UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Gig Economy in India
Source: Business Standard

Why in News?
The Fairwork India Ratings 2024 report examines the changing nature of platform work as platforms increasingly take control of when and for how long workers can provide services, or gigs. The report titled ‘Fairwork India Ratings 2024: Labour Standards in the Platform Economy’ is the sixth consecutive annual study of this nature conducted by the Fairwork India Team. It is a joint effort by the Centre for IT and Public Policy (CITAPP), International Institute of Information Technology, Bangalore (IIIT-B), in association with Oxford University.
What is Gig Economy?
- A gig economy refers to a free market system where organizations hire or contract workers for short durations.
- Positions in this economy are temporary and designed to meet the immediate needs of the company through short-term engagements.
- Startups such as Ola, Uber, Zomato, and Swiggy are key players in establishing the gig economy in India.
Who is a Gig Worker?
- As defined by the Code on Social Security, 2020 (India), a gig worker is someone who engages in work or work arrangements and earns from such activities outside the traditional employer-employee relationship.
- Gig workers can be independent contractors, online platform workers, contract firm workers, on-call workers, and temporary workers.
What is the Size of Gig Economy in India?
- A NITI Aayog study on “India’s Booming Gig and Platform Economy” estimates that currently, approximately 47 percent of gig work involves medium-skilled jobs, 22 percent high-skilled, and 31 percent low-skilled jobs.
- This data highlights the significance of the gig workforce within the Indian economy, suggesting that ensuring their comfort and security is vital for a progressive future.
- Participating in the gig economy is generally higher in developing countries (5-12 percent) compared to developed nations (1-4 percent).
- Most gig jobs fall under lower-income categories such as deliveries, ridesharing, microtasks, and care services.
- In 2020-21, about 77 lakh workers were involved in the gig economy, with expectations for the workforce to grow to 2.35 crore by 2029-30.
What is the Average Age/Income of Gig Workers in India?
- The median age of gig workers in India is 27 years, and their average monthly income is Rs 18,000.
- About 71 percent of these workers are the sole earners for their families, with an average household size of 4.4 members.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers:
- Despite the employment opportunities provided by platform companies, gig work often comes with challenges such as:
- Low wages
- Unequal gender participation
- Lack of opportunities for upward mobility within organizations
- These issues have led to protests from workers employed by companies like Swiggy, Zomato, Ola, Uber, and Urban Company.
- Gig workers are typically contracted by companies and do not share the same benefits as full-time employees, which means they often lack access to paid sick leave, casual leaves, travel and housing allowances, and provident fund savings.
What Needs to be done in Order to Improve the Living Standards of these Gig Workers?
- Fiscal Incentives
- NITI Aayog recommends providing fiscal incentives such as tax breaks or startup grants for businesses that employ a significant number of women workers.
- Retirement Benefits
- Companies should implement policies offering retirement plans and insurance coverage for emergencies like the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Income Support
- Providing income support to gig workers is essential for ensuring minimum earnings and social security in times of uncertainty or work irregularity.
- Offering paid sick leave and insurance coverage is also recommended.
Case Study: The Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Act 2023
- The Rajasthan State Assembly has passed the Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Act 2023.
- This law establishes a board to oversee the registration and welfare of gig workers, addressing their vulnerabilities and allowing for collective bargaining and negotiations.
- The board will also function as an independent grievance redress mechanism.
- Additionally, the Act includes a provision for a social security fund, which will be financed through fees collected on each transaction.
Fairwork India Ratings 2024 report:
- This report assesses the working conditions of platform workers across various digital platforms in India.
- It notes that many platforms fail to ensure that their workers receive a local living wage and are often resistant to the collectivization of workers.
- The report also discusses possible legislative reforms for gig workers in states like Karnataka and Jharkhand.
Key Findings of the Report:
- Overall Ratings
- No platform received more than 6 out of 10 points in the assessment.
- Platforms were evaluated based on five key principles: Fair Pay, Fair Conditions, Fair Contracts, Fair Management, and Fair Representation.
- Assessment of Fair Pay
- Only Bigbasket earned a point under Fair Pay by ensuring a minimum wage that meets or exceeds the local minimum wage, after accounting for work-related expenses.
- No platform was able to provide proof that workers earn above work-related costs.
- Evaluation of Fair Conditions
- Platforms like Amazon Flex, BigBasket, BluSmart, Swiggy, Urban Company, and Zepto received points for providing safety equipment and training.
