UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Understanding India's Natural Catastrophe Risks and Economic Impacts
Source: Nature
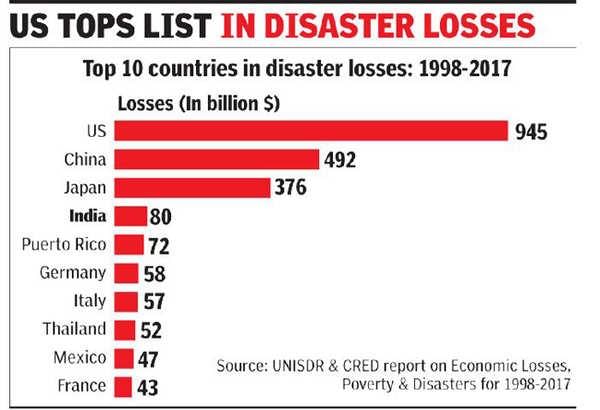 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has been facing a significant rise in economic losses due to natural disasters, exacerbated by the increasing frequency of extreme weather events. In 2023, it is reported that natural disasters led to an estimated $12 billion in economic losses, surpassing the previous decade's annual average of $8 billion, as highlighted in a report by the global insurance company Swiss Re.
- 2023 witnessed major natural disasters, including floods and cyclones, resulting in substantial economic damage.
- India's vulnerability to natural catastrophes is heightened by its geographical and climatic conditions.
- Underinsurance remains a critical issue, with 90% of households and businesses inadequately covered against losses.
- Strategic measures are essential for improving disaster preparedness and resilience in high-risk areas.
Additional Details
- Key Events in 2023:
- Floods in Northern India and Sikkim (July 2023): Heavy rains caused significant damage in Himachal Pradesh and Delhi, disrupting daily life.
- Tropical Cyclone Biparjoy (June 2023): A Category 3 cyclone impacted Kutch, Gujarat, leading to the shutdown of major ports and extensive damage.
- Tropical Cyclone Michaung (December 2023): This cyclone hit Chennai, Tamil Nadu, bringing extreme rainfall and urban disruptions.
- Monsoon-Driven Floods: Over the last two decades, floods have accounted for an average of 63% of India’s annual economic losses, primarily during the Summer and Northeast Monsoons.
- Economic and Industrial Exposure: States like Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu, which contribute significantly to India's industrial output, are particularly vulnerable to floods and cyclones.
- Earthquake Risks: Urban areas such as Ahmedabad face significant earthquake hazards, with the potential for catastrophic losses reminiscent of the 2001 Bhuj earthquake.
- Challenges in Resilience and Insurance: Despite significant economic losses, 90% of households and businesses remain under- or uninsured, creating substantial protection gaps.
In conclusion, while India's economic growth continues at a rapid pace, it is crucial to address the vulnerabilities associated with natural disasters. The increasing frequency of extreme weather events necessitates robust disaster preparedness strategies, improved insurance penetration, and proactive resilience-building measures. By tackling these challenges effectively, India can better protect its economy and citizens from the escalating risks posed by natural disasters.
GS2/International Relations
Delhi Must Look Beyond H-1B
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The potential return of Donald Trump to the White House has initiated significant discussions in India, primarily focused on the implications of the H-1B visa program. While the export of Indian technical talent to the United States is a critical issue, it is essential to explore the broader effects of Trump's technology policies on the global landscape and geopolitical dynamics involving India, China, and the U.S.
- The H-1B visa program is crucial for India-U.S. relations, enabling skilled Indian professionals to contribute to American innovation.
- Economic concerns surrounding immigration play a significant role in the H-1B debate, highlighting the need for balance between benefits and domestic sentiments.
- India must enhance diplomatic engagement and technological collaboration with the U.S. while addressing concerns over illegal immigration.
Additional Details
- H-1B Visa Program: This program allows highly skilled workers from India to fill gaps in the U.S. labor market, particularly in technology, thus benefiting both economies.
- Economic Imperatives: Technology companies advocate for the expansion of H-1B visas to address labor shortages and maintain America's competitive edge.
