UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 30th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Indian Society
The Copyright Conundrum in Carnatic Music
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The issue of copyright in Carnatic music has gained significant attention, especially after the recent Margazhi music season in Chennai, highlighting the inadequacies of the existing legal framework in protecting performers. This has raised important questions about the need for copyright law to evolve in order to better reflect the realities of this unique form of Indian classical music.
- Carnatic music, rooted in oral traditions, faces unique challenges under current copyright laws.
- Most foundational compositions are in the public domain, complicating the application of copyright protections.
- There is a pressing need for legal reform to protect the rights of performers and their improvisations.
Additional Details
- Improvisation in Carnatic Music: The essence of Carnatic music lies in its improvisatory nature, including elements such as raga alapana (melodic improvisation) and kalpana swaras (spontaneous note sequences), which are not fixed in writing and challenge existing copyright definitions.
- Public Domain Compositions: Works by composers like Tyagaraja and Purandara Dasa predate copyright laws, making them freely available for performance but complicating the protection of innovative performances.
- Performers' Rights: While performers have rights to prevent unauthorized recordings, their improvisations often lack formal recognition under current laws, leading to exploitation without compensation.
The current copyright framework fails to adequately address the complexities of Carnatic music, leaving performers vulnerable. Recognizing the unique contributions of musicians through legal reform can ensure they receive the protection and financial recognition they deserve.
GS3/Economy
Only a radical policy shift can lift farmers from widespread distress
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Agriculture has been largely overlooked, despite alarming statistics from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) indicating that 1,00,474 farmers and agricultural workers committed suicide between 2015 and 2022.
- Government failure to implement the Minimum Support Price (MSP) as promised.
- Increasing costs of agricultural inputs are burdening farmers financially.
- Declining government support and investments in agricultural infrastructure.
Additional Details
- Unmet Minimum Support Price (MSP) Promise: The government has not fulfilled its commitment to set MSP at C2+50%, as recommended by the M.S. Swaminathan Commission. This lack of support has exacerbated farmers' financial struggles.
- Rising Input Costs and Economic Burden: The prices of essential agricultural inputs like fertilizers, seeds, and electricity have been continuously increasing, placing additional financial strain on farmers.
- Inadequate Government Support and Infrastructure: Funding for agriculture has decreased from 5.44% of the total budget in 2019 to just 3.15% in 2024, leading to insufficient public investment in irrigation and power infrastructure.
Policy Reform Strategies
- Implementation of MSP: Establishing a statutory MSP at C2+50% is crucial to ensure fair compensation for farmers, potentially reducing financial distress and the incidence of suicides.
- Subsidy Increases and Cost Controls: The government should enhance subsidies for agricultural inputs and regulate prices charged by private corporations to stabilize costs.
- Comprehensive Loan Waiver: A one-time loan waiver could alleviate immediate debt burdens, complemented by long-term financial management strategies to prevent future indebtedness.
Government Support and Institutional Frameworks
- Financial Assistance and Subsidies: Subsidies for fertilizers and seeds, along with direct income support programs like the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN), help alleviate farmers' financial pressures.
- Crop Insurance and Risk Mitigation: Schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) provide insurance against crop losses, protecting farmers from unforeseen events.
- Market Access and Price Support: Government procurement schemes, facilitated by the Food Corporation of India (FCI), ensure fair prices for farmers, acting as a safety net during market fluctuations.
- Agricultural Credit and Loans: Institutions like NABARD offer affordable loans, enabling farmers to invest in better practices or recover from losses. Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) provide short-term credit for immediate needs.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Infrastructure and Support Systems: Investing in irrigation, power supply, and crop insurance will help farmers manage climate-related challenges and reduce reliance on private traders.
- Enhance Financial Accessibility and Risk Management: Improving access to affordable credit and implementing statutory MSP at C2+50% will help farmers manage debts and reduce vulnerability to market fluctuations.