- BigBasket, Swiggy, Urban Company, and Zepto were acknowledged for providing accident insurance and compensation for income loss due to medical issues.
- Several platforms facilitated transparent and accessible contracts and had procedures to protect worker data.
- Some platforms offered mechanisms for appealing disciplinary actions and conducted regular external audits to mitigate biases in work allocation.
- Despite the growth in platform worker collectivization over the last six years, no platform demonstrated evidence of recognizing collective worker bodies or unions.
Implications & Future Prospects:
- The report emphasizes the increasing focus on gig worker welfare in political and legislative discussions.
- However, it expresses concern regarding the slow pace of actual implementation of necessary reforms.
- It advocates for a collaborative approach where government bodies and worker collectives work together to enhance the living and working conditions of gig workers in India.
- Overall, the report serves as a critical reminder of the challenges faced by gig workers and the existing gaps in ensuring fair working conditions across digital labor platforms in India.
GS3/Environment
Halari donkey
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The Halari donkey, which is native to the Halar region in Gujarat, is facing the threat of extinction. This breed is known for its intelligence and the strong connections it forms with humans.
About Halari donkey:
- Originates from the semi-arid regions of Gujarat, particularly around Jamnagar and Dwarka.
- Characterized by its white coloration, it is larger and more resilient compared to other donkey breeds.
- These donkeys are social animals that develop strong bonds with humans, making them reliable companions for various tasks.
Uses:
- The Bharwad and Rabari pastoralist communities primarily utilize Halari donkeys as pack animals, aiding in the transportation of luggage during migrations alongside small ruminants.
- Additionally, the Kumbhar community, known for pottery, employs these donkeys in their craft, particularly in the Dwarka region of Jamnagar.
- Halari donkey milk is prized for its sweetness and can be processed into milk powder that may sell for over ₹7,000 per kilogram in international markets. This milk is also utilized in cosmetic products.
Conservation status:
- The Halari donkey is classified as endangered, with fewer than 500 individuals remaining in existence.
GS2/Governance
‘Humsafar Policy’ for Wayside Amenities along the National Highways
Source: AIR

Why in news?
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has introduced the 'Humsafar Policy' in New Delhi to enhance travel convenience on National Highways and support the development of wayside amenities.
About the ‘Humsafar Policy’
- The Humsafar Policy aims to improve the convenience and overall experience of travelers on National Highways (NHs).
- It focuses on the development of amenities along highways to provide various facilities for users, ensuring smooth, safe, and comfortable journeys.
- The policy also promotes environmental sustainability by integrating eco-friendly practices such as:
- Water conservation
- Utilization of solar energy
- Waste recycling
Features of the Humsafar Policy
- Comprehensive Amenities: Includes food courts, fuel stations, EV charging facilities, parking spaces, clean toilets, ATMs, and pharmacies.
- Standardized Facilities: Ensures that services provided are well-maintained and hygienic for all travelers.
- Visibility for Service Providers: Amenities are featured on the ‘Rajmarg Yatra’ app, which provides signage space and waivers of renewal fees for highly rated service providers.
- Monitoring and Inspection: Regular third-party inspections will be conducted to maintain service quality, with alerts issued for facilities receiving low ratings.
- Environmental Focus: Encourages the use of solar energy, practices for water conservation, and effective waste recycling measures.
Significance
- Enhanced User Experience: The policy aims to improve travel experiences by providing high-quality facilities.
- Economic Impact: It is expected to generate jobs and support local communities along the highways.
- Standardization: Ensures consistent quality of services and accountability among providers.
- Technological Integration: The ‘Rajmarg Yatra’ app provides real-time information about facilities and allows users to give feedback.
GS3/Science and Technology
Hanle Dark Sky Reserve Star Party observed in Ladakh

Why in news?
Expert astro-photographers and astronomers have gathered at the Hanle Dark Sky Reserve for the second Star Party. This event is a significant gathering of amateur astronomers who travel to Hanle to observe and capture celestial phenomena. It was hosted by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) and saw participation from over 45 astronomy enthusiasts from across India. Participants brought their own telescopes and cameras to capture unique celestial events, including faint galaxies, Zodiacal Light, and the rare sight of Venus casting a shadow.
Star Party and Its Details
- The Star Party at Hanle Dark Sky Reserve is a platform for amateur astronomers.
