UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd September 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
The Deposit Issue: Why Banks are Struggling to Lend
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
Recent discussions highlight the challenges faced by banks in India regarding lending practices and the factors influencing the economy's growth. Key areas of concern include government spending, credit gaps, and changing investment behaviors.
Introduction:
- India is recognized as one of the fastest-growing major economies, largely fueled by increased government investment in infrastructure.
- Despite this growth, obstacles such as insufficient job creation and weak private sector investment remain significant, as noted in reports from the World Bank and the Economic Survey for 2023-2024.
Growth Driven by Government Spending:
- The rise in government capital expenditure has markedly enhanced the economy's productive capabilities.
- However, private investment, which is essential for job creation, has been underwhelming.
- In the fourth quarter of FY24, private Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) fell to a four-quarter low of 6.46%, down from 9.7% in the prior quarter.
- GFCF measures the investment in physical assets such as buildings and machinery, which are vital for production and growth.
- From FY19 to FY23, the proportion of private non-financial corporations in GFCF saw only a slight increase from 34.1% to 34.9%.
- The government has encouraged the private sector to spearhead economic growth.
Widening Credit Gap:
- A major challenge affecting private investments is the banks' diminished willingness to lend to the private sector.
- Reports indicate that credit growth is projected to decline to 14% this financial year, compared to 16% last year.
- The growing disparity between credit and deposit growth is leading to a liquidity crisis, with deposit growth averaging 11.1% over the past two years, while credit growth has averaged 16.8%.
- This disparity has worsened due to a decrease in the share of Current and Savings Accounts (CASA) within total deposits.
Lagging Behind Asian Peers:
- India's credit-to-GDP ratio is lower than that of other Asian nations with similar income levels, such as Thailand, Malaysia, and China.
- This shortfall is partly due to stringent regulatory requirements, like the proposed Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) guidelines, which could further hinder credit expansion.
- LCR mandates that banks maintain a specific amount of high-quality liquid assets (e.g., cash or government bonds) that can be quickly liquidated to meet short-term obligations in financial stress.
Changing Investment Habits and Impact on Deposits:
- Households are increasingly favoring investments in capital markets over traditional bank deposits, spurred by favorable market returns post-pandemic.
- This shift is altering the deposit landscape, impacting the money multiplier and the processes for deposit creation.
- Additionally, reduced government spending ahead of elections has intensified the deposit shortage, with government cash balances at the RBI increasing significantly.
Private Sector Investment Cycle:
- There are early indicators of a revival in private sector investment, driven by government infrastructure spending and a recovery in the housing market.
- However, a comprehensive recovery is still a long-term prospect.
- Despite initiatives such as corporate tax reductions in 2019 and the introduction of the Production Linked Investment (PLI) scheme, corporate tax contributions to government revenue have not risen proportionately.
Conclusion:
- While India's economy continues to grow at a rapid pace, challenges like low private investment, an expanding credit-deposit gap, and evolving investment behaviors present substantial risks.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining growth and achieving a balanced economic recovery.
GS3/Economy
Spike in India’s trade deficit
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
India's trade deficit has significantly widened after a strong start in goods exports at the beginning of the 2024-25 fiscal year. Export values fell by 1.5% in July and saw a sharper decline of 9.3% in August, hitting an eight-month low. In contrast, imports surged to a record $64.4 billion in August, resulting in a merchandise trade deficit of $29.7 billion, just shy of the record $29.9 billion deficit observed in October 2023.
Export Contraction Amid Rising Imports
- In July and August 2024, India's exports declined, with a 1.5% drop in July followed by a 9.3% fall in August.
- Conversely, imports increased by 7.5% in July and 3.3% in August, pushing the trade deficit to a nine-month high of $23.5 billion in July and widening it by an additional $6.2 billion in August.
Sectoral Performance and Key Export Declines
- Although many of India's top export sectors showed growth, significant declines were observed in major areas such as petroleum and gems and jewellery.
- Oil exports fell sharply by 22.2% in July and 37.6% in August, while jewellery exports dropped by over 20% in both months.
- Growth also slowed in critical sectors like pharmaceuticals and electronics due to the economic slowdown in China.
