UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Pandemic Fund Project
Source: PIB
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying inaugurated the Pandemic Fund Project aimed at strengthening animal health security in India for pandemic preparedness and response, in New Delhi.
About Pandemic Fund Project:
- The initiative is valued at $25 Million and is supported by the G20 Pandemic Fund.
- Its primary goal is to bolster the country's animal health security by enhancing and expanding animal health laboratories and establishing laboratory networks.
Implementation Partners:
- This fund will be executed in collaboration with the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the World Bank, and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), with an expected utilization by August 2026.
Key Support Areas:
- The fund aims to support existing departmental initiatives by improving disease surveillance, which includes genomic and environmental monitoring for early warnings.
- It will facilitate laboratory infrastructure development and promote cross-border cooperation to create a more cohesive system for monitoring and managing zoonotic diseases.
Human Capacity Development:
- The initiative is also focused on enhancing the skills and capabilities of personnel working in animal health through dedicated capacity-building programs.
Data Management and Analytics:
- Funds will be allocated to upgrade data management systems, thereby improving analytics capabilities for better risk assessment.
- This will enhance decision-making processes and enable more effective communication strategies regarding animal health risks.
Institutional Capacity Strengthening:
- The project aspires to strengthen institutional frameworks at both national and regional levels by aiding the establishment of a disaster management framework specifically for the livestock sector.
GS3/Science and Technology
India's Ambitious Space Vision
Source: The Week

Why in News?
In a recent address, ISRO Chairman S. Somanath outlined India’s goals to increase its share in the global space economy, enhance indigenous technological capabilities, and advance a series of high-impact space missions. The vision highlights India's roadmap for space exploration and collaboration, aiming to boost India's position in the space industry significantly.
India’s Space Economy:
- India currently contributes about 2% to the global space economy, with a goal to increase this share to at least 10% over the next decade.
- Achieving this milestone requires concerted efforts from both ISRO and other stakeholders, including private enterprises and start-ups, within India’s evolving space ecosystem.
Participation of the Private Sector:
- The Indian space sector has experienced a surge of activity due to recent policy reforms and the opening up of the industry to private enterprises.
- There is growing enthusiasm among young entrepreneurs and companies, leading to a collaborative environment where private players are assuming roles previously managed solely by ISRO.
Scientific Contributions and Legacy of ISRO:
- Chandrayaan missions, particularly Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-3, have made groundbreaking scientific discoveries, including confirming the presence of water on the Moon.
- These missions have improved scientific understanding through advancements in soft-landing technologies and data collection.
- Astrosat, India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, has facilitated extensive astronomical research, resulting in over 400 scientific papers and more than 30 PhDs.
- The success of Astrosat has set a strong foundation for future contributions to space science, including the recently launched Aditya-L1 and XPoSat missions.
Key Upcoming Missions of ISRO:
- Gaganyaan mission: India’s first manned space mission, scheduled for 2026, marks a significant milestone in India’s human spaceflight program.
- Chandrayaan-4 Sample Return mission: Planned for 2028, this mission will focus on returning lunar samples to enhance understanding of the Moon’s geology and resources.
- LUPEX/Chandrayaan-5 mission: A collaborative project with Japan’s JAXA, this mission is expected after 2028 and aims to advance lunar science with a 350-kg rover provided by Japan and the lander by India.
- NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission: This US-India joint mission, which has faced delays, is scheduled for launch in 2025 and aims to monitor natural resources and hazards using radar imaging.
Way Ahead for India’s Space Vision:
- India has significantly reduced its dependence on imported space technologies over the past decade, but many critical components still come from abroad.
- There is a pressing need to develop domestic manufacturing capabilities for advanced research and technologies in the space sector.
- ISRO is promoting the indigenisation of research, development, and manufacturing to ensure critical items for the space sector can be produced domestically.
- This shift is crucial for meeting the demands of upcoming missions and achieving self-sufficiency in space technology.
Conclusion:
- India’s evolving space program under ISRO’s leadership is set to become a major force in global space exploration.
- With a focus on indigenous technology, private sector engagement, and ambitious missions, India aims to contribute 10% to the global space economy and establish a robust foundation for long-term space exploration and scientific advancement.
GS3/Economy
What is Coking Coal?
