UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 6th February 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Supreme Court Directive on Sacred Groves
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
On December 18, 2024, the Supreme Court mandated Rajasthan's Forest Department to map all sacred groves using satellite and ground surveys, emphasizing their cultural and ecological significance, irrespective of their size.
- Rajasthan is home to approximately 25,000 sacred groves, locally known as orans, covering about 6 lakh hectares.
- The Supreme Court's order raises concerns regarding its conflict with the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006.
Implications of the Supreme Court Order
- Conflict with the Forest Rights Act: The order challenges the FRA, which aims to recognize and confer forest rights to gram sabhas, shifting control to the Forest Department.
- Loss of Community Autonomy: Traditionally protected by local communities, sacred groves may now fall under state governance, disrupting cultural conservation practices.
- Potential Erosion of Traditional Governance Systems: Management transfer risks weakening customary laws and traditional practices that have preserved these groves.
- Legal Precedence for Future Cases: The emphasis on the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA), 1972, over the FRA may set a precedent for similar takeovers of community-managed lands.
- Impact on Livelihoods and Religious Practices: Communities relying on sacred groves for religious and medicinal purposes may face restrictions due to new classifications as 'community reserves.'
Legal Context
- T.N. Godavarman v. Union of India: This landmark case broadened the definition of 'forest land' to include any area recorded as forest, regardless of ownership, and instructed states to create expert committees for proper identification.
Traditional Conservation Practices
- Watershed & Ecological Functions: Sacred groves play critical roles in protecting water sources and preventing soil erosion. For example, orans in Rajasthan sustain perennial water streams and serve as key grazing lands.
- Strict Protection through Customary Laws: Communities enforce prohibitions against resource extraction. For instance, Sarpa Kavu in Kerala, dedicated to serpent deities, forbids tree cutting.
- Religious & Cultural Practices: Rituals and community prayers enhance the spiritual significance of these groves. For example, Devara Kadu in Karnataka involves annual worship ceremonies promoting local conservation efforts.
- Community Governance & Management: Local elders or village councils oversee protections. Jahera in Odisha and Chhattisgarh showcases tribal communities managing sacred spaces.
- Role in Biodiversity Preservation: Sacred groves serve as biodiversity hotspots, safeguarding endemic species. For example, Law Kyntang in Meghalaya is home to rare orchids and medicinal herbs.
Way Forward
- Harmonizing Legal Frameworks: Amend policies to recognize gram sabhas' authority in managing sacred groves while fostering ecological conservation.
- Community-Centric Conservation: Empower local communities to manage sacred groves, integrating traditional practices with scientific conservation methods.
This directive highlights the critical balance needed between ecological conservation and the rights of local communities to manage their sacred groves, ensuring both environmental sustainability and cultural preservation.
GS3/Science and Technology
Brucellosis Disease
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
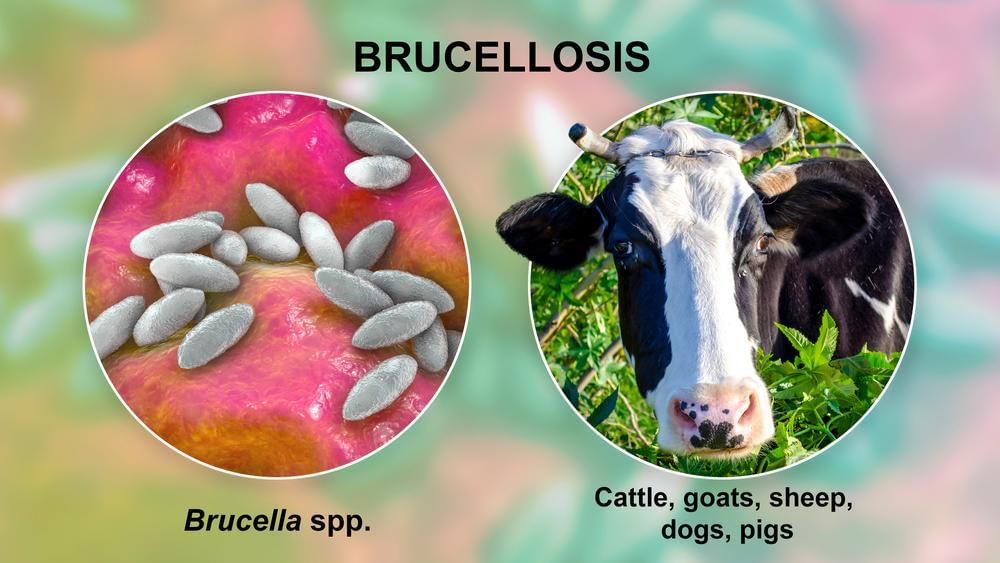
Recently, an eight-year-old girl from Kottakkal in Malappuram district of Kerala tragically passed away following nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis, highlighting the severity of this infectious disease.