- Political Polarization: The debate around immigration, including H-1B, reflects larger societal divisions in the U.S., complicating the immigration landscape.
- India's Role: India's growing tech ecosystem positions it as a vital player in the global labor market, necessitating a proactive approach to U.S. policies.
- Strategic Collaboration: Engaging in areas like defense technology and AI research can solidify India's role as a key partner to the U.S.
In conclusion, while the H-1B visa issue is significant, India must adopt a broader viewpoint by recognizing the transformative potential of U.S. technology policies under Trump. By aligning its strategic priorities with U.S. interests, India can ensure its relevance in the evolving global order.
GS3/Environment
Understanding the Sada Region
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The land-use patterns in the Sada region are undergoing significant changes, with increasing conversion of croplands to orchards and residential areas. This transformation highlights the need to understand the ecological and geographical significance of the Sada terrain.
- The term sada refers to a large, flat area formed by centuries of erosion.
- Located in the Konkan region of Maharashtra, the Sada exhibits distinctive geological features.
- It is characterized by barren landscapes that transform during the monsoon season.
Additional Details
- Geographical Characteristics: The Sada is similar to the plateaus, known locally as pathar, found in the Satara district of Maharashtra, with the Kaas Plateau being a prominent example.
- The landscape is predominantly rocky and showcases unique endemic flora during the monsoon period.
- It consists of a highly weathered lateritic soil layer that serves as a crucial catchment for rainwater, effectively recharging the groundwater supply.
Biodiversity
- The Sada region is home to a remarkable diversity of life, including:
- 459 plant species, with 105 endemic to the Konkan region.
- 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- The area also features ancient works of art known as geoglyphs, dating back approximately 10,000 years.
In conclusion, the evolving land-use patterns in the Sada region present both challenges and opportunities for conservation and sustainable development, emphasizing the need for awareness and action in preserving this unique ecological landscape.
GS3/Environment
Pavana River: Rejuvenation Efforts
Source: Hindustan Times
Why in News?
The National Green Tribunal has recently instructed the state-appointed rejuvenation committee to gather stakeholders in order to establish a new timeline for the action plan aimed at reducing pollution in the Pavana River.
- The Pavana River is located in the western region of Maharashtra, specifically in the Pune District.
- This river plays a significant role in traversing Pune city and separates Pune from the Pimpri-Chinchwad area.
Additional Details
- Source of the River: The Pavana River originates from the Western Ghats, about 6 km south of Lonavala.
- The river flows initially eastward before shifting to a southward direction, passing through the suburbs of Dehu, Chinchwad, Pimpri, and Dapodi.
- It merges with the Mula River near Pune, which subsequently combines with the Mutha River, forming the Mula-Mutha River system, eventually draining into the Bhima River, the largest tributary of the Krishna River.
- Total Length: The Pavana River stretches approximately 60 km.
- A significant structure on this river is the Pavana Nagar Dam, an earthfill gravity dam measuring 1,329 m (4,360 ft) in length and 42.37 m (139.0 ft) in height, with a gross storage capacity of 30,500.00 km3.
- The dam is constructed to provide adequate water supply to nearby localities and is essential for drinking water provision in Pune and Pimpri-Chinchwad.
The ongoing efforts to rejuvenate the Pavana River are crucial for environmental conservation and public health in the region.
GS3/Science and Technology
Purulia Observatory
Source: The Tribune
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A new astronomical observatory has been established by the S N Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS) in the Purulia district of West Bengal. This facility aims to enhance scientific observations and training in the field of astrophysics.
- Location: Panchet Hill, Purulia District, West Bengal.
- Equipped with a 14-inch diameter telescope for scientific observations.
- Altitude: Approximately 600 meters above sea level.
- Longitude: Approximately 86° E.
- Significant addition to observatories along the 86° East longitude.
Additional Details
- Astronomical Significance: The observatory will facilitate the study of various astronomical objects, contributing to global astrophysics research.
- Training Opportunities: It will provide training for students in telescope handling and data recording, fostering the next generation of astronomers.