- Participants engage in observing celestial events and capturing images with their equipment.
- It emphasizes the community aspect of astronomy, bringing enthusiasts together.
About Hanle Dark Sky Reserve (HDSR)
- HDSR is located in the Changthang region of eastern Ladakh.
- It was established to control man-made light pollution and protect the naturally dark night skies.
- The reserve covers approximately 1,073 square kilometers.
- It houses the Indian Astronomical Observatory, which is operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
- The area is known for promoting astrophotography.
- Hanle is also home to the second-highest optical telescope in the world, established in 2001.
Special Features of HDSR and the Surrounding Region
- High Altitude: Hanle’s elevation allows for clearer skies with minimal atmospheric interference.
- Minimal Light Pollution: Low light pollution makes it ideal for observing faint celestial objects.
- Dry Climate: The region's dry weather enhances visibility, reducing the humidity's negative impact on astronomical observations.
Significance of HDSR
- Astrophotography and Research: Dark skies enable detailed observations of celestial phenomena and attract enthusiasts and researchers.
- Astro-Tourism: The reserve encourages astro-tourism, helping boost the local economy by creating jobs and supporting infrastructure.
- Preservation of Night Skies: HDSR is crucial for maintaining the natural darkness of the sky, reducing light pollution in the region.
- International Attention: The reserve draws both amateur and professional astronomers from India and beyond, establishing it as a hub for astronomical events.
GS2/Governance
What is Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)?
Source: Mint

Why in news?
Ola Electric, a manufacturer of electric two-wheelers, has recently received a show-cause notice from the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) due to alleged breaches of consumer rights, misleading advertisements, and practices deemed unfair.
About Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA):
- The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 was enacted on August 9, 2019, and became effective on July 20, 2020, replacing the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- The CCPA was established in July 2020 under the provisions of this Act.
- The primary goal of the CCPA is to safeguard consumer rights by addressing unfair trade practices and false or misleading advertisements that adversely affect public and consumer interests.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution oversees the CCPA.
CCPA is empowered to:
- Protect, promote, and enforce consumer rights as a collective, ensuring violations of these rights do not occur.
- Prevent unfair trade practices and ensure that individuals refrain from engaging in such practices.
- Ensure that no false or misleading advertisements are published regarding any goods or services that violate the Act or any associated rules or regulations.
- Prevent any individual from participating in the dissemination of false or misleading advertisements.
Composition:
- The CCPA will be led by a Chief Commissioner, along with two other commissioners.
- One commissioner will focus on matters related to goods, while the other will handle issues concerning services.
Powers:
- The CCPA holds the authority to intervene when necessary to avert consumer harm stemming from unfair trade practices.
- It can initiate class action suits, implement product recalls, and enforce refunds or returns of products.
- The authority has an investigative wing, led by a director-general, responsible for inquiries or investigations into violations of consumer law.
- The CCPA has extensive powers, including the ability to take suo-motu actions, recall products, mandate reimbursements for goods or services, and revoke licenses.
- It can file class action lawsuits if a consumer complaint affects multiple individuals.
- The CCPA can also issue orders to cease practices that are unfair and detrimental to consumer interests and impose penalties for false or misleading advertisements.
GS2/Health
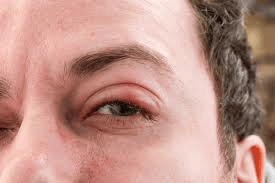
What is Trachoma?
Source: NDTV
Why in news?
Recently, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has declared that the Government of India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem becoming the third country in the South-East Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
About Trachoma:
- Trachoma is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the eyes.
- The infection is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis.
How it spreads?
- Trachoma is highly contagious, spreading through direct contact with the eyes, eyelids, nose, or throat secretions of infected individuals.
- If left untreated, it can lead to irreversible blindness.
- This disease is prevalent in communities living under poor environmental conditions.
Neglected Tropical Disease:
- WHO classifies Trachoma as a neglected tropical disease.
- It is estimated that around 150 million people globally are affected by Trachoma, with approximately 6 million at risk of becoming blind or facing visually disabling complications.
Initiatives of Government of India
- The Government of India launched the National Trachoma Control Program in 1963.
- Trachoma control efforts have since been integrated into India's National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
- In 2017, India was officially declared free from infective Trachoma.
- However, ongoing surveillance for trachoma cases has been maintained across all Indian districts from 2019 to 2024.
