Class 10 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 3 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Class-X
Science Theory
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
1. The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper.
All questions are compulsory.
2. Section-A - Question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts thereof are of one mark each. These questions contain multiple-choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion - reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one sentence.
3. Section-B - Question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
4. Section-C - Question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
5. Section-D - Question no. - 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
6. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
7. Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION A
Q.1. In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution : (1 mark)
(i) exchange of atoms takes place
(ii) exchange of ions takes place
(iii) a precipitate is produced
(iv) an insoluble salt is produced
The correct option is :
(a) (B) and (D)
(b) (A) and (C)
(c) only (B)
(d) (B), (C) and (D)
Ans. d
Solution. Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Q.2. Baking soda is a mixture of: (1 mark)
(a) Sodium carbonate and acetic acid
(b) Sodium carbonate and tartaric acid
(c) Sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid
(d) Sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic acid
Ans. b
Q.3. Two statements are given - one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R).
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
Assertion (A): Esterification is a process in which a sweet-smelling substance is produced.
Reason (R): When esters react with sodium hydroxide an alcohol and sodium salt of the carboxylic acid is obtained. (1 Mark)
Options~
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. b
Solution.
Esterification is a reaction in which alcohol like ethanol reacts with carboxylic acids to form esters and water in the presence of sulphuric acid. Esters are generally sweet-smelling substances.
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH ➝ CH3COOCH2CH3
Q.4. Two statements are given - one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R).
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
Assertion (A): In the process of nuclear fission, the amount of nuclear energy generated by the fission of an atom of uranium is so tremendous that it produces 10 million times the energy produced by the combustion of an atom of carbon from coal.
Reason (R): The nucleus of a heavy atom such as uranium, when bombarded with low energy neutrons, splits apart into lighter nuclei. The mass difference between the original nucleus and the product nuclei gets converted to tremendous energy. (1 Mark)
Options~
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. a
Q.5. Both a spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of (-)15 cm. What type of mirror and lens are these ? (1 Mark)
Ans. Both are concave. The alternative answer that should be given credit: Plano-concave lens
Q.6. What is fertilisation ? Where does it occur in a human female? (1 Mark)
Ans. Fusion of male and female gamete is known as fertilization. It occurs in the fallopian tube.
OR
What is micturition?
Ans. It is the expulsion of urine from the body.
Q.7. Mention the respiratory unit of the lungs and the excretory unit of the kidneys. (1 Mark)
Ans. Respiratory unit of lungs — Alveoli
Excretory unit of kidneys — Nephrons.
Q.8. When a small amount of acid is added to water, the phenomena which occur are : (1 Mark)
(A) Dilution
(B) Neutralisation
(C) Formation of H3O+ ions
(D) Salt formation
The correct statements are :
(a) (A) and (C)
(b) (B) and (D)
(c) (A) and (B)
(d) (C) and (D)
Ans. a
Q.9. Two unequal resistances are connected in parallel. If you are not provided with any other parameters (eg. numerical values of I and R), what can be said about the voltage drop across the two resistors? (1 Mark)
Ans. Voltage-drop is the same across both.
OR
Some work is done to move a charge Q from infinity to a point A in space. The potential of point A is given as V. What is the work done to move this charge from infinity in terms of Q and V?
Ans. W = QV.
Q.10. At the time of short circuit, the electric current in the circuit: (1 Mark)
(a) vary continuously
(b) does not change
(c) reduces substantially
(d) increases heavily
Ans. d
Q.11. At noon the sun appears white as (1 Mark)
(a) light is least scattered
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away
(c) the blue colour is scattered the most
(d) the red colour is scattered the most
Ans. (a) Sun is directly over the head and sunlight travel a relatively shorter distance causing only a little of the blue and violet colours to be scattered.
Q.12. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire? (1 Mark)
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Ans. (d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Solution.
The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire. On applying the right-hand thumb rule, we find the direction of the magnetic field. The field is in the form of concentric circles centred on the wire carrying current.
Q.13. With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a? (1 Mark)
(a) Consumer
(b) Producer
(c) Producer and consumer
(d) Producer and decomposer
Ans. (a) Consumer
OR
If a grasshopper is eaten by a frog, then the energy transfer will be from?
