NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties | Chemistry Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which of the following statements are true? [NEET 2025]
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C and D only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) A, B and E only
(d) C and E only
Ans: (d)
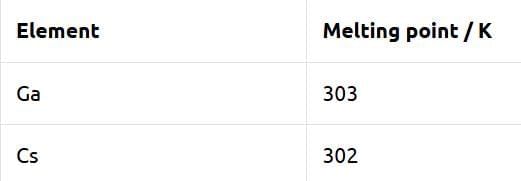
Statement A: "Unlike Ga that has a very high melting point, Cs has a very low melting point."
- This statement is False. Gallium (Ga) has a relatively high melting point, while Cesium (Cs) has an almost equal melting point.
Statement B: "On Pauling scale, the electronegativity values of N and Cl are same."
- This statement is incorrect. Nitrogen (N) has an electronegativity of 3.04, and Chlorine (Cl) has an electronegativity of 3.16 on the Pauling scale, so they have different electronegativities.
Statement C: "K⁺, Cl⁻, Ca²⁺ and S²⁻ are all isoelectronic species."
- This statement is true. All these ions (K⁺, Cl⁻, Ca²⁺, and S²⁻) have the same number of electrons (18 electrons), making them isoelectronic species.
Statement D: "The correct order of the first ionization enthalpies of Na, Mg, Al, and Si is Si > Al > Mg > Na."
- This statement is incorrect. The correct order of ionization enthalpies is Si > Al > Mg > Na. Magnesium (Mg) has a higher ionization enthalpy than Aluminum (Al), and Sodium (Na) has the lowest ionization enthalpy due to its larger atomic size and lower nuclear charge compared to others.
Statement E: "The atomic radius of Cs is greater than that of Li and Rb."
- This statement is correct. While Cesium (Cs) has a larger atomic radius than Lithium (Li), it is also larger than Rubidium (Rb). The atomic radius increases as you move down a group in the periodic table, so Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs..
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option d) C and E only.
Q2: Which among the following electronic configurations belong to main group elements? [NEET 2025]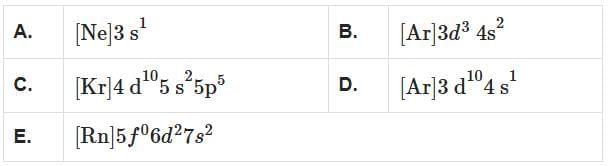
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
(a) D and E only.
(b) A, C and D only.
(c) B and E only.
(d) A and C only.
Ans: (d)
Analyze the given electronic configurations to determine whether they belong to main group elements:
- A. [Ne]3s1: This corresponds to sodium (Na), which is in Group 1. It is a main group element.
- B. [Ar]3d34s2: This corresponds to vanadium (V), which is a transition metal (Group 5). It is not a main group element.
- C. [Kr]4d105s25p5: This corresponds to iodine (I), which is in Group 17. It is a main group element.
- D. [Ar]3d104s1: This corresponds to copper (Cu), which is a transition metal (Group 11). It is not a main group element.
- E. [Rn]5f06d27s2: This corresponds to thorium (Th), which is an actinide and not a main group element.
So, only A and C belong to main group elements.
2024
Q1: Arrange the following elements in increasing order of electronegativity: [NEET 2024]N, O, F, C, Si
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) Si < C < N < O < F
(b) Si < C < O < N < F
(c) O < F < N < C < Si
(d) F < O < N < C < Si
Ans: (a)
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons (or electron density) towards itself in a chemical bond. The Pauling scale is the most commonly used scale to measure electronegativity. According to this scale:
The electronegativity of Fluorine (F) is the highest among the elements at around 3.98.
Oxygen (O) follows next with an electronegativity of about 3.44.
Nitrogen (N) has an electronegativity of approximately 3.04.
Carbon (C) has an electronegativity value close to 2.55.
Silicon (Si), being further down the group in the periodic table than Carbon, has a lower electronegativity of about 1.90.