National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT only) Survey
- A National Trachomatous Trichiasis Survey has been conducted in 200 endemic districts under the NPCBVI from 2021 to 2024.
- This survey was mandated by WHO to validate India's elimination of Trachoma as a public health issue.
SAFE Strategy for Elimination
- To eradicate Trachoma as a public health concern, WHO recommends the SAFE strategy, which includes:
- Surgery to address the blinding stage (trachomatous trichiasis).
- Antibiotics, particularly azithromycin, to eliminate the infection.
- Promoting facial cleanliness and enhancing environmental conditions, especially improving access to water and sanitation.
Other Countries That Have Eliminated Trachoma
- Alongside India, 17 other countries have successfully eliminated Trachoma, including:
- Benin
- Cambodia
- China
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Islamic Republic of Iran
- Lao People’s Democratic Republic
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mexico
- Morocco
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Oman
- Saudi Arabia
- Togo
- Vanuatu
GS2/International Relations
Exercise Malabar
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
Recently, the naval fleet exercise Malabar-2024 was inaugurated at the Eastern Naval Command (ENC) in Visakhapatnam.
About Exercise Malabar:
- Initiated in 1992, Exercise Malabar began as a bilateral naval exercise between India and the US Navy.
- The first Malabar Exercise conducted in the Bay of Bengal took place in 2007.
- In 2015, the exercise expanded to a trilateral format with the inclusion of Japan.
- In 2020, the Australian Navy joined, further evolving it into a quadrilateral naval exercise.
- The exercise is held annually, alternating between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Oceans.
- The primary aim is to bolster cooperation and enhance security in the Indo-Pacific region.
Focus of Malabar 2024:
- Malabar 2024 will include a wide range of activities aimed at improving cooperation and operational capabilities.
- Discussions will cover special operations, surface warfare, air defense, and anti-submarine warfare through Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE).
- Complex maritime operations will be conducted, focusing on surface warfare and air defense exercises at sea.
- There will be significant emphasis on enhancing situational awareness within the maritime domain.
Participation and Assets:
- Various Indian naval platforms will participate, including guided missile destroyers, multi-purpose frigates, submarines, fighter aircraft, and helicopters.
GS3/Science and Technology
India AI Mission: MeitY Relaxes AI Compute Procurement Norms to Accommodate Start-ups
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
Under its ambitious AI Mission, the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) has relaxed some provisions in its norms to procure computing capacity for artificial intelligence (AI) solutions, addressing concerns from smaller companies.
What is India's AI Mission?
The Prime Minister of India announced the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) mission during the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi. The mission, to be implemented by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC), aims to:
- Establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs), which are crucial for processing images and enhancing 3D graphics rendering.
- Develop foundational models trained on datasets that encompass major Indian languages, focusing on key sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Create AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50 line ministries.
- Design an AI marketplace to provide AI as a service and pre-trained models for AI application developers.
- Implement AI infrastructure through a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding.
- Allocate Rs 4,564 crore from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore specifically for building computing infrastructure.
7 Key Features of India AI Mission:
- India AI Compute Capacity: This feature aims to create a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands from India's expanding AI startups and research initiatives.
- India AI Innovation Centre: This centre will focus on developing and deploying indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and foundational models tailored to critical sectors.
- India AI Datasets Platform: This initiative aims to facilitate streamlined access to quality non-personal datasets essential for AI innovation.
- India AI Application Development Initiative: This initiative will promote the development of AI applications in critical sectors based on problem statements from Central Ministries and State Departments.
- India AI FutureSkills: Designed to lower barriers to entry into AI education, this initiative will increase the number of AI courses across undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. programs.
- India AI Startup Financing: This feature is intended to support deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for innovative AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: This pillar focuses on ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects, including the development of indigenous tools and frameworks.
Significance of India AI Mission:
- The mission aims to promote the vision of "Making AI in India and Making AI Work for India."
- It seeks to present the positive applications of AI technology to the international community, enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- The mission aims to establish a comprehensive ecosystem that catalyzes AI innovation through strategic programs and partnerships in both public and private sectors.
- It will foster creativity and enhance India's internal capabilities, ensuring the country's technological autonomy.
- The initiative is expected to generate employment opportunities that require advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantages.
Changes Introduced by the MeitY under its AI Mission:
- Lowered annual turnover requirements: The threshold for primary bidders has been reduced from Rs 100 crore to Rs 50 crore, and for non-primary members, it has been halved to Rs 25 crore, allowing more startups to participate in bidding.
