Geography: August 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Monsoon, El Nino And Their Impact on Agriculture |

|
| Equatorial Origin Cyclones and Pacific Decadal Oscillation |

|
| El Nino Southern Oscillation |

|
| Container Terminal Project at Deendayal Port |

|
Monsoon, El Nino And Their Impact on Agriculture
Why in News?
The 2023 southwest monsoon season in India started late, with the initial two weeks experiencing a significant rainfall deficiency of 52.6% below the normal long-period average(LPA).
- However, as of July 30, 2023 there was an overall 6% surplus rainfall. This turnaround has positively impacted kharif crop plantings. However, concerns persist regarding the potential impact of the approaching El Nino phenomenon on rabi crops.
What is the Long-Period Average (LPA) of Rainfall?
- The IMD defines the "LPA of rainfall" as the average rainfall recorded over a specific region for a long period, like 30 or 50 years. Based on this, the IMD classifies rainfall into five categories on an all-India scale:
- Normal or near normal: Rainfall between 96-104% of LPA.
- Below normal: Rainfall between 90-96% of LPA.
- Above normal: Rainfall between 104-110% of LPA.
- Deficient: Rainfall less than 90% of LPA.
- Excess: Rainfall more than 110% of LPA.
What are Kharif and Rabi Crops?
- Kharif crops:
- Kharif crops are sown during the monsoon season, from June to October, and harvested in the late summer or early autumn.
- They depend on the southwest monsoon for irrigation and growth.
- Major Kharif crops include rice, maize, sorghum, pearl millet (bajra), finger millet (ragi), groundnut and pulses like pigeon pea (arhar) and green gram (moong).
- They account for about 55% of the total foodgrain production in India.
- Rabi Crops:
- These crops are sown around the Retreating Monsoon and Northeast monsoon season, which begins in October and are called rabi or winter crops.
- The harvest for these crops happens typically during April and May, during the summer season.
- Major Rabi crops are wheat, gram, peas, barley etc.
- A warm climate is required for seed germination and cold climate for the growth of crops.
What is the Impact of Monsoon on Indian Agriculture?
Positive Impacts:
- Increased Crop Production: A major portion of the country's crop area is completely dependent on Monsoon rains as they're not equipped with methods of manual irrigation.
- Adequate rainfall during the monsoon season leads to increased soil moisture and promotes the growth of crops, resulting in higher agricultural output.
- The availability of water supports the cultivation of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, millets, and pulses.
- Economic Boost: Successful monsoon seasons contribute to rural prosperity by providing income to farmers and laborers, which, in turn, stimulates demand for goods and services in the rural economy.
- This increased economic activity has a positive impact on overall national growth.
- Recharge of Groundwater: The monsoon helps recharge groundwater resources, which is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices in regions where water scarcity is a challenge.
Negative Impacts:
- Erratic Monsoon Patterns: The monsoon's timing, intensity, and distribution are unpredictable, leading to uncertainties in agricultural planning and crop management.
- Delayed or early monsoons can disrupt planting schedules and affect crop yields.
- Droughts and Floods: Monsoon failure or excess rainfall can lead to droughts or floods, respectively.
- Both scenarios can be disastrous for agriculture. Droughts result in water shortages, crop failures, and reduced yields, while floods can damage crops, wash away fertile topsoil, and lead to livestock losses.
- Crop Losses: Prolonged and excessive monsoon rains can cause crop diseases, reducing crop quality and yield. These conditions also hinder farmers' ability to conduct agricultural operations effectively.
- Soil Erosion: Heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion, which depletes soil fertility and affects agricultural productivity in the long run.
- Soil erosion also impacts water bodies and can lead to siltation in reservoirs, reducing their storage capacity.
- Food Price Inflation: Inconsistent monsoon patterns can affect crop production and lead to shortages, resulting in food price inflation.
- This can have adverse effects on the economy, especially for low-income households that spend a significant portion of their income on food.
What is El Nino and Its Implications on Agriculture?
- About:
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
- It can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world, including India.
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
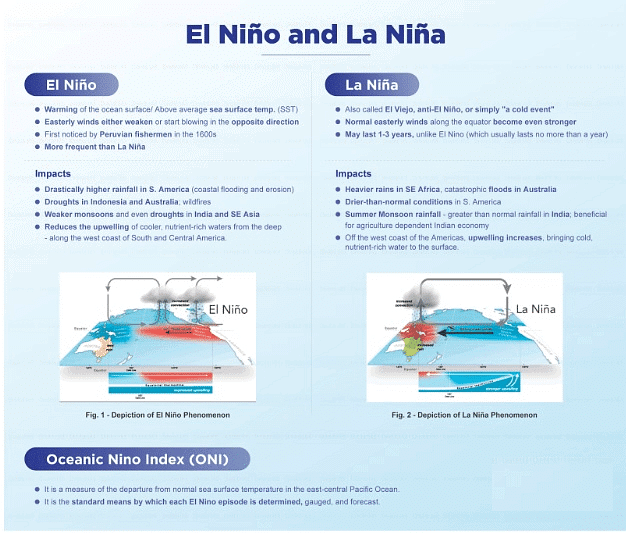
- The Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) reached 0.8 degrees Celsius in June, 2023 surpassing the El Nino threshold of 0.5 degrees.