Source: Business Line

Why in News?
India’s coking coal imports for the first six months of the current fiscal (April – September) reached a six-year high of 29.6 million tonnes (mt), with shipments from Russia experiencing a significant increase of over 200 percent during this period.
About Coking Coal:
- Coking coal, also referred to as metallurgical coal, is a type of sedimentary rock that occurs naturally and is found in the Earth's crust.
- This coal variant generally has a higher carbon content, lower ash content, and reduced moisture compared to thermal coal, which is primarily utilized for generating electricity.
- Coking coal is crucial in steel production, making it one of the most extensively utilized construction materials globally.
- It is classified as bituminous coal, possessing qualities that render it suitable for producing metallurgical coke, commonly known as coke.
- Coke is the primary output from the high-temperature carbonization of coking coal.
- In steelmaking, coke serves as an essential input material, utilized to generate pig iron in blast furnaces, functioning both as a reducing agent for iron ore and as a structural support for the furnace charge.
- Approximately 770 kilograms of coking coal are required to produce one ton of steel, with around 70 percent of global steel being manufactured in basic oxygen blast furnaces.
- The leading producers of coking coal include:
- China: 676 million tons in 2022 (62% of global production)
- Australia: 169 million tons in 2022 (15% of global production)
- Russia: 96 million tons in 2022 (9% of global production)
- USA: 55 million tons in 2022 (5% of global production)
- Canada: 34 million tons in 2022 (3% of global production)
GS3/Economy
Indian Stock Market Slide
Source: Mint

Why in News?
The Indian stock market has experienced a steady downturn over the last month, with major indices like the Sensex and Nifty dropping nearly 1% on October 25, marking the fifth consecutive day of losses. This decline equates to a 7.5% decrease for the Sensex over the past month, making it the largest fall among global markets during this time.
Introduction to the Indian Stock Market:
- Understanding shares:
- Shares are units representing ownership in a company, rather than physical assets.
- Companies issue shares to generate funds for various operational needs.
- Trading shares requires engaging with a broker or stock exchange, with prices fluctuating based on market demand and supply.
- Types of investments:
- Long-term (Equity investments): These are aimed at long-term growth and are favored for their potential to yield high returns over time.
- Short-term (Debt investments): Generally lower-risk, these investments are designed for quicker returns.
- How does the share market work in India?
- The Indian stock market mainly comprises two key exchanges:
- National Stock Exchange (NSE): A prominent stock exchange in India.
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): One of the oldest and most renowned exchanges in the country.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) oversees these exchanges to maintain fair practices and protect investors.
- Various securities, including equities, bonds, ETFs, and derivatives, are traded at prices influenced by market demand and supply.
- The Indian stock market mainly comprises two key exchanges:
- Purpose of the stock market:
- The stock market operates as a regulated, centralized platform facilitating interactions between companies and investors.
- Its primary aim is to support business growth by enabling companies to raise capital through share sales, while providing investors opportunities for profit and growth.
Market Overview:
- Sensex performance:
- The BSE’s 30-share Sensex fell by 662.87 points (0.83%) on Friday, closing at 79,402.29.
- Nifty performance:
- The Nifty 50 decreased by 218.6 points (0.9%), finishing at 24,180.8.
- One-month trend:
- Between September 26 and October 25, the Sensex dropped by 7.5%, while other global indices saw smaller declines or even gains.
Reasons Behind the Decline:
- Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) sell-off:
- FPIs have withdrawn a record total of Rs 85,790 crore in October.
- Geopolitical tensions in West Asia:
- Uncertainties stemming from the West Asian conflict have dampened investor sentiment.
- Corporate Q2 results:
- Lower-than-anticipated corporate earnings have negatively influenced market confidence, with net profit growth for 502 companies slowing to 4.1% in Q2.
- Shift to primary markets:
- Funds have shifted from the secondary market to initial public offerings (IPOs), leading to liquidity shortages.
Global Comparison:
- Among major indices, India has experienced the steepest decline at 7.5%.
- In contrast, other indices such as Shanghai (9.99%) and Hang Seng (3.85%) have seen increases.
Sectoral Impact on Small and Mid-Cap Stocks:
- High valuations and liquidity shortage:
- Small- and mid-cap stocks have decreased by over 8% due to high valuations and limited liquidity, as retail investors shift funds toward IPOs.