- Comparison: Other notable observatories in India include ARIES Observatory in Nainital, Vainu Bappu Observatory in Kavalur, and the Indian Astronomical Observatory in Hanle, Ladakh.
This observatory is poised to become a major scientific hub, not just in eastern India but also on a global scale, addressing a significant gap in astronomical research facilities along its longitude.
GS2/International Relations
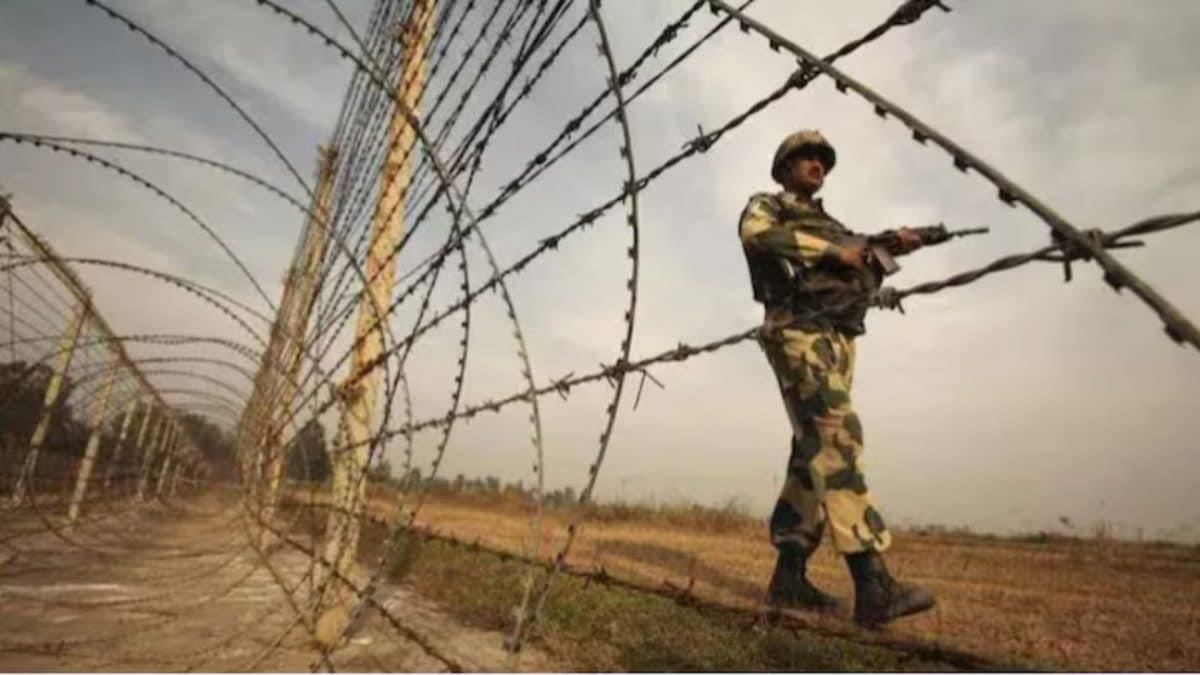
Border Fencing Row with Bangladesh
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has summoned Bangladesh's Acting High Commissioner regarding issues related to border security and fencing after Bangladesh raised concerns about alleged violations by the Border Security Force (BSF). This diplomatic tension escalated following an earlier summoning of India’s High Commissioner in Dhaka, Pranay Verma, by Bangladesh, which claimed that BSF's actions were in breach of a bilateral agreement. The situation worsened when the Border Guards Bangladesh (BGB) attempted to obstruct the ongoing construction of fencing along the West Bengal-Malda border.
- The India-Bangladesh border is the longest border of India, measuring 4096.7 km.
- Significant portions of the border remain unfenced due to various challenges, including local objections and difficult terrain.
- Recent incidents have heightened tensions, particularly in Malda's Kaliachak and Cooch Behar areas.
Additional Details
- Border Length: The India-Bangladesh border stretches 4096.7 km, traversing states such as West Bengal (2216.7 km), Assam (263 km), Meghalaya (443 km), Tripura (856 km), and Mizoram (318 km).