- Global weather agencies forecast El Nino to persist and strengthen through the 2023-24 winter.
- Impacts:
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
- Elevated temperatures can adversely impact crops, leading to heat stress and reduced yields, especially for sensitive crops like fruits and vegetables.
- Pest and Disease Outbreaks: El Nino conditions can create a conducive environment for certain pests and diseases that affect crops.
- Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to increased pest populations, posing additional challenges to farmers.
- Impact on Livestock: Reduced availability of fodder and water scarcity during El Nino can affect livestock and animal husbandry, leading to lower milk and meat production.
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
Equatorial Origin Cyclones and Pacific Decadal Oscillation
Context
The changing patterns of equatorial-origin cyclones and the factors influencing their frequency and intensity.
Details
- Cyclones originating near the Equator have historically been devastating but subdued in recent decades.
- Last major equatorial cyclone in India: Cyclone Okchi in 2017, impacting Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Sri Lanka.
Factors Influencing Equatorial Cyclones
- Combination of global warming and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) could increase the frequency of equatorial cyclones.
- Study published in Nature Communications suggests changing patterns.
- Equatorial-origin cyclones decreased by 43% (1981-2010) compared to (1951-1980) due to the positive PDO phase.
Understanding PDO and ENSO
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) cycle: Repeats every 20-30 years, affecting cyclone frequency.
- Positive PDO phase: Warmer Western Pacific, cooler Eastern Pacific, leading to more equatorial cyclones.
- El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO): El Nino (warm) and La Nina (cool) phases influence India's rainfall patterns.
- El Nino corresponds to reduced India rainfall, La Nina to excessive rainfall.
PDO's Influence on Cyclone Formation
- PDO's warmer phase enhances equatorial cyclone formation, driven by warm Central Equatorial Pacific waters.
- Cyclones can intensify due to increased moisture and warm waters.
- PDO's positive phase is detected after years of ocean temperature and atmosphere interaction observation.
Recent Developments and Predictions
- In 2019, PDO shifted to a cooler, negative phase.
- Potential impact: Increased equatorial-origin cyclones during post-monsoon months.
- S. Ajayamohan, meteorologist, suggests warm waters near the Equator intensify cyclone potential.
El Nino's Impact on Rainfall
- Developing El Nino in the Pacific affects central and southern India.
- Recorded rainfall deficits in central and southern India: 7% and 17%, respectively.
- El Nino's influence on India's rainfall patterns due to changing ocean temperatures.
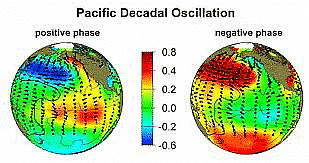
What is Pacific Decadal Oscillation?
- The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a climate pattern affecting the Pacific Ocean region.
- Characterized by long-term variations in sea surface temperatures.
- Reflects multi-decadal climate variability.
Phases of PDO
- Positive Phase:
- The Central and eastern Pacific Ocean experience warmer sea surface temperatures.
- Western Pacific Ocean tends to be cooler.
- Negative Phase:
- Central and eastern Pacific Ocean become cooler.
- Western Pacific Ocean becomes warmer.
El Nino Southern Oscillation
Context
The complex interplay between the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO), global warming, and their impact on monsoon rainfall patterns in different regions of India.
Details
- The El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a climate phenomenon characterized by sea surface temperature changes in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- ENSO affects monsoon rainfall patterns in India, with varying impacts across different regions.
- El Nino (warming phase) suppresses monsoon rainfall, while La Nina (cooling phase) enhances it.
Recent Research Findings
- A research paper published in Nature Scientific Reports in August 2023 reveals the changing impact of ENSO on India's monsoon rainfall.
- The impact varies across regions: greater in northern, lesser in central, and relatively constant in southern India.
- Global warming contributes to this phenomenon.
El Nino and Monsoon Suppression
- El Nino causes subsidence of air, suppressing monsoon rainfall.
- ENSO-related events were announced by World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- A recent La Nina phenomenon ended in March 2023.
Local Factors in Monsoon Rainfall
- Monsoon rainfall is influenced by ENSO and local factors like monsoon trough strength and frequency of low-pressure areas.
- Monsoon depressions play a crucial role in causing rainfall during the monsoons.