- Brucellosis is a bacterial infection caused by various species of Brucella.
- Humans can contract brucellosis through contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Symptoms can be mild and may often go undiagnosed.
- Prevention methods include vaccination and pasteurization of milk.
Additional Details
- Brucellosis: This disease primarily affects livestock, including cattle, swine, goats, sheep, and dogs. Humans can become infected through various means, with unpasteurized milk and cheese being common sources.
- Symptoms include fever, weakness, weight loss, and general discomfort, with a variable incubation period of one week to two months.
- High-risk individuals include farmers, butchers, veterinarians, and laboratory personnel who are frequently in contact with potentially infected animals.
- Treatment typically involves the use of antibiotics.
- Preventive measures, such as the vaccination of livestock and ensuring the pasteurization of milk, are crucial in reducing transmission to humans.
This incident underscores the importance of awareness and preventive measures regarding brucellosis, particularly in areas with high livestock interaction.
GS3/Defence & Security
Iskander-M Tactical Ballistic Missile System
Source: Eurasian Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Russian Federation is reportedly preparing to commence large-scale production of the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missiles, which are significant for both regional and global security dynamics.
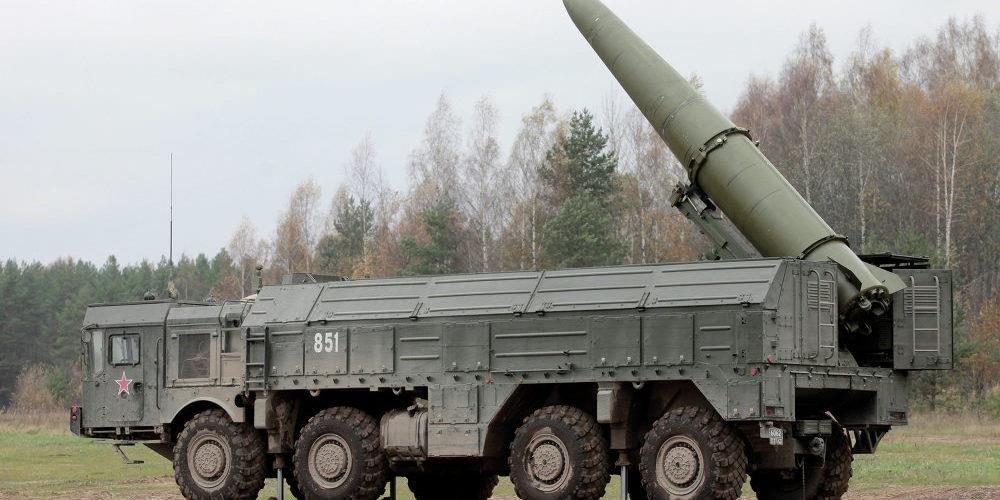
- The Iskander-M, known in Western reports as SS-26 Stone, is a short-range ballistic missile system.
- It was introduced into Russian military service in 2006 and first deployed in conflict during the 2008 war with Georgia.
- This missile system is designed for tactical strikes against high-value land targets.
Additional Details
- Specifications: The Iskander-M measures 7.3 meters in length, has a diameter of 0.92 meters, and a launch weight of 3,750 kilograms.
- Range and Payload: It can reach a maximum range of 500 km and can carry payloads between 480 kg and 700 kg, including conventional and nuclear warheads.
- The missile can travel at speeds up to Mach 7 and reach altitudes exceeding 30 miles.
- Maneuverability: It employs a maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV) and decoys to evade theater missile defense systems.
- The system is equipped with in-flight correction and self-targeting capabilities to enhance its effectiveness against missile defense.
The Iskander-M represents a significant advancement in Russia's tactical missile capabilities, with implications for military strategy and international relations in the region.