Oil Import Bill and Trade Deficit Dynamics
- In August, a decrease in oil prices (by $6 per barrel) resulted in a 30% drop in India's oil import bill, bringing it down to $11 billion, the lowest level in three years.
- Despite this reduction, the widening trade deficit was primarily driven by falling gems and jewellery exports, alongside some contributions from miscellaneous products and electronics.
Gold Import Surge
- India's gold imports skyrocketed to a record $10.1 billion in August, more than doubling the July figure, contrasting sharply with a 10.7% decrease in July.
- This surge was attributed to cuts in gold import duties (from 15% to 6%) in the Budget, rising gold prices, and seasonal stockpiling by domestic jewellery manufacturers.
- Economists anticipate that the effects of these duty cuts will continue to influence the import bill in the upcoming months.
No Significant Economic Risk Amid Trade Deficit
- Despite the increasing trade deficit, experts highlighted that India’s robust growth rate will likely lead to a demand for global products that surpasses global demand for its exports.
- The trade deficit is viewed as non-threatening for a rapidly growing economy, provided there are no foreign exchange issues.
Strong Foreign Capital Inflows and Forex Reserves
- India has experienced positive foreign capital inflows in recent months, with foreign exchange reserves reaching a record $675 billion by August 2, 2024.
- This amount is sufficient to cover 11.6 months of imports, although it might decrease slightly if imports continue to exceed $60 billion.
Services Exports Provide Stability
- India's services exports have grown by over 10% from April to August 2024, providing stability and acting as a buffer against the widening trade deficit, positively contributing to the economy.
Global Trade Outlook for 2024: Tepid Demand in Developed Markets
- Although global trade is anticipated to grow faster in 2024 than in 2023, demand remains weak in most developed markets.
- Geopolitical tensions, ongoing conflicts, and the upcoming U.S. elections, combined with tariff increases on Chinese goods, create a challenging landscape for India and other economies.
Impact of U.S.-China Trade Tensions
- As China's economy weakens and U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods rise, China may redirect its focus to non-U.S. markets, potentially flooding these markets with low-priced products.
- This shift could adversely affect India, especially with a decline in China's demand for imports.
Oil Prices and Export Concerns
- Low global demand is expected to keep oil prices subdued, adversely impacting India's prospects for oil exports.
- While lower oil prices benefit importers, they pose challenges for India's oil export ambitions, amidst growing concerns regarding global demand.
India’s Export Goals and Challenges Ahead
- India aims to enhance services and goods exports to $1 trillion each by 2030, but faces significant challenges along the way.
- Economic analysts have pointed out that a global economic slowdown, rising tariffs, non-tariff barriers, and new trade policies like the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism and Deforestation Rules represent major hurdles.
- While short-term opportunities for export growth may arise, the long-term outlook remains challenging.
GS2/International Relations
Quad Summit 2024
Source: The Hindu
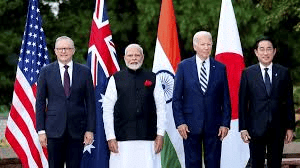
Why in news?
PM Modi participated in the sixth Quad Leaders’ Summit in Wilmington, Delaware (USA). This year’s summit was hosted by the US.
Key outcomes of Quad Summit 2024
- The sixth Quad Leaders' Summit focused on enhancing cooperation among India, Australia, the US, and Japan.
- Discussions centered on maritime security, climate change, and collaborative responses to global challenges.
About
- The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, consists of four democratic nations: India, Australia, the US, and Japan.
- The primary goal is to maintain a free and open international order governed by law in the Indo-Pacific region.
Objectives
- Enhance maritime security in the Indo-Pacific.
- Address the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic through vaccine diplomacy.
- Combat the impacts of climate change.
- Create favorable conditions for investment in the region.
- Foster technological innovations among member countries.
Evolution of Quad
- The Quad was initiated after the Indian Ocean tsunami when India, Japan, Australia, and the US collaborated on disaster relief.
- In 2007, the Quad was formally proposed by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe but faced challenges due to Chinese opposition and India's hesitation.
- Revival of the Quad occurred during the 2017 ASEAN Summits, leading to a ministerial-level meeting in September 2019.
