Important Diagrams: Life Processes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cross Section of a Leaf |

|
| Structure of Stomata |

|
| Human Digestive System |

|
| Human Respiratory System |

|
| Exchange of Gases in Lungs |

|
| Human Excretory System |

|
| Human Heart |

|
| Digestion in Amoeba |

|
Cross Section of a Leaf
A leaf cross-section shows the upper epidermis (protective layer), palisade mesophyll (photosynthesis), spongy mesophyll (gas exchange), vascular bundles (water and nutrient transport), lower epidermis (stomata for gas exchange), and guard cells (control stomata openings).
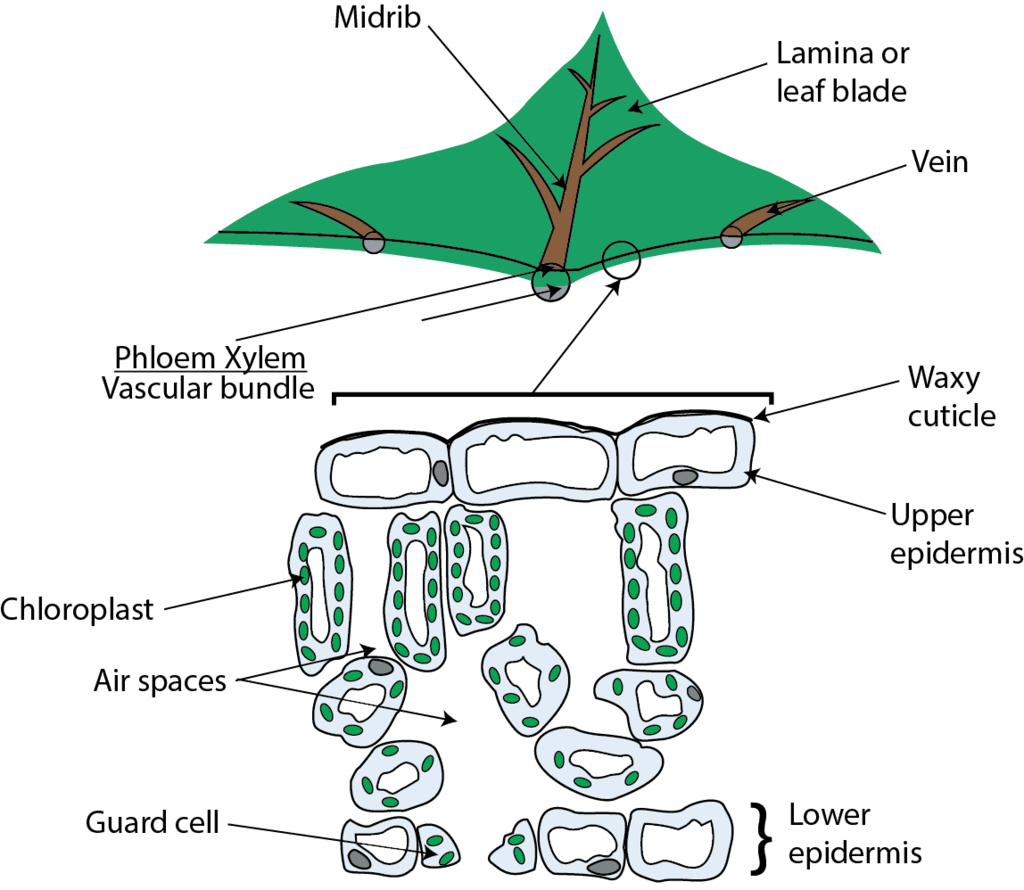 Cross Section of a Leaf
Cross Section of a Leaf
Structure of Stomata
Stomata are small pores on the leaf surface, mainly surrounded by guard cells that regulate their opening and closing. These cells control gas exchange, allowing CO₂ to enter for photosynthesis and O₂ to exit, while also managing water loss through transpiration. The stomatal pore is the opening between the guard cells, and subsidiary cells assist in their function.
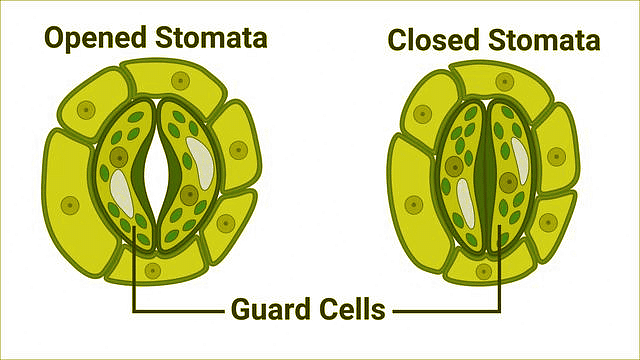 Structure of Stomata
Structure of Stomata
Human Digestive System
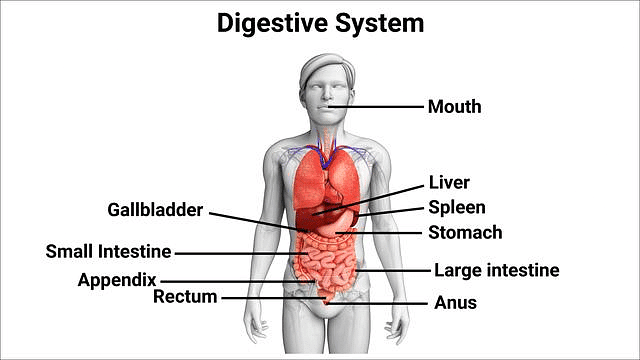
The human digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients through several organs. Food enters the mouth, where digestion begins. It moves down the esophagus to the stomach, where it's mixed with digestive juices. In the small intestine, nutrients are absorbed, with help from the liver (which produces bile), gallbladder (stores bile), and pancreas (produces enzymes). The large intestine absorbs water and salts, and the remaining waste is eliminated through the rectum and anus.