Based on these values, we can arrange the elements in order of increasing electronegativity as follows:
Si < C < N < O < F
Thus, considering the options provided:
Option A: Si < C < N < O < F is the correct answer since it correctly ranks the elements from the lowest to the highest electronegativity.
Q2: Arrange the following elements in increasing order of first ionization enthalpy: [NEET 2024]
Li, Be, B, C, N
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Li < Be < B < C < N
(b) Li < B < Be < C < N
(c) Li < Be -< C < B < N
(d) Li < Be < N < B < C
Ans: (b)
The first ionization enthalpy, also known as ionization energy, is the energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a neutral atom in the gaseous phase to form a cation. The trend of first ionization energies generally increases across a period from left to right in the periodic table. This is due to the increasing nuclear charge and the decreasing atomic radius, which cause the valence electrons to be attracted more strongly to the nucleus.
However, there are notable exceptions based on the electron configuration stability and electron pairing in orbitals. Let's analyze the given elements:
Lithium (Li): Being the first element in the period, it has the smallest nuclear charge and only one electron in its outer shell, which makes it easy to remove an electron.
Beryllium (Be): This element has two electrons in the 2s orbital. The removal of one electron slightly disturbs the fully filled 2s sub-shell, creating more stability than having an unpaired electron. Therefore, Be has a higher ionization energy than Li.
Boron (B): This element has a half-filled 2p orbital configuration (one electron in the 2p orbital), which is relatively less stable compared to a full or empty p orbital, leading to a slightly lower ionization energy than Be.
Carbon (C): With two electrons in separate 2p orbitals (following Hund's rule), C experiences more effective nuclear shielding and electron-electron repulsion compared to a single electron in Boron's 2p orbital. This makes it relatively easier to remove an electron from B than from C, but harder than removing one from Be.
Nitrogen (N): It has exactly half-filled 2p orbitals, which provides extra stability and hence has a higher ionization energy than Carbon. Contrarily, the configuration of three p electrons is stable owing to the exchange energy and symmetric distribution in space.
Given these points, we can order the elements by increasing first ionization enthalpy as follows:
Li < B < Be < C < N
This matches with Option B. Thus, the correct answer is:
Option B
Li < B < Be < C < N
Q3: Identify the incorrect statement: [NEET 2024]
(a) The oxidation state and coordination number (or covalency) of Al in [AlCl(H₂O)₅]²⁺ are +3 and 6, respectively.
(b) Na₂O is a basic oxide and Cl₂O₇ is an acidic oxide.
(c) The following four species are called isoelectronic species: O²⁻, F⁻, Na⁺, and Mg²⁺.
(d) Among the four species Mg, Al, Mg²⁺, and Al³⁺, the smallest one is Al.
Ans: (d)
Statement 1: The oxidation state of Al in [AlCl(H₂O)₅]²⁺ is +3, and the coordination number (covalency) is 6, which is correct for this complex. Thus, Statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: Na₂O is indeed a basic oxide (since Na is an alkali metal), and Cl₂O₇ is an acidic oxide (since it is formed by a non-metal). Therefore, Statement 2 is correct.
Statement 3: O²⁻, F⁻, Na⁺, and Mg²⁺ all have the same number of electrons (10 electrons), making them isoelectronic species. Therefore, Statement 3 is correct.
Statement 4: Mg has an atomic radius larger than Mg²⁺, Al is larger than Al³⁺. Therefore, the smallest ion among Mg, Al, Mg²⁺, and Al³⁺ is Al³⁺, not Al. Hence, Statement 4 is incorrect.
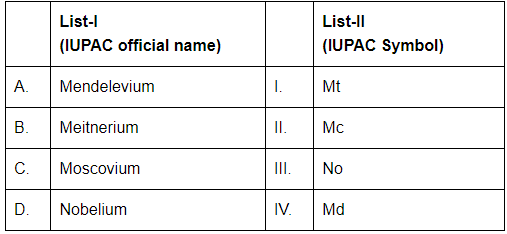
Q4: Match List-I with List-II : [NEET 2024]
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(c) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Ans: (c)
A. Mendelevium
The symbol for Mendelevium is Md.
