UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 10th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas convention, a significant event held biannually to honor the contributions of the Indian diaspora to their homeland. This year's theme was “Diaspora’s contribution to a Viksit Bharat.”
- The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas convention was inaugurated by PM Modi.
- The event celebrated the contributions of the Indian diaspora towards India's development.
- The theme for this year focused on the diaspora's role in achieving a developed India.
Additional Details
- What is Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD): Observed on January 9, PBD aims to strengthen the engagement of the Indian community overseas with the Indian government and reconnect them with their roots. This date was chosen as it marks the return of Mahatma Gandhi to India from South Africa in 1915.
- The first PBD was celebrated on January 9, 2003, in New Delhi, and since 2015, it has been organized once every two years.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award: Conferred during the convention to overseas Indians for significant contributions in various fields, this award is the highest honor for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs).
- Indian Diaspora Statistics: The Indian diaspora includes approximately 5 crore individuals, primarily from countries such as the USA, UAE, Canada, and Saudi Arabia, contributing significantly to India's economy through remittances, which amounted to $125 billion in 2023.
The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas serves not only as a platform for celebrating the contributions of the Indian diaspora but also highlights India's expanding global role and its commitment to peace and development. PM Modi's message reinforced the importance of collaborative efforts to achieve a developed India by its 100th year of independence in 2047.
GS3/Economy
Decoding India’s Growth Slowdown: Key Insights and Recommendations
Source: Zee Business
Why in News?
The current economic landscape in India is marked by a notable slowdown in growth rates, raising concerns among economists and policymakers. An in-depth analysis reveals several underlying factors contributing to this situation, necessitating strategic recommendations for revitalization.
- India's GDP growth rate is projected at 6.4% for 2024-25, a decline from 8.2% in 2023-24.
- Discrepancies in GDP calculations have emerged due to issues with the Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- Private investment remains weak despite corporate tax cuts aimed at boosting economic activity.
- Sectoral performance varies, with certain sectors like public administration and defence projected to grow.
- Fiscal strains are evident, with significant revenue shortfalls and a dilemma regarding fiscal discipline.
Additional Details
- Current Growth Scenario: The National Statistics Office (NSO) estimates a GDP growth rate decline, signaling economic challenges that need addressing.
- Data Discrepancies: Concerns have been raised about the reliance on WPI as a deflator for GDP estimates, leading to inconsistencies with the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Challenges in Private Investment: Corporate tax cuts have not translated into increased private investment in critical sectors, with a shift towards non-productive asset investment.
- Sectoral Analysis: Manufacturing initially showed promise but has since slowed, while public administration stands out as a growing sector.
- Fiscal Strains: As of November 2024, revenue generation is below targets, impacting public expenditure and investment plans.
- Policy Recommendations: Suggestions include enhancing revenue mobilization, encouraging private investment, and improving public spending on infrastructure.
In conclusion, India’s economic growth faces multifaceted challenges stemming from weak private investments, sectoral disparities, and fiscal pressures. A balanced approach combining improved revenue strategies, targeted public expenditure, and strong private sector incentives is crucial for overcoming these hurdles. Additionally, addressing statistical discrepancies and implementing long-term structural reforms will be vital for achieving sustainable economic growth.
GS2/Polity
Section 152 of BNS: Safeguarding Dissent Against Misuse
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?In the recent case of Tejender Pal Singh v. State of Rajasthan, the Rajasthan High Court cautioned against the misuse of Section 152 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) to stifle valid criticism and peaceful dissent.
- Section 152 should not be used as a substitute for sedition.
- The Rajasthan High Court emphasized the importance of judicial oversight in applying Section 152.
- The potential for abuse due to vague definitions in Section 152 raises concerns about freedom of speech.
Additional Details
- Terminology and Scope:
- Section 124A of the IPC explicitly criminalizes acts causing hatred or contempt towards the government, termed as sedition, focusing on inciting disaffection.
- In contrast, Section 152 includes broader language that can criminalize acts jeopardizing the sovereignty and integrity of India without explicitly labeling them as sedition.
- Penalties:
- Section 124A prescribes a punishment ranging from life imprisonment to a minimum of three years in prison with possible fines.
- Section 152 increases potential penalties to life imprisonment or up to seven years, along with mandatory fines, making it more severe.