- The first virtual summit of Quad leaders was held in March 2021, followed by the first in-person meeting in September 2021 hosted by the US.
Naval Exercise
- In November 2020, the navies of the Quad countries conducted the Malabar exercise, marking the first joint military drill with all four nations participating since 2007.
Quad Wilmington Declaration
- The summit resulted in the adoption of the Quad Wilmington Declaration, aimed at advancing the Quad agenda and cooperation among member nations.
Quad Cancer Moonshot
- A new initiative, the Quad Cancer Moonshot, was launched to tackle cancer in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This initiative focuses initially on cervical cancer, leveraging investments, scientific knowledge, and contributions from various sectors to reduce its prevalence.
Maritime Initiative For Training In Indo-Pacific
- The Maritime Initiative for Training in the Indo-Pacific (MAITRI) was announced to improve regional partners' utilization of tools from the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness.
- This initiative aims to strengthen monitoring, security, and law enforcement in regional waters, with India set to host the inaugural workshop in 2025.
Quad-at-Sea Ship Observer Mission To Be Held in 2025
- The Quad nations plan to conduct the first-ever Quad-at-Sea Ship Observer Mission in 2025, focusing on enhancing maritime safety and interoperability among the coast guards.
Quad Indo-Pacific Logistics Network launched
- A pilot project for the Quad Indo-Pacific Logistics Network was launched to improve airlift capabilities and strengthen logistical responses during disasters across the region.
Quad Ports of the Future Partnership launched
- This partnership aims to utilize the collective expertise of the Quad nations to support the development of sustainable and resilient port infrastructure in the Indo-Pacific.
Semiconductor Supply Chains Contingency Network Memorandum of Cooperation
- This memorandum aims to enhance the resilience of semiconductor supply chains among Quad nations, ensuring better stability in this critical sector.
Other announcements
- A collective effort to boost energy efficiency through the deployment and manufacturing of high-efficiency cooling systems was emphasized.
- India announced a space-based web portal for Mauritius, aimed at promoting open science and monitoring climate impacts.
- A new sub-category under the Quad STEM Fellowship was introduced, allowing students from the Indo-Pacific to pursue engineering degrees at Indian institutes.
- India will host the next Quad Leaders’ Summit in 2025, which was welcomed by all leaders.
GS2/International Relations
India - US Bilateral Ties
Source: NDTV
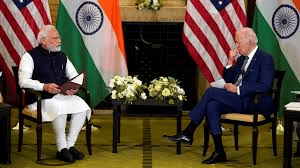
Why in news?
As the Prime Minister of India is on his 3-day visit to America, to meet the US President and participate in the QUAD summit, there is the need to analyse the transformation in the India - US ties over the years.
Transformation in India-US Bilateral Relations:
- Background:
- The US-India relationship has experienced fluctuations over the last 75 years.
- For instance, the US enacted sanctions against India following its nuclear tests in 1974 and 1998, leading to a gradual normalization that was solidified by the Indo-US nuclear deal in 2008.
- As of 2022, the US emerged as India's largest trading partner, with bilateral trade in goods and services surpassing US$ 191 billion.
- Transformation Phases:
- The first significant shift occurred between 2001 and the end of Donald Trump's presidency, during which the US began to accommodate India's national interests while still addressing unresolved issues.
- The second transformation emerged under President Joe Biden, focusing on shared interests and strategic alignment, especially in response to China's rising influence.
- In 2023, both nations launched the India-US initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET), signaling a commitment to technological collaboration.
- Joint defence exercises and the establishment of the Strategic Trade Dialogue underscore ongoing efforts to strengthen ties.
- Five 2+2 meetings have been conducted involving defence and foreign ministers, and notable military supplies, such as C-130Js and MH60R helicopters, are enhancing India’s military capabilities.
- Challenges in the Modi-Biden Era:
- India's growing oil imports and military dependencies pose challenges.
- Disagreements regarding the war in Ukraine and differing perspectives on human rights present additional hurdles.
- Despite these challenges, the strategic framework for deeper partnerships between the two nations remains intact.
- The expectation is that cooperation will continue as the next American president takes office later this year.