(a) producer to decomposer
(b) producer to primary consumer
(c) primary consumer to secondary consumer
(d) secondary consumer to primary consumer
Ans. (c)
Solution.
If a grasshopper is eaten by a frog then the energy transfer will be from primary consumer to secondary consumer. The food chain is given below :
 In the above food chain plants are eaten by grasshopper is eaten by a frog. So, the food chain represents plants as producers, grasshopper as primary consumer and frog as a secondary consumer.
In the above food chain plants are eaten by grasshopper is eaten by a frog. So, the food chain represents plants as producers, grasshopper as primary consumer and frog as a secondary consumer.
Q.14. Directions: For question number 14, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R).
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below : (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): The resistivity of the conductor increases with the increasing temperature.
Reason (R): The resistivity is the reciprocal of the conductivity.
Options~
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (b)
Solution.
The resistivity of the conductors is directly proportional to temperature.
Q.15. Directions: For question number 15, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below : (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Sunlight reaches us without dispersion in the form of white light and not as its components.
Reason (R): Dispersion takes place due to variation of refractive index for different wavelength but in a vacuum, the speed of light is independent of wavelength and hence vacuum is a non-dispersive medium.
Options~
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans. (a)
Solution.
In a vacuum speed of light is independent of wavelength. Hence, no dispersion takes places in a vacuum. Thus, a vacuum is a non-dispersive medium in which all colours travel at the same speed.
Q.16. Directions: For question numbers 16, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below : (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
Reason (R): Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction.
Options~
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Q.17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v) All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen. (1 Mark)
(i) Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by
(a) Breathing
(b) Tissue respiration
(c) Organ respiration
(d) Digestion of food
Ans. (b) Tissue respiration.
(ii) The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D.
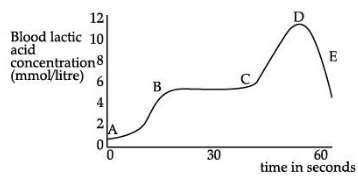
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event?
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(c) Fermentation
(d) Breathing
Ans. (b) Anaerobic respiration.
(iii) Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed.
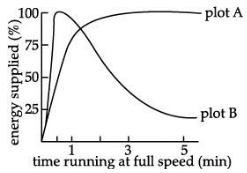
Choose the correct combination of plots and justification provided in the following table.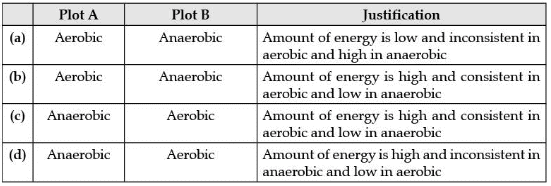
Ans. 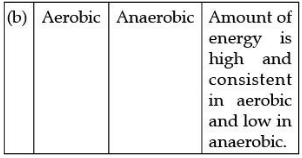
(iv) The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration is
(I) presence of oxygen
(II) release of carbon dioxide
(III) release of energy
(IV) release of lactic acid
Options~
(a) (I), (II) only
(b) (I), (II), (III) only
(c) (II), (III), (IV) only
(d) (IV) only
Ans. (c) (ii), (iii), (iv) only
(v) Study the table below and select the row that has incorrect information.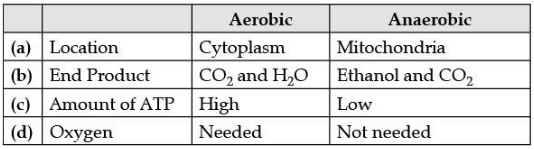
Ans. a) Location
Aerobic-Cytoplasm
and Anaerobic-Mitochondria
Q.18. The given diagram represents the female reproductive system. Study the diagram and answer any four questions.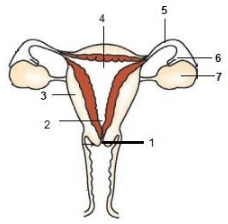
(a) Which part produces ovum? (1 Mark)
(i) 4
(ii) 5
(iii) 6
(iv) 7
Ans. (iv)
Solution.
Label 7 represents ovary. Ovum is produced by ovaries.