In conclusion, addressing the root causes of agrarian distress through comprehensive policy reforms and government support is essential for improving the livelihood of farmers and ensuring food security in India.
GS2/Governance
BHASHINI Platform
Source: Money Control
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Tripura has become a trailblazer in Northeast India by implementing advanced artificial intelligence technologies for promoting digital inclusion through the BHASHINI initiative, which utilizes cutting-edge text-to-speech technology.
- BHASHINI stands for BHASHa INterface for India, focusing on breaking language barriers.
- The platform aims to enhance digital access and services in various Indian languages.
- Launched in July 2022 under the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM), it supports 22 scheduled Indian languages.
Additional Details
- Objective: The BHASHINI platform seeks to provide translation services using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), making these technologies accessible for Indian MSMEs, startups, and individual innovators.
- Implementation: The initiative is managed by the Digital India BHASHINI Division, which operates under the Digital India Corporation, a Section 8 Company of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Accessibility: Users can access the platform through dedicated apps for Android and iOS, ensuring a user-friendly experience.
- Crowdsourcing: The platform includes a specific section named ‘Bhasadaan’, which encourages individuals to participate in various crowdsourcing initiatives.
This initiative represents a significant leap towards digital inclusivity, allowing for seamless communication across different Indian languages and fostering a culture of technology-driven innovation.
GS3/Environment
F11 Bacteria: A Breakthrough in PFAS Decomposition
Source: Science Direct
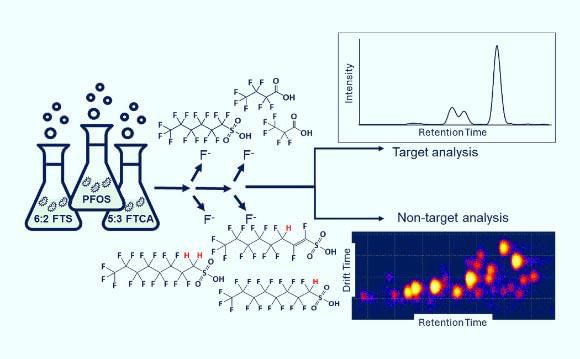 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has identified the bacterial strain Labrys portucalensis F11 (F11) as an effective agent in breaking down the strong carbon-fluorine bonds present in polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), also known as "forever chemicals." This discovery is significant for environmental remediation efforts.
- Adaptation: F11 bacteria thrive in polluted environments, utilizing contaminants as energy sources.
- Isolation: This strain was first isolated from contaminated industrial soil in Portugal.
- PFAS Decomposition: F11 can break down multiple types of PFAS and some of their toxic byproducts.
Additional Details
- Forever Chemicals: These are man-made hazardous substances that persist in the environment, posing significant health risks. They have a tendency to remain in the atmosphere, soil, and rainwater indefinitely.
- Due to their stability, forever chemicals contribute to ongoing environmental degradation, affecting all forms of life, including humans.
- PFAS can migrate into soil, water, and air during their production and usage, making them widespread pollutants.
- They are recognized under international agreements such as the Stockholm Convention, which aims to eliminate or restrict the use of hazardous substances.
The findings regarding F11 bacteria present a promising avenue for addressing the challenges posed by forever chemicals, highlighting the potential for bioremediation in contaminated environments.
GS3/Economy
National Critical Minerals Mission: A Step Towards Self-Reliance
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Union government of India has recently approved the National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMM) with an aim to reduce the country’s reliance on imported critical minerals.
- The mission has a total outlay of ₹34,300 crore over a period of seven years.
- It aims to enhance domestic exploration and processing of critical minerals essential for green energy technologies.
Objectives and Key Features of the Mission
- Enhancing Domestic Exploration: A significant portion of the mission's funding will be directed toward intensifying mineral exploration across India, including offshore areas.
- Reducing Import Dependence: The mission seeks to decrease India’s heavy reliance on imported minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements, which are crucial for electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies.
