UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 26th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Rakhigarhi |

|
| Shompens |

|
| Doctrine of Merger |

|
| Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary |

|
| Pangsau Pass |

|
| NVS-02 Satellite |

|
| SANJAY Surveillance System |

|
| Use of loudspeakers not essential part of religion |

|
GS1/History and Culture
Rakhigarhi
Source: The Print
Why in News?
A recently uncovered reservoir in Haryana's Rakhigarhi showcases the advanced engineering of the Harappan civilization and contributes to the ongoing research about the ancient Saraswati River.
About Rakhigarhi
- Rakhigarhi is an archaeological site situated in the Hisar district of Haryana, within the Ghaggar-Hakra river plain.
- It is among the oldest and largest cities of India's earliest known Bronze Age urban culture, the Indus Valley or Harappan Civilization.
- Rakhigarhi is the largest site of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The site was initially discovered in the 1960s by the Archaeological Survey of India.
Findings
- Recent explorations around Rakhigarhi have identified seven archaeological mounds spread over approximately 350 hectares.
- These findings indicate occupation during the Early and Mature Harappan periods, with the site being abandoned during the Late Harappan period.
- Excavations have revealed evidence of a planned township from the mature Harappan phase, featuring mud-brick and burnt-brick houses with an advanced drainage system.
- The ceramic industry at the site is represented by various red ware items, including dishes, vases, jars, bowls, beakers, perforated jars, goblets, and handis.
- Ritual practices of the Harappans are indicated by the discovery of animal sacrificial pits, triangular and circular fire altars, and a cylindrical seal with Harappan characters and an alligator symbol.
- Other significant finds include blades, terracotta and shell bangles, semi-precious stone beads, shell and copper objects, animal figurines, a toy cart frame and wheel, bone points, and inscribed steatite seals and sealings.
- The excavations have also uncovered extended burials, likely from a later period, possibly medieval times.
- Rakhigarhi is notably recognized for providing the only DNA evidence from the Harappan era.
GS1/ Geography
Shompens
Source:The Hindu
Why in News?
Recently, the director of the Andaman and Nicobar Tribal Research Institute (ANTRI) emphasized the findings of his report on the Shompens, a major aboriginal group living in the interior forests and coastal regions of the Great Nicobar Islands (GNI).
About Shompens
- Primitive and Isolated: The Shompens are among the most primitive tribes in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and are also one of the most isolated tribes on Earth.
- Vulnerable Tribal Group: They are one of the least studied groups classified as Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India.
- Habitat: The Shompens live in the dense tropical rainforests of Great Nicobar Island, where around 95% of the island is covered in rainforest.
- Ethnic Background: Unlike other primitive tribes in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Shompens are of Mongoloid stock rather than Negrito. Their physical features, such as light yellow-brown skin, straight hair, narrow eyes, and stocky build, resemble those of people from Myanmar and Indonesia.
- Biological Hotspot: Their habitat is also an important biological hotspot, featuring two National Parks—Campbell Bay and Galathea—and one Biosphere Reserve, the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve.
- Population: The exact population of the Shompens is unknown, although the 2011 Census estimated it at 229. Most Shompens live deep in the forest with little or no contact with outsiders.
- Lifestyle: The Shompens are hunter-gatherers who live in small, nomadic groups. Their territories are identified by the rivers that flow through the rainforest. They typically set up forest camps where they live for a few weeks or months before moving to a new location.
- Diet: They collect a wide variety of rainforest plants, but their staple food is the pandanus fruit, known locally as larop. They also cultivate small gardens growing plants such as lemon, chillies, and betel.
- Language: The Shompens speak their own language, which has various dialects. Members of one group may not understand the dialect of another group.
- Family Structure: Shompen families are typically nuclear, consisting of a husband, wife, and their unmarried children. The eldest male member of the family controls all activities of the women and children. Monogamy is the general practice, but polygamy is also accepted.
- Beliefs: The Shompens worship the moon, known as Houou, as their goddess. They believe that she created the universe.
GS2/Polity and Governance
Doctrine of Merger
Source:Live Law