(b) The process of fertilisation takes place in which of the following part? (1 Mark)
(i) 4
(ii) 5
(iii) 6
(iv) 7
Ans.
Solution.
(ii) label 5 represent oviduct / fallopian tube. It is the site of fertilisation.
(c) Where does the implantation of the embryo takes place? (1 Mark)
(i) Part 1
(ii) Part 2
(iii) Part 3
(iv) Part 4
Ans. (iv)
Solution.
Implantation of the embryo takes place in part 4, which represents the uterus.
(d) In which part, the block is created surgically to prevent fertilisation? (1 Mark)
(i) Part 4
(ii) Part 5
(iii) Part 6
(iv) Part 7
Ans. (ii) In part 5, which represents the oviduct, the block is created surgically to prevent
fertilization.
(e) Which of the following events is likely to take place, if the nuclei from an 8-celled stage of an embryo are transplanted into enucleated eggs? (1 Mark)
(i) Recipient egg dies
(ii) Donor nuclei die in the new environment
(iii) Cleavage occurs but is arrested after some time
(iv) Formation of the viable embryo in the recipient eggs
Ans. (iv)
Solution.
The zygote divides repeatedly to form a mass of cells known as an embryo. This embryo gets attached to the inner layer of the uterine cavity, i.e., the endometrium. It thickens every month and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. Soon it gets covered by rapidly dividing uterine cells. This leads to pregnancy.
Q.19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v) (1 Mark)
Sumati wanted to see the stars of the night sky. She knows that she needs a telescope to see those distant stars. She finds out that the telescopes, which are made of lenses, are called refracting telescopes and the ones which are made of mirrors are called reflecting telescopes.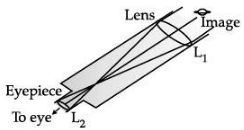
So she decided to make a refracting telescope. She bought two lenses, L1 and L2. out of which L1 was bigger and L2 was smaller. The larger lens gathers and bends the light, while the smaller lens magnifies the image. Big, thick lenses are more powerful. So to see far away, she needed a big powerful lens.
Unfortunately, she realized that a big lens is very heavy.
Heavy lenses are hard to make and difficult to hold in the right place. Also, since the light is passing through the lens, the surface of the lens has to be extremely smooth. Any flaws in the lens will change the image. It would be like looking through a dirty window.
(i) Based on the diagram shown, what kind of lenses would Sumati need to make the telescope?
(a) Concave lenses
(b) Convex lenses
(c) Bifocal lenses
(d) Flat lenses
Ans. (b) Convex lenses
(ii) If the powers of the lenses L1 and L2 are in the ratio of 4: 1, what would be the ratio of the focal length of L1 and L2?
(a) 4 : 1
(b) 1 : 4
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 1 : 1
Ans. (b) 1/4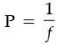
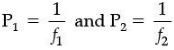
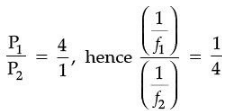
Hence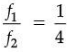
(iii) What is the formula for magnification obtained with a lens?
(a) Ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object
(b) Double the focal length.
(c) Inverse of the radius of curvature.
(d) Inverse of the object distance.
Ans. (a) Ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
(iv) Sumati did some preliminary experiment with the lenses and found out that the magnification of the eyepiece (L2) is 3. If in her experiment with L2 she found an image at 24 cm from the lens, at what distance did she put the object?
(a) 72 cm
(b) 12 cm
(c) 8 cm
(d) 6 cm
Ans. (c) 8 cm
m = v/u
3 = 24/4
Hence u = 8 cm
(v) Sumati bought not-so-thick lenses for the telescope and polished them. What advantages, if any, would she have with her choice of lenses?
(a) She will not have any advantage as even thicker lenses would give clearer images.
(b) Thicker lenses would have made the telescope easier to handle.
(c) Not-so-thick lenses would not make the telescope very heavy and also allow a considerable amount of light to pass.
(d) Not-so-thick lenses will give her more magnification.
Ans. (c) Not-so-thick lenses would not make the telescope very heavy and they will also allow a considerable amount of light to pass through them.