The Agenda for the Indian PM's Recent Visit to the US:
- Boosting Bilateral Ties:
- The leaders discussed strategies for enhancing cooperation across various sectors, establishing a "comprehensive global strategic partnership."
- Expanding India's Global Role:
- President Biden commended India's leadership on the global stage, particularly during its G20 presidency and in strengthening the Quad.
- Emphasis was placed on the necessity for a "free, open, and prosperous Indo-Pacific."
- Collaboration in Emerging Technologies:
- Leaders committed to regular engagements to boost collaboration in sectors such as space, AI, quantum computing, and biotechnology.
- Plans for a semiconductor fabrication facility were highlighted as crucial for national security and next-generation telecommunications.
- Strengthening Defence Ties:
- President Biden acknowledged the progress in India’s acquisition of 31 General Atomics MQ-9B remotely piloted aircraft, which will bolster India's intelligence and surveillance capabilities.
- He also noted India's efforts to simplify its tax structure for maintenance and repair services, which is a significant move towards establishing a robust aviation ecosystem.
- Clean Energy Initiatives:
- The White House announced an initiative to unlock $1 billion in multilateral financing aimed at supporting projects in the clean energy sector.
- Promoting Global Health and Development:
- The leaders celebrated the introduction of the new US-India Drug Policy Framework to combat the illicit production and trafficking of synthetic drugs.
- The inaugural U.S.-India Cancer Dialogue was also applauded, emphasizing the need for collaborative efforts in cancer research and treatment.
- Both sides reaffirmed their commitment to enhancing cooperation in agriculture, focusing on improving productivity and sharing best practices.
GS3/ Economy
Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs)
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The Finance Ministry recently asked banks to put in place effective monitoring and oversight mechanisms for efficient management of pending cases in Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs).
About Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs):
- Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs) are special courts set up under the Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993 (also known as the DRT Act).
- DRTs play an important role in protecting the rights of creditors and speeding up the process of recovering debts according to Indian law.
- Types of Cases Handled:
- The main job of DRTs is to settle disputes related to debt recovery from banks, financial institutions, and other designated organizations.
- DRTs can take on cases from banks for loans that are disputed and exceed Rs 20 Lakh.
- The Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets & Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 (known as the SARFAESI Act) allows banks and financial institutions to recover secured debts from borrowers without needing to go to court initially.
- If someone is unhappy with actions taken by secured creditors under the SARFAESI Act, they can file Securitisation Appeals (SAs) with the DRTs.
- Structure of DRT:
- President: A judicial officer appointed by the central government who must be qualified to serve as a District Judge.
- Members: Administrative and technical members who are also appointed by the central government.
- According to Section 22(2)of the DRT Act, DRTs have the following powers:
- Summoning individuals and requiring them to appear and testify under oath.
- Requesting the discovery and presentation of documents.
- Accepting evidence through affidavits.
- Issuing commissions to examine witnesses or documents.
- Reviewing their own decisions.
- Dismissing applications for default or making decisions without the presence of one party.
- Reversing any dismissal of an application for default or any ex parte orders.
- Handling any other matters as may be prescribed.
- Jurisdiction: Each DRT operates within a specific geographical area. Their authority includes cases related to debt recovery for banks and financial institutions located within that area.
- Appeals and Enforcement: If a party is not satisfied with a DRT's decision, they can appeal to the Debts Recovery Appellate Tribunal (DRAT).
- Currently, there are 39 DRTs and 5 DRATs operating across the country. Each DRT and DRAT is led by a Presiding Officer and a Chairperson, respectively.
GS1/History and Culture
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd September 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Tirupati Balaji Temple
Source: Hindustan Times

Why in News?
Amid the escalating controversy surrounding the Tirupati Laddu, AR Dairy, a company that supplied ghee to the famous Lord Balaji temple, defended the quality of its products.
About Tirupati Balaji Temple:
The Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, also referred to as the Tirupati Balaji Temple, is a significant Hindu temple located in the hill town of Tirumala in Tirupati, within the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is positioned at an elevation of 853 meters above sea level on Venkata Hill, one of the seven hills known as Saptagiri.
- This temple is dedicated to Lord Sri Venkateswara, who is considered an incarnation of Vishnu.