Why is it News?
- The Supreme Court clarified the concept of the Doctrine of Merger in the context of legal decrees and orders.
- The Court emphasized that there can only be one decree or operative order governing a specific subject matter at any given time.
- This explanation was given while discussing the merger of a trial court's decree with that of a High Court's decree in second appeals.
Understanding the Doctrine of Merger
- The Doctrine of Merger is a principle in common law aimed at maintaining the decorum and hierarchy of courts and tribunals.
- When an appellate court (a higher court) issues an order, the order from the lower court merges with the appellate order.
- The rationale behind this doctrine is to ensure that there is not more than one decree or operative order governing the same subject matter simultaneously.
- This doctrine addresses the issue of which order should be enforced and given precedence when multiple orders exist from subordinate and superior courts on the same issue.
- Although not recognized statutorily, the Doctrine of Merger reflects judicial propriety and aims to instill discipline in the functioning of subordinate adjudicating authorities, whether they are judicial, quasi-judicial, or administrative.
- The application of this doctrine is not universal or unlimited; it depends on the nature of the jurisdiction exercised by the superior forum and the content or subject matter of the challenge.
GS 3/Environment
Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
Source:Times of India

Why in News?
The Forest Department is taking steps to revise the boundaries of the Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary in order to address and resolve existing legal issues.
Overview of Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Aravalli hills, approximately 20 kilometers from Jaipur, Rajasthan.
- Historical Significance: The sanctuary is named after Nahargarh Fort, a historic fort built in the 18th century by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II, who also founded the city of Jaipur.
- Area: The sanctuary covers an area of 720 hectares.
- Nahargarh Biological Park: This park, which is part of the Nahargarh sanctuary, is known for its lion safaris, offering visitors a unique opportunity to see these majestic animals up close.
Flora and Fauna
- Flora: The vegetation in the sanctuary consists of dry deciduous forests, scrublands, and grasslands.
- Fauna:The sanctuary is home to a variety of wildlife, including:
- Mammals: Common species include leopards, wild boars, deer, lions, tigers, sloth bears, and several small mammals.
- Birds:. wide range of bird species can be seen here, such as peacocks, owls, and eagles, making it a great destination for bird watchers.
- Reptiles and Amphibians: The sanctuary is also home to reptiles like Indian rock pythons and monitor lizards, as well as amphibians like frogs and toads.
GS1/Geography
Pangsau Pass
Source:Times of India 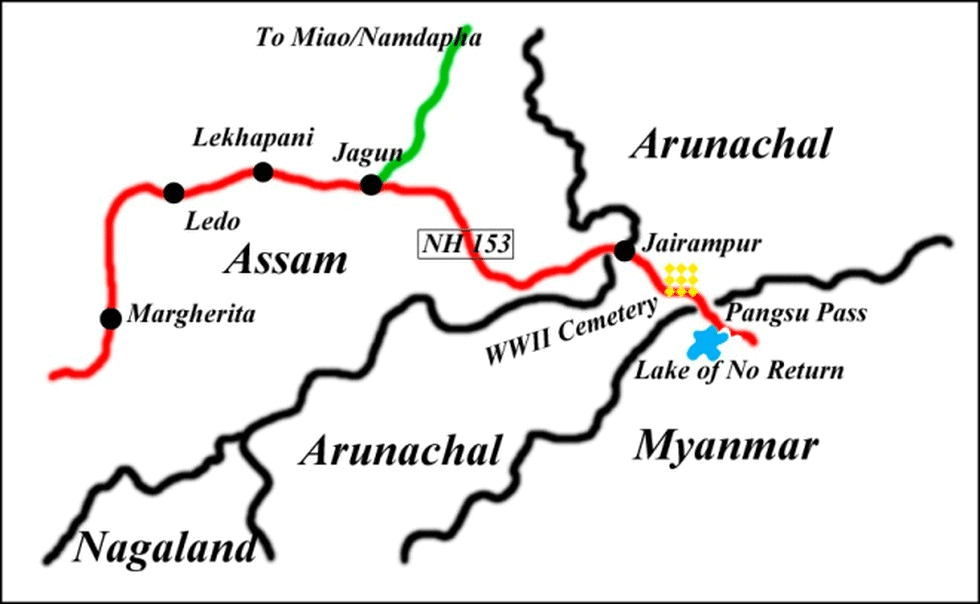
Why in News?
Recently, Arunachal Pradesh witnessed the celebration of the Pangsau Pass International Festival in Nampong.
About Pangsau Pass
- Location and Altitude: Pangsau Pass, also known as Pan Saung Pass, is situated at an altitude of 3,727 feet (1,136 meters) on the Patkai Hills along the India-Myanmar border.
- Gateway to Myanmar: The pass provides one of the most accessible routes from the Assam plains into Myanmar.
- Historical Significance: The pass is named after the nearby Burmese village of Pangsau, located just 2 kilometers east of the pass. It is historically known as the route used by the Ahoms, a Shan tribe, during their 13th-century invasion of Assam.
- World War II Importance: During World War II, Pangsau Pass gained fame as the initial challenge faced by American General “Vinegar Joe” Stilwell and his forces in their attempt to establish a land route to isolated China following the Japanese occupation of Burma.
- Scenic View: From Pangsau Pass, visitors can see the famous Lake of No Return located on the Myanmar side.