Q.20. Read the following and answer any 4 questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v). (1 Mark)
A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through which a current is run in order to create a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the solenoid is the superposition of the fields due to the current through each coil. It is nearly uniform inside the solenoid and close to zero outside and is similar to the field of a bar magnet having a north pole at one end and a south pole at the other depending upon the direction of current flow. The magnetic field produced in the solenoid is dependent on a few factors such as the current in the coil, the number of turns per unit length etc.
The following graph is obtained by a researcher while doing an experiment to see the variation of the magnetic field with respect to the current in the solenoid.
The unit of the magnetic field as given in the graph attached is in milli-Tesla (mT) and the current is given in Ampere.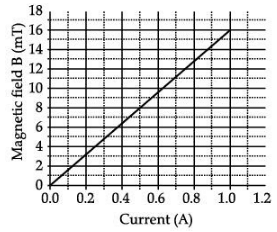 (i) What type of energy conversion is observed in a linear solenoid?
(i) What type of energy conversion is observed in a linear solenoid?
(a) Mechanical to Magnetic
(b) Electrical to Magnetic
(c) Electrical to Mechanical
(d) Magnetic to Mechanical
Ans. (c) Electrical to Mechanical
(ii) What will happen if a soft iron bar is placed inside the solenoid?
(a) The bar will be electrocuted resulting in short-circuit.
(b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
(c) The bar will be magnetised permanently.
(d) The bar will not be affected by any means.
Ans. (b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
(iii) The magnetic field lines produced inside the solenoid are similar to that of … (a) a bar magnet
(b) a straight current-carrying conductor
(c) a circular current carrying loop
(d) electromagnet of any shape
Ans. (a) A bar magnet
(iv) After analysing the graph a student writes the following statements.
1. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is inversely proportional to the current.
2. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to the current.
3. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to the square of the current.
4. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is independent of the current.
Choose from the following which of the following would be the correct statement(s).
(a) Only IV
(b) I and III and IV
(c) I and II
(d) Only II
Ans. (d) Only II
(v) From the graph deduce which of the following statements is correct.
(a) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 13 mT.
(b) For larger currents, the magnetic field increases non-linearly.
(c) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 1.3 mT.
(d) There is not enough information to find the magnetic field corresponding to 0.8 A current.
Ans. (a) For a current of 0.8 A the magnetic field is 13 mT.
Section B
Q. 21. In birds and mammals, the left and right side of the heart are separated. Give reasons. (2 Mark)
Ans. The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs (birds and mammals) which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Q.22. State the events occurring during the process of photosynthesis. Is it essential that these steps take place one after the other immediately? (2 Mark)
Ans.
Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
These steps need not take place one after the other immediately. For example, desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
Q.23. State one difference between Kilowatt and Kilowatt-hour? Express 1 kWh in joules. (2 Mark)
Ans. (i) Kilowatt (kW)—a large unit of electric power Kilowatt-hour (kWh)—a commercial unit of electric energy. 1 kWh—3.6 × 106 Joules
OR
A bulb is rated 5V; 500 mA. Calculate the rated power and resistance of the bulb when it glows.
Ans. Potential difference 5V; current 500 mA = 500 × 10–3 A
P = VI
= 5V × 500 × 10–3 A = 2.5 W
R =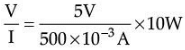
R = 100 Ω
Q. 24. The electronic configuration of an element ‘X’ is 2, 8, 6. To which group and period of the modern periodic table do ‘X’ belong. State its valency. (2 Mark)
Ans. X : 2, 8, 6
(a) Since ‘X’ has three energy shells and the period number of an element is equal to the
number of energy shells. X belongs to the 3rd period.
(b) X has 6 valence electrons it belongs to group 16.
(c) Valency will be 2. To acquire noble gas configuration it will gain 2 electrons.
Q.25. What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of the magnetic field at a point in a magnetic field determined using field lines? (2 Mark)
Ans. A magnetic field line is a path along which a free north-pole tends to move. The direction of a magnetic field at a point is determined by placing a small compass needle. The N - pole of the compass indicates the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
Q.26. What is a scattering of light? Explain with the help of an example. (2 Mark)
Ans. The phenomenon of change in the direction of propagation of light caused by a large number of particles present in the atmosphere is called the scattering of light.
Example: The path of the beam of light becomes visible through a colloidal solution due to the scattering of light.