- Reduced computing capacity requirements: The requirement for FP16 performance has been lowered from 300 TFLOPS to 150 TFLOPS, and AI compute memory has been reduced from 40 GB to 24 GB.
- Experience criteria: Companies must now demonstrate prior experience in providing AI services, detailing the number of clients served and a minimum billing of Rs 10 lakh over the past three financial years.
- Local sourcing mandate: Bidders are required to procure components for cloud services from Class I or Class II local suppliers, aligning with the 'Make in India' initiative.
- Data sovereignty: All AI services must be operated from data centers within India, ensuring that user data remains secure within the country's borders.
- Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model: The implementation of the AI mission will follow a PPP model, with 50% viability gap funding allocated for building computing infrastructure.
Significance of these changes:
These changes are expected to encourage greater participation from smaller firms, thereby enhancing the AI landscape in India.
GS2/International Relations
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th October 2024
|
Download as PDF |
What does USCIRF report say about India?
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
On October 2, the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), based in Washington DC, published a country update on India. The report emphasizes what it describes as deteriorating conditions for religious freedom within the country.
Mandate of the USCIRF
- The USCIRF’s primary responsibility is to monitor the universal right to freedom of religion or belief (FoRB) in countries outside of the U.S.
- It assesses violations based on international human rights standards, particularly focusing on Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- Annual Reports: The commission produces yearly reports that evaluate the state of religious freedom and recommends countries for designation as “Countries of Particular Concern” (CPC) or for inclusion on the “Special Watch List” (SWL).
- Policy Recommendations: USCIRF provides policy advice to the President, Secretary of State, and Congress concerning actions needed to address violations of religious freedom.
How does the USCIRF designate a country as a ‘Country of Particular Concern’?
- Criteria for CPC Designation: A country is labeled a CPC if it engages in or tolerates “systematic, ongoing, and egregious violations” of religious freedom. This may include severe actions such as torture, prolonged detention without charges, and other significant denials of fundamental rights.
- Recommendation Process: The USCIRF evaluates countries based on its findings and recommends those that fulfill the CPC criteria. The final decision on whether to accept these recommendations and designate countries accordingly lies with the U.S. Secretary of State.
How has the Indian government reacted to the report?
- Rejection of Findings: The Indian government has firmly dismissed the USCIRF’s report, calling it biased and politically motivated.
- Officials argue that the commission misrepresents facts concerning religious freedom in India.
- Defense of Policies: The Ministry of External Affairs has asserted that India is dedicated to protecting the rights and freedoms of all citizens, regardless of their faith, and has urged USCIRF to avoid agenda-driven narratives.
Way forward:
- Engage in Diplomatic Dialogue: India should actively engage with international bodies like USCIRF to address concerns, clarify its stance, and present factual data on religious freedom, fostering mutual understanding.
- Strengthen Domestic Protections: India ought to enhance legal and institutional frameworks to safeguard minority rights and religious freedoms, ensuring transparent mechanisms to address grievances and counter negative perceptions globally.
GS2/International Relations
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The Prime Minister is set to strengthen India’s strategic ties with Southeast Asia as he heads to Vientiane, Laos, for the 21st ASEAN-India Summit.
About Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization consisting of ten Southeast Asian nations.
- It was founded on August 8, 1967, in Bangkok, Thailand, through the signing of the ASEAN Declaration, commonly known as the Bangkok Declaration.
- The organization's primary goal is to enhance economic and security cooperation among its member countries.
Members:
- The founding members of ASEAN include Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Brunei, which joined in 1984.
- Vietnam became a member in 1995, followed by Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999.
- The ASEAN Secretariat is located in Jakarta, Indonesia.
Fundamental principles of ASEAN are:
- Mutual respect for the independence, sovereignty, equality, territorial integrity, and national identity of all member nations.
- The right of each state to conduct its national affairs without external interference, subversion, or coercion.
- Non-interference in the internal affairs of member states.
- Resolution of disputes or differences through peaceful means.
- Rejection of the use or threat of force.
- Effective cooperation among member nations.
Institutional mechanism of ASEAN includes:
- ASEAN Summit: This annual meeting addresses regional issues and sets policy directions.
- ASEAN Coordinating Council (ACC): Responsible for overseeing the implementation of ASEAN agreements and decisions.