- Intent Requirement:
- Section 124A requires proof of intent to incite disaffection.
- Section 152 lowers this requirement, allowing prosecution if a person “knowingly” shares information that could incite rebellion or separatism, even without malicious intent.
Impact on Freedom of Speech and Legitimate Dissent
- Chilling Effect: The ambiguous nature of what constitutes an act endangering sovereignty can deter individuals from expressing dissenting opinions due to fear of legal repercussions.
- Potential for Abuse: The broad and vague language in Section 152 enables authorities to interpret it expansively, potentially criminalizing legitimate dissent under the pretext of national security.
- Judicial Oversight: The High Court stressed that Section 152 should protect national security without suppressing legitimate criticism, calling for careful application and judicial oversight.
Legal and Constitutional Implications
- Constitutional Rights: Enforcing Section 152 raises concerns about violating Articles 14 (Right to Equality) and 19 (Freedom of Speech) of the Indian Constitution, as vague definitions may lead to arbitrary enforcement.
- Judicial Precedents: The judiciary has historically supported a consequentialist approach regarding free speech, insisting on a direct causal link between speech and its impact for it to be considered an offence.
- Need for Guidelines: There is a pressing need for the Supreme Court to establish clear guidelines for applying Section 152, akin to those formed in previous cases, to delineate acceptable boundaries for criticism while safeguarding civil liberties.
The Supreme Court's intervention is crucial to ensure a balance between national security and the fundamental right to freedom of speech, thereby preventing the misuse of Section 152 against legitimate dissent.
GS2/Polity
Is India Open to the Idea of Dual Citizenship?
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Recently, External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlighted the complexities surrounding the concept of dual citizenship for Indians abroad. He indicated that while challenges exist, the Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) program is a step towards addressing the needs of the Indian diaspora, and discussions about dual citizenship are ongoing.
- The Indian Constitution currently prohibits dual citizenship.
- Arguments exist both for and against the concept of dual citizenship in India.
- India's stance on dual citizenship contrasts sharply with many other democracies.
- The OCI program offers limited rights to certain individuals of Indian origin.
Arguments Against Dual Citizenship
- Divided Loyalties: Critics believe that dual citizenship may lead to divided loyalties, potentially compromising national integrity. This could create conflicts of allegiance between India and another nation, which poses risks to India's sovereignty.
- Legal Restrictions: The Indian Constitution stipulates that acquiring citizenship in another country results in the automatic loss of Indian citizenship, complicating the pursuit of dual citizenship.
- Historical Context: The Citizenship Amendment Act of 2019 demonstrates a cautious stance toward citizenship rights, emphasizing loyalty to India and limiting citizenship to those who renounce foreign nationality.
Arguments For Dual Citizenship
- Global Integration: Supporters argue that allowing dual citizenship could enhance connections between India and its diaspora, promoting economic and cultural exchanges in a globalized context.
- Economic Contributions: Dual citizenship is viewed as a potential means to attract foreign investments and encourage Indian expatriates to contribute to India's economy without the fear of losing their original nationality.
India’s Position on Dual Citizenship
- According to Article 9 of the Indian Constitution, any Indian citizen who voluntarily acquires the citizenship of another country ceases to be an Indian citizen. This is further reinforced by the Citizenship Act of 1955, which asserts that Indian citizenship is singular and does not recognize dual nationality.
Comparison with Other Democracies
- United States: The U.S. allows dual citizenship without restrictions, reflecting a permissive attitude towards multiple nationalities.
- Canada: Canada recognizes dual citizenship, promoting a diverse, multicultural society.
- Australia: Similar to Canada, Australia permits dual nationality and provides full consular support regardless of other nationalities.
- Germany: Germany has specific regulations that generally require individuals to choose one nationality unless they meet certain conditions, indicating a nuanced approach compared to India's outright prohibition.
Current Legal Frameworks
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI): Established in 2005, the OCI allows individuals of Indian origin from certain countries to reside in India without a visa. Although it grants some rights similar to Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), OCIs do not possess voting rights or the ability to hold constitutional offices.
- Eligibility: The OCI scheme primarily caters to individuals who were Indian citizens or eligible for Indian citizenship at the Constitution's commencement, excluding those from Pakistan and Bangladesh. It is dependent on the individual's home country permitting some form of dual citizenship.