- Developing Processing and Recycling Capabilities: Investment will be encouraged in mineral processing parks and recycling technologies.
- Overseas Mineral Acquisitions: Public sector enterprises and private companies will be supported in acquiring mineral assets internationally to secure a stable supply of critical minerals.
- Regulatory and Financial Support: The mission aims to streamline regulatory processes and provide financial incentives for mineral exploration and development.
Significance of Critical Minerals
- Critical minerals like copper, lithium, nickel, and cobalt are vital for various modern industries, including:
- Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Used in wind turbines, solar panels, and electricity networks.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Essential for batteries and charging infrastructure.
- Electronics & High-Tech Industries: Important for devices like smartphones, defense equipment, and medical devices.
- As the global shift towards clean energy accelerates, ensuring domestic availability of these minerals is key for India's economic and technological security.
Government Strategy and Implementation
- The Union Cabinet, under PM Modi’s leadership, has approved a government expenditure of ₹16,300 crore, with an additional ₹18,000 crore expected from public sector undertakings and private companies.
- Key Implementation Measures:
- Expedited Mining Approvals: Establishment of a fast-track regulatory process for mining projects.
- Stockpile Development: Creation of a strategic stockpile of critical minerals to safeguard supply chains.
- Policy Reforms: Amendments to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 to facilitate auctioning of strategic mineral blocks.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) Exploration Projects: GSI has initiated 368 mineral exploration projects, with plans for 227 more by 2025-26.
- Import Duty Waivers: Removal of customs duties on several critical minerals in the FY25 budget to promote domestic processing.
Impact on India’s Energy Transition
The NCMM is anticipated to:
- Secure mineral supply chains for India's clean energy sector.
- Boost domestic manufacturing of EV batteries and renewable energy components.
- Strengthen India’s position in the global critical minerals market.
- Attract foreign and private investment in mining and mineral processing.
Challenges & Way Forward
Despite its significance, the mission faces several challenges:
- Geopolitical Risks: The acquisition of mineral assets overseas could be affected by global political dynamics.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased mining activities raise the need for ecological conservation.
- Investment Risks: Ensuring strong policy support is crucial for private sector participation.
To address these challenges, the government intends to collaborate with research institutions, industries, and international partners to ensure the sustainable and effective implementation of the mission.
In conclusion, the National Critical Minerals Mission represents a landmark initiative aimed at reducing import dependency, bolstering domestic mining capabilities, and securing India's clean energy future. By integrating exploration, processing, recycling, and international collaboration, India is strategically progressing towards self-reliance and aiming for global leadership in critical mineral supply chains.
GS3/Economy
How Can the Budget Arrest Growth Decline?
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The growth rate of India is currently lower than government expectations. Historical trends show that the period from 2004 to 2011 experienced significant growth and poverty reduction due to welfare programs and government interventions.
Key Takeaways
- The World Bank forecasts India's GDP growth to soften to 6.5% for FY 2024-25, down from previous expectations of 7%.
- The IMF has revised its growth forecast to 7% for FY 2024 and 6.5% for FY 2025, acknowledging challenges despite robust domestic demand.
Additional Details
- State Intervention and Welfare Programs: The 2004-2011 period saw a resurgence of state interventions through rights-based legislation and welfare schemes, significantly contributing to economic growth and reducing absolute poverty. Notably, programs like the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA) provided jobs and established higher wage floors, benefiting the rural poor.
- Rising Consumption Among Lower Income Groups: Despite increasing income inequality, the consumption share of the bottom 80% grew faster than that of the richest 20%, aided by targeted fiscal policies that enhanced the consumption capacity of lower-income groups.
- Increased Fiscal Expenditure on Social Services: There was a marked rise in social services and developmental expenditures, positively impacting consumption patterns across various commodity categories for lower-income groups.
Does the Nature of Fiscal Expenditure Matter for Private Consumption?