- Challenging Terrain: The pass is often referred to as “Hell Gate” or “Hell Pass” due to the difficult terrains found in the Patkai Mountain Range.
Pangsau Pass International Festival
- Annual Celebration: The Pangsau Pass International Festival is celebrated every year in Nampong, a town in the Changlang district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Purpose: The festival aims to promote cross-border trade and cultural exchange between India and Myanmar. It provides a platform for showcasing Myanmar’s culture and products.
GS3/Science and Technology
NVS-02 Satellite
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully launched the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rocket carrying the NVS-02 satellite, which is a crucial component of the NavIC navigation system.
About NVS-02 Satellite
- NVS-02 is the second satellite in the series of five second-generation satellites being developed by ISRO to replace the existing satellites in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
- Launch Details: The GSLV-F15 rocket will place NVS-02 in a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- Predecessor: NVS-01, the first in the series, was launched in 2023 aboard GSLV-F12, featuring an indigenous atomic clock for the first time.
Features of NVS-02
- Weight and Power: NVS-02 weighs 2,250 kg and has a power capacity of around 3 kW.
- Navigation Payload: It is equipped with a navigation payload operating in three frequency bands: L1, L5, and S bands, along with a ranging payload in the C-band, similar to its predecessor, NVS-01.
- Atomic Clock: The satellite features a Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard (RAFS) for precise timekeeping.
- Lifespan: NVS-02 has an extended lifespan of 12 years and is equipped with more accurate atomic clocks developed indigenously.
- Replacement: It will replace the older NavIC satellite, IRNSS-1E, and will be positioned at 111.75°E in orbit.
- Development: The satellite was designed, developed, and integrated at the U R Satellite Centre (URSC).
Significance
- Global Compatibility: By incorporating new L1 band signals, NVS-02 enhances NavIC’s compatibility with global navigation systems. This improvement ensures wider adoption and better service, making NavIC more interoperable with other international navigation systems.
GS3/ Science and Technology
SANJAY Surveillance System
Source:PIB
Why is it News?
Recently, the Defence Minister launched 'SANJAY - The Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS)' from South Block, New Delhi.
About SANJAY Surveillance System
- The SANJAY Surveillance System is an advanced automated surveillance tool designed for the battlefield. It gathers information from various ground and aerial sensors, verifies this data, eliminates duplicates, and combines it to create a unified surveillance picture of the battlefield. This process happens over secure Army Data Networks and Satellite Communication Networks.
- Features of SANJAY
- Advanced Technology: The system is built with cutting-edge sensors and analytics.
- Border Monitoring: It will oversee the extensive land borders, prevent unauthorized entries, and assess situations with high precision.
- Force Multiplier: The system will significantly enhance Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities.
- Operational Flexibility: Commanders will be able to conduct both conventional and unconventional operations in a Network-Centric Environment.
- Phased Induction: The system will be deployed to all operational Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Indian Army in three phases.
- Development: The SANJAY system has been developed indigenously by the Indian Army in collaboration with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Significance: Its introduction marks a significant advancement towards data and network-centric operations in the Indian Army. It will improve battlefield transparency and revolutionize future battlefields through a Centralized Web Application. This application will provide crucial information to Command and Army Headquarters, as well as support decision-making processes within the Indian Army.