Challenges
- Political Loyalty Concerns: There is widespread apprehension that dual citizenship could lead to divided loyalties, particularly concerning political rights.
- Public Sentiment and Political Will: Significant public opposition exists against dual citizenship due to fears regarding national security and sovereignty.
- Complexity of Implementation: Implementing a dual citizenship framework would necessitate extensive legal reforms, complicating India’s existing immigration and nationality legislation. The challenge lies in harmonizing the diaspora's interests with the need for a unified national identity.
Way Forward
- Gradual Legal Reforms: India could adopt a phased approach to dual citizenship, initially permitting it for specific categories such as diaspora members with strong economic or cultural ties to India, while ensuring political rights remain exclusive to Indian citizens.
- Enhanced OCI Benefits: Expanding the rights of OCI holders could be considered, granting them additional privileges like voting rights or eligibility for certain offices without conferring full dual citizenship.
The debate surrounding dual citizenship in India remains complex, involving considerations of national integrity, legal constraints, and the potential benefits of a more connected global Indian community.
GS2/Governance
The Dam Safety Act of 2021
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Supreme Court has criticized the Union government for its inaction in fully implementing the Dam Safety Act, nearly five years after its enactment.
- The Dam Safety Act aims to ensure the structural and operational safety of over 5,700 large dams in India.
- Establishes a framework for monitoring, maintenance, and emergency preparedness for dams.
Additional Details
- Objectives: The Act's key objectives include:
- Preventing dam-related disasters by ensuring dam safety.
- Establishing institutions for monitoring and emergency preparedness.
- National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS): Chaired by the Chairperson of the Central Water Commission (CWC), it develops policies, guidelines, and standards related to dam safety.
- National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA): Responsible for implementing NCDS guidelines and regulating dam safety standards.
- State Committees on Dam Safety (SCDS): Provide oversight at the state level and report to the NDSA.
- Responsibilities of Dam Owners: They must form Dam Safety Units, implement Emergency Action Plans (EAPs), and conduct Comprehensive Safety Evaluations (CSEs).
- Emergency Preparedness: Mandatory EAPs are required for rapid response in emergencies.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Violations can result in imprisonment up to two years, fines, or both.
Why is Dam Safety a Priority Concern in India?
- Third-Highest Number of Dams Globally: India has over 4,407 large dams, ranking after China and the USA.
- Aging Dams: By 2025, over 1,115 dams will be more than 50 years old, and by 2050, 4,250 dams will exceed this age.
- Decreasing Storage Capacity: Sedimentation significantly reduces reservoir efficiency, impacting water availability for irrigation and hydropower.
- Structural Vulnerabilities: Poor sedimentation management and extreme environmental events increase structural weaknesses in dams.
- Lack of Data and Monitoring: Insufficient documentation hampers preparedness for dam safety issues.
Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
- [2018] Suppose the Government of India is thinking of constructing a dam in a mountain valley bound by forests and inhabited by ethnic communities. What rational policy should be resorted to in dealing with unforeseen contingencies?
- [2019]What is common to the places known as Aliyar, Isapur, and Kangsabati?
- (a) Recently discovered uranium deposits
- (b) Tropical rain forests
- (c) Underground cave systems
- (d) Water reservoirs
The Dam Safety Act of 2021 is a crucial legislative measure aimed at enhancing the safety and reliability of India's extensive dam infrastructure, addressing both current challenges and future risks linked to dam management.