Changing ENSO Impact
- Analysis of data from 1901 to 2018 reveals evolving trends.
- Strength of monsoon trough and low-pressure areas declining across India.
- El Nino forming later in the year, impacting monsoon rainfall delay.
Compensation Effect and Weakening Relationship
- Warming of the Arabian Sea due to global warming sends moisture to central India.
- The compensation is leading to a weakening of the relationship between monsoon rainfall over central India and El Nino.
Shift in Monsoon Depressions
- Monsoon depressions moving southward in recent decades.
- This has reduced their influence over northern India and has increased the influence of El Nino on the region.
- Southward movement reasons were currently unknown.
Historical Trends and Uncertain Future
- The relationship between ENSO and monsoon rainfall strengthens till 1940, remains stable till 1980, and weakens thereafter.
- Future changes are uncertain due to evolving ENSO patterns and global warming effects.
Incorporating Differential Impact for Improved Forecasting
- There is a need to incorporate varying El Nino impact into climate models for better regional rainfall forecasts.
- There is a shifting of the ENSO onset region from the extreme eastern Pacific to the east-central Pacific Ocean.
- The differential impact of El Nino has to be incorporated into climate modelling for accurate regional forecasts during ENSO events.
About El Nino Southern Oscillation
- El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a complex and recurring climate phenomenon that involves interactions between the ocean and the atmosphere.
- It has significant impacts on weather patterns, sea surface temperatures, and ecosystems across the globe, particularly in the Pacific Ocean region and beyond.
Key Components of ENSO
- El Nino Phase: Warm Anomaly
- El Nino refers to the warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- This phase disrupts the normal atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to far-reaching effects on global climate.
- Warmer waters in the Pacific lead to changes in wind patterns, rainfall distribution, and ocean currents.
- La Nina Phase: Cool Anomaly
- La Nina is the opposite phase of ENSO, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
- It triggers distinct atmospheric patterns, including increased trade winds and upwelling of cold oceanic waters along the coasts of South America.
ENSO Cycle
- The ENSO cycle typically oscillates between El Nino and La Nina phases every 2 to 7 years, although the intervals can vary.
- The transitions between these phases are often associated with shifts in atmospheric pressure systems, wind patterns, and oceanic circulation.
Impacts of ENSO
- Global Weather Patterns
- ENSO influences weather patterns worldwide, affecting regions far from the Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino can lead to droughts, heatwaves, and reduced rainfall in some areas, while causing heavy rains, flooding, and increased cyclone activity in others.
- La Nina, on the other hand, can result in increased rainfall, cooler temperatures, and heightened hurricane activity.
- Agriculture and Food Security
- ENSO-induced droughts or excessive rainfall can impact crop yields, leading to agricultural losses and affecting food production.
- Crop failures and disrupted growing seasons can threaten food security in affected regions.
- Economic and Environmental Consequences
- ENSO-related weather extremes can lead to economic losses due to damaged infrastructure, reduced agricultural output, and increased disaster management costs.
- Ecosystems, fisheries, and marine life can also be disrupted by changes in ocean temperatures and currents.
Prediction and Monitoring
- Scientists and meteorological agencies closely monitor ENSO indicators, such as sea surface temperatures and atmospheric pressure patterns, to predict its phases.
- Advanced forecasting models help anticipate potential impacts on weather and climate, allowing for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Container Terminal Project at Deendayal Port
Why in News?
Recently, the Deendayal Port Authority and Dubai-based DP World, a multinational logistics company, partnered for the Mega Container Terminal Project at Tuna Tekra, Gujarat. The initiative was initiated by India's Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW).
- With the aim to enhance port capacity, foster multimodal logistics, and promote global connectivity, this venture signifies a pivotal step in public-private partnership.
What are the Key Highlights of Container Terminal?
- The terminal will have an annual capacity to handle 2.19 million twenty foot equivalent units (TEUs) with capability to handle next-generation vessels carrying more than 18,000 TEUs.
- Mega Container Terminal Project is fully compliant with the green port guidelines.
- The terminal will connect Northern, Western and Central India with the Global market.
- The project aligns with India’s Vision 2047 to quadruple port handling capacity.
- The terminal will be a part of the National Infrastructure Pipeline complementing PM Gati Shakti.
- The Container Terminal is expected to transform the economic landscape of Kutch, with the creation of several ancillary services like warehousing, etc. and also result in the creation of direct and indirect employment opportunities.
