UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 6th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Governance
Building a System That Sees the Migrant Worker
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoL&E) in India recently declared the e-Shram portal as the largest database of unorganised workers globally, with over 300 million workers registered. Launched in May 2021 in response to the Supreme Court's directive, the portal aims to address the distressing plight of migrant workers during the COVID-19 pandemic by creating a unified national database. Despite this ambitious initiative, challenges in its implementation and gaps in its utility highlight the pressing need for more robust measures to ensure social protection and inclusion for India's vulnerable unorganised workforce.
- The e-Shram portal is a significant step towards registering unorganised workers in India.
- Historical efforts to document migrant workers have largely failed, prompting the need for the e-Shram initiative.
- Migrant workers face numerous socio-economic challenges and barriers to accessing rights and services.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: The concept of maintaining a database for migrant and unorganised workers is not new. Previous initiatives, such as the Interstate Migrant Workmen Act (1979) and the Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act (2008), aimed to establish worker records and identity cards, respectively. However, these efforts lacked effective implementation, leaving many workers unregistered.
- Vulnerability of Migrant Workers: Many migrant workers are employed informally in sectors like construction and agriculture, leading to job insecurity and exploitative conditions. Their absence of unionisation exacerbates these challenges, preventing collective bargaining for better conditions.
- Challenges of Disenfranchisement: Migrant workers often lack access to voting rights and essential social services due to the transient nature of their employment. This disenfranchisement not only alienates them politically but also denies them a voice in crucial decisions affecting their lives.
- Technological Barriers: Digital illiteracy among unorganised workers poses a significant barrier to accessing the e-Shram portal. Many workers lack the necessary resources, such as smartphones and internet access, to navigate the registration process independently.
In conclusion, while the e-Shram portal represents a foundational step towards addressing long-standing challenges faced by unorganised workers, its success hinges on overcoming systemic barriers and integrating inclusive, sustainable policies that prioritize the rights and welfare of this vital workforce.
GS3/Environment
Mucuna bracteata Management in Kanniyakumari
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Tamil Nadu Forest Department, along with a local NGO from Kanniyakumari, is initiating a pilot project aimed at eradicating Mucuna bracteata from rubber plantations and forested areas within the district. This initiative comes in response to the invasive nature of this cover crop, which poses significant threats to local ecosystems.
- Mucuna bracteata is a leguminous vine originally introduced as a protective weed cover for rubber trees.
- It has become invasive, spreading rapidly across various regions, particularly in the Western Ghats of Kanniyakumari.
- The project targets areas where Mucuna bracteata has begun to dominate, affecting native flora and fauna.
Additional Details
- Invasive Nature:Mucuna bracteata was initially valued for its drought tolerance and ability to regulate soil nitrogen levels. However, its unchecked growth has led to it overpowering rubber trees and native vegetation.
- Areas affected include Kaliyal, Kadayalumoodu, Aarukani, Kodayar, and Kulasekaram, with significant impact noted in the Kodayar region.
- Its expansion threatens ecosystems adjacent to the Kalakkad-Mundanthurai tiger reserve, designated as a critical tiger habitat.
The ongoing efforts to control Mucuna bracteata are crucial for preserving the biodiversity of the region and ensuring the health of rubber plantations. Continued monitoring and management practices will be essential to mitigate its impact on local ecosystems.
GS3/Science and Technology
How Zebrafishes are Able to Repair Damaged Hearts
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has highlighted the remarkable ability of zebrafish, a popular aquarium species, to regenerate damaged heart muscle within a span of 60 days. This regenerative capability is not present in humans. The research has identified the Hmga1 protein as a crucial factor in this process, offering promising insights for potential heart repair mechanisms in mammals.
- Zebrafish can regenerate heart muscle damage efficiently within 60 days.
- The Hmga1 protein is vital for activating genes involved in regeneration.
- This regeneration capability is absent in humans.