B. Meitnerium
The symbol for Meitnerium is Mt.
C. Moscovium
The symbol for Moscovium is Mc.
D. Nobelium
The symbol for Nobelium is No.
Thus, the correct match is: A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
So, the correct answer is (c).
Q5: The correct decreasing order of atomic radii (pm) of Li, Be, B, and C is: [NEET 2024]
(a) Be > Li > B > C
(b) Li > Be > B > C
(c) C > B > Be > Li
(d) Li > C > Be > B
Ans: (b)
The atomic radius generally decreases as we move across a period from left to right, due to the increase in nuclear charge, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus. On the other hand, the atomic radius increases as we move down a group because the number of electron shells increases, making the atom larger.
Now, let's look at the elements in question:
- Li (Lithium): Group 1, Period 2
- Be (Beryllium): Group 2, Period 2
- B (Boron): Group 13, Period 2
- C (Carbon): Group 14, Period 2
- Li has the largest atomic radius because it's in Group 1 and Period 2, so it has the least nuclear charge compared to the others.
- Be has a smaller atomic radius than Li because it is in Group 2, and its increased nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer.
- B has a smaller atomic radius than Be, as it is further across the period (Group 13).
- C has the smallest atomic radius, as it is in Group 14 and further along the period, with the highest nuclear charge.
Thus, the correct order is: Li > Be > B > C.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b).
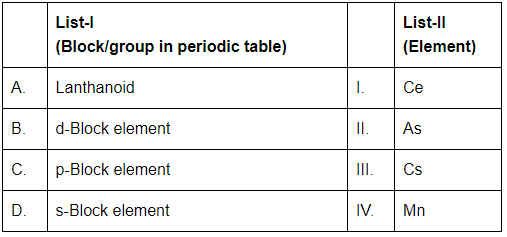
Q6: Match List-I with List-II [NEET 2024]
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(b) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(c) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(d) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
Ans: (c)
A. Lanthanoid
Lanthanoids are elements in the f-block of the periodic table. The element Ce (Cerium) is a lanthanoid.
So, A-I: Ce.
B. d-Block element
d-block elements are transition metals. The element Mn (Manganese) belongs to the d-block.
So, B-IV: Mn.
C. p-Block element
p-block elements are located in groups 13 to 18. The element As (Arsenic) is a p-block element.
So, C-II: As.
D. s-Block element
s-block elements are found in groups 1 and 2. The element Cs (Cesium) is an s-block element.
So, D-III: Cs.
Thus, the correct answer is (C) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III.
2023
Q1: The element expected to form the largest ion to achieve the nearest noble gas configuration is: [NEET 2023]
(a) Sodium (Na)
(b) Oxygen (O)
(c) Fluorine (F)
(d) Nitrogen (N)
Ans: (d)
To determine which element forms the largest ion to achieve the nearest noble gas configuration, we need to consider how each element achieves a stable electron configuration and the size of the resulting ion.
- Sodium (Na): Sodium has an atomic number of 11 and typically forms a Na⁺ ion by losing 1 electron. The electron configuration of Na is [Ne]3s¹, and when it loses one electron, it achieves the electron configuration of Ne (a noble gas). The ion Na⁺ is smaller compared to the neutral atom.
- Oxygen (O): Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 and typically forms an O²⁻ ion by gaining 2 electrons. The electron configuration of O is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴, and when it gains 2 electrons, it achieves the electron configuration of Ne (a noble gas). The ion O²⁻ is larger than the neutral oxygen atom due to the increased electron-electron repulsion after gaining electrons.
- Fluorine (F): Fluorine has an atomic number of 9 and typically forms an F⁻ ion by gaining 1 electron. The electron configuration of F is 1s² 2s² 2p⁵, and when it gains 1 electron, it achieves the electron configuration of Ne (a noble gas). The ion F⁻ is also larger than the neutral fluorine atom due to the increased electron-electron repulsion.
