UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 31st December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
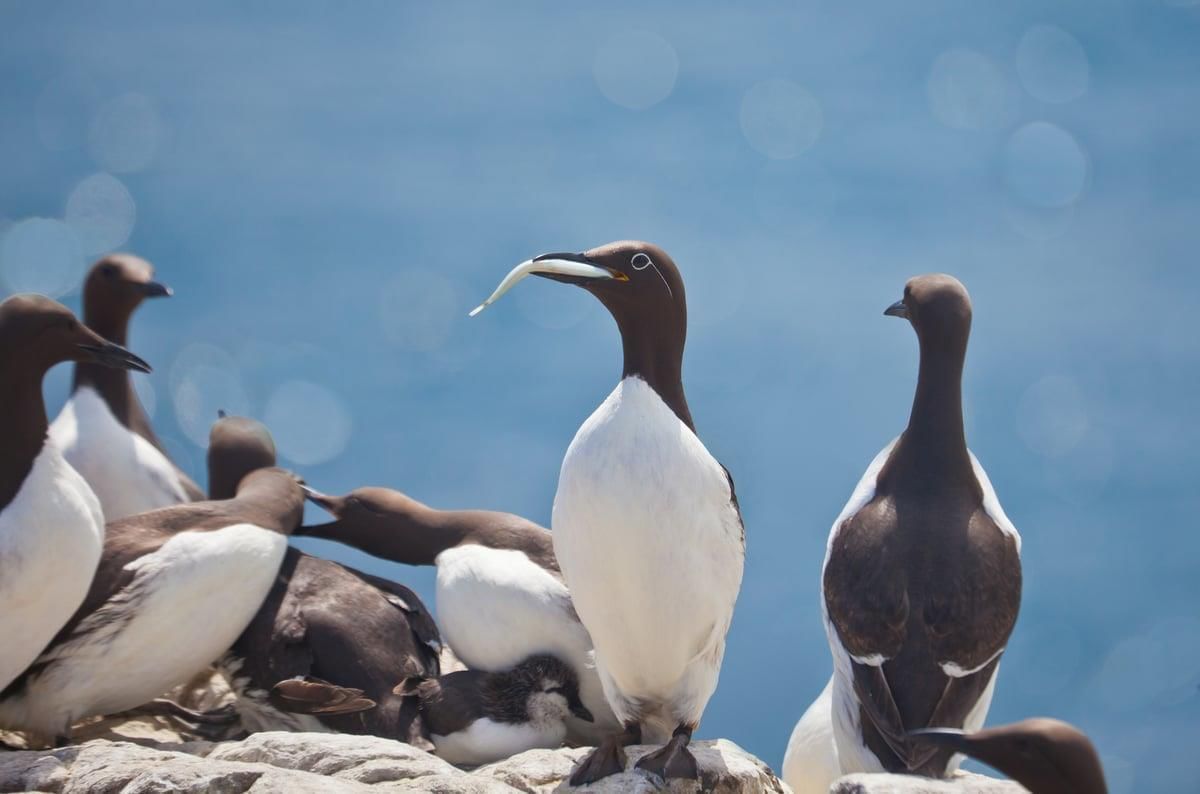
Marine Heatwave Killed Four Million Alaska Seabirds
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The 2014-2016 Pacific marine heatwave (MHW) resulted in the death of over four million common murres (Uria aalge) in Alaska. This event is noted for being the largest recorded die-off of vertebrates associated with warming oceans, as reported in a study published in Science.
- The marine heatwave led to significant ecological impacts, particularly on seabird populations.
- Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of marine heatwaves globally.
- MHWs are critical stressors on marine ecosystems, leading to large-scale disruptions.
Additional Details
- Marine Heat Waves (MHWs): Defined by NOAA as prolonged periods when sea surface temperatures rise 3 to 4°C above average for at least five consecutive days. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) also defines MHWs similarly, emphasizing the temperature above the 90th percentile for a minimum of five days.
- MHWs can last from weeks to years, depending on their intensity and extent, and are increasingly recognized for their severe impact on marine ecosystems.
- The 2014-2016 Pacific MHW exemplifies the severe consequences of such events, having caused a drastic decline in the common murre population, with half of them perishing during this period.
- Impacts include mass mortality of species such as kelps and corals, leading to habitat degradation and disrupting the entire food web.
The increasing occurrence of MHWs poses significant challenges for marine biodiversity, as many species face survival difficulties due to their limited adaptability to rapid environmental changes.
GS3/Economy
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey, 2023-24
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023-24 reveals significant trends in consumption behaviors across India. This survey is conducted by the National Statistical Office (NSO) every five years, providing vital insights into economic conditions.