- Capital Expenditure vs. Revenue Expenditure:
- Capital Expenditure (Capex): Focused on large infrastructure projects, primarily benefits high-income groups and corporations, resulting in a lower short-term impact on consumption.
- Revenue Expenditure: Expenditures on social welfare, wages, and pensions immediately boost demand by increasing disposable income among lower-income groups.
- Leakages in Capex: Large projects often involve imports (e.g., heavy machinery), leading to capital outflows instead of stimulating the domestic economy.
- Higher Consumption Propensity of Lower-Income Groups: Funds spent on welfare programs reach individuals with a higher tendency to spend, resulting in a larger multiplier effect on domestic demand.
How Would an Increase in Revenue Expenditure Help? (Way Forward)
- Higher Incomes for Workers: By providing better wages and job opportunities through social programs, disposable income among lower-income populations would rise, thereby boosting overall consumption levels.
- Stimulating Private Investment: Enhanced consumer demand can create a favorable environment for businesses to invest. As disposable incomes rise, businesses may respond by increasing production capacity, fostering a cycle of investment and growth.
- Reversing Economic Slowdown: A strategic shift towards increasing revenue expenditure can help combat the current economic slowdown by fostering a more inclusive growth model that benefits a broader segment of society.
This approach emphasizes the importance of targeted fiscal policies and social spending to stimulate economic growth and improve consumption among lower-income groups, thus addressing the current economic challenges.
GS2/International Relations
Darfur Region
Source: MSN
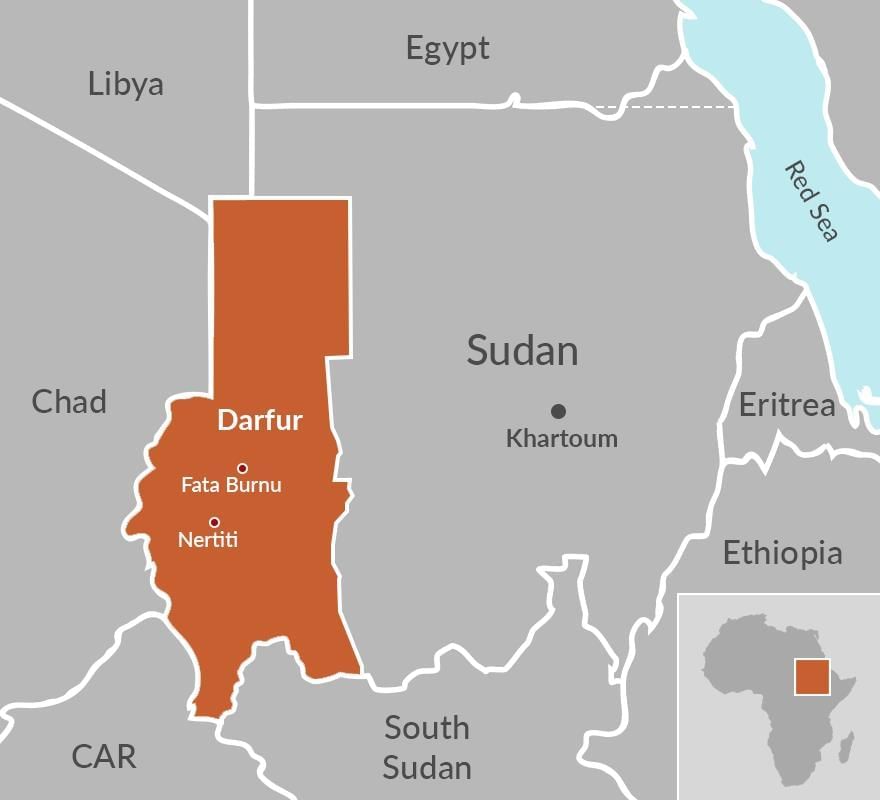 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, a drone strike on one of the last operational hospitals in El-Fasher, located in Sudan's Darfur region, resulted in the deaths of 67 individuals and left many others injured. This incident underscores the ongoing humanitarian crisis in the area.