- Individual stock performance:
- Many small-cap stocks have experienced declines of 20-30%, primarily due to valuation concerns.
Outlook and Future Expectations:
- Market analysts remain cautiously optimistic about a potential recovery within the next two months.
- Despite current short-term pressures, the medium to long-term growth prospects of the Indian economy are still deemed strong.
- Current valuations indicate a moderate overvaluation, but not to a degree that would significantly deter long-term investment.
GS3/Defence & Security
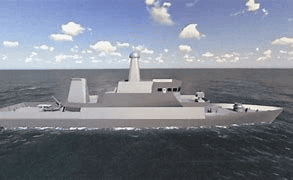
Abhay Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC)
Source: The Week
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the seventh Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC), named 'Abhay', was launched.
About Abhay Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC):
- Constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), a prominent shipbuilding and repairing firm in India.
- This vessel marks the seventh addition to an eight-ship ASW SWC series, which stems from a 2019 agreement between the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and GRSE.
- The ships are designed with over 80% indigenous components, emphasizing self-reliance in defense manufacturing.
- They are specifically built for anti-submarine operations in coastal areas and can also perform Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and mine-laying tasks, significantly improving the Navy’s operational capabilities along India’s coast.
- Each ship measures 77 meters in length and 10 meters in width, engineered for efficient subsurface surveillance in coastal waters.
- These vessels are capable of tracking a range of surface and underwater targets and can conduct coordinated anti-submarine missions in collaboration with aircraft.
- The ASW SWCs are compact and equipped with waterjet propulsion systems, allowing them to achieve speeds of up to 25 knots, enhancing their tactical agility.
- Fitted with a sophisticated anti-submarine warfare suite, these ships can deploy lightweight torpedoes, ASW rockets, and mines, making them effective assets for coastal defense.
- They are armed with a 30 mm Close-in Weapon System (CIWS) and 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote-Control Guns, providing a strong defense against aerial and surface threats.
- Equipped with a Hull-Mounted Sonar and Low-Frequency Variable Depth Sonar, these ships possess advanced underwater surveillance capabilities, improving their detection and engagement in anti-submarine operations.
GS3/Defence & Security
Triton Island
Source: The Week

Why in News?
Recent satellite imagery has indicated a notable increase in military presence on Triton Island, which is the closest landmass in the contested Paracels archipelago to Vietnam.
About Triton Island:
- Triton Island is a small landmass situated within the Paracel Islands located in the South China Sea.
- The island has a minimal land area of approximately 1.2 square kilometers.
- It measures about 4,000 feet in length and 2,000 feet in width, and was previously uninhabited.
- The Paracel Islands are subject to territorial claims from several countries, mainly China, Vietnam, and Taiwan, which adds to the region's political sensitivity.
- Despite being uninhabited, Triton Island is strategically significant due to its location in the South China Sea, an area recognized for its abundant fishing resources and potential oil and gas deposits.
Key Facts about South China Sea:
- The South China Sea is an extension of the western Pacific Ocean, bordering the Southeast Asian mainland.
- It is surrounded by several nations, including China, Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei, and Vietnam.
- This sea connects to the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait and to the Philippine Sea through the Luzon Strait, both of which are marginal seas of the Pacific Ocean.
- Along with the East China Sea, the South China Sea is part of what is referred to as the China Sea.
- The main archipelagos in this region are the Paracel Islands, governed by China, and the Spratly Islands.
- The climate in the South China Sea is tropical and heavily influenced by monsoon patterns.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Cybersquatting?
Source: The Indian Express
Why in News?
Recently, a Delhi based developer registered the domain, 'JioHotstar,' which ignited a debate on cybersquatting.
About Cybersquatting:
- Cybersquatting refers to the practice of registering or utilizing a domain name to gain profit from an existing trademark, or the corporate or personal name of an individual.
- This practice is often viewed as a form of extortion or an attempt to undermine a rival's business.