- Rural Spending: Monthly per capita consumption expenditure (MPCE) rose by 9.3% to ₹4,122 in 2023-24, up from ₹3,773 in 2022-23, showing a notable increase from ₹1,430 in 2011-12.
- Urban Spending: MPCE increased by 8.3% to ₹6,996, compared to ₹6,459 in 2022-23 and ₹2,630 in 2011-12.
- Rural-Urban Gap: The gap narrowed to 69.7% in 2023-24, down from 71.2% in the previous year and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Food Expenditure: The share of food expenditure rose to 47.04% in rural and 39.68% in urban households, marking a reversal of a long-term decline.
- Dietary Shifts: Increased spending on beverages and processed foods indicates changing dietary preferences.
- Non-Food Expenditure: Comprises the majority of expenses, at 52.96% in rural areas and 60.32% in urban areas.
Additional Details
- Major Rural Non-Food Expenses:
- Conveyance: 7.59%
- Medical expenses: 6.83%
- Clothing & Bedding: 6.63%
- Major Urban Non-Food Expenses:
- Conveyance: 8.46%
- Entertainment: 6.92%
- Durable goods: 6.87%
- Regional Variations:
- Highest MPCE recorded in Sikkim (Rural: ₹9,377; Urban: ₹13,927) and Chandigarh (Rural: ₹8,857; Urban: ₹13,425).
- Lowest MPCE found in Chhattisgarh (Rural: ₹2,739; Urban: ₹4,927).
- States with the largest rural-urban gaps include Meghalaya (104%), Jharkhand (83%), and Chhattisgarh (80%).
- Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient decreased from 0.266 to 0.237 in rural areas and from 0.314 to 0.284 in urban areas, signifying reduced income disparity.
This survey highlights important trends in consumption, emphasizing the need for policy interventions to stabilize prices for essential goods, improve rural infrastructure, and foster urban employment growth to tackle rising expenses and income inequalities.
GS2/International Relations
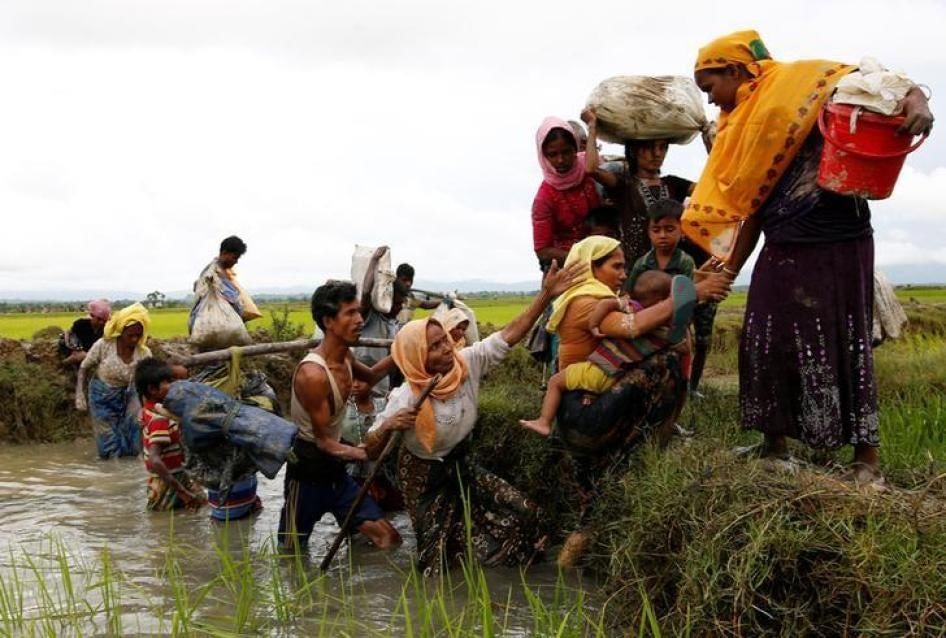
India’s Obligations Towards the Rohingya: Security Issues
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?A recent study by The Azadi Project and Refugees International highlights serious violations of basic rights faced by Rohingya refugees detained in India. The report criticizes India for not fulfilling its responsibilities under international human rights agreements.
- Rohingya refugees in India experience significant human rights violations, including arbitrary detention and poor living conditions.
- The report calls for revisions to India's outdated laws, such as the Foreigners Act of 1946, to better align with international refugee standards.
Additional Details
- Human Rights Violations: Rohingya refugees are subjected to "gross violations of constitutional and human rights," with reports of inhumane treatment in detention centers.
- Call for Legal Revisions: The study urges India to clarify the legal status of Rohingya refugees and revise outdated laws to conform with international norms.