Additional Details
- Role of Hmga1: In zebrafish, the Hmga1 gene is instrumental in activating dormant genes necessary for heart regeneration. It works by removing molecular “roadblocks” on chromatin (the structure that packages DNA), transitioning genes from an inactive state to one that promotes regeneration.
- Gene Activity: Unlike in mice and humans, where the Hmga1 gene becomes inactive after birth, it remains active in zebrafish during heart regeneration, facilitating the repair process.
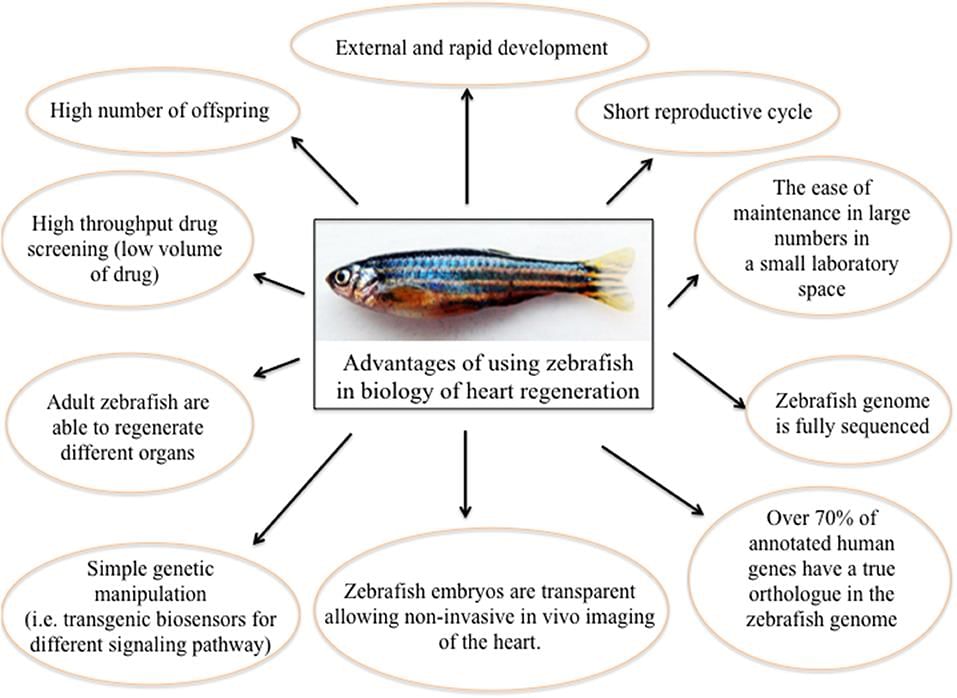
- About Zebrafish: Zebrafish are small freshwater fish, typically 2-3 cm in length, known for their distinctive horizontal blue stripes. They are native to the Indo-Gangetic plains of South Asia and thrive in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Conservation Status: The IUCN classifies zebrafish as Least Concern due to their widespread distribution and stable population.
- Significance in Research: Zebrafish can regenerate various major organs, including the heart, brain, eyes, and spinal cord, making them vital models for developmental biology and disease research. They share about 70% of their genes with humans, and over 80% of human disease-related genes have equivalents in zebrafish, enhancing their utility for studying genetic disorders.
- They produce hundreds of embryos in a single clutch, allowing for extensive research studies and are increasingly preferred over rodent models for certain vertebrate development studies.
- Due to their cost-effectiveness and rapid breeding, zebrafish are widely used in regenerative biology and drug discovery.
The unique regenerative abilities of zebrafish not only enhance our understanding of biological repair mechanisms but also pave the way for potential therapeutic strategies for heart damage in humans.
GS3/Science and Technology
Groundbreaking Atomic Clock Developed in the UK
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?A revolutionary atomic clock has been developed at a classified laboratory in the UK, aiming to enhance the security of military operations through the application of experimental quantum technology.
- The atomic clock measures time with unprecedented accuracy using atomic vibrations.
- Cesium atoms, known for their stability, serve as the basis for these precise timekeeping devices.