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7 and typically forms a N³⁻ ion by gaining 3 electrons. The electron configuration of N is 1s² 2s² 2p³, and when it gains 3 electrons, it achieves the electron configuration of Ne (a noble gas). The N³⁻ ion is the largest among the ions because it gains 3 electrons, which causes the largest increase in size due to electron-electron repulsion.
Thus, the N³⁻ ion formed by Nitrogen (N) is the largest, as it gains 3 electrons and achieves the noble gas configuration of Ne.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) Nitrogen (N).
Q2: Which one of the following represents all isoelectronic species? [NEET 2023]
(a) Na⁺, Cl⁻, O⁻, NO⁺
(b) N₂O, N₂O₄, NO⁺, NO
(c) Na⁺, Mg²⁺, O⁻, F⁻
(d) Ca²⁺, Ar, K⁺, Cl⁻
Ans: (d)
To determine which set of species are isoelectronic, we need to check if they all have the same number of electrons.
Isoelectronic species:These are species that have the same number of electrons but may differ in their nuclear charge.Let's check the electron count for each option:Option (a): Na⁺, Cl⁻, O⁻, NO⁺
- Na⁺: Atomic number of Na = 11, so Na⁺ has 10 electrons.
- Cl⁻: Atomic number of Cl = 17, so Cl⁻ has 18 electrons.
- O⁻: Atomic number of O = 8, so O⁻ has 9 electrons.
- NO⁺: Nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7 and oxygen (O) has an atomic number of 8. NO⁺ has 9 electrons (8 from oxygen and 1 from nitrogen, after losing an electron).
So, these species are not isoelectronic.
Option (b): N₂O, N₂O₄, NO⁺, NO
- The electron count for each of these species would need to be checked individually, but from the atomic structure, it's clear that they do not all have the same number of electrons. So, they are not isoelectronic.
Option (c): Na⁺, Mg²⁺, O⁻, F⁻
- Na⁺: 10 electrons (from earlier)
- Mg²⁺: Atomic number of Mg = 12, so Mg²⁺ has 10 electrons.
- O⁻: 9 electrons.
- F⁻: Atomic number of F = 9, so F⁻ has 10 electrons.
These species are not all isoelectronic, as O⁻ has 9 electrons, while the others have 10.
Option (d): Ca²⁺, Ar, K⁺, Cl⁻
- Ca²⁺: Atomic number of Ca = 20, so Ca²⁺ has 18 electrons.
- Ar: Atomic number of Ar = 18, so Ar has 18 electrons.
- K⁺: Atomic number of K = 19, so K⁺ has 18 electrons.
- Cl⁻: Atomic number of Cl = 17, so Cl⁻ has 18 electrons.
All these species have 18 electrons and are isoelectronic with each other.
Conclusion: The correct answer is (d) Ca²⁺, Ar, K⁺, Cl⁻ because they all have the same number of electrons (18) and are isoelectronic.
Q3: Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? [NEET 2023]
(a) Basic oxides - In₂O₃, K₂O, SnO₂
(b) Neutral oxides - CO, NO₂, N₂O
(c) Acidic oxides - Mn₂O₇, SO₂, TeO₃
(d) Amphoteric oxides - BeO, Ga₂O₃, GeO
Ans: (c)
Basic oxides: Basic oxides are typically oxides of metals that react with acids to form salts and water. Examples include In₂O₃, K₂O, and SnO₂.
However, SnO₂ is slightly amphoteric, so this option is not entirely accurate.
Neutral oxides: Neutral oxides are oxides that do not react significantly with either acids or bases. CO, NO₂, and N₂O are all neutral oxides.
- CO (Carbon monoxide) is neutral.
- NO₂ (Nitrogen dioxide) and N₂O (Dinitrogen monoxide) are neutral oxides as well.
- So, option (b) is incorrect.