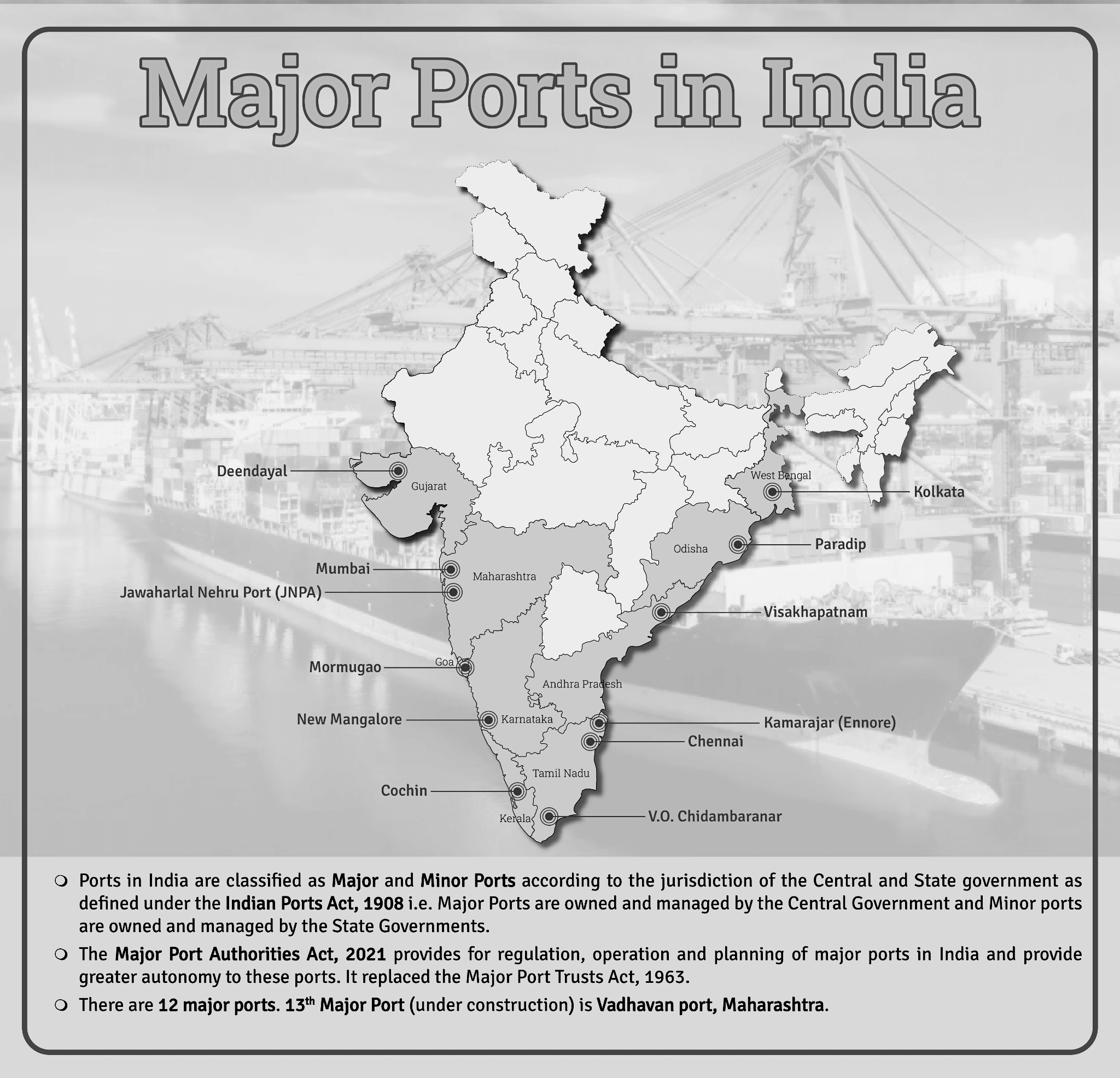
What are the Key Points About Deendayal Port?
- Deendayal Port, also known as Kandla port, is one of the twelve Major Ports in India and is located on the West Coast of India, in the Gulf of Kutch in the State of Gujarat.
- Deendayal Port primarily services northern India, including the landlocked Jammu and Kashmir, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Deendayal Port’s journey began in 1931 with the construction of RCC Jetty by Maharao Khengarji. After the independence of India in 1947, Deendayal Port emerged to be India’s No. 1 Port in the year 2007-08 and has retained the top position for the 14th consecutive year since then.
- In 2016, Deendayal Port created history by handling 100 MMT cargo in a year – the first Major Port to achieve this milestone.
- It is the largest port in India by volume of cargo handled.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on Geography: August 2023 UPSC Current Affairs - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the impact of monsoon and El Nino on agriculture? |  |
| 2. How do equatorial origin cyclones affect agriculture? |  |
| 3. What is the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and its relevance to agriculture? |  |
| 4. How does El Nino Southern Oscillation impact agriculture? |  |
| 5. What is the geographical relevance of monsoon and its impact on agriculture? |  |