- Applications of atomic clocks span across GPS systems, telecommunications, and scientific research.
Additional Details
- Atomic Clock: An atomic clock is a device that measures time by referencing the oscillations of electrons within atoms, particularly cesium atoms. It is recognized as the most accurate timekeeping instrument available, with a margin of error of just a few billionths of a second per day.
- Working Principle: Atomic clocks utilize a microwave cavity filled with cesium vapor, where microwave signals induce vibrations in cesium atoms. The emitted radiation is detected and compared to a standard frequency, enabling precise time adjustment.
- Applications:
- GPS Systems: Atomic clocks are essential for calculating accurate locations by measuring the time taken for signals to travel from satellites to Earth.
- Telecommunications: These clocks synchronize signal timings across long distances in telecommunication networks.
- Scientific Research: Atomic clocks facilitate experiments requiring highly precise timing, such as atomic and molecular behavior studies.
In conclusion, the advancement of atomic clock technology holds significant potential for enhancing military operations and various commercial applications, reinforcing the importance of precise timekeeping in modern technology.
GS3/Defence & Security
Completion of Banihal Bypass on NH-44
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?The Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways has recently announced the completion of a crucial infrastructure project: the 4-lane, 2.35 km Banihal Bypass, which is located on National Highway 44 (NH-44). This development is significant for easing chronic traffic congestion in the region.
- The Banihal Bypass is a 2.35 km long, four-lane bypass designed to alleviate traffic snarl-ups in Banihal town, Jammu & Kashmir.
- This bypass was constructed at a cost of Rs 224.44 crore, enhancing connectivity on the Ramban-Banihal section of NH-44.
- It features 4 viaducts totaling 1,513 meters and 3 culverts, effectively mitigating bottlenecks caused by roadside markets.
- The infrastructure will significantly reduce travel time and congestion for tourists and defense vehicles heading towards the Kashmir Valley.
Additional Details
- NH-44: Known as the Old NH 7, NH-44 is the longest national highway in India, stretching over 3,745 kilometers (2,327 miles) and connecting Srinagar in Jammu & Kashmir to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- It traverses through a total of 11 Indian states, including Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Notably, NH-44 passes significant cities such as Agra, Delhi, Hyderabad, and Bangalore.
- This highway is not a continuous route but rather a combination of seven previously existing national highways, emphasizing its historical significance and infrastructural complexity.
The completion of the Banihal Bypass marks a vital step towards improving road connectivity in Jammu & Kashmir, facilitating smoother transit not just for local residents but also for tourists and the defense sector.
GS2/Polity
What is a Chargesheet?
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
The Supreme Court has recently clarified that offences mentioned in a chargesheet must not rely solely on vague claims of connivance.
- A chargesheet is a final report filed by police after completing an investigation.
- It initiates prosecution proceedings against an accused once submitted to the court.
- There are strict time limits for filing chargesheets, depending on the type of court.
Additional Details
- Definition of a Chargesheet: A chargesheet is a formal document that summarizes the findings of an investigation conducted by police officers. It is also referred to as a police report or final report.
- Contents of a Chargesheet:
- Names of involved parties
- Description of the information gathered
- Names of witnesses acquainted with the events
- Details about the alleged offence and the accused
- Information regarding the arrest and release of the accused
- Benefits of a Chargesheet:
- It includes statements from the accused and witnesses.
- Marks the commencement of a criminal trial.
- Specifies the charges for which the court will proceed against the accused.
- Facilitates obtaining bail for the accused by clearly stating the offences.
- Time Limit for Filing a Chargesheet:
- Must be filed within 60 days of the accused's arrest in lower courts.
- Must be filed within 90 days for cases triable by the Court of Sessions.
- If the chargesheet is not filed within these timelines, the accused is entitled to default bail.
- Is Filing a Chargesheet Compulsory?
- Filing a chargesheet is mandatory for cognizable offences.
- It is not compulsory for non-cognizable offences unless directed by the court.