SECTION C
Q.27. Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions? (3 Mark)
(i) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(ii) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
(iii) Carbon-dioxide is passed through lime water.
Ans.
(i) 2Al + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
(ii) Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
(iii) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Q.28. Give a reason why carbon can neither form C4+ cations nor C4– anions but forms covalent compounds. Also, state the reason to explain why covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting and boiling points? (3 Mark)
Ans. Carbon cannot form C4+ cation because the removal of 4 electrons from a carbon atom would require a large amount of energy. Carbon cannot form C4– anion because it would be difficult for the nucleus with 6 protons to hold on to 10 electrons. Hence, carbon atoms share electrons forming covalent compounds. Covalent compounds do not form ions/ charged particles and therefore do not conduct electricity. Intermolecular forces of attraction are weak, hence they have low melting and boiling points.
Q.29. (i) Define Genetics.
(ii) Who is regarded as the ‘Father of Genetics’? Name the plant on which he performed his experiment.
(iii) Why did he select that specific plant for his experiments? (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) Genetics is the branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity and variations.
(ii) Gregor Johann Mendel, garden pea.
(iii) Garden pea plants were easily available / they grow in one season/fertilization was easy.
Q.30. (a) Which of the following reactions is/ are an endothermic reaction(s) where decomposition also happens? (3 Mark)
- Respiration
- Heating of lead nitrate
- Decomposition of organic matter
- Electrolysis of acidified water
Ans. (a) Heating of lead nitrate; and electrolysis of acidified water
(b) Silver chloride when kept in the open turns grey. Illustrate this with a balanced chemical equation.
Ans. (b) 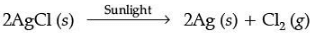
(No deduction for not mentioning the state of reactants and products.)
Q.31. The following table shows the position of five elements A, B, C, D and E in the modern periodic table. (3 Mark)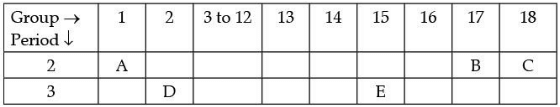 Answer the following giving reasons :
Answer the following giving reasons :
(i) Which element is a metal with valency two?
(ii) Which element is the least reactive?
(iii) Out of D and E which element has a smaller atomic radius?
Ans. (i) D, as it is on the left side of the table in group 2
(ii) C, as it is in the group 18/ Noble gas
(iii) E, as we move from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases.
Q.32. What is meant by the power of a lens? Write the SI unit? A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of – 20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens? (3 Mark)
Ans. Power of lens = Ability to converge/diverge light rays passing through it/ reciprocal of the focal length in meters 1/f (in meters),
SI unit of power is Dioptre
Power of 1st lens P1
Nature: Converging lens/Convex lens,
Power of 2nd lens P2 = 
Nature : Diverging lens / Concave lens
Q.33. What is meant by Solenoid? How does a current-carrying Solenoid behave? Give its main use. (3 Mark)
Ans. A closely wound cylindrical coil of insulated metallic wire. A current-carrying solenoid behaves as an electromagnet. The uniform magnetic field inside it may magnetise a steel rod permanently.
Detailed Answer :
A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a Solenoid. The field lines around a current-carrying solenoid are similar to those produced by a bar magnet. This means that a current-carrying solenoid behaves as having a north pole and a south pole. The strong magnetic field produced inside a solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the coil.
SECTION D
Q.34. An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to determine the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) in this case.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to justify your answer to the part (ii). (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) u = – 30 cm, f = –30 cm, v = ?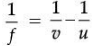
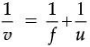
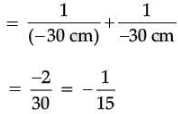
∴ v = – 15 cm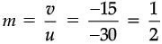
The distance of the image will be 20 cm in front of the lens.
(ii) Nature: Virtual
Position: 15 cm from lens on the same side as the object
Size: Diminished
Erect/Inverted : Erect
(iii)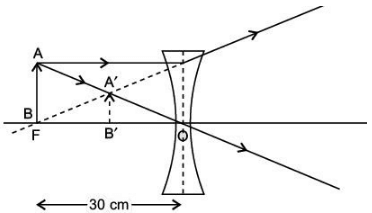
OR
(i) A lens produces a magnification of – 0.5. Is this a converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the lens is 6 cm, draw a ray diagram showing the image formation in this case.