Acidic oxides: Acidic oxides are oxides that react with water to form acids and can react with bases to form salts. Examples include Mn₂O₇, SO₂, and TeO₃.
- Mn₂O₇ (Manganese heptoxide) is acidic.
- SO₂ (Sulfur dioxide) is acidic.
- TeO₃ (Tellurium trioxide) is also acidic.
Therefore, option (c) is correct.
Amphoteric oxides: Amphoteric oxides can act both as acids and bases. Examples include BeO, Ga₂O₃, and GeO.
- BeO (Beryllium oxide) is amphoteric.
- Ga₂O₃ (Gallium oxide) is amphoteric.
- GeO (Germanium oxide) is also amphoteric.
- This matches well with the definition of amphoteric oxides, making option (d) correct.
Conclusion: The correct answer is (c) Acidic oxides - Mn₂O₇, SO₂, TeO₃.
Q4: The correct sequence given below contains neutral, acidic, basic, and amphoteric oxide each, respectively is:
(a) NO, ZnO, CO₂, CaO
(b) ZnO, NO, CaO, CO₂
(c) NO, CO₂, ZnO, CaO
(d) NO, CO₂, CaO, ZnO [NEET 2023]
Ans: (d)
- NO (Nitric oxide) is a neutral oxide, as it does not react significantly with acids or bases.
- CO₂ (Carbon dioxide) is an acidic oxide, as it reacts with water to form an acid (H₂CO₃) and with bases to form salts.
- CaO (Calcium oxide) is a basic oxide, as it reacts with acids to form salts and water.
- ZnO (Zinc oxide) is amphoteric, as it can react with both acids and bases to form salts.
So, the correct sequence is: NO (neutral), CO₂ (acidic), CaO (basic), ZnO (amphoteric).
Thus, the correct answer is (d) NO, CO₂, CaO, ZnO.
2022
Q1: The IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 119 is (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) ununoctium
(b) ununennium
(c) unnilennium
(d) unununnium
Ans: (b)
IUPAC name of element : 119 : ununennium
Q2: Gadolinium has a low value of third ionisation enthalpy because of (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) small size
(b) high exchange enthalpy
(c) high electronegativity
(d) high basic character
Ans: (b)
Electronic configuration of Gadolinium
Gd :- [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
In case of 3rd ionisation enthalpy electron will be removed from 5d and resultant configuration will be [Xe]4f7 that is stable electronic configuration as it will have high exchange energy, hence less energy will be required to remove 3rd electron.
Q3: The correct order of first ionization enthalpy for the given four elements is :
(a) C < F < N < O
(b) C < N < F < O
(c) C < N < O < F
(d) C < O < N < F (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
- Generally, on moving left to right in a period. First ionization enthalpy of elements increases due to increase in effective nuclear charge.
- Due to more stable half-filled outer electronic configuration (2s22p3) of N, its first ionization enthalpy is more than O.
So, correct order of IP is : C < O < N < F
Q4: Decrease in size from left to right in actinoid series is greater and gradual than that in lanthanoid series due to
(a) 5f orbitals have greater shielding effect
(b) 4f orbitals are penultimate
(c) 4f orbitals have greater shielding effect
(d) 5f orbitals have poor shielding effect (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
Due to more diffused nature of 5f orbitals as compared to 4f orbitals the shielding effect of 5f is poor, resulting in the decrease in size from left to right in actinoid series which is greater and gradual than that in lanthanoid series
Q5: Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine because : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) F-F bond has a low enthalpy of dissociation.
(b) Fluoride ion (F
(c) Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than chlorine.
