? |  |
| 3. What were the main objectives of the English East India Company when it was established in 1599? |  |
| 4. How did the French presence in India in 1667 differ from that of the Portuguese and other European powers? |  |
| 5. What were the broader implications of the transition from trading to ruling for European powers in India? |  |
