- A drone attack in El-Fasher has caused significant casualties.
- Darfur is experiencing a severe humanitarian crisis, affecting healthcare services.
Additional Details
- Geographical Overview: Darfur is situated in western Sudan, bordered by Kordofan to the east and Wadai to the west. The region extends southward to the Al-Ghazāl (Gazelle) River and northward to the Libyan Desert, covering an area of approximately 440,000 sq.km.
- Topography: The central part of Darfur is characterized by the volcanic highlands of the Marrah Mountains, which dominate the rolling plains of the region.
- Historical Context: Darfur was an independent sultanate until its annexation by Sudan in 1916. The name “Darfur” translates to “the land of the Fur” in Arabic, reflecting its rich cultural heritage.
- Population Diversity: The region is home to around 80 tribes and ethnic groups, including both nomadic and sedentary communities. While Arabs make up the majority in the northern part, Arabs and the Fur ethnic group are predominant in the south. Other ethnic groups include Beja, Zaghawa, Nubian, and Daju peoples.
This recent attack highlights the urgent need for international attention and humanitarian assistance in the Darfur region, where conflict and instability continue to threaten the lives and wellbeing of its inhabitants.
GS3/Science and Technology
RNA Therapy
Source: The Hindu
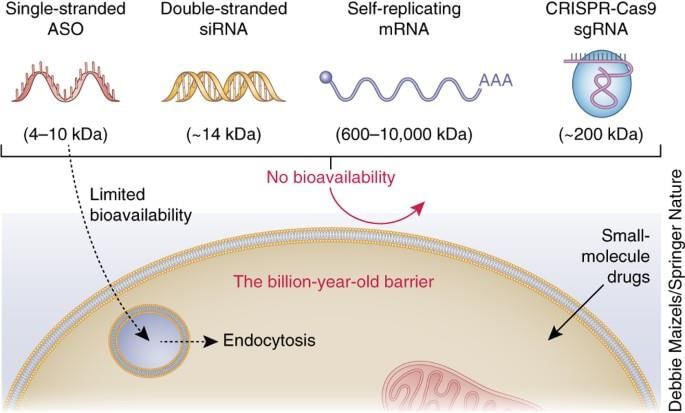 Why in News?
Why in News?
RNA-based precision therapeutics are gaining recognition as a transformative approach for treating genetic disorders, particularly inherited retinal diseases (IRDs).
- RNA therapy utilizes RNA-based molecules to influence biological pathways for treating specific conditions.
- Unlike gene-editing methods, RNA therapies provide a safer alternative by inducing temporary changes that do not affect future generations.
Additional Details
- RNA Editing with ADAR Enzymes: This technique can rectify specific genetic mutations at the RNA level, potentially restoring protein production in retinal cells without altering the underlying DNA. This approach presents a novel treatment avenue for retinal degenerative diseases linked to single-point mutations.
- Suppressor tRNAs: This method aims to overcome stop-codon mutations, which can prematurely interrupt protein synthesis in retinal cells. By facilitating the production of full-length proteins, this strategy may help restore normal retinal function in patients with IRDs.
- PTC124 Method: Also known as ataluren, this therapy is currently employed in treating patients with cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs): ASOs have been effectively used to address diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
With ongoing advancements in RNA therapies, there is growing potential for innovative treatments that could significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from genetic disorders.
GS3/Economy
Bridge the Milk Divide for a Nutritionally Secure India
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The upcoming Union Budget 2025-26 presents an opportunity to address the significant disparities in milk consumption across various socio-economic groups in India, despite the country's status as the largest milk producer globally. Ensuring equitable distribution of milk is crucial for improving nutrition among vulnerable populations.
- India's dairy sector has seen remarkable production achievements, yet access to milk remains inequitable.
- Milk is vital for nutrition, particularly for children, but disparities exist based on income, geography, and social background.