Human Respiratory System
The human respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide. Air enters through the nose/mouth, travels down the trachea, and into the bronchi leading to the lungs. In the lungs, the bronchioles branch into tiny air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is expelled. The diaphragm helps in the process by aiding airflow into and out of the lungs.
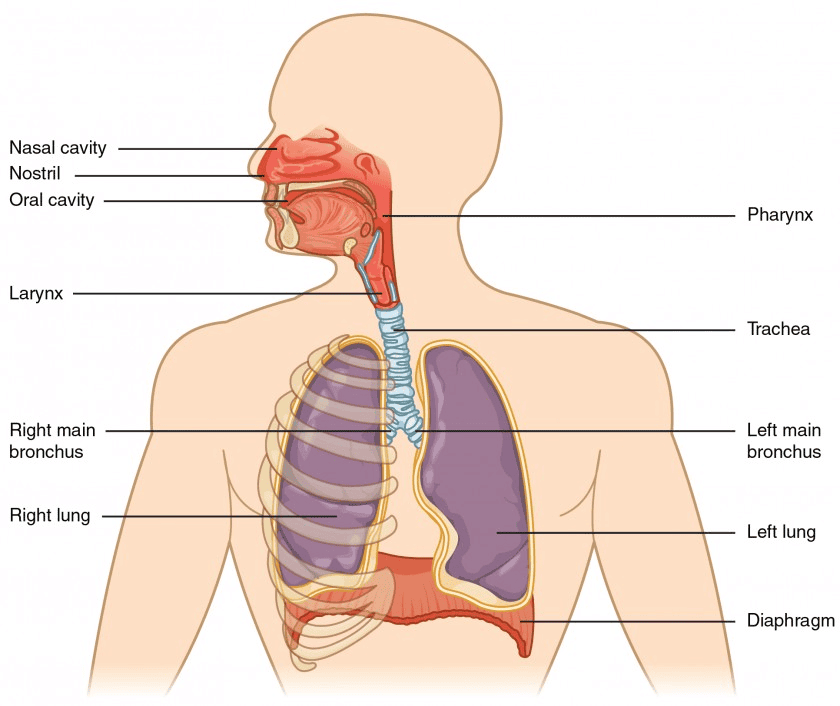 Human Respiratory System
Human Respiratory System
Exchange of Gases in Lungs
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen from inhaled air diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli to be exhaled. This process ensures oxygen is supplied to the body and carbon dioxide is removed.
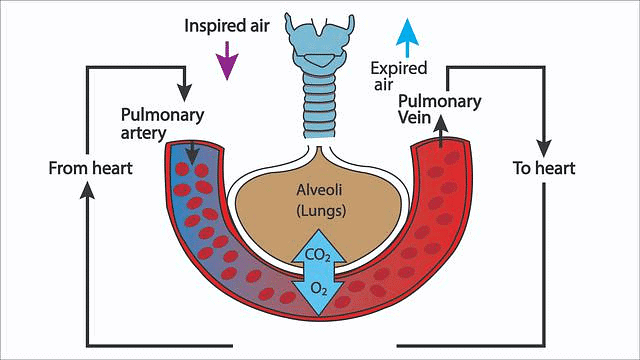 Exchange of Gases in Lungs
Exchange of Gases in Lungs
Human Excretory System
The human excretory system removes waste and excess substances from the body. It consists of the kidneys, which filter blood to produce urine, ureters that transport urine to the bladder for storage, and the urethra, through which urine is excreted.
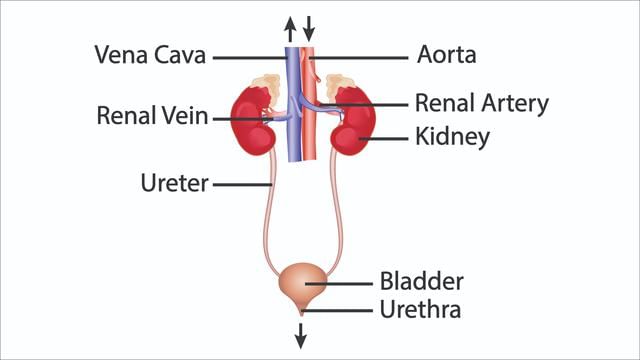 Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System
Human Heart