GS2/ Polity and Governance
Use of loudspeakers not essential part of religion
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
- The Bombay High Court has recently directed the state to curb noise pollution caused by places of worship using loudspeakers, stating that such practices are not essential to any religion.
- This ruling emphasizes the need to control noise pollution, irrespective of the religious significance of the places involved.
Essential Religious Practices (ERP) Doctrine
The ERP Doctrine, established by the Supreme Court, determines which religious practices are protected under Articles 25 and 26 of the Indian Constitution. It aims to balance the freedom of religion with the state's authority to regulate practices.
Overview
- The ERP Doctrine is a legal framework by the Supreme Court to balance freedom of religion and state regulation.
- It protects only those religious practices considered essential to a particular religion.
Key Features
- Freedom of Religion: The doctrine safeguards practices vital to a religion under the constitutional provisions of freedom of religion.
- State's Role in Social Reforms: It permits the state to implement social reforms without interfering with essential religious practices.
- Bifurcation of Practices: The doctrine differentiates between essential and non-essential religious practices, offering protection solely to those deemed essential.
Historical Context
- First Articulation: The doctrine was first articulated in the 1954 case The Commissioner Hindu Religious Endowments, Madras v. Sri Lakshmindra Thirtha Swamiar of Sri Shirur Mutt .
- Criticism: The application of the doctrine has faced criticism for its inconsistency and lack of coherence.
Notable Examples
- The Durgah Committee, Ajmer v. Syed Hussain Ali (1961): The court ruled that only practices essential and integral to a religion are protected.
- Ismail Faruqui v. Union of India (1994): The court determined that a mosque is not an essential practice for the religion of Islam.
Bombay High Court on Loudspeaker Use
In a notable ruling, the Bombay High Court has determined that the use of loudspeakers is not a fundamental practice of any religion.
Court Observations
- The use of loudspeakers is not a core aspect of any religion and therefore is not protected under Article 25, which guarantees freedom of religion.
- Noise pollution poses a public health risk and needs to be regulated strictly to protect citizens' rights.
- Law enforcement agencies must ensure adherence to noise regulations and take proactive measures rather than being passive in enforcement.
Case Background
- Residents of Nehru Nagar, Kurla East, filed a petition highlighting noise pollution caused by religious places exceeding permissible decibel levels and operating beyond allowed hours.
- Permissible Decibel Limits: 55 decibels during the day and 45 decibels at night in residential areas.
- Complaints made to local police stations were ignored, prompting the residents to approach the Bombay High Court.
Key Directives from the Court
- Police are required to measure decibel levels using mobile applications and confiscate equipment that violates noise regulations.
- Initial violations should result in warnings, while repeated offenses may lead to fines, equipment seizure, and cancellation of licenses.
- Police must ensure the anonymity of complainants to prevent any form of retaliation.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 26th January 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the historical significance of Rakhigarhi in India? |  |
| 2. Who are the Shompens and what is their cultural relevance? |  |
| 3. What is the Doctrine of Merger in the context of Indian law? |  |
| 4. What are the key features of Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Pangsau Pass in India-Myanmar relations? |  |




