GS3/Science and Technology
Nuclear Energy Mission (NEM)
Source: Reuters
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26 introduced the Nuclear Energy Mission, aiming to develop at least 5 indigenous Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) by 2033. This initiative seeks to bolster India's nuclear power capacity significantly.
- 100 GW Nuclear Target by 2047 as part of India’s clean energy transition.
- ₹20,000 crore allocated for research and development, along with public-private collaboration in advanced nuclear technologies.
- Amendments to the Atomic Energy Act of 1962 will allow private sector participation.
- Changes to the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act of 2010 to attract foreign investment.
- Deployment of Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs) and SMRs to replace coal plants and power remote areas.
Additional Details
- Expansion of Nuclear Power Capacity: Current capacity is 8,180 MW with a target of 22,480 MW by 2031-32. There are 10 reactors under construction, contributing 8,000 MW across various states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and more.
- Deployment of Advanced Nuclear Reactors:
- Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs): 220 MWe PHWRs aimed at industrial decarbonization.
- Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (500 MWe) at Kalpakkam has achieved significant milestones in 2024.
- Development of High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors (HTGRs) and Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs) leveraging India's thorium reserves.
- Recent developments include the discovery of a new uranium deposit at Jaduguda Mines, extending its life by over 50 years.
- Operationalization of the first two 700 MWe PHWR units at Kakrapar, Gujarat (KAPS-3 & 4).
- The NPCIL-NTPC Joint Venture (ASHVINI) has been launched to build nuclear plants, and Rajasthan Atomic Power Project-7 (RAPP-7) reached criticality in 2024.
The Nuclear Energy Mission represents a significant step towards enhancing India’s nuclear energy capabilities, focusing on sustainability and energy independence. The ambitious goals set forth reflect India's commitment to a cleaner and more efficient energy future.
GS2/International Relations
India Must Address Illegal Emigration with Empathy and Urgency
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent surge in deportations of Indian nationals from the U.S. has brought the issue of illegal immigration to the forefront. This situation is driven by intensified enforcement operations aimed at managing undocumented immigration.
- The U.S. is enhancing its Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) operations, leading to increased deportations of Indian nationals.
- A significant number of Indians are attempting to migrate illegally due to economic hardships, especially from states like Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana.
- Approximately 725,000 undocumented Indians reside in the U.S., with a notable increase in deportations over the past three years.
Additional Details
- Legal Migration Channels: The Indian government is focused on maintaining legal pathways for migration, such as H-1B visas for skilled workers and student visas.
- Deportations have surged by 400% in the last three years, with 1,529 Indians deported in 2024 compared to just 292 in 2021.
- Impact on Labor Market: The deportation of Indian workers could create labor shortages in sectors like construction and hospitality, which are heavily reliant on immigrant labor.
- The political fallout in India may escalate, with opposition parties potentially holding the government accountable for inadequate domestic job creation.
In summary, India faces a critical challenge regarding illegal emigration, necessitating a multifaceted approach that combines diplomatic efforts, public awareness, and the strengthening of legal migration channels to address the root causes of illegal migration.
GS1/Geography
Santorini Island
Source: BBC
 Why in News?
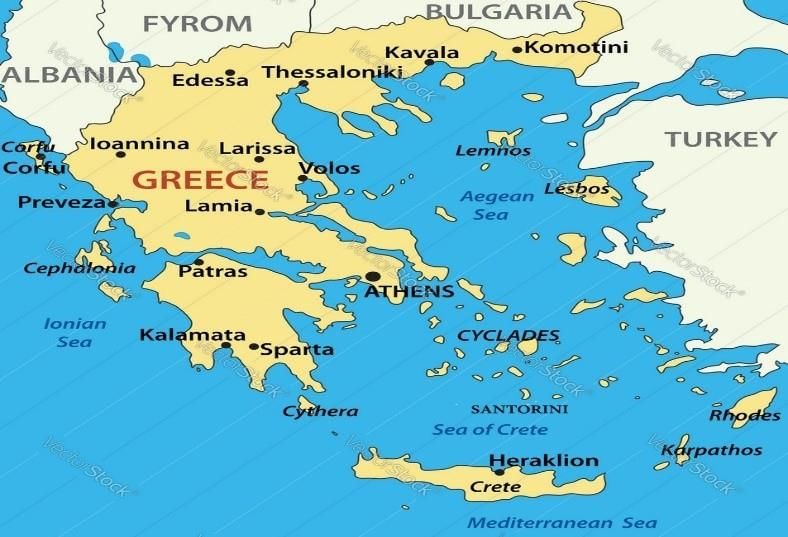
Why in News?Recently, thousands of residents have evacuated Santorini Island due to a series of earthquakes that struck the Greek islands in the Aegean Sea.