The human heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It has four chambers: the right atrium and right ventricle (which pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs) and the left atrium and left ventricle (which pump oxygenated blood to the rest of the body). The heart functions by contracting and relaxing, maintaining a continuous blood flow that delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removes waste products.
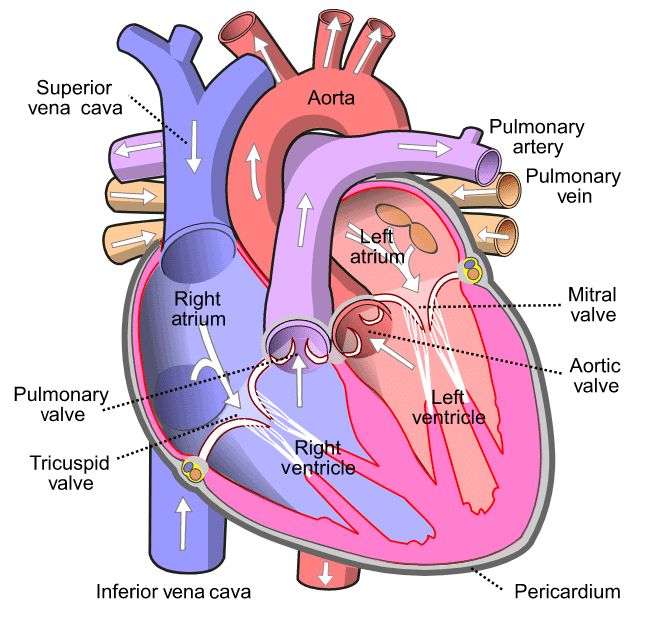 Human Heart
Human Heart
Digestion in Amoeba
In amoeba, digestion occurs inside the food vacuole. When an amoeba engulfs food, usually bacteria or small organisms. This fuses with lysosomes containing digestive enzymes, breaking down the food into nutrients. The digested nutrients are absorbed into the amoeba's cytoplasm, and any undigested material is expelled from the cell.
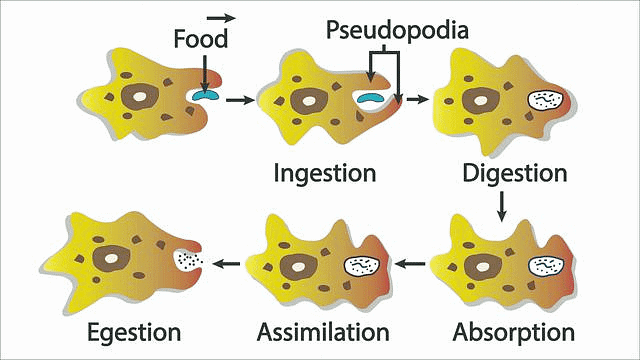 Digestion in Amoeba
Digestion in Amoeba
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Life Processes - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the structure of stomata and how do they function in plants? |  |
| 2. How does the human digestive system work to break down food for absorption of nutrients? |  |
| 3. What is the process of gas exchange in the lungs and how does it support respiration? |  |
| 4. How does the human excretory system function to remove waste products from the body? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the human heart in the circulatory system and how does it function to pump blood throughout the body? |  |
