- Fencing Coverage: Currently, 3,141 km of the border have been fenced, with 81.5% of the West Bengal-Bangladesh border secured. Remaining sections are unfenced due to local objections and ongoing negotiations with Bangladesh.
- Challenges: The Ministry of Home Affairs identifies several challenges, including non-cooperation from the West Bengal government, pending land acquisition, and the inherent difficulties posed by the riverine sections of the border, which comprise over 900 km.
- 1975 Border Guidelines: According to the 1975 Joint India-Bangladesh Guidelines, the construction of defense structures within 150 yards of the international boundary is prohibited, although India does not categorize wire fencing as such.
- Recent incidents, such as the fencing dispute in Mekhliganj, highlight the ongoing complexities of border management and local villagers' involvement.
The ongoing border fencing dispute between India and Bangladesh raises significant diplomatic and logistical challenges. Despite India's emphasis on border security and management, the concerns of local residents and bilateral agreements complicate the situation. Continued dialogue and negotiation are essential to finding a resolution that respects both countries' interests and addresses the needs of residents living along the border.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Zombie Deer Disease?
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Scientists are raising alarms about the potential for the fatal and untreatable 'zombie deer' disease to affect humans.
- Zombie Deer Disease, scientifically known as Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), is a severe neurological disorder.
- CWD primarily impacts deer, elk, moose, and reindeer and is caused by infectious proteins known as prions.
Additional Details
- Cause of CWD: This disease is triggered by prions, which are misfolded proteins that induce other proteins in the brain to misfold as well. This process leads to significant brain damage and the formation of spongy holes in brain tissue.
- Transmission: CWD prions are highly contagious and can spread through body fluids such as saliva, feces, blood, or urine. They can be transmitted through direct contact or environmental contamination. Once in an area, prions can remain infectious in soil, water, and vegetation for years, posing long-term threats to wildlife.
- Symptoms:The incubation period for CWD is notably long, averaging 18 to 24 months, during which infected animals may appear normal. Key symptoms include:
- Progressive weight loss
- Behavioral changes, such as decreased social interaction and loss of awareness
- Increased drinking, urination, and excessive salivation
- Treatment: Currently, CWD is always fatal for infected animals, and there is no known vaccine or treatment available.
- Can Humans Get CWD?: Although there have been no confirmed cases of CWD transmission to humans, scientists remain vigilant and cautious regarding its potential to evolve and cause human infection.
As research continues, understanding CWD is critical to monitoring its impact on wildlife and potential risks to human health.
GS3/Defence & Security
What is Bhargavastra?
Source: Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has successfully tested the Bhargavastra, marking its entry into the realm of advanced defense technologies with the country's first micro-missile system specifically designed to counter the emerging threat posed by swarm drones.
- Bhargavastra is India's first indigenous micro-missile system.
- Developed by Economic Explosives Ltd., it can effectively counter swarm drones.
- Capable of hitting targets over 2.5 km and detecting incoming threats at over 6 km.
Additional Details
- Micro-Missile System: The Bhargavastra can quickly deploy on mobile platforms and is designed to simultaneously fire more than 64 micro missiles, making it highly effective against multiple threats.
- Operational Capability: This system is engineered to operate in all terrains, including high-altitude areas, thus meeting the specific requirements of the armed forces.
- Counter-Drone Technology: As the first counter-drone system utilizing micro missiles, it heralds a significant advancement in aerial defense mechanisms.
The Bhargavastra represents a strategic enhancement in India's defense capabilities against swarm drone technologies, providing the armed forces with a robust tool to neutralize multiple aerial threats effectively.
GS3/Science and Technology
India Meteorological Department's (IMD) 150th Anniversary
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has emphasized India's significant progress in meteorology, highlighting its crucial contributions to disaster management, economic resilience, and international cooperation. The recent event celebrating the 150th anniversary of the India Meteorological Department (IMD), established in 1875, also presented ambitious plans for its future development.
- The IMD was founded to address the need for centralized meteorological services following catastrophic weather events.
- Significant achievements in meteorological technology and forecasting have been recognized during the anniversary celebration.
- Future objectives include improving forecasting accuracy and developing innovative weather management systems.