- Santorini is located in the southern Aegean Sea and is part of the Cyclades island group.
- The island is known for its volcanic origins, dramatic landscapes, and beautiful architecture.
- It is home to one of the few active volcanoes in Greece and Europe.
Additional Details
- Santorini: A volcanic crater island approximately 128 nautical miles southeast of the Greek mainland and 63 nautical miles north of Crete, formed from the remains of an ancient volcanic eruption.
- Geographical Features: The island features a stunning sea-filled volcanic caldera surrounded by high, colorful cliffs, along with iconic whitewashed houses and breathtaking views of the Aegean Sea.
- Significance: Santorini is renowned for its spectacular sunsets, the ancient settlement of Thira, and attracts numerous tourists each year due to its unique beauty.
The recent earthquakes have raised concerns about the safety of residents and tourists on Santorini, highlighting the island's geological activity and the need for preparedness in such natural events.
GS3/Economy
A Budget That is Mostly Good but With One Wrong Move
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Union Budget for 2025-26 is significant as it aims to enhance the country's economic development, improve tax structures, and manage fiscal consolidation amidst emerging challenges. Analyzing its components, such as GDP projections, government expenditure, tax revenues, and fiscal transparency, is crucial to understanding its impact.
- The nominal GDP growth is projected at 10.1%, supported by a focus on capital expenditure.
- There is a structural shift from indirect taxes to direct taxes, with direct taxes increasing from 52% to 59% in gross tax revenues.
- Concerns arise from the lack of clear fiscal deficit targets, which may affect fiscal transparency and investor confidence.
- Investment in Artificial Intelligence (AI) infrastructure is emphasized as a critical area for future competitiveness.
Additional Details
- Economic Growth and Capital Expenditure: The government has set a capital expenditure estimate of ₹11.2 lakh crore for 2025-26, slightly up from ₹11.1 lakh crore in the previous budget. This increase, although modest, aims to boost infrastructure and industrial investments, necessary for achieving a sustainable growth rate of around 8% in real terms.
- Tax Revenues and Structural Shifts: The Budget reflects a positive shift in the tax structure towards direct taxes. However, GTR growth is declining, with personal income tax growth slowing significantly due to new tax concessions.
- Concerns Over Fiscal Transparency: The abandonment of the fiscal deficit glide path raises questions about the government’s commitment to fiscal discipline. Relying on various debt-to-GDP scenarios without specific targets creates ambiguity in fiscal planning.
- Recommendations for Improved Fiscal Policy: Suggestions include reintroducing clear fiscal deficit targets, providing a detailed debt reduction strategy, ensuring conservative GDP growth assumptions, and enhancing transparency in budgetary disclosures.
In conclusion, while the 2025-26 Union Budget outlines a structured approach to economic growth and fiscal management, its departure from transparent fiscal deficit targets invites scrutiny. A clear and specific fiscal policy framework is essential for maintaining accountability and fostering investor confidence.
GS3/Environment
Mount Taranaki: A Unique Natural Feature
Source: MSN
 Why in News?
Why in News?Mount Taranaki, also known as Taranaki Maunga, has gained significant attention for being recognized as a legal entity, akin to a human being. This status reflects a growing acknowledgment of the cultural and spiritual significance of natural features among Indigenous communities.
- Mount Taranaki is a dormant stratovolcano located in New Zealand's North Island.
- It stands at an elevation of 8,261 feet, making it the second highest mountain in the region.
- The mountain has been recognized as a sacred ancestor by the Indigenous Maori people.
Additional Details
- Geological Formation: Mount Taranaki is formed from alternating layers of ash and lava flows, characteristic of stratovolcanoes, which are also known as composite cones. The formation was a result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Australian Plate.
- Symmetry and Landscapes: It is considered one of the most symmetrical volcanic cones in the world, featuring a circular ring plain of volcanic material that has resulted from lahars and landslides.