- Cognizable vs. Non-Cognizable Offences:
- Cognizable Offences: These are serious crimes that allow police to investigate without a magistrate's order and arrest without a warrant.
- Non-Cognizable Offences: These are less serious crimes that require a magistrate's order for police to investigate.
In conclusion, a chargesheet plays a crucial role in the criminal justice system as it outlines the evidence against the accused and establishes the foundation for trial proceedings.
GS3/Science and Technology
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change has recently proposed amendments to the rules concerning the selection of experts for the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC). These changes aim to enhance transparency and governance in the approval process for genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Introduction of conflict of interest disclosures for expert members.
- Requirements for transparency in professional affiliations over the past decade.
- Enhanced governance to strengthen regulatory processes for GMOs.
- Compliance with Supreme Court directives regarding GM crop approvals.
- Improved operational integrity to ensure unbiased scientific evaluations.
Additional Details
- Conflict of Interest Disclosure: Expert members are now required to disclose any potential conflicts of interest that could impact their responsibilities. If a conflict exists, the member must step back from decision-making unless specifically invited to participate by the committee.
- Transparency Measures: Each member must provide a comprehensive record of their professional affiliations for the last 10 years to promote accountability and reduce bias.
- Participation Restrictions: Experts with conflicts must report these issues before meetings and ensure that their affiliations do not sway GEAC's decisions.
- Supreme Court Compliance: The amendments are in line with a Supreme Court directive from 2023, aimed at addressing conflict of interest concerns in the GM crop approval process, thereby enhancing public trust in the GEAC's operations.
- Governance Enhancement: These changes are set to fortify the regulatory framework regarding GMOs, ensuring decisions are made fairly and without external influences.
The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) serves as the principal regulatory authority in India for overseeing the release of genetically engineered organisms into the environment. Established under the Rules for the Manufacture, Use/Import/Export, and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms/Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells (1989), the GEAC operates under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. Its structure includes a Chairperson from the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change, a Co-Chairperson from the Department of Biotechnology, and 24 members representing key scientific institutions. The GEAC plays a crucial role in evaluating proposals for GMOs, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and engaging with stakeholders to maintain transparency and address public concerns.
GS3/Environment
Zoos Put on Alert as Avian Flu Kills 3 Tigers
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Three tigers and a leopard at a rescue center in Nagpur, India, have died from avian influenza (H5N1), marking a rare instance of the virus affecting rescued wildlife in the country. In response, the Union government has issued an advisory urging zoos across the nation to remain vigilant, adhere to preventive measures, and monitor for symptoms in captive animals and surrounding areas.
- Three tigers and one leopard have died due to avian flu in Nagpur.
- The Union government has issued an advisory for zoos to enhance vigilance and containment measures.
- The mortality rate for humans infected with H5N1 can be as high as 60%.
Additional Details
- Avian Influenza (H5N1): This is a subtype of the influenza A virus that causes severe respiratory illness in birds, particularly poultry and wild birds. Human cases are rare, but when they do occur, they are often fatal.
- Spread of H5N1: The virus has been detected in various mammals, including terrestrial and marine species, raising concerns about its zoonotic potential and the risk of cross-species transmission.
- Government Response: The Union Animal Husbandry Ministry has directed all states to quarantine infected animals and has initiated containment measures, including the deployment of a National Joint Outbreak Response Team.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Enhanced biosecurity measures have been mandated, including temporary closures of affected facilities, disinfection procedures, and protective gear for zoo staff.
This situation underscores the need for a comprehensive approach to manage the health risks posed by avian influenza to both animal and human populations. Authorities emphasize a "One-Health" strategy, integrating efforts across human, animal, and wildlife health sectors.
GS1/History & Culture
Indus Valley Script
Source: Hindustan Times
Why in News?
In a significant announcement, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin has offered a $1 million prize for anyone who successfully deciphers the ancient Indus Valley Script.
- The Indus Valley Script is an ancient writing system that remains undeciphered.
- Recent theories suggest its use was practical, possibly for trade and taxation.