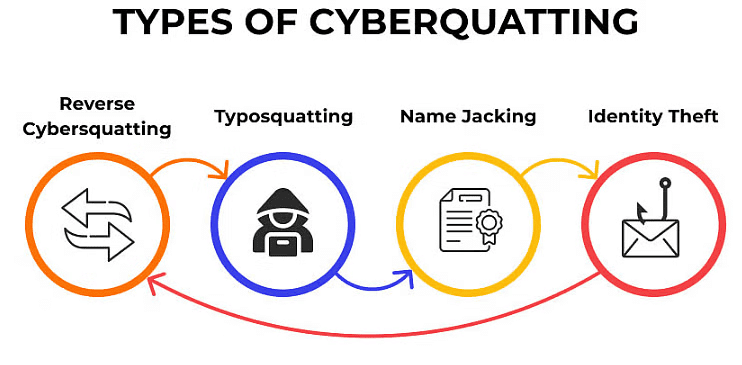
Types of Cybersquatting
- Typo squatting:This involves purchasing domain names that contain typographical errors of well-known brands. For example, domains like:
- yajoo.com
- facebok.com
- The main goal of typo squatting is to redirect users who misspell a domain name to the squatter's site.
- Identity theft: This occurs when a website replicates an existing brand's site with the aim of confusing consumers. The squatter creates a site that looks similar to the genuine brand's, leading to potential deception.
- Name jacking: Involves impersonating a famous individual or celebrity online. Examples include creating fake social media profiles or websites that use a celebrity’s name, misleading fans and followers.
- Reverse cybersquatting: This is a less common scenario where an individual falsely claims a trademark as their own and then unjustly accuses the actual domain owner of cybersquatting. Essentially, it is the inverse of typical cybersquatting.
Legal Framework in India
- Currently, India lacks specific laws that directly address or penalize cybersquatting.
- However, under the Trademark Act of 1999, domain names are recognized as trademarks. Therefore, anyone utilizing a domain name that is identical or similar to a registered trademark can be held responsible for trademark infringement as per Section 29 of the Trademark Act, 1999.
GS2/Governance
Government issues advisory to curb hoax bomb threats on social media
Source: Zee News

Why in news?
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has issued a directive urging social media platforms to take accountability for managing threats against flights operating from India. This advisory highlights the alarming proliferation of hoax bomb threats, exacerbated by social media features that allow for easy forwarding, resharing, and reposting of content.
- Recent bomb threats affecting various airlines
- Aviation security architecture overview
- Challenges in handling security threats and proposed solutions
- Advisory measures to mitigate hoax bomb threats on social media
In recent weeks, Indian airlines, including those from the Tata group (Air India, Vistara, and Air India Express), Indigo, Alliance Air, and Star Air, have experienced a spate of hoax bomb threats. These incidents have necessitated emergency protocols, including flight rerouting and military intercepts in international airspace when emergency transponder codes were deployed. Despite being false alarms, these threats have led to substantial delays and financial losses estimated between ₹13 lakh to ₹17 lakh per hour for the airlines.
Nature and Source of Threats
- Most threats have been traced back to social media platforms.
- Intelligence agencies are actively investigating these threats by tracking IP addresses and VPN usage.
- Despite initial beliefs that these were hoaxes, all threats have been taken seriously due to the scale of approximately 4,000 flight operations daily in India.
- Since these incidents began, around 275 threats have impacted nearly 48,000 flights.
ICAO’s Aviation Security Guidelines and Directives
- The majority of aviation security protocols are based on the International Civil Aviation Organization’s (ICAO) Annex 17 on Aviation Security.
- These guidelines, along with the Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs), are part of the Chicago Convention, mandating global actions against unlawful interference in civil aviation.
- The ICAO Aviation Security Manual (Doc 8973) supplies member states with comprehensive security procedures which are regularly updated to address evolving threats and technological advancements.
Security Agencies and Measures in India
- The Bureau of Civil Aviation Security is tasked with creating security standards for civilian flights.
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is responsible for overseeing flight safety.
- Other agencies involved include the Airports Authority of India, Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), National Security Guard (NSG), Intelligence Bureau (IB), Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), Ministry of Home Affairs, and the judiciary.
Proposed Amendments to Strengthen Aviation Security Laws
- In light of recent security threats, amendments are being considered for the Aircraft Act 1934, Aircraft Rules 1937, and other relevant legislation.
- Potential updates include harsher penalties, provisions for a no-fly list, and expanded legal options for addressing security breaches on the ground.