GS3/Environment
Tirupati Stampede: Causes and Mitigation Strategies
Source: The Hindu
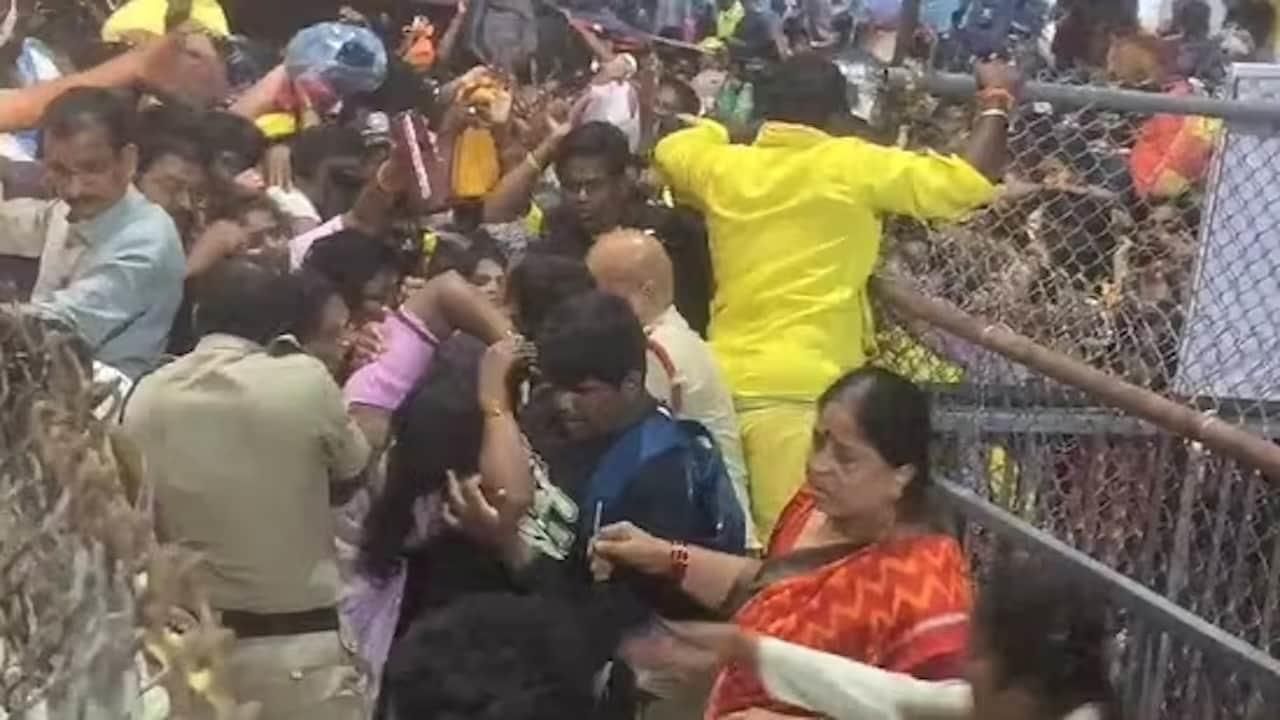 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, a tragic incident occurred in Tirupati where six individuals lost their lives in a stampede while waiting to collect tokens for a darshan of Lord Venkateswara. This incident highlights the critical issues surrounding crowd management and safety during large gatherings.
- Stampedes are chaotic movements of crowds, often triggered by panic.
- Inadequate crowd management can exacerbate dangerous situations.
- Human psychology plays a significant role in the dynamics of crowd behavior.
- Physical organization of spaces contributes to the risk of stampedes.
- Effective strategies can mitigate the risks associated with large crowds.
Additional Details
- Causes of Stampedes: Stampedes often occur in venues exceeding their safe capacity, creating dangerously crowded conditions. Inadequate planning and poor crowd control measures can lead to confusion and panic.
- Panic Response: Panic can spread rapidly in crowds, with individuals acting irrationally, leading to a domino effect of pushing and shoving.
- Physical Organization Issues: Narrow exits and blocked pathways create bottlenecks, making evacuation difficult. Poorly designed crowd flow can exacerbate congestion, while inadequate lighting can hinder visibility and increase panic.
- Prevention Strategies: Effective crowd management includes limiting crowd size, improving infrastructure, and utilizing technology for real-time monitoring. Educating attendees on safety protocols is also crucial.
In summary, understanding the dynamics behind stampedes and implementing effective crowd management strategies is essential to prevent future tragedies. By addressing both psychological and physical factors, we can create safer environments for large gatherings.
GS3/Economy
World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report, 2025
Source: India Today
Why in News?
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released its Future of Jobs Report for 2025, highlighting the impact of global macro trends such as technological advancements, demographic changes, and the green transition. The report predicts that these factors will lead to the creation of approximately 170 million new jobs by 2030.
- The report is based on insights from over 1,000 leading global companies, representing 14 million workers across 22 industry sectors and 55 economies.