- ASEAN Secretariat: Provides support and facilitates ASEAN activities and initiatives.
- ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF): A platform for dialogue and cooperation on political and security matters among ASEAN members and their partners.
Decision Making:
- Decisions within ASEAN are made through consultation and consensus, ensuring that all member states are involved in the process.
GS3/Environment
2023 driest for global rivers in 33 years, reveals WMO’s report
Source: DTE

Why in news?
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) released its October 2024 report, highlighting that 2023 marked the driest year for global rivers in the past 33 years, which has heightened stress on water supplies worldwide.
Factors Contributing to 2023 Being the Driest Year for Global Rivers
- Record High Temperatures: The year 2023 was noted as the hottest on record, leading to prolonged drought conditions that resulted in diminished river flows across various regions around the globe.
- Climate Change Impact: Rising temperatures have caused erratic hydrological cycles, resulting in both extreme droughts and flooding. This unpredictability has intensified water shortages in numerous areas.
- Transition from La Niña to El Niño: The climatic shift occurring in mid-2023 significantly altered weather patterns, leading to widespread dry conditions in many regions while simultaneously causing floods in others.
- Glacier Melting: The report noted that glaciers experienced their most significant mass loss in 50 years, threatening long-term water security for millions who depend on glacial meltwater.
- Impact of Climate Change on Global Water Resources and Glacier Conditions
- Increased Water Scarcity: The report indicated that approximately 3.6 billion people currently lack reliable access to water for at least one month each year. This number is projected to exceed 5 billion by 2050 due to worsening water scarcity.
- Glacier Dependency: Many regions rely on glacial meltwater for their river systems. As glaciers continue to diminish, future water availability is jeopardized, especially in areas such as Europe and North America.
- Erratic Water Supply: The accelerated hydrological cycle leads to unpredictable rainfall patterns, resulting in both droughts and floods that disrupt agricultural and industrial water supplies.
Implications for Global Water Access and Management
- Increased Demand vs. Supply Shortages: With growing populations and rising demand for water resources, current trends indicate a critical imbalance between supply and demand, leading to heightened competition for available water resources.
- Need for Improved Monitoring: The WMO emphasizes the necessity for enhanced data collection and sharing regarding water resources, which is crucial for effective management strategies that can adapt to changing conditions.
- Urgent Action Required: There is an immediate need for global cooperation and action to tackle these challenges. Enhanced monitoring systems and international collaboration are essential to mitigate the impacts of climate change on water resources.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Water Resource Management and Adaptation Strategies: Governments should implement integrated water resource management (IWRM) plans to effectively address both water scarcity and flooding risks.
- Enhance Global Cooperation and Data-Driven Decision Making: Countries must prioritize data-sharing, improve monitoring of water resources, and foster cross-border collaborations to manage shared water systems effectively.
GS3/Science and Technology
MACE Observatory
Source: Deccan Herald

Why in news?
Recently, the MACE Observatory has been inaugurated by the Secretary DAE & Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission, at Hanle, Ladakh.
About
- The Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory stands as the largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
Location
- Situated at an impressive altitude of approximately 4,300 meters.
- Recognized as Asia's Largest and the World's Highest Imaging Cherenkov Observatory.
Project Objectives
- The MACE project aims to cultivate international collaborations, enhancing India's contributions to space research.
- It seeks to elevate India's standing in the global scientific community.
Construction and Support
- The observatory has been indigenously constructed by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- It has received support from the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, along with various Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- MACE will significantly aid the scientific community in deepening its understanding of:
- Astrophysics
- Fundamental physics
- Particle acceleration mechanisms
- The MACE telescope is designed to observe high-energy gamma rays.
- This observation contributes to global efforts aimed at understanding high-energy cosmic events, such as:
- Supernovae
- Black holes
- Gamma-ray bursts
Socio-Economic Impact
- MACE plays a crucial role not only in advancing scientific research but also in fostering socio-economic development in the Ladakh region.
|
39 videos|4541 docs|970 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the gig economy and how is it impacting employment in India? |  |
| 2. What is the 'Humsafar Policy' and how does it relate to wayside amenities in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Hanle Dark Sky Reserve in Ladakh? |  |
| 4. What is the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) and its role in India? |  |
| 5. What does the USCIRF report say about India's religious freedom situation? |  |


























