HTML URL Encode & HTML vs XHTML | HTML for Junior Classes - Class 3 PDF Download
HTML Uniform Resource Locators
A URL is another word for a web address.
A URL can be composed of words (e.g. w3schools.com), or an Internet Protocol (IP) address (e.g. 192.68.20.50).
Most people enter the name when surfing, because names are easier to remember than numbers.
URL - Uniform Resource Locator
Web browsers request pages from web servers by using a URL.
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is used to address a document (or other data) on the web.
scheme://prefix.domain:port/path/filename
Explanation:
- scheme - defines the type of Internet service (most common is http or https)
- prefix - defines a domain prefix (default for http is www)
- domain - defines the Internet domain name (like w3schools.com)
- port - defines the port number at the host (default for http is 80)
- path - defines a path at the server (If omitted: the root directory of the site)
- filename - defines the name of a document or resource
Common URL Schemes
The table below lists some common schemes: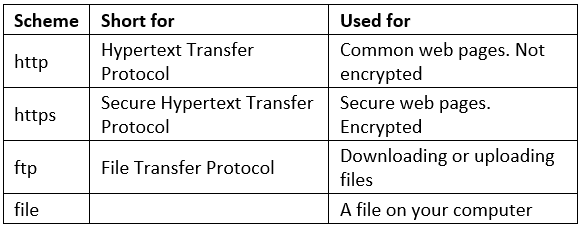
URL Encoding
URLs can only be sent over the Internet using the ASCII character-set. If a URL contains characters outside the ASCII set, the URL has to be converted.
URL encoding converts non-ASCII characters into a format that can be transmitted over the Internet.
URL encoding replaces non-ASCII characters with a "%" followed by hexadecimal digits.
URLs cannot contain spaces. URL encoding normally replaces a space with a plus (+) sign, or %20.
ASCII Encoding Examples
Your browser will encode input, according to the character-set used in your page.
The default character-set in HTML5 is UTF-8.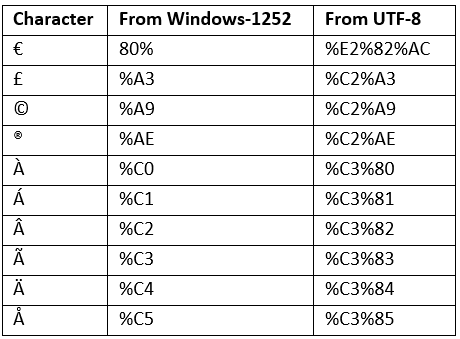
HTML Versus XHTML
XHTML is a stricter, more XML-based version of HTML.
What is XHTML?
- XHTML stands for EXtensible HyperText Markup Language
- XHTML is a stricter, more XML-based version of HTML
- XHTML is HTML defined as an XML application
- XHTML is supported by all major browsers
Why XHTML?
XML is a markup language where all documents must be marked up correctly (be "well-formed").
XHTML was developed to make HTML more extensible and flexible to work with other data formats (such as XML). In addition, browsers ignore errors in HTML pages, and try to display the website even if it has some errors in the markup. So XHTML comes with a much stricter error handling.
The Most Important Differences from HTML
- <!DOCTYPE> is mandatory
- The xmlns attribute in <html> is mandatory
- <html>, <head>, <title>, and <body> are mandatory
- Elements must always be properly nested
- Elements must always be closed
- Elements must always be in lowercase
- Attribute names must always be in lowercase
- Attribute values must always be quoted
- Attribute minimization is forbidden
XHTML - <!DOCTYPE ....> Is Mandatory
An XHTML document must have an XHTML <!DOCTYPE> declaration.
The <html>, <head>, <title>, and <body> elements must also be present, and the xmlns attribute in <html> must specify the xml namespace for the document.
Example
Here is an XHTML document with a minimum of required tags:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Title of document</title>
</head>
<body>
some content here...
</body>
</html>
XHTML Elements Must be Properly Nested
In XHTML, elements must always be properly nested within each other, like this:
Correct:
<b><i>Some text</i></b>
Wrong:
<b><i>Some text</b></i>
XHTML Elements Must Always be Closed
In XHTML, elements must always be closed, like this:
Correct:
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
<p>This is another paragraph</p>
Wrong:
<p>This is a paragraph
<p>This is another paragraph
XHTML Empty Elements Must Always be Closed
In XHTML, empty elements must always be closed, like this:
Correct:
A break: <br />
A horizontal rule: <hr />
An image: <img src="https://cn.edurev.in/appy.gif" alt="Happy face" />
Wrong:
A break: <br>
A horizontal rule: <hr>
An image: <img src="https://cn.edurev.in/appy.gif" alt="Happy face">
XHTML Elements Must be in Lowercase
In XHTML, element names must always be in lowercase, like this:
Correct:
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
</body>
Wrong:
<BODY>
<P>This is a paragraph</P>
</BODY>
XHTML Attribute Names Must be in Lowercase
In XHTML, attribute names must always be in lowercase, like this:
Correct:
<a href="https://www.w3schools.com/html/">Visit our HTML tutorial</a>
Wrong:
<a HREF="https://www.w3schools.com/html/">Visit our HTML tutorial</a>
XHTML Attribute Values Must be Quoted
In XHTML, attribute values must always be quoted, like this:
Correct:
<a href="https://www.w3schools.com/html/">Visit our HTML tutorial</a>
Wrong:
<a href=https://www.w3schools.com/html/>Visit our HTML tutorial</a>
XHTML Attribute Minimization is Forbidden
In XHTML, attribute minimization is forbidden:
Correct:
<input type="checkbox" name="vehicle" value="car" checked="checked" />
<input type="text" name="lastname" disabled="disabled" />
Wrong:
<input type="checkbox" name="vehicle" value="car" checked />
<input type="text" name="lastname" disabled />
|
14 videos|31 docs|24 tests
|




