Additional Details
- Origin and Significance: The IMD was established in 1875 after devastating events like the tropical cyclone of 1864, highlighting the urgent need for organized meteorological services. It operates under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India.
- Commemorative Releases: The anniversary included the launch of the Vision Document 2047, which outlines a roadmap for IMD's future advancements.
- Technological Advancements: The IMD has pioneered indigenous technologies such as the RADAR system since 1958 and has collaborated with ISRO for satellite development since 1983.
- Mission Mausam: A recent initiative aimed at enhancing weather surveillance through advanced high-resolution observations and next-generation technology.
- International Collaboration: The IMD has been recognized for its long-standing representation at the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and its support to neighboring countries with critical weather forecasts.
In conclusion, PM Modi reiterated the vital role of meteorological advancements in protecting lives and fostering global collaboration. With the ambitious Vision Document 2047 and the launch of Mission Mausam, the IMD aims to shift from traditional weather forecasting to comprehensive weather management, aspiring to establish India as a "weather-ready nation" by 2047.
GS3/Environment
Falcated Duck Sightings in India
Source: DTE
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, birdwatchers at the Sultanpur National Park in Gurugram, Haryana, were thrilled to observe the rare Falcated Duck, a species not commonly seen in India.The Falcated Duck, also known as falcated teal (Mareca falcata), is a dabbling duck similar in size to a gadwall.
- This species inhabits regions from eastern Siberia and Mongolia to northern Japan, migrating to wintering grounds in southeast Asia and eastern India.
Additional Details
- Habitat: Falcated Ducks are typically found in freshwater lakes, ponds, rivers, and marshes surrounded by forested areas.
- Breeding Season: Their breeding occurs from May to early July, with nests built on the ground near water, often in tall grass or brush.
- Diet: Primarily herbivorous, their diet consists of vegetable matter, seeds, rice, and aquatic plants, though they occasionally consume small invertebrates and soft-shelled mollusks.
- Conservation Status: According to the IUCN, the Falcated Duck is classified as Near Threatened, primarily due to hunting for food and feathers.
- Sightings of the Falcated Duck in India are considered rare, making their recent observation noteworthy.
The presence of the Falcated Duck at Sultanpur National Park highlights the importance of conservation efforts and the need for continued protection of migratory bird habitats.
GS3/Environment
Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary
Source: The Tribune
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Government of India has designated certain areas surrounding the Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary as eco-sensitive zones (ESZs) to mitigate the impacts of urbanization and developmental activities on the surrounding protected areas.
- Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh.
- The sanctuary covers a middle altitudinal range from 1,800 to 3,400 meters, featuring diverse ecosystems.
- It was established in 1962 and is named after the goddess Shikari Devi, with a sacred temple situated at an elevation of 2,850 meters.
Additional Details
- Flora:The sanctuary boasts a rich variety of flora due to its altitudinal variation, encompassing seven different forest types as classified by Champion and Seth (1968), including:
- Alpine Pasture
- Sub-alpine Forest
- Moist Temperate Deciduous Forest
- West Himalayan Upper Oak/Fir Forest
- Kharsu Oak Forest
- Western Mixed Coniferous Forest
- Ban Oak Forest
- Fauna:The sanctuary is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including:
- Goral
- Monal
- Black Bear
- Barking Deer
- Musk Deer
- Cat Leopard
- Himalayan Black Bear
- Himalayan Palm Civet
- Marten
- Indian Porcupine
- Kashmiri Flying Squirrel
- Common Langur
- Leopard
- Common Squirrel
- Snow Leopard
The sanctuary not only plays a critical role in biodiversity conservation but also maintains ecological balance in the region, making it a vital area for both wildlife and the local community.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th January 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the major natural catastrophe risks faced by India? |  |
| 2. How do natural disasters impact India's economy? |  |
| 3. What measures can be taken to mitigate natural catastrophe risks in India? |  |
| 4. What role does the India Meteorological Department (IMD) play in disaster management? |  |
| 5. How has climate change influenced natural disaster patterns in India? |  |
