Additional Details
- Nutritional Importance of Milk: Milk is a critical source of protein, calcium, and micronutrients, essential for complementing the predominantly plant-based diets in India. It has been linked to improved child growth outcomes and decreased risks of stunting and underweight among children aged six months to five years.
- Income-Based Disparities: The richest 10% of households consume three to four times more milk per capita than the poorest 10%. The poorest 30% account for only 18% of total milk consumption, indicating a significant gap in access.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Urban households consume about 30% more milk per capita than rural households, largely due to higher incomes and better access to organized retail.
- Regional Disparities: Milk consumption varies by state, with northern and western regions consuming significantly more than eastern states, reflecting differences in dairy culture and economic conditions.
- Social and Cultural Disparities: Scheduled Tribe households consume considerably less milk compared to General Category households, due to economic constraints and dietary traditions.
- Out-of-Home Consumption: Approximately 50% of India's milk production is consumed outside the home, which is often underreported, leading to misconceptions about consumption inequities.
- Policy Interventions: Enhancing milk access through government nutrition programs, leveraging dairy markets for targeted support, and raising awareness about nutrition can help bridge the divide.
India's dairy revolution has greatly improved milk production, but the challenge of equitable access remains. Implementing targeted policies and awareness campaigns can ensure that all sections of society benefit from this vital resource, fulfilling the vision of a nutritionally secure nation.
GS3/Science and Technology
Organophosphate Poisoning in J&K
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent mysterious illness in Jammu & Kashmir has led to 17 fatalities, with medical professionals suspecting that organophosphate poisoning from pesticides could be a significant factor.
- Organophosphates are commonly used as pesticides and insecticides in agriculture.
- They disrupt the nervous system by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (AChE), resulting in excessive nerve stimulation.
- Symptoms of poisoning can be acute and chronic, requiring immediate medical intervention.
Additional Details
- What are Organophosphates? Organophosphates (OPs) are a class of chemical compounds widely utilized in agriculture, household pest control, and even in chemical warfare (e.g., nerve agents like Sarin). Common examples include malathion, chlorpyrifos, and diazinon.
- Effects of OP Poisoning:
- Acute Symptoms: These can include excessive sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle twitching, difficulty breathing, seizures, and coma.
- Chronic Effects: Long-term exposure may lead to neurological disorders, memory loss, muscle weakness, and reproductive toxicity.
- Treatment for Organophosphate Poisoning:Immediate medical attention is crucial to avert serious complications. Treatment protocols include:
- Decontamination: Remove any contaminated clothing, wash exposed skin thoroughly, and administer activated charcoal if ingestion has occurred.
- Medical Treatment:
- Atropine: This medication blocks excessive nerve stimulation.
- Pralidoxime (2-PAM): It helps restore enzyme function.
- Oxygen Therapy: May be necessary along with ventilator support in severe cases.
- Supportive Care: Includes intravenous fluids, anti-seizure medications, and hospitalization for those in severe condition.
In conclusion, organophosphate poisoning is a serious health concern, particularly highlighted by the recent incidents in Jammu & Kashmir, necessitating immediate medical response and public awareness regarding the risks associated with these chemicals.
GS3/Science and Technology
Labrys portucalensis F11
Source: Science Direct
Why in the News?
A research team has discovered that Labrys portucalensis F11, a strain of aerobic bacteria from the Xanthobacteraceae family, has the capability to break down and transform various types of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which are persistent environmental pollutants.
- Discovery Location: First identified in contaminated soil at an industrial site in Portugal.
- Pollutant Breakdown: Capable of removing fluorine from certain chemical pollutants, thereby reducing their toxicity.
- PFAS Properties: Known as "forever chemicals" because they are resistant to breakdown in the environment.
- Impact on Pollution: Can digest PFAS, aiding in the cleanup of polluted soil and water.