- International Engagement: The report advocates for the release of vulnerable detainees and encourages international actors, such as the U.S. and UNHCR, to address these issues with India.
India’s stance on refugee policies is complicated by its non-signatory status to the 1951 Refugee Convention, which has implications for the treatment of Rohingya refugees. Despite this, some judicial interpretations suggest potential pathways for legal protections under Indian law, particularly regarding fundamental rights.
What does the 1951 Refugee Convention state?
- Non-refoulement: This principle prohibits returning individuals to countries where they may face persecution, forming a cornerstone of international refugee law.
- Rights of Refugees: The Convention outlines the rights of refugees, including access to legal assistance, work, education, and social services.
Though India is not a signatory to the 1951 Convention, it is bound by various international human rights treaties that imply obligations regarding the treatment of individuals at risk of torture or inhumane treatment.
India’s Stand
- Non-signatory Status: India argues that its non-signatory status to the 1951 Convention absolves it of legal obligations concerning asylum or non-refoulement.
- Detention Practices: The government classifies Rohingya refugees as illegal migrants, leading to continued detention under domestic laws.
- Judicial Interpretation: Some High Courts have suggested that international norms may apply under Article 21 of the Constitution, indicating a potential for legal protections despite non-signatory status.
What are India’s International Obligations?
- International Treaties: India is a party to treaties like the ICCPR, which includes provisions against refoulement, imposing obligations on the treatment of refugees.
- Constitutional Mandates: Article 51(c) of the Indian Constitution encourages respect for international law, influencing domestic legal interpretations.
Way Forward
- Establish a Comprehensive Refugee Policy: India should enact a uniform refugee law that aligns with international principles, ensuring clarity and protection for all refugees, including the Rohingya.
- Strengthen Collaboration with UNHCR and Civil Society: Engage with international agencies and local organizations to enhance refugee support systems and ensure humane treatment.
In summary, India’s approach to the Rohingya refugee crisis involves complex legal and humanitarian considerations, necessitating urgent reforms to align with international obligations and human rights standards.
GS3/Science and Technology
Significance of ISRO's Docking Mission for India's Space Ambitions
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully launched its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) as part of its advancements in space technology. This mission is pivotal for India's future space endeavors and positions the country among the elite nations capable of sophisticated space operations.
- India joins the select group of nations with space docking capabilities.
- Docking technology is essential for future missions, including lunar exploration and building a space station.
- Advanced technologies and biological experiments were demonstrated during the SpaDeX mission.
Additional Details
- SpaDeX Mission: This mission is focused on demonstrating in-space docking technology by maneuvering two satellites, SDX01 and SDX02, into precise alignment for docking, enabling future modular assembly and crew transfer operations.
- Joining an Elite Club: With SpaDeX's success, India becomes the fourth nation globally to achieve docking capabilities, following the United States, Russia, and China.
- Foundation for Future Missions: The docking capability is crucial for India's upcoming lunar missions, including Chandrayaan-4, which will require assembling multiple spacecraft components in orbit.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): SpaDeX is a significant step towards establishing India's own space station, with the first module expected to launch by 2028.
- Technological Advancements: New sensors and systems, including Laser Range Finders and Rendezvous Sensors, were employed to ensure accurate docking processes.
- Biological Experiments: The mission introduced biological studies in microgravity through the CROPS module, aiming to understand plant growth in space.
The successful SpaDeX mission not only showcases India's technological prowess but also lays the groundwork for future explorations in space, enhancing the nation's capabilities for lunar and interplanetary missions.
GS3/Economy
UPI Duopoly’s Rise and Market Vulnerabilities
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?In just eight years, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has become a cornerstone of digital transactions in India, processing nearly 80% of the country's digital payments, which amounted to ₹20.60 lakh crore in August. However, this dominance is primarily held by two major players, PhonePe and Google Pay, raising concerns about market concentration and its implications.
- UPI now accounts for a significant majority of India's digital transactions.
- PhonePe and Google Pay dominate the UPI market, controlling over 85% of the market share.
- The concentration of market power poses systemic vulnerabilities and risks to competition.
Additional Details
- Systemic Vulnerability: The dominance of PhonePe and Google Pay creates a risk of systemic failure, as a disruption in their services could significantly impact the entire UPI ecosystem.
- Reduced Competition and Innovation: High market concentration discourages new entrants and innovation, as smaller players face significant barriers due to the resources and scale of the dominant platforms.
- Foreign Dominance Risks: Both leading TPAPs are foreign-owned, raising concerns about data security and the sovereignty of sensitive information related to Indian users.