- Revisions to the Suppression of Unlawful Acts against Safety of Civil Aviation Act 1982 would empower authorities to manage in-flight and on-ground security threats more effectively.
Systemic Issues
- The recent incidents have uncovered systemic weaknesses, such as deficiencies in standardized procedures, guidelines, training, technological limitations, communication challenges, and regulatory enforcement within the aviation security framework.
Recommended Technological Investments and Innovations
- Experts suggest that effectively addressing hoax calls will necessitate investments in advanced call tracking, AI-based call analysis, and voice stress analysis.
- Emerging technologies like quantum computing and aviation cybersecurity frameworks could significantly bolster security measures.
- Additionally, the implementation of AI-enabled chatbots for initial threat assessments and psychological profiling of callers is recommended to better gauge motivations and threat levels.
Proposed Strategies for Deterrence and Awareness
- To deter potential offenders, experts propose publicly sharing images of offenders on social media and displaying them in airports as a warning.
- Establishing a global database for hoax calls and offering rewards for individuals who report such threats can also help in encouraging public vigilance.
In its advisory, MeitY has instructed all social media platforms to adhere to regulations outlined in the Information Technology (IT) Rules and the Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita (BNS). These platforms must make concerted efforts to promptly remove any posts related to bomb threats, as failure to comply could result in legal accountability.
Legal Framework Under IT Act, 2000 and IT Rules, 2021
- The Ministry’s advisory emphasizes reliance on existing legal frameworks to compel platforms to act against misinformation that poses a threat to public safety.
- The Information Technology Act, 2000, and the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, mandate that intermediaries swiftly eliminate harmful misinformation.
- Previously, similar legal provisions were enforced to counter the spread of deepfake videos, citing Rule 3(1)(b) of the IT Rules.
- Rule 3(1)(b)(v) specifically prohibits misinformation and blatantly false information.
Potential Consequences for Non-Compliance
- Platforms that fail to comply with the advisory may lose their intermediary liability protections, potentially exposing them to legal actions as publishers of harmful content.
- Legal actions could be initiated under both the IT Act and the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023, if platforms do not exercise due diligence.
GS3/Environment
Great Indian Bustard
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
In a remarkable development, a baby great Indian bustard was successfully born through Artificial Insemination (AI) at the Sudasari Great Indian Bustard Breeding Centre located in the Jaisalmer district of Rajasthan.
About Great Indian Bustard:
- Native to the Indian subcontinent.
- One of the heaviest flying birds.
- Habitat includes dry grasslands and scrublands.
- Primarily found in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan, home to around 100 individuals.
- Also inhabits arid regions in Maharashtra (Solapur), Karnataka (Bellary and Haveri), and Andhra Pradesh (Kurnool).
Features:
- Large bird with a distinct horizontal body and long, bare legs, resembling an ostrich.
- Sexes are similar in size, with the largest individuals weighing up to 15 kg (33 pounds).
- Identifiable by the black crown on its forehead, contrasting with a pale neck and head.
- Brownish body with wings featuring black, brown, and grey markings.
- Breeding predominantly occurs during the monsoon season, with females laying a single egg on the ground.
- Lifespan ranges from 12 to 15 years.
- Opportunistic feeders with a diverse diet that includes grass seeds, insects (such as grasshoppers and beetles), and occasionally small rodents and reptiles.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- Protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- CITES: Appendix 1
GS3/Economy
21st Livestock Census
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying launched the 21st Livestock Census in New Delhi.
About 21st Livestock Census:
- The Livestock Census is conducted every five years.
- This census involves counting the number of domesticated animals, poultry, and stray animals across the nation.
- It gathers detailed information regarding the species, breed, age, sex, and ownership of these animals.
- Since its inception in 1919, a total of 20 livestock censuses have been conducted, with the most recent one in 2019.
- The enumeration for the 21st census is set to occur between October 2024 and February 2025.
Focus of 21st Livestock Census:
The census will collect information on sixteen different animal species, including:
- Cattle
- Buffalo
- Mithun
- Yak
- Sheep
- Goat
- Pig
- Camel
- Horse
- Ponies
- Mule
- Donkey
- Dog
- Rabbit
- Elephant
- The census aims to document 219 indigenous breeds of these species, as recognized by ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR).