(ii) A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from a laser torch by directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was surprised to see that in a particular direction, the beam of light continues to move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason for her observation. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
Ans. (i) The image will be real and inverted since the magnification has a negative value. The lens that can produce a real and inverted image is a converging/ convex lens.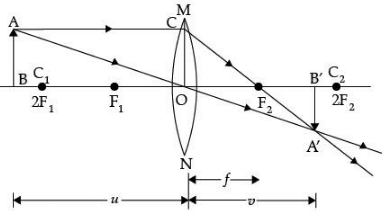 In the figure OF1 = OF2 = 6 cm.
In the figure OF1 = OF2 = 6 cm.
(Marks will be deducted if arrows are not shown)
(ii) The girl must have directed the ray of light along the direction of the optical centre of the lens because the ray of light passes straight through the optical centre of the lens.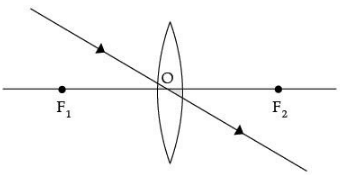
Q.35. (a) List in the tabular form any three chemical properties on the basis of which metals and nonmetals are differentiated.
(b) State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron. (5 Mark)
Ans. (a)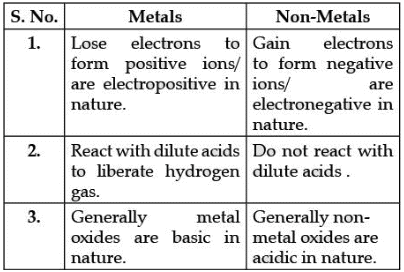
(b) (i) Painting
(ii) Oiling
(iii) Galvanization
(vi) Alloying
Q.36. What is the Tyndall effect? What are its causes? Name and explain two phenomena observed in daily life that are based on the Tyndall effect. (5 Mark)
Ans. Tyndall effect: The phenomena of scattering of light by dust, smoke and water droplets suspended in air is known as the Tyndall effect.
Cause of Tyndall effect: The earth's atmosphere is a heterogeneous mixture of minute particles. These particles include smoke, tiny water dropLets, suspended particles of dust and molecules of air. When a beam of light strikes such fine particles, the path of the beam becomes visible. The light reaches us, after getting diffused and reflected by these particles. The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particLes gives rise to the Tyndall effect.
Some applications of the Tyndall effect are:
(1) When a fine beam of sunlight enters a smoke-filled room through a small hole, the smoke particles become visible due to the scattering of light
(2) When sunlight passes through a canopy of a dense forest, the tiny water droplets in the mist scatter light and become visible.
OR
(A) What is the scattering of light? How does it take place in the earth's atmosphere? List the factors on which scattering of light depends. Name two phenomena that are based on the scattering of light.
(B) Tyndall effect can be observed when sunlight passes through a canopy of a dense forest. Identify the scatter.
Ans. (A) Scattering of light is the phenomenon of inter play of light with minute sized particles. As a result of such interplay, light spreads in different directions and also becomes visible.
The earth's atmosphere is a heterogeneous mixture of minute particLes including smoke, tiny water dropLets, suspended dust particLes and molecules of air. When a beam of light strikes these particles, the path of the beam becomes visible due to scattering. The factors on which scattering of light depends are:
(i) Size of scattering particles
(ii) Wavelength of light
(B) Two phenomenon which is based on the scattering of light are:
(i) Blue coLour of the sky
(ii) Colour of water in the deep sea
(iii) The reddening of the sun at sunrise and sunset
(iv) Tyndall effect.
(Any two)
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 3 - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the CBSE sample question paper for Class 10 Science? |  |
| 2. Why is it important to solve CBSE sample question papers for Class 10 Science? |  |
| 3. Where can I find CBSE sample question papers for Class 10 Science? |  |
| 4. Are CBSE sample question papers for Class 10 Science the same as the actual board exam question paper? |  |
| 5. Can solving CBSE sample question papers guarantee success in the Class 10 Science exam? |  |

