- Legal Recognition: Mount Taranaki is now the third natural feature in New Zealand to be granted human status, following Te Urewera National Park and the Whanganui River.
The recognition of Mount Taranaki as a legal entity emphasizes the importance of cultural respect and environmental stewardship, highlighting the relationship between the land and the Indigenous Maori community.
GS3/Economy
A Green Signal for India to Assert Its Health Leadership
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Union Budget for 2025-26 is a crucial juncture in India's healthcare evolution, emphasizing its aspirations to emerge as a global leader in healthcare and innovation. Strategic allocations, policy initiatives, and investments aim not only to improve the accessibility and quality of health services but also to establish India as a hub for global healthcare solutions.
- India's healthcare transformation from limited infrastructure to a global leader.
- Significant budget allocations for medical infrastructure and education.
- Focus on addressing non-communicable diseases and improving treatment accessibility.
- Integration of technology and innovation in the healthcare sector.
Additional Details
- Medical Infrastructure Investment: The budget allocates ₹90,958 crore to enhance medical infrastructure, including the establishment of daycare cancer centres to provide specialized care in underserved areas.
- Educational Advancements: Plans to create 75,000 new medical seats over five years, indicating a commitment to producing more healthcare professionals.
- Non-Communicable Diseases: The establishment of 200 daycare cancer centres aims to improve early diagnosis and treatment outcomes for diseases like cancer.
- Cost Reduction Measures: Customs duty exemptions on 36 life-saving drugs will lower treatment costs, making healthcare more affordable for the population.
- Technological Integration: The budget promotes the establishment of National Centres of Excellence for research and innovation in health-tech, positioning India as a leader in healthcare technology.
In conclusion, the Union Budget 2025-26 reflects the Indian government's commitment to health care as a cornerstone of national growth and development. By advancing these initiatives, India aims not only to heal its population but also to contribute significantly to global health solutions.
GS2/Governance
PRASHAD Scheme
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?A Parliamentary committee has urged the government to establish a clear-cut Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and secure necessary approvals from relevant authorities to ensure the timely execution of projects under the Spiritual Tourism Circuits associated with the PRASHAD scheme.
- The PRASHAD (Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spirituality Augmentation Drive) scheme was initiated by the Ministry of Tourism in 2014.
- The scheme aims to enhance cultural preservation and spiritual travel to designated pilgrimage destinations.
Objectives
- Infrastructure Improvement: Upgrading and maintaining the infrastructure at pilgrimage sites, including roads, water supply, sanitation, and waste management systems.
- Travel Connectivity: Enhancing travel conditions through improvements in road, rail, and air connectivity.
- Conservation Projects: Initiating projects aimed at preserving the cultural and spiritual significance of pilgrimage sites.
- Cultural Advocacy: Promoting the cultural and spiritual importance of these sites to attract both domestic and international tourists.
- Community Opportunities: Creating skill development and livelihood generation programs for local communities linked to pilgrimage tourism.
- Sustainable Practices: Adopting eco-friendly tourism practices to promote sustainable development.
Key Components
- Infrastructure Development: Focus on upgrading existing roads.
- Connectivity Enhancement: Improving transport links to pilgrimage sites.
- Pilgrim Experience Augmentation: Enhancing the overall experience for pilgrims.
Funding
- The scheme is funded entirely through a 100% public funding model for eligible project components.
- It also includes voluntary contributions from Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP).
These initiatives are crucial for the development of spiritual tourism, aiming to bolster both the infrastructure and the cultural significance of pilgrimage sites across India.
GS1/Indian Society
Guru-Shishya Parampara Scheme
Source: Nagaland Tribune
Why in News?
The Ministry of Culture has announced the implementation of a Central Sector scheme titled ‘Financial Assistance for Promotion of Guru-Shishya Parampara (Repertory Grant)’. This initiative aims to bolster traditional performing arts in India.
- The scheme was launched in the financial year 2003-04.
- It focuses on the preservation and promotion of India's traditional performing arts.
- Financial support is provided to both Gurus (mentors) and Shishyas (students) in various art forms.
Additional Details
- Aims and Objectives:The scheme is designed to:
- Preserve and revive rare art forms through direct knowledge transfer.
- Support traditional artists by providing financial aid for sustainable livelihoods.
- Encourage young talent by facilitating training under experienced Gurus.
- Promote classical, folk, and tribal art forms through structured mentorship.