- It identifies emerging and declining job roles, trends in required skills, and the overall effects of global changes on the labor market.
Additional Details
- Job Projections: By 2030, a net increase of 78 million jobs is anticipated, even after accounting for 92 million displaced roles.
- Fast-Growing Roles: Key roles expected to grow include AI and machine learning specialists, big data experts, FinTech engineers, and farmworkers.
- Declining Roles: Clerical jobs such as data entry clerks and cashiers are projected to decline due to automation.
- Employers predict that 39% of skills will change by 2030, with a rising demand for AI proficiency, creative thinking, and resilience.
- To address the skills gap, 85% of businesses are investing in reskilling and upskilling programs.
- Collaboration among governments, academia, and industries is essential to align educational outcomes with future job demands.
The Future of Jobs Report serves as a crucial resource for understanding the evolving job landscape and highlights the importance of adapting to technological and economic changes to meet future labor market needs.
GS3/Science and Technology
PM Unveils Genome Data of 10K Indians
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced the successful completion of the Genome India Project, highlighting its significance as a major milestone in India's biotechnology advancements. During a video message at the Genomics Data Conclave organized by the Department of Biotechnology, he revealed the sequencing database comprising genetic information from 10,000 Indians. This sequencing data will now be made available to researchers via the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC).
- The Genome India Project aims to create a comprehensive catalogue of genetic variations within the Indian population.
- 10,000 genomes from diverse regions of India have been sequenced, producing a substantial database for research.
- Access to genetic data is regulated to ensure privacy and security for the individuals involved.
Additional Details
- Genome Sequencing: This process involves determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome. It is essential for understanding genetic makeup and differences among individuals.
- Human Genome Project (HGP): Initiated in 1990, the HGP aimed to sequence the entire human genome, completing it in 2023 with a minimal error rate, enabling insights into genetic predispositions to diseases.
- Genome India Project: Launched in 2020, this project focuses on sequencing genomes from over 10,000 individuals across various Indian populations to identify unique genetic variants and enhance personalized medicine.
- Significance of Genetic Research: By studying India's genetic diversity, researchers can uncover genetic risk factors for diseases prevalent in the country, such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Future of Personalized Medicine: The initiative will potentially facilitate the development of targeted therapies and improve drug efficacy based on the genetic profiles of the Indian population.
The Genome India Project's extensive sequencing work not only enriches the scientific community's understanding of genetic diversity but also promises advancements in healthcare tailored to India's unique genetic landscape. This project marks a significant step toward enhancing the biotechnology and biopharma sectors in India.
GS3/Environment
Miyawaki Technique
Source: PIB
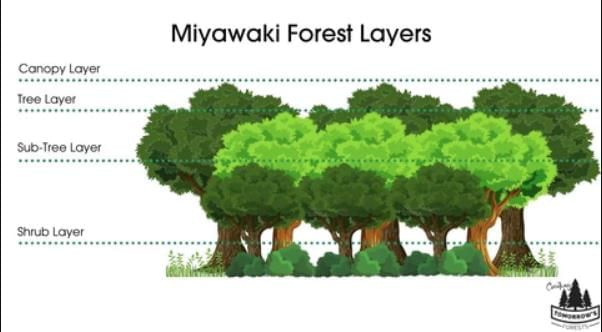 Why in News?
Why in News?In preparation for the Mahakumbh Mela in Uttar Pradesh, the Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has implemented the Japanese Miyawaki technique to establish dense “oxygen bank” forests. This initiative aims to ensure cleaner air and promote ecological balance for the millions of devotees attending the event.
- The Miyawaki technique is a method designed for creating dense forests in limited spaces.
- Developed by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki in the 1970s, it mimics natural forest ecosystems.
- This technique supports urban afforestation projects worldwide.
Additional Details
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted closely together, allowing rapid growth—up to ten times faster than traditional methods.
- Native Species: The technique emphasizes the use of local plant varieties, which helps in replicating the natural ecosystem.
- Improved Biodiversity: By enhancing species richness, the Miyawaki technique supports a greater variety of flora and fauna.
- Carbon Absorption: The closely planted trees are more effective at absorbing carbon, contributing to the reduction of urban pollution.
