Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Oxides
Oxides | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
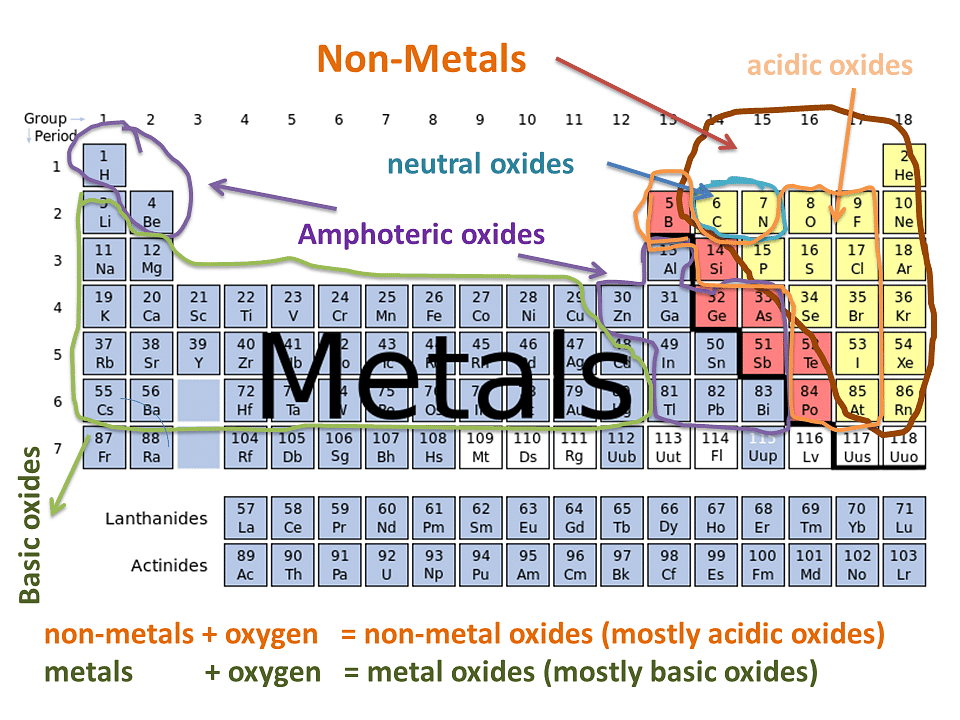
Classifying Oxides
- Oxides are compounds formed by combining oxygen with another element
- Examples of oxides are MgO, ZnO, K2O, CO2, SO2, and H2O
- Oxides can be categorized based on their acid-base properties
Acid and Basic Oxides
- Acidic and basic oxides exhibit distinct pH values and properties
- Variations in pH arise from their connection to either a metal or a non-metal
- The nature of the element influences the acidity or basicity of the oxide
- Metals form basic oxides while non-metals form acidic oxides:
Acidic Oxides
- Acidic oxides are produced when a non-metal reacts with oxygen.
- They interact with bases to create salts and water.
- When dissolved in water, they generate an acidic solution with a low pH.
- Common examples include CO2, SO2, NO2, and SiO2.
Basic Oxides
- Basic oxides form when a metal combines with oxygen.
- They react with acids to produce salts and water.
- When dissolved in water, they result in a basic solution with a high pH.
- Common examples include CuO and CaO.
Question for OxidesTry yourself: Which type of oxide is formed when a non-metal combines with oxygen?View Solution
Amphoteric Oxides
Neutral Oxides
- Some oxides, such as N2O, NO, and CO, do not react with acids or bases and are considered neutral.
Amphoteric Oxides
- Amphoteric oxides can act as both acidic and basic depending on the reactant. They form salt and water in both cases.
- Examples of amphoteric oxides are zinc oxide (ZnO) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
- The hydroxides of zinc and aluminum also exhibit amphoteric behavior.
- An example is aluminum oxide acting as a base in the reaction: Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O.
- When reacting with hydrochloric acid: Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
- Example of aluminium oxide behaving as an acid: Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
- This dual behavior is not simply explained by proton exchange. The Lewis acid-base theory offers insight into these scenarios.
The document Oxides | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Oxides - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are amphoteric oxides? |  |
Ans. Amphoteric oxides are compounds that can act as both acidic and basic oxides depending on the reaction conditions.
| 2. Can you provide examples of amphoteric oxides? |  |
Ans. Some examples of amphoteric oxides include aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and zinc oxide (ZnO).
| 3. How do amphoteric oxides react with acids? |  |
Ans. Amphoteric oxides can react with acids to form salts and water. They can act as bases in these reactions.
| 4. How do amphoteric oxides react with bases? |  |
Ans. Amphoteric oxides can react with bases to form salts and water. They can act as acids in these reactions.
| 5. What are the properties of amphoteric oxides that make them unique? |  |
Ans. The ability of amphoteric oxides to exhibit both acidic and basic properties allows them to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions, making them versatile compounds in various industrial processes.
Related Searches