- Financial Assistance:Monthly financial support is structured as follows:
- Gurus: ₹15,000
- Shishyas: ₹2,000 to ₹10,000, based on experience.
- Accompanist: ₹7,500
- Additional Shishyas (up to four per Guru): ₹3,750 each.
- Eligibility:The scheme is open to:
- Indian citizens engaged in traditional performing arts.
- Gurus aged between 45-70 years with national-level recognition.
- Implementation & Monitoring: Each Guru is responsible for training 5-8 Shishyas, with a focus on rural and tribal artists. Periodic reviews and expert evaluations are conducted to ensure effective fund utilization.
This scheme represents a significant effort to maintain India's rich cultural heritage by fostering a mentorship tradition that has been central to the transmission of performing arts across generations.
GS3/Defence & Security
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicles
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?As the Indian Prime Minister prepares for a visit to Washington DC, attention is drawn to several defense agreements in progress, notably the proposed co-production of Stryker infantry combat vehicles.
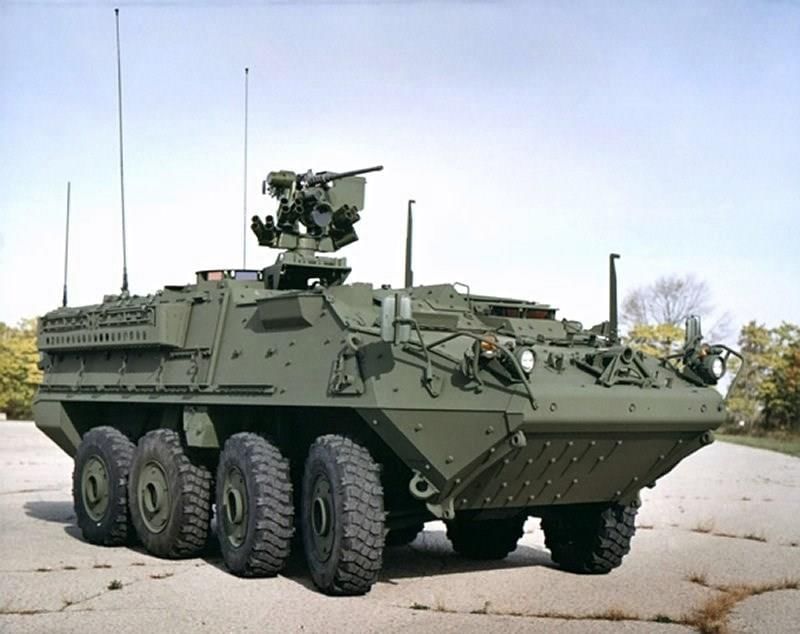
- The Stryker is a family of eight-wheel-drive combat vehicles designed for the US Army.
- Developed by General Dynamics Land Systems in collaboration with Canada and the US, it marks the first new military vehicle inducted into the US Army since the Abrams tank in the 1980s.
- Various configurations of the Stryker include Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, anti-tank guided missile carrier, and reconnaissance vehicle.
- Noted for their speed and flexibility, Strykers are particularly effective in urban warfare and rapid response situations.
Additional Details
- Transportation: Stryker vehicles can be transported overland via trucks or by air using C-17 and C-130 aircraft, which are part of the Indian Air Force's inventory.
- Key Features:
- Armament: The vehicles are equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Hull Construction: They feature a V-hull design made from high-hardness steel, enhanced with an additional layer of ceramic tile armor for superior protection.
- Crew and Capacity: Operated by a two-person crew and capable of carrying a nine-member infantry squad.
- Range: The operational range is approximately 483 kilometers.
- Top Speed: Stryker vehicles can reach speeds of around 100 km/h.
The ongoing discussions regarding the Stryker infantry vehicle deal highlight the importance of military collaboration between India and the United States in enhancing defense capabilities.
|
38 videos|5246 docs|1106 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 6th February 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Supreme Court Directive on Sacred Groves in India? |  |
| 2. How does brucellosis affect livestock and human health? |  |
| 3. What are the capabilities of the Iskander-M Tactical Ballistic Missile System? |  |
| 4. What are the objectives of India's Nuclear Energy Mission (NEM)? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for India to address illegal emigration with empathy and urgency? |  |





