Additional Details
- Mechanism of Action: The bacteria attack strong chemical bonds in PFAS, effectively removing fluorine atoms and utilizing carbon from PFAS as food, aiding its growth while diminishing pollution.
- Environmental Suitability: Thrives in oxygen-rich environments, making it ideal for industrial waste site cleanups.
- Efficiency: Demonstrated the ability to break down 90% of PFOS, a particularly harmful PFAS chemical, within 100 days.
- Advanced Degradation: Unlike most bacteria, it can also break down PFAS remnants, further enhancing safety.
The discovery of Labrys portucalensis F11 represents a significant advancement in bioremediation technologies, offering a promising solution to combat the environmental crisis posed by PFAS contamination.
Back2Basics: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
- Definition: PFAS are synthetic chemicals widely used in various industrial and consumer products due to their waterproof, grease-resistant, and non-stick properties.
- Environmental Persistence: Often referred to as "forever chemicals" because they do not naturally decompose in the environment or human body.
- Common Applications: Found in non-stick cookware (Teflon), waterproof clothing, food packaging, fire-fighting foams, and various industrial uses.
Environmental and Health Concerns
- Persistence and Impact: PFAS are resistant to degradation, accumulating in soil, water, and living organisms.
- Health Risks: Linked to serious health issues, including cancer, liver damage, disruption of the immune system, and hormonal imbalances.
Regulatory Actions
- 2023 EPA Designation: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identified PFOS, a type of PFAS, as a hazardous substance, necessitating strict monitoring and remediation efforts.
- Global Response: Governments worldwide are phasing out PFAS usage and investing in bioremediation technologies such as the F11 bacteria-based cleanup approach.
- Indian Standards: In 2020, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) adopted international criteria for sampling and testing certain PFAS compounds like PFOA and PFOS, though comprehensive regulations are still lacking.
Previous Year Question (PYQ)
2013: Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
- Arsenic
- Sorbitol
- Fluoride
- Formaldehyde
- Uranium
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- (a) 1 and 3 only
- (b) 2, 4 and 5 only
- (c) 1, 3 and 5 only
- (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
GS3/Environment
Why Greenland’s Crystal Blue Lakes Have Turned Brown?
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has highlighted that over 7,500 lakes in western Greenland have turned brown, indicating a deterioration in water quality and an increase in carbon emissions due to extreme weather events that occurred in 2022.
- Record-breaking heatwaves and heavy rainfall in 2022 replaced the usual snowfall.
- Thawing of permafrost has released organic carbon and minerals into the lakes.
- Atmospheric rivers caused intense precipitation, resulting in runoff of organic materials.
- Increased sedimentation has reduced light penetration, impacting phytoplankton and carbon absorption.
Additional Details
- Greenland: The world's largest island, covered by an extensive ice sheet that harbors nearly 8% of the world's freshwater. It is home to numerous glacial-fed lakes known for their pristine water quality.
- Impact of Extreme Weather: The extreme weather in 2022 led to unprecedented changes in the lakes within months, indicating significant climate impact.
- Carbon Emissions: The lakes, once natural carbon sinks, are now releasing 350% more carbon dioxide, which accelerates global warming.
- Water Quality Concerns: The lakes, which provide drinking water, now have higher levels of organic pollutants, affecting both human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Future Projections: Studies suggest that atmospheric rivers may become 50-290% more frequent by the century's end, impacting freshwater ecosystems globally.
This study contributes to the growing body of evidence that Earth's natural carbon sinks are failing, posing significant challenges for climate mitigation efforts.
|
49 videos|5376 docs|1137 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 30th January 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key challenges faced by Carnatic music in terms of copyright issues? |  |
| 2. How does the copyright system in India affect Carnatic musicians? |  |
| 3. What steps can be taken to improve the copyright framework for Carnatic music? |  |
| 4. How do international copyright laws influence Carnatic music? |  |
| 5. What role does technology play in addressing copyright issues in Carnatic music? |  |





