(d) Fluorine has a very small size.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given :
(a) (b) and (c) only
(b) (a) and (b) only
(c) (a) and (c) only
(d) (a) and (d) only
Ans: (b)
Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine due to
(i) Low dissociation enthalpy of F-F bond
(ii) High hydration enthalpy of F− ion
2020
Q1: Identify the incorrect match. (NEET 2020)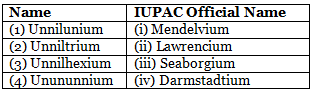
(a) (3), (iii)
(b) (4), (iv)
(c) (1), (i)
(d) (2), (ii)
Ans: b
101 - Unnilunium - Mendelevium
103 - Unniltrium - Lawrencium
106 - Unnilhexium - Seaborgium
111 - Unununium - Roentgenium
110 - Ununnilium - Darmstadtium
Q2: Match the following : (NEET 2020)
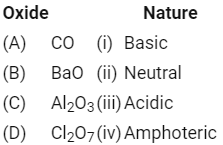
Which of the following is correct option?
(a) 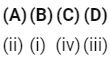
(b) 
(c) 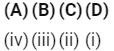
(d) 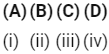
Ans: (a)
CO : Neutral oxide
BaO : Basic oxide
Al2O3 : Amphoteric oxide
Cl2O7 : Acidic oxide
2019
Q1: For the second period elements the correct increasing order of first ionisation enthalpy is: (NEET 2019)
(a) Li < Be < B < C < N < O < F < Ne
(b) Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne
(c) Li < B < Be < C < N < O < F < Ne
(d) Li < Be < B < C < O < N < F < Ne
Ans: (b)
Ionisation enthalpy increases in a period from left to right, because of increased nuclear charge and decrease in atomic radii. But because of half filled orbitals of Be, N and fully filled orbitals of Ne, stability of those atoms inceases.
So, the correct increasing order of first ionisation enthalpy will be :
Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne
2018
Q1: The correct order of atomic radii in group 13 elements is (NEET 2018)
(a) B < Al < In < Ga < Tl
(b) B < Al < Ga < In < Tl
(c) B < Ga < Al < Tl < In
(d) B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Ans: (d)
Ga is slightly smaller than Al due poor shielding of d e– so Zeff increasing.
So, Atomic size : B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Q2: Which of the following oxides is most acidic in nature? (NEET 2018)
(a) MgO
(b) BeO
(c) BaO
(d) CaO
Ans: (b)
In metals, on moving down the group, metallic character increases, so basic nature increases hence most acidic will be BeO. In fact, BeO is amphoteric oxide while other given oxides are basic oxides.
2017
Q1: The element Z = 114 has been discovered recently. It will belong to which of the following family/groupand electronic configuration ? (NEET 2017)
(a) 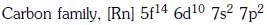
(b) 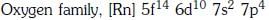
(c) 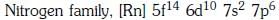
(d) 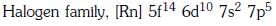
Ans: (a)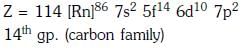
2015
Q1: The species Ar, K+ and Ca2+ contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase ?
(a) K+< Ar < Ca2+
(b) Ar < K+< Ca2+
(c) Ca2+ < Ar < K+
(d) Ca2+ < K+ < Ar (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
Ans: (d)
⇒ Ca2+ < K+ < Ar
Ar, K+ and Ca2+ are isoelectronic i.e with the same number of electrons, 18. For isoelectronic species, ionic radii decrease with increases in effective (relative) positive charge. Also Ar, K and Ca belong to the same period.
2014
Q.9. Which of the following orders of ionic radii is correctly represented? (NEET 2014)
(a) F- > O2- > Na+
(b) Al3+ > Mg2+ > N3-
(c) H- > H. > H
(d) Na+ > F > O2-
Ans: (c)
Cation loose electrons are smaller in size than the parent atom, where anions gain electrons are larger in size than the parent atom.
Hence the order is H- > H. > H+
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - Chemistry Class 11
| 1. What is the modern periodic table and how is it arranged? |  |
| 2. How many periods and groups are there in the periodic table? |  |
| 3. What are the trends in atomic size and ionization energy across a period in the periodic table? |  |
| 4. How do elements in the same group of the periodic table exhibit similar chemical properties? |  |
| 5. Why do noble gases have very low reactivity compared to other elements in the periodic table? |  |

