- It is mentioned in several sacred texts, including the Garuda Purana and the Brahma Purana.
History
- The temple has ancient origins that date back to the Pallava dynasty, which greatly influenced the area in the 9th century.
- The Chola dynasty later contributed significantly to the temple's growth and support.
- During the rule of the Vijayanagara Empire, the temple received many donations and support, strengthening its importance in South Indian religion.
- In the 12th century, the well-known saint Ramanuja played a key role in revitalizing the temple and its rituals.
- The temple is known to be one of the richest in the world, receiving large amounts of donations and wealth.
- A common practice among devotees is to donate hair and various items to honor the deity.
- The famous sweet known as Tirupati Laddu is offered as a prasad at the temple and has a Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
Architecture
- The temple is built in a style known as Dravidian architecture, with construction believed to have begun around 300 AD.
- There are three entrances to the inner sanctum, the first of which is called Mahadwaram.
- A large gopuram (gateway) stands at the entrance, measuring 50 feet tall.
- Two paths for circumambulation (known as parikrama) are present around the temple.
- The main shrine features a gold-plated tower named Ananda Nilayam, which houses the main deity.
- The temple's expansive courtyards, pillars, and halls are decorated with beautiful sculptures and designs that reflect the essence of Hindu spirituality.
GS1/Geography
Key Facts about Falkland Islands
Source: BBC

Why in News?
Researchers have found evidence that the treeless, rugged, grassland landscape of the Falkland Islands was home to a lush, diverse rainforest up to 30 million years ago.
About Falkland Islands:
- Also known as the Malvinas Islands, the Falkland Islands is a self-governing territory of the United Kingdom.
- The islands are an archipelago located in the South Atlantic Ocean, about 500 km from the coast of South America.
- It consists of two main islands (East Falkland and West Falkland) along with several hundred smaller islands.
- The two large islands are divided by the Falkland Sound (a strait).
- The islands are located in both the southern and western hemispheres of the Earth.
- Climate: The islands have a cool temperate oceanic climate with gentle weather conditions.
- Capital: The capital of the Falkland Islands, Stanley (also known as Port Stanley), is on East Falkland.
- Demographics: The population mainly speaks English and is mostly made up of people of African-Irish descent (about 88% of the population).
- Economy: Most of the land outside of Stanley on the main islands is used for sheep farming.
- Currency: The official currency is the Falkland pound, which is equal in value to the British pound.
- Government: The British crown holds executive authority, and a governor appointed by the crown leads the islands' government.
- The islands are self-governing, but the British government manages foreign affairs and defense.
GS3/Environment and Ecology
Emu
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Researchers have uncovered a fascinating mechanism behind the reduction and asymmetry of emu wing bones.
About Emu:
- It is part of a group of flightless running birds called ratites, which are the oldest among modern bird families.
- The Emu is the second-largest bird alive today, with the ostrich being the largest.
- Distribution:
- Emus are found only in Australia.
- They inhabit most areas of the continent, from coastal areas to the Snowy Mountains.
- Features:
- Emus can grow to be over 1.5 meters (5 feet) tall and can weigh over 45 kg (100 pounds).
- Adult female emus are generally larger and heavier than males.
- Both male and female emus have a brownish color with a dark gray head and neck.
- They have long necks and legs, but their wings are quite small, measuring less than 20 centimeters (8 inches).
- Their feet have three toes and contain fewer bones and muscles compared to flying birds.
- Emus can run at speeds of nearly 50 km (30 miles) per hour, and if threatened, they can kick with their strong three-toed feet.
- Their powerful legs also enable them to jump up to 2.1 meters (7 feet) high.
- Emus are omnivores.
- Their lifespan ranges from five to ten years.
- Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN Red List, their status is Least Concern.
|
39 videos|4837 docs|1047 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd September 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the current state of banks' ability to lend in India? |  |
| 2. How has India's trade deficit impacted the economy? |  |
| 3. What were the key outcomes of the Quad Summit 2024? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Quad Wilmington Declaration? |  |
| 5. How does the Quad Cancer Moonshot initiative aim to improve healthcare? |  |
