The Miyawaki technique is increasingly recognized for its efficiency and effectiveness in restoring degraded ecosystems and barren lands, thereby promoting environmental sustainability and urban green spaces.
Previous Year Question (PYQ):
- The “Miyawaki method” is well known for the:
- (a) Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
- (b) Development of gardens using genetically modified flora
- (c) Creation of mini forests in urban areas
- (d) Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces
GS1/History & Culture
Centre Grants Classical Language Status to Marathi
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, the Union Government formalized the grant of classical language status to Marathi, following months of deliberation after the initial conferral.
- The official notification recognizes Marathi as a classical language.
- This status promotes the preservation of Marathi's rich historical and cultural significance.
Criteria for Declaring a Classical Language
- 2004 (Tamil Declaration): A language must have high antiquity of over 1,000 years, a significant body of ancient literature, and an original literary tradition.
- 2005 (Sanskrit Declaration): A language should have a history of 1,500 to 2,000 years, with a substantial body of literature that is original and distinct from other linguistic influences.
- 2024 (Updated Criteria): Literature must include knowledge texts, prose, inscriptions, and demonstrate distinctiveness from modern forms.
List of Recognized Classical Languages
- Tamil (2004)
- Sanskrit (2005)
- Telugu (2008)
- Kannada (2008)
- Malayalam (2013)
- Odia (2014)
- Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali (2024)
- Marathi (2024)
Significance of Classical Language Status
- Preserves the historical roots and unifies cultural heritage.
- Promotes academic research, translation, and creates scholarly employment opportunities.
- Enhances global awareness and usage in technology and academia.
- Ensures government support and funding for preservation and institutional development.
Historical Significance of Marathi Language
- Marathi's history spans over 2,000 years, meeting the antiquity criterion.
- Early mentions of Marathi include forms like Maharashtri Prakrit and Jain Maharashtri.
- Over 100 stone inscriptions, notably in the Naneghat Caves (20 BCE), feature Marathi commands alongside Sanskrit.
- Significant literary works from the Yadava period (12th-13th century AD) include:
- Leelacharitra: A biography of Chakradhar Swami.
- Dnyaneshwari: A commentary on the Bhagavad Gita by Sant Dnyaneshwar.
- The Pathare Committee (2013) and a postcard campaign with 500,000 letters to the Prime Minister supported the recognition of Marathi.
- The Dnyaneshwar Mulay Committee addressed administrative hurdles to finalize the proposal in February 2024.
Previous Year Question (PYQ)
[2015] Which one of the following was given classical language status recently?
- (a) Odia
- (b) Konkani
- (c) Bhojpuri
- (d) Assamese
This recognition of Marathi as a classical language underscores its historical and cultural significance, ensuring its preservation for future generations while fostering academic and cultural advancements.
GS3/Economy
Government Revises Gold Import Data Amid Discrepancies in Trade Figures
Source: Business Standard
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has recently revised the gold import figures for November 2024, reducing the reported value by $5 billion. This correction has important implications for India’s trade deficit and raises concerns regarding the accuracy of trade statistics.
- The reported gold imports for November were corrected from $14.8 billion to $9.9 billion.
- The trade deficit for November decreased from $38 billion to $33 billion.
Additional Details
- Error in Gold Import Reporting: The overestimation resulted from a data migration issue between SEZ Online and the Indian Customs Electronic Gateway (ICEGATE), leading to double counting of imports into Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
- Technical Transition and Challenges: The migration to ICEGATE aimed to streamline EXIM declarations, but discrepancies arose as both systems initially transmitted data separately, resulting in ongoing technical issues.
- Broader Implications: Frequent revisions have raised concerns about the credibility of economic statistics, creating uncertainty for investors and policymakers.
- Gold Import Trends: India, being the second-largest gold consumer globally, relies significantly on imports, especially during festive seasons.
- Market Stability: The revised data alleviated concerns regarding potential increases in import duties, with no unusual surge in demand observed post-revision.
The revision of gold import data underscores the necessity for robust data management systems and transparency in reporting. Ensuring accurate trade statistics is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and economic stability. Proactive measures are essential to address potential discrepancies and enhance the reliability of official statistics.
|
49 videos|5376 docs|1137 tests
|
