- It will also include a count of various poultry species such as:
- Fowl
- Chicken
- Duck
- Turkey
- Geese
- Quail
- Ostrich
- Emu
- The upcoming census will be fully digitized, similar to the last one in 2019.
- This digitization will encompass:
- Online data collection via a mobile application.
- Monitoring at various levels through a digital dashboard.
- Recording the latitude and longitude of data collection locations.
- Generating the livestock census report using specialized software.
- For the first time, the census will gather new data points, including:
- Information on pastoral animals and the contributions of pastoralists to the livestock sector, along with their socio-economic status and livestock holdings.
- More detailed data, such as the percentage of households whose primary income is generated from the livestock sector.
- Data regarding the gender of stray cattle.
GS2/International Relations
Israel launches retaliatory strikes on military targets in Iran
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
Israel executed targeted airstrikes on Iranian military positions early on October 26, responding to an earlier Iranian attack on Israel. This marks a significant escalation in hostilities between the two nations.
Reasons behind Israel's attack on Iran
- The relationship between Iran and Israel has dramatically deteriorated following the October 7 Hamas attacks.
- Iran, which does not recognize Israel's legitimacy, supports militant groups such as Hamas and Hezbollah in their opposition to Israel.
- Israel's airstrike on April 1 targeted the Iranian consulate in Syria, resulting in the deaths of 16 individuals, including key commanders from Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- In retaliation, Iran launched a missile and drone attack on Israel on April 13, prompting Israel to target Iranian missile defenses.
Historical context of the Israel-Iran enmity
- The animosity between Iran and Israel escalated following Iran's Islamic Revolution in 1979, which established a regime opposed to Israel's existence.
- Iran's leaders have continuously called for the destruction of Israel, with Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei labeling Israel as a "cancerous tumor."
- Both countries have engaged in a "shadow war," targeting each other's assets while denying responsibility for the attacks.
Impact of the Israel-Iran conflict on India
- A direct conflict between Israel and Iran could significantly disrupt shipping routes through the Red Sea, impacting global trade.
- India is particularly vulnerable due to its reliance on these routes for over $400 billion in trade with Europe, the US, Africa, and West Asia.
- Heightened tensions involving Hezbollah and allied groups increase the risk of assaults on commercial vessels in these critical shipping channels.
Background of the October 7 Hamas attack
- On October 1, Israel vowed to respond after Iran's ballistic missile attack.
- This recent military action by Israel was a calculated response to the ongoing threats posed by Iran.
- The conflict has been exacerbated by the killing of key figures from both Hamas and Hezbollah by Israeli forces, further inflaming tensions.
Fears of Protracted Red Sea Disruption
- The potential for a prolonged conflict between Israel and Iran threatens the stability of the Red Sea shipping lane.
- India's energy exports have already been affected, with a notable decline in petroleum product exports due to rising shipping costs and regional instability.
- In August 2024, India saw a 9% drop in exports, primarily due to a 38% decrease in petroleum exports, highlighting the economic implications of the conflict.
European Market Challenges
- The European market, responsible for 21% of India's petroleum exports, has faced significant challenges due to increased shipping costs.
- A report from Crisil indicated that these additional costs could negatively impact profit margins for Indian exporters.
- Despite an overall increase in exports to the EU, sectors like machinery and gems have reported declines, stressing the economic strain on these industries.
Trade Opportunities in West Asia
- Amidst the conflict, India's trade with Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries has grown by 17.8% in early 2024.
- India's exports to Iran also saw a 15.2% increase, benefiting from the neutrality of regional powers who are not involved in the conflict.
Risk to India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- The conflict in West Asia poses a threat to the development of the IMEC, a key project aimed at enhancing connectivity between India, the Gulf, and Europe.
- This initiative seeks to create faster trade routes, reducing reliance on the Suez Canal.
- However, escalating tensions may delay or complicate the progress of this vital economic corridor.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is coking coal and why is it important for India? |  |
| 2. How does cybersquatting affect businesses in India? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of cybersquatting? |  |
| 4. What legal frameworks exist in India to combat cybersquatting? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of India's ambitious space vision? |  |
