- The ongoing archaeological work in Tamil Nadu, particularly in Keezhadi, relates to the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC).
Additional Details
- Bahata Ansumali Mukhopadhyay’s Theory: This theory posits that the script served commercial purposes, such as trade permits and tax stamps, highlighting its practical use rather than any religious or literary functions.
- Asko Parpola’s Dravidian Hypothesis: Parpola proposes a logo-syllabic system where pictograms represent words or phonetic sounds, linking the script to Dravidian languages and challenging Sanskrit-based interpretations.
- The excavations at Keezhadi have drawn parallels to the practices of the Indus Valley Civilization.
About the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)
- The Harappan Civilization, also known as the IVC, flourished between 2600 BCE and 1900 BCE, with earlier settlements dating back to 3200 BCE.
- Its origins trace back to Mehrgarh in Balochistan, which dates to 7000 BCE.
- Considered one of the three earliest civilizations alongside Egypt and Mesopotamia.
- The civilization spanned over 1.5 million sq. km, covering parts of modern-day India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
Key Features of the IVC
- Well-planned cities with a grid layout, including intersecting streets and fortified structures.
- Advanced drainage systems featuring underground sewers and covered drains, indicating a strong emphasis on hygiene.
- Granaries, warehouses, and dockyards that point to organized trade and food storage.
- Discovery of seals made of steatite, often engraved with animals and an undeciphered script, suggesting a sophisticated administrative system.
- Notable craftsmanship in pottery, bead-making, terracotta figurines, metal artifacts, and weaving.
- Advanced water management systems, including reservoirs, wells, and baths, showcasing an understanding of hydraulic engineering.
Archaeological Discoveries
- Two ASI archaeologists, Daya Ram Sahni and Rakhal Das Banerji, were instrumental in the discoveries at Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, respectively.
- John Marshall identified similarities between artifacts from Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, despite the sites being 640 km apart.
Artifacts and Sculptures
The Indus Valley Civilization is renowned for its remarkable artifacts and sculptures, which reflect its advanced culture and daily life.
- Key finds include seals with animal motifs, inscriptions of animals and mother goddesses, and intricately crafted beads and ornaments made of gold, silver, and semi-precious stones.
- Iconic sculptures like the bronze “Dancing Girl” and the steatite “Priest-King” highlight artistic sophistication.
- Practical items such as pottery, toys, and tools demonstrate technological advancement and societal organization.
- These discoveries provide insights into the civilization's trade, religious beliefs, and aesthetic achievements.
Previous Year Question (PYQ)
[2013] Which of the following characterizes/characterize the people of Indus Valley Civilization?
1. They possessed great palaces and temples.
2. They worshipped both male and female deities.
3. They employed horse-drawn chariots in warfare.
Select the correct statement/statements using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of the statements given above is correct
This overview underscores the significance of the Indus Valley Civilization in understanding ancient human societies and their achievements.
GS1/Indian Society
Rollback of the No-Detention Policy in India
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, the Union government revised the Rules of the Right to Education Act, 2009, permitting schools to retain students in Classes 5 and 8 if they fail to meet the promotion criteria based on a year-end examination. This amendment has significant implications for the Indian education system.
- The no-detention policy has been effectively rolled back.
- Students in Classes 5 and 8 can be detained if they do not pass year-end exams, with a re-examination opportunity provided.
- The amendment aims to address significant learning gaps exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Additional Details
- Significant Learning Gaps: Surveys like the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) indicated that many students, particularly in Class 5, lacked foundational skills necessary for their grade level.
- Declining Academic Performance: National Achievement Surveys highlighted a concerning decline in student performance from Class 3 to Class 8.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic intensified existing learning gaps, leading to a reevaluation of educational policies.
- Ineffective Implementation of Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE): Many schools neglected assessments, resulting in automatic promotions without proper evaluation of student learning.
The rollback of the no-detention policy signifies a shift towards more accountable educational practices, emphasizing the need for effective evaluation methods to enhance student learning outcomes.