Regulatory Effectiveness
- Regulatory Challenges: The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has set a market share cap of 30% for TPAPs, but enforcement has been lax, allowing dominant players to maintain their positions.
- Limited Impact of Existing Regulations: Despite attempts to mitigate risks, the continued growth of PhonePe and Google Pay suggests that current regulations are insufficient and may inadvertently entrench their market dominance.
Strategies for Smaller Players
- Innovation and Niche Services: Smaller players should focus on specialized services that meet specific user needs, differentiating themselves from larger competitors.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Forming alliances with banks and fintech firms can help smaller players enhance their offerings and expand their reach.
- User Education and Trust Building: Investing in user education about digital payments can build trust and attract users hesitant to switch from established platforms.
Way Forward for the Indian Government
- Enforce and Strengthen Regulatory Caps: Strict enforcement of market share caps and timely compliance are essential to prevent excessive concentration, with penalties for non-compliance.
- Promote Indigenous Development: The government should provide financial incentives and support for Indian TPAPs to enhance their competitiveness and encourage innovation.
The rise of UPI and the concentration of power among a few players highlight the need for regulatory vigilance and support for a diverse and competitive digital payments ecosystem in India.
GS3/Defence & Security
Pangong Lake: Strategic Importance and Recent Developments
Source: The Tribune
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Indian Army recently installed a statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj on the banks of Pangong Lake, located at an altitude of 14,300 feet. This area is strategically significant as it lies close to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China in the eastern Ladakh region.
- Pangong Lake is known for its unique geographical and strategic features.
- The installation of the statue symbolizes the cultural and strategic importance of this region.
- Recent tensions between India and China have highlighted the significance of Pangong Lake in military and geopolitical contexts.
Additional Details
- Pangong Lake (Pangong Tso): The name is derived from the Tibetan term meaning "high grassland lake." It is an endoreheic lake, which means it has no outflow to external water bodies.
- Geographical Features:
- Length: 134 km, with approximately one-third in India and two-thirds in the Tibetan Autonomous Region, China.
- Altitude: Located at 4,350 meters above sea level.
- Size: Covers an area of 604 sq. km, with a width of about 5 km at its widest point.
- Water Type: The lake contains brackish water and freezes completely during winter.
- Color Variations: The lake exhibits varying colors based on sunlight and weather conditions, displaying shades of blue, green, and red.
- Wildlife: It serves as a breeding ground for species such as Bar-Headed Geese and Brahmini Ducks.
- Strategic Significance: Pangong Lake is located along the Chushul approach, a crucial route for potential military offensives by China, and was a key site during the 1962 war.
- Political Features: The northern bank of the lake is contested territory, with differing perceptions of the boundary between India and China.
- 2020 Standoff: Tensions escalated on May 5, 2020, leading to clashes in the area, with disengagement completed in 2021. The resolution of final friction points occurred in October 2024.
- Symbolism: The unveiling of the Shivaji statue coincided with the resolution of the standoff, underscoring the area's strategic and cultural significance.
Pangong Lake remains a focal point of military and diplomatic interest due to its geographical location and the ongoing tensions between India and China. The recent developments highlight both the cultural heritage and the strategic landscape of this important region.
GS3/Defence & Security
Exercise SURYA KIRAN
Source: Business Today
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Indian Army contingent has recently departed for Nepal to participate in the 18th edition of the Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
About the Exercise Surya Kiran
- Conducted Annually: Exercise Surya Kiran is a bilateral joint military exercise held annually between India and Nepal since 2011.
- Location and Duration: The exercise is taking place in Saljhandi, Nepal, from 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Participating Forces: The Indian Army contingent consists of 334 personnel, led by a battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles, while the Nepal Army is represented by the Srijung Battalion.
- Aim: The exercise aims to enhance interoperability in areas such as jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrains, and humanitarian assistance under the United Nations Charter.
Features and Significance
- Combat Readiness: Strengthens combat readiness in jungle warfare and counter-terrorism.
- Exchange of Knowledge: Facilitates the exchange of ideas, experiences, and best practices between the armies of both nations.
- Cultural Ties: Reinforces the strong cultural and historical ties shared by India and Nepal.
- Addressing Security Challenges: Prepares both nations to address shared security challenges effectively.
|
49 videos|5376 docs|1137 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 31st December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What factors contributed to the marine heatwave that killed four million seabirds in Alaska? |  |
| 2. How does the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) impact economic policy in India? |  |
| 3. What are India's security obligations towards the Rohingya refugees? |  |
| 4. Why is ISRO's recent docking mission significant for India's space ambitions? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of the UPI duopoly for the Indian digital payments market? |  |
