GS3/Environment
Golden Jackal
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
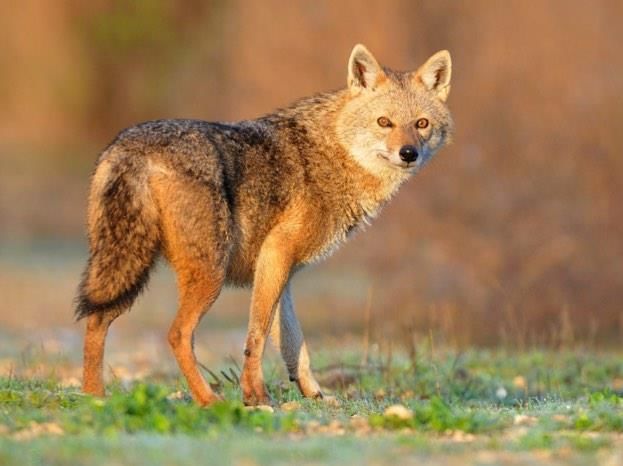
Why in News?Recent observations by environmentalists indicate that golden jackals are adapting to urban environments and have become less averse to human presence.
- The golden jackal, also referred to as the common jackal, is a medium-sized canid resembling a wolf.
- This species exhibits nocturnal behavior in human-populated areas but may be partially active during the day in less disturbed regions.
- Golden jackals are monogamous, forming lifelong pair bonds.
- They have a diverse omnivorous diet and are opportunistic foragers.
- Habitat includes valleys, riverbanks, and coastal areas, but they are less common in mountainous regions.
- Golden jackals are found throughout North and East Africa, Southeastern Europe, and South Asia, with a significant presence in India.
Additional Details
- Conservation Status: The golden jackal is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN and is listed in CITES Appendix III. They are also protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Threats: Habitat loss due to human encroachment and inadequate management practices pose significant threats to their survival.
- Ecological Significance: Golden jackals are vital for maintaining the biodiversity of ecosystems, particularly in mangrove and grassland habitats.
In summary, the golden jackal's adaptability to urban environments highlights the importance of understanding wildlife interactions with human activities, as well as the need for effective conservation strategies to protect these animals and their habitats.
GS3/Economy
LEADS 2024 Report Released
Source: India Today
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report has been released by the Union Minister, highlighting key objectives and performance metrics aimed at enhancing India's logistics sector.
- The primary aim is to improve logistics efficiency across states and union territories (UTs).
- States are encouraged to collaborate with the private sector to attract investments in logistics.
- Emphasis on promoting green logistics and sustainable practices.
- Advocacy for the integration of advanced technologies to enhance operational efficiency.
- Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development.
Additional Details
- Aims and Objectives: The report aims to enhance logistics performance, facilitate trade, and reduce transaction costs essential for economic growth.
- Parameters Evaluated:LEADS 2024 evaluates logistics performance based on four pillars:
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services
- Operating and Regulatory Environment
- Sustainable Logistics
- Key Performance Highlights: Various states are recognized as achievers based on their logistics performance, including Gujarat and Karnataka for the Coastal Group, and Haryana and Uttar Pradesh for the Landlocked Group.
- Role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): PPPs are crucial for enhancing infrastructure, establishing multi-modal logistics hubs, and promoting transparency in logistics projects.
- Importance of Skill Development: Skill development initiatives are emphasized to foster workforce inclusivity and equip workers with advanced technological knowledge.
In conclusion, the LEADS 2024 report serves as a strategic framework for enhancing India's logistics sector through sustainable practices, technological integration, and collaborative efforts between public and private sectors.
|
55 videos|5392 docs|1142 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 6th January 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of Mucuna bracteata in Kanniyakumari? |  |
| 2. How does genetic engineering impact agricultural practices in India? |  |
| 3. What measures are being taken to address the avian flu outbreak affecting tigers? |  |
| 4. What are the key features of the new atomic clock developed in the UK? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) in India? |  |
















